MCAT-Behavioral Science Unit 11
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Sociology
The study of society: how we create society, how we interact within and change society, and how we define what is normal and abnormal in society.
What do sociologists study at
1) Micro level
2) Meso level
3) Macro level
1) Family groups and local communities
2) Organizations. institutions, and ethnic subcultures
3) National and international systems
What is symbolic interactionism?
The study of human actions and interactions through the use of symbols for communication.
What are the three assumptions of symbolic interactionism?
1) Humans act toward symbols based on the meanings that these symbols carry.
2) The meanings symbols carry from social interaction.
3) Humans interpret the meaning of symbols, and this interpretation influences action.
Social construct
Any idea that has been created and accepted by the people in a society.
Social Constructionism
Attempt to understand a society through the study of the society’s social constructs.
Rationale Choice (Exchange) Theory
People will weigh the costs and benefits when making choices, ranking their options based on maximizing perceived benefits.
Conflict Theory
A macro theory that attempts to understand society by examining the inevitable conflicts between groups in society.
What is Capitalism?
It is an economic system in which individuals and corporations, rather than the government, own and control the means of production (property, machinery, etc.)
In Karl Marx’s model of capitalism, what are the two classes?
1) Capitalist (Bourgeoisie) Class
2) Worker (Proletariat) Class
Interest Groups
Organizations of people with shared goals who try to influence public policy and government decisions
Structural-Functionalism
Compare the society to an organism and different groups of people are different type of organs and they all have essential functions to perform.
Manifest Function
The intended consequences of an action.
Latent Function
The unintended, but beneficial consequences of an action.
Dysfunctions
Negative consequences of an action.
What does the feminist theory argue?
Men seek power and domination over women through societal privilege and institutional discrimination.
What does the term Glass Ceiling refer to?
Processes that limit the progress of women to higher job positions.
What does the term Glass Escalator refer to?
Processes that push men to higher job positions, even though men do not want to.
Social institutions
Well-established social structures that dictate certain patterns of behavior or relationships and are accepted as a fundamental part of culture.
Patterns of kinship
The rules and systems cultures use to define family relationships
Hidden Curriculum
The unwritten, unofficial lessons, norms, values, and perspectives students learn in school.
Teacher Expectancy
Teachers tend to get what they expect from students.
Religiosity
How religious one considers oneself to be, including the strength of one's religious beliefs, engagement in religious practices, and attitudes about religion itself.
Denomination
A distinct, organized religious body with shared beliefs which is a group within a larger faith.
Sect
A religious group that chooses to break off from the parent religion.
Fundamentalism
Maintenance of strict adherence to the religious code.
What does the word “Secularize” mean?
Move away from religion to rationality and scientific thinking.
Democracy
Every citizens have a political voice.
Monarchies
Includes a royal ruler (either a King or a Queen) whose power can be limited by a constitution, a parliamentary system, or some other legislative body.
Dictatorship
A system where a single person holds power.
Theocracy
Power given to religious leaders.
Charismatic authority
A leader with a compelling personality.
Which kind of economic focuses on free market trade and laissez-faire policies, where government interventions are as little as possible?
Capitalist economies
Division of labor
Specific components of a larger task are separated and assigned to skilled and trained individuals.
Which kind of economic treat large industries as collective, shared businesses, and compensation is provided based on the work contribution of each individual into the system.
Socialist economies
Sick role
Describes the socially expected behaviors, rights, and obligations of someone who is ill, granting them temporary exemption from normal duties (work, school) while requiring them to seek competent help and strive for recovery
What does the term “Medicalized” mean?
Behaviors that have been defined and treated as medical conditions.
Illness experience
The subjective, personal, and social reality of being sick.
Social epidemiology
The effects of racial and economic inequality or government safety net legislation on health and access to healthcare.
Beneficence
The physician has a responsibility to act in the patient’s best interest.
Nonmaleficence
do no harm: must avoid treatment in which the potential to harm outweighs the potential for benefit.
Respect for patient autonomy
The physician has a responsibility to respect patients’ decisions and choices about their own healthcare.
Justice
The physician has a responsibility to treat similar patients with similar care, and to distribute resources equally.
Artifacts
Material items that they make, possess, and value.
Material culture
The physical objects, resources, and spaces that people create, use, and give meaning to, reflecting their society's values, technology, and traditions.
Symbolic culture (Nonmaterial Culture)
Refers to the intangible ideas, beliefs, values, norms, language, and customs that give meaning to a society.
Culture lag
Symbolic culture is usually slower to change than material culture.
Cultural barriers
Obstacles to effective communication and interaction caused by differences in language, values, beliefs, norms, nonverbal cues, and perceptions (like time or hierarchy) between cultures, leading to misunderstandings, conflict, or reduced productivity
What is the difference between “Value” and “Belief”?
