year 2- tricky AO1
1/145
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
146 Terms
Explain how foetuses developed two different genes for haemoglobin when humans originated with a single gene?
Duplication mutation occurred
Copy of gene developed mutations
Both genes are expressed
Natural selection- genes passed on
Explain how mutation in ion channel protein in cell membrane leads to symptoms of cystic fibrosis (thick mucus)
Channels non functioning
Fewer ions transported out of cells lining airways
Water gradient not established so less movement of water by osmosis
Mucus is thicker
Explain how mutation in gene encoding an enzyme/ protein may be damaging?
Amino acid sequence/ Primary structure altered
Changes in bonding
Tertiary structure altered
No longer complementary/ cant form complexes
Explain how a mutation in calcium ion channel genes could stimulate muscles to contract in response to anaesthetic?
Mutation alters shape of calcium ion channel receptor
Anaesthetic complementary to receptor
Channels stimulated by anaesthetic to open
Calcium ions diffuse out of SR
Ions bind to tropomyosin, exposing myosin binding sites
Actin-myosin cross bridges form causing muscle to contract
Explain how T tubules help initiation of muscle contraction?
Form connection between sarcolemma and sarcoplasmic reticulum
Depolarisation carried to centre of muscle cell quicker, calcium ions released quicker
Define a stem cell?
Can divide an unlimited number of times
Undifferentiated cell
Can differentiate into a specialised cell
Suggest why its advantageous for scientists to use island populations for investigations into inheritance?
All individuals in population can be sampled
Less sampling error
Little gene flow- more chance of genetic drift
Explain what epigenetic modifications are?
Factors affecting gene expression
Without altering DNA base sequence
Define ‘induced pluripotent stem cell’?
An adult somatic cell with the properties of pluripotent stem cell
Treated by transcription factors turning on genes allowing differentiation
Define epigenetic modifications?
Heritable changes to DNA
Without changes to base sequence of DNA
Explain how stem cells develop into specialised cells?
Stimulus e.g. chemical/ hormone
Some genes activated
Activated genes transcribed- producing mRNA
mRNA translated into proteins
Proteins modify cell, determining structure and function
Cell becomes specialised
Explain how siRNA silence genes?
bind to complementary mRNA strand
mRNA cut into fragments
by protein complex
preventing translation into polypeptide
Describe siRNA?
small double stranded RNA molecules
which breakdown mRNA preventing transcription
Describe methylation and explain how it makes genes inactive?
The addition of methyl groups
To the cytosine bases on DNA
DNA less accessible to transcriptional factors
RNA polymerase does not bind and transcribe section of DNA
Gene not expressed
Explain the different types of stem cells?
Pluripotent- differentiate into almost any cell type, found in zygote
Totipotent- differentiate into any body cell type, found in embryo
Multipotent- differentiate into limited number of cell types, found umbilical cord/ some tissues
Unipotent- differentiate into a single type of cell,
Define a Mutation?
Change in base sequence
Results in formation of a new allele
Why has lactose tolerance only increased in frequency recently despite cattle farming originating centuries ago?
Selection pressure is weak to availability of alternative food sources
Mutations are infrequent
Human lifespan is long therefore genes passed on slower
Explain how mutagenic substances in red meat could lead to cancer?
Change base sequence of DNA
By addition/ substitution mutation
Primary and tertiary structure altered, protein shape changed
Loss of function of tumour suppressor genes
Cell division dysregulated
Explain why speciation may occur is small populations?
Genetic drift
Reduced gene pool
Alleles do not have equal chance of being passed on due to small population
Alleles passed on increase in frequency faster
Explain what discontinuous variation is?
Where the allele phenotype has a discrete value e.g. colour.
Mutations happen within gene at different locations resulting in new allele variants
Explain how the structure of myofibril changes during muscle contraction?
Sarcomere shortens
A band remains same length
Define term silent mutation
Change in nucleotide base sequence that does not alter amino acid sequence
No effect on protein synthesized
Explain how mutation x leads to formation of new protein?
Change in nucleotide base sequence
Primary structure altered
Different bond formations so secondary structure altered
Different tertiary structure leads to new protein w dif shape
Explain why stores of glycogen are found in fast muscle fibres?
Hydrolysed into glucose for anaerobic respiration
Large amounts of glucose required to produce sufficient ATP for muscle contraction
Compare the structure of actin and myosin?
Actin is thin fibre
Made up of two filaments twisted around each other
Myosin is a thick fibre
Consisting of long tails and globular heads
Suggest why slow muscle fibres contain large amounts of myoglobin?
Stores O2 in muscle
More O2 available for aerobic respiration
To produce ATP for contraction
Describe what a tendon is and its function?
Lengths of connective tissue
Joining skeletal bone to muscle
What defines Positive feedback?
A deviation away from the norm leads to further deviation away from the norm.
What is the difference between spatial and temporal summation at synapses?
Temporal: impulses reach the same synaptic knob quickly,
Spatial: impulses reach different knobs simultaneously.
How is blood filtered in the kidney?
Blood enters through afferent arteriole,
High hydrostatic pressure in glomerular capillaries,
Filtrate is formed from water and small molecules,
Large proteins cannot pass through.
Explain selective reabsorption in the kidney.
Sodium transported into blood,
Low sodium in epithelial cells lining the PCT,
Sodium diffuses out of PCT into epithelial cells,
Glucose/ Amino Acids cotransported with sodium,
All glucose reabsorbed.
How is water reabsorbed in the loop of Henle?
Sodium ions leave ascending limb creating a gradient,
Water exits descending limb,
Ascending limb is impermeable to water.
What happens in the DCT and collecting ducts?
Filtrate is dilute,
Water moves out via osmosis,
Remaining filtrate forms urine.
How is low water potential of blood corrected?
Osmoreceptors detect changes in water potential,
Hypothalamus produces ADH.
How does ADH increase permeability in the DCT and collecting duct?
ADH binds to receptors,
Activates phosphorylase,
Vesicles with aquaporins fuse to membrane.
Describe the structure of the glomerular capillary endothelium?
One cell thick,
Basement membrane,
Podocytes with gaps.
How is the PCT adapted for reabsorption?
Microvilli increase surface area,
Many mitochondria for active transport.
Explain how the endocrine system brings about change in body?
Releases Hormones
Hormones transported in blood to target organs
Hormones bind to complementary receptors on target organs
Explain how negative feedback mechanism work
Receptors detect changes in conditions
Corrective mechanisms return conditions to within normal range
Explain how insulin lowers blood glucose concentration
binds to complementary receptors on cell membranes of target cells
stimulates glucose transporter channel proteins to fuse with cell membrane
this increases permeability of tissues to glucose
activates enzymes involved in glycogenesis
Explain why its advantageous for adrenaline to be amplified through secondary messenger model
Many cAMP produced,
Large numbers of enzymes activated,
Glucose conc raised rapidly
Explain how glucagon causes an increase in blood glucose?
Binds to complementary receptors on target cells
Activates adenylate cyclase
ATP converted to cAMP which is the second messenger model
Protein kinase enzymes activated,
Activates cascade for breakdown of glycogen into glucose
Explain how IAA causes cell elongation
Binds to receptor on cell membrane
Stimulates proton pump, protons pumped into cell wall
Cell wall acidified, cellulose myofibrils weakened
K+ channels open and K+ enters cytoplasm
Water enters cytoplasm down gradient
Compare visual acuity of rod and cone cells
Multiple rod cells synapse with a single bipolar cell (which multiple bipolar synapse with ganglion etc)
Single cone cell synapse with single bipolar cell so brain recieves specific impulse
Explain how summation occurs in rod cells?
Multiple rod cells stimulated,
Combined generator potentials is enough to meet threshold and stimulate action potential in bipolar neurone
Greater visual sensitivity compared to cones
Explain how heart beats
SAN is group of cells in right atrium,
initiates wave of depolarisation causing atria to contract.
Non conductive tissue prevents depolarisation reaching ventricles, passed to AVN
AVN sends impulse down bundle of His after delay,
Purkyne tissue carries impulse to base of ventricles.