Values are what a person deems important in life, which dictate one’s ethical principles and standards of behavior.
Belief is what people accept as truth.
Life course perspective (Life course approach)
Considering an individual’s age and cumulative life experiences when analyzing their personality, social status, health, and other social metrics.
Ageism
Prejudice, stereotypes, or discrimination based on age.
Dependency ratio
The ratio of the population that is not in the workplace to the population that is in the workplace.
Youth ratio
The population below age 15 divided by the population between ages 15 and 65.
Stable population
A population’s fertility rate and mortality rate remain relatively consistent over a long period of time.
Gender roles
Expected behavioral traits associated with a particular sex.
Gender identity
Individuals’ behaviors that project the expected behavior of a gender that the individuals wish to portray.
Gender segregation
Separation of individuals based on perceived gender.
Gender inequality
Intentional or unintentional empowerment of one gender to the detriment of others.
Gender stratification
Any inequality in access to social resources based on gender.
Radicalization
The social process by which racial groups are associated with specific attributes or characteristics.
Symbolic ethnicity
A sociological concept describing the connection to one's ethnic heritage, where individuals pick and choose specific cultural symbols (like food, holidays, or traditions) to express pride without fully adopting the ethnic group's everyday practices, beliefs, or language.
Sexual orientation
The direction of an individual’s sexual interest.
Heterosexual
Attraction to an individual of a different sex.
Bisexual (Pansexual)
Attraction to members of multiple sexes.
Homosexual
Attraction to individuals of the same sex.
Kinsey Scale: What do “0” and “6” represent?
“0” represents total heterosexuality, and
“6” represents total homosexuality.
Generation status
The place of birth of a specific person or that person’s parents.
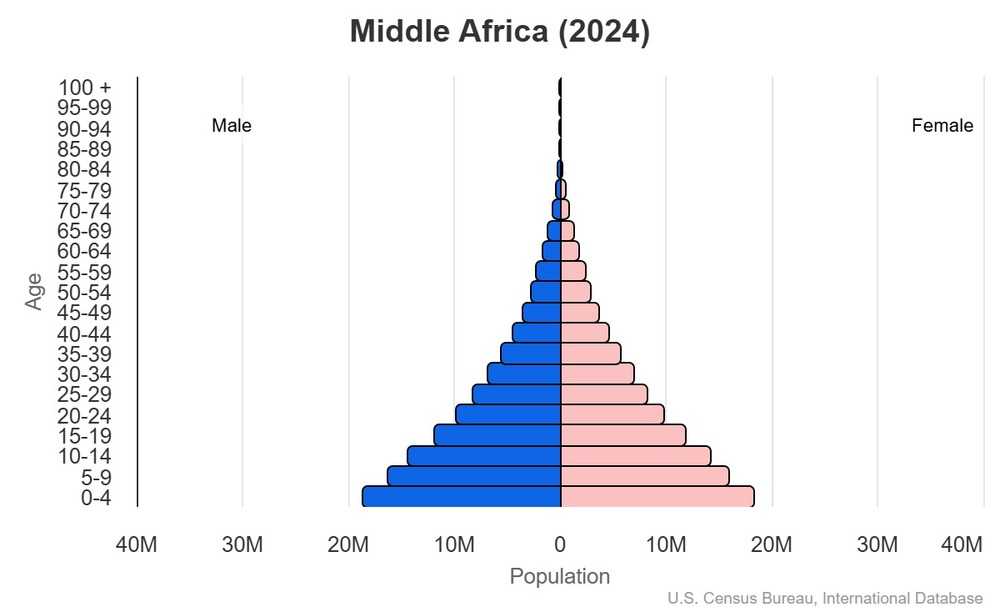
This image is an example of ___.
Population pyramid
Fertility rate
The average number of children born to a woman over a lifetime in a population.
Mortality rate
The number of deaths in a population per unit time.
What are the four stages of the Demographic Transition Theory?
1) Preindustrial society; birth and death rates are both high, resulting in a stable population.
2) Economic progress leads to improvements in healthcare, nutrition, sanitation, and wages, causing a decrease in death rates. Thus, the total population increases.
3) Improvements in contraception, women’s rights, and a shift from an agricultural to an industrial economy cause birth rates to drop.
4) An industrialized society; birth and death rates are both low, resulting in a relatively constant total population.
Malthusian theory
The exponential growth of the human population will exceed the growth of the food supply and lead to social degradation and disorder.
Social movements
Large, organized efforts by groups of people to achieve or resist social or political change
Relative deprivation
The feeling of lacking something (resources, status, opportunities) compared to a reference group or expectation.
What do the terms “proactive” and “reactive” mean regarding social movements?
1) Proactive: social movements that promote social change.
2) Reactive: social movements that resist social change.
Resource mobilization
The process of gathering and effectively using financial, human, and material assets to achieve organizational goals.