Ventricles contract from base
Explain effect of exercise on heart rate
Increased conc of CO2 and decrease in blood pressure
Detected by chemoreceptors in carotid,
Send impulse to medulla (acceleratory centre)
Impulses via sympathetic neurones to SAN,
Noradrenaline secreted at synapse,
SAN stimulated increasing frequency of depolarisation waves
Explain process of lactate fermentation
Pyruvate is reduced to lactate by NADH
NAD is regenerated
Enzyme is lactate dehydrogenase
Pyruvate is final hydrogen acceptor
Lactate can be oxidised back to pyruvate or converted into glycogen for storage
Explain process of ethanol fermentation?
Pyruvate is decarboxylated to ethanal,
Ethanal reduced to ethanol by NADH
NAD regenerated
Ethanal is final hydrogen acceptor
Enzyme is alcohol dehydrogenase
Explain how alternative respiratory substrates are used in respiration
Proteins hydrolysed into amino acids
Undergo deamination
Converted to either pyruvate or intermediates in Krebs cycle
Lipids hydrolysed into glycerol and fatty acids
Glycerol phosphorylated into triose phosphate (enters in glycolysis)
Fatty acids converted into acetyl CoA (enter Krebs cycle)
Explain why damage to proteins in electron transport chain inhibits growth
Fewer electrons passed down chain
Fewer protons transported across thylakoid membrane
Reduced chemiosmotic gradient
Less ATP and NADPH synthesised
Light independent reaction slows
Rate of photosynthesis reduced
Explain nitrogen nutrient cycle?
Nitrogen fixing bacteria convert N2 gas into ammonia
Ammonium ions oxidised into nitrite then nitrate ions (nitrification)
Nitrate ions absorbed by plants
Saprobionts feed on dead organic matter and release ammonium ions
Denitrifying bacteria convert nitrates to N2 gas in anaerobic conditions
Define a saprobiont?
Bacteria or fungi
feed on dead organic matter
Carry out extracellular digestion- secrete enzymes onto food
Explain how saprobionts obtain nutrients from animal waste?
Carry out extracellular digestion
Secrete enzymes onto food
Absorb nutrients
Explain how a mutation in a transcription factor which activates tumour suppressor genes can lead to cancer?
Tertiary structure of transcription factor is altered
Transcription factor no longer complementary to promotor region
RNA polymerase doesn’t bind and transcription is inhibited
Cell cycle and cell division becomes dysregulated leading to uncontrolled cell division - tumours.
Explain how including leguminous plants in crop rotations improves yields?
Contain nitrogen fixing bacteria in roots/nodules
when crops die/harvested additional nitrogen compounds are released into soil
Explain how an impulse is transmitted across a neuromuscular junction leading to muscle contraction?
Presynaptic membrane depolarised
Calcium ions diffuse into neurone
Vesicles (containing A choline) fuse w membrane
A choline released and diffuses across junction
A choline binds to receptor proteins on sarcolemma
Sodium ions diffuse in, depolarising sarcolemma
Action potential passes down Ttubules to muscle fibre
Calcium ions diffuse out of sarcoplasmic reticulum into sarcoplasm
Explain process of natural selection?
Genetic variation due to mutations
Change in environment leads to selection pressure
Individuals with advantageous alleles survive
Reproduce and advantageous alleles passed on through generations
Frequency of allele in gene pool increases
Explain the oestrogen stimulation pathway?
Oestrogen diffuses into cytoplasm through cell surface membrane
Oestrogen enters nucleus through nuclear pore
Oestrogen binds to oestrogen receptor attached to protein complex
Receptor undergoes conformational change, detaching from protein complex
Receptor diffuses towards gene to be expressed
Receptor binds to cofactor, allowing it to bind to promoter region of gene
RNA polymerase stimulated to bind and transcribe
Explain how allopatric speciation occurs
Geographical isolation due to physical barrier
Gene pools become separated, no interbreeding between populations
Variation exists within each population due to mutations
Different selection pressures- abiotic/biotic factors in environment
Advantageous alleles passed on
Alelle frequencies change due and gene pools different
Reproductive isolation- no longer breed to produce fertile offspring
Explain how Sympatric speciation occurs
No geographical isolation
Mutation occurs
Populations become reproductively isolated
Different selection pressures
Advantageous alleles passed on
Change in allele frequencies
No longer produce fertile offspring
Explain why two species cannot occupy the same niche?
Interspecific competition
One species will out compete the other
Describe how a gene can be isolated from human DNA?
Using restriction enzyme/ endonuclease
To cut DNA in a specific place
Describe how an isolated gene can be replicated by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR)?
Heat DNA to 90-95
Strands separate
Add primers and nucleotides
Temperature lowered (55) so that primers bind to DNA
(temp increased to 72) DNA polymerase joins complementary nucleotides
Cycle repeated 20-40 times
Explain how modified plasmids are made by genetic engineering and how use of markers enables detection of plasmid containing bacteria?
Desired gene isolated from another organism
Using restriction enzymes to cut DNA
Producing sticky ends
Ligase used to join wanted gene to plasmid
Marker gene included
Plasmid inserted into bacteria to grow
On medium that selects for marker
Bacteria not killed have inserted plasmid
Describe one way Embryonic Stem Cells may lead to more harm to patient?
Might divide out of control
Leading to tumour/ Cancer
Suggest how the growth of new blood vessels into damaged heart tissues could increase the rate of repair of tissues?
Greater blood supply
Bringing more O2/ glucose for respiration
Brings more amino acids for protein synthesis
For cell repair/ mitosis
Explain how transcription factors result in expression of gene?
Transcription factors move from cytoplasm into nucleus
Bind to complementary promoter region on DNA
Initiates transcription of gene/ RNA polymerase bind
mRNA is translated to produce polypeptide
Suggest how the binding of interferon gamma to its receptor protein leads to the production of phosphorylated STAT1?
Binds to complementary receptor, altering its tertiary structure
Enzyme stimulated
Phosphorylates STAT1 using ATP
Explain how an activated oestrogen receptor affects the target cell?
Binds to promoter, stimulating RNA polymerase
Initiates transcription
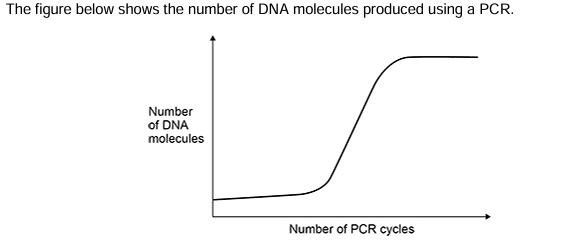
Explain shape of curve?
Number of fragments doubles each cycle- exponential increase
Few fragments initially
Plateaus when no more nucleotides/ primers
Explain how scientists used a radioactively labelled DNA probe to show that the cells of tobacco plant leaves contained the SUT1 gene?
Extract DNA and add restriction enzymes
Separate fragments using gel electrophoresis
Treat DNA to form single strands
Probe binds to complementary gene
Use autoradiography to identify bound probe
Suggest how the production of ‘antisense’ SUT1 mRNA in plants would reduce the expression of the SUT1 gene?
Antisense mRNA is complementary to (sense)mRNA
Antisense binds to mRNA
Ribosomes cannot bind
Preventing translation into polypeptide
Define a DNA probe?
Short, single strand of DNA
Complementary bases to specific target gene
Describe how DNA is broken down into smaller fragments?
Restriction endonucleases
Cut DNA at specific base sequences/ restriction sites
Break phosphodiester bonds
What would the scientists have inserted into the plasmid along with the spider gene to ensure that the spider gene was only expressed in the silk glands of the silkworms?
Promoter region
Explain how plants containing gene from insect can synthesise insect protein?
Genetic code is universal
Insect gene can be transcribes
Translated into polypeptide using same amino acids
Suggest why DNA replication stops during PCR?
Limited number of nucleotides
DNA polymerase eventually denatured
Explain how the drop in pH during exercise reduces the ability of calcium ions to stimulate muscle contraction?
Low pH alters the tertiary structure of calcium ion receptors
Fewer calcium ions bind to tropomyosin causing it to change shape
Fewer myosin binding sites exposed
Fewer cross bridges from
Describe the roles of calcium ions and ATP in muscle contraction?
Calcium ions diffuse into myofibrils from sarcoplasmic reticulum
Causing tropomyosin to move
Exposing binding sites on actin
Myosin heads attach to binding sites
Hydrolysis of ATP on myosin heads causes them to bend
Pulling actin molecules
Attachment of new ATP molecule onto myosin head causes detachment from actin
Explain why if myosin molecules cant bind to each other muscles cannot contract?
Cant form thick myosin filament
Actin not pulled/ filaments don’t slide past each other
Myosin heads not attached/ fixed therefore move
Sarcomere not shortened
Describe the role of saprobionts in the nitrogen cycle?
Secrete enzymes to digest proteins/ urea in organic matter
Release ammonia/ ammonium compounds into soil
Explain why some of the most productive fishing areas are found in coastal waters?
Leaching of nitrates into water
Nitrates absorbed by producers/ algae
Lots of producers/ food so more fish
Explain why freshwater marshes have a high NPP?
Low rates of respiration
More biomass/ growth
Describe and explain how succession works?
Colonisation by pioneer species
Change environment/ named factor
Environment becomes less hostile/ more suitable for other species
Biodiversity increases
Until climax community reached
Suggest why petroleum is used as a comparison when evaluating biofuels?
Widely used
Benchmark/ reference- produces known amount of CO2
Produces large amount of CO2
Is a decreasing resource- could be replaced by biofuel
Why did scientists use animals of same breed for investigation?
Same breed so similar alleles
Factor controlled so only independent variable affects results
Explain when scatter graph is suitable for data?
Relationship between two discrete/ independent variables
Describe the process of glycolysis?
Glucose phosphorylated using 2 ATP
(Lysis) into triose phosphate
Triose phosphate oxidised then decarboxylated
Into pyruvate
NAD reduced
Net gain of 2 ATP (4 produced through substrate level phosphorylation)
Suggest why apparatus in respiration (air bubble) practical is left for 10 mins?
Reach equilibrium
Allow for pressure changes in apparatus
Allow rate of respiration of seeds to stabilise
Describe how acetyl coenzyme A is formed in the link reaction?
Oxidation of pyruvate
Decarboxylation releasing CO2
Addition of coA
Explain how a high density of cones in fovea allows predator to see prey in detail?
High visual acuity
Each cone synapsed to a single neurone
Brain receives separate impulses
Explain how high density of rod cells allows predator to hunt at night?
High visual sensitivity
Multiple rod cells synapsed to a single neurone
Threshold to generate action potential reached by spatial summation
Enough neurotransmitter to overcome threshold
Explain how resting potential of -70mV is maintained in sensory neurone?
Membrane more permeable to K+ ions, less permeable to Na+ ions
Sodium potassium pump actively transports Na+ out of axon and K+ in
Higher conc of K+ inside axon, higher conc of Na+ out of axon
Explain how applying pressure to Pacinian Corpuscle results in changes to membrane potential?
Layers of membrane deformed
Sodium ion channels open, Na+ diffused into axon
More channels open, more Na+ diffuses in
Explain how damaged myelin sheaths results in slower responses to stimuli?
No saltatory conduction
Depolarisation occurs along entire length of axon
Explain when a t test would be selected?
When determine significant differences between means
Explain how damage to myelin sheaths of neurones can cause muscle paralysis?
Depolarisation occurs along entire length of neurone
Slower transmission of impulses
Neuromuscular junction affected
Suggest advantages of simple reflexes?
Rapid
Protect against damage to body tissues
Do not have to be learnt
Escape from predators
Enable homeostatic control
Explain how IAA results in curvature of shoot?
IAA produced in shoot tip
Diffuses into shoot
Accumulates on shaded side
Stimulates cell elongation