Neurological System, HA Exam 3
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering major neurological structures, cranial nerves, assessment tests, and key clinical terms from the lecture.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Central Nervous System (CNS)
The brain and spinal cord; integrates and coordinates all bodily functions.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
All neural tissue outside the CNS, including cranial nerves, spinal nerves, and reflex arcs.
Brain
Primary organ of the CNS housed in the skull; controls cognition, sensation, and motor activity.
Spinal Cord
CNS pathway in the vertebral canal transmitting impulses to and from the brain.
Cranial Nerves
Twelve paired nerves emerging from the brain that control sensory and motor functions of head and neck.
Spinal Nerves
31 pairs of mixed nerves arising from the spinal cord, supplying the body below the head.
Reflex Arc
Involuntary neural pathway producing a reflex action without conscious thought.
Cerebellum
Brain structure that coordinates balance, posture, and skilled movements.
Brainstem
Midbrain, pons, and medulla; regulates vital functions such as respiration and heart rate.
Midbrain
Upper part of brainstem involved in visual and auditory reflexes.
Pons
Middle brainstem section relaying signals between cerebrum and cerebellum; aids breathing.
Medulla Oblongata
Lower brainstem controlling heart rate, blood pressure, and swallowing.
Hypothalamus
Brain region regulating temperature, hunger, thirst, and pituitary hormone release.
Thalamus
Relay station for sensory impulses traveling to the cerebral cortex.
Basal Ganglia
Deep brain nuclei coordinating voluntary movement and posture.
Corpus Callosum
Large fiber bundle connecting the two cerebral hemispheres.
Internal Capsule
White-matter tract carrying motor and sensory fibers between cortex and spinal cord.
Monovision
A technique where one eye is corrected for distance vision and the other eye is corrected for near vision
Olfactory Nerve
(CN I) Sensory nerve for the sense of smell.
Optic Nerve
(CN II) Sensory nerve transmitting visual information from retina to brain.
Color, size, and shape
Test for visual acuity
Oculomotor Nerve
(CN III) Motor nerve controlling most extra-ocular muscles, pupil constriction, and lens shape.
Test for pupil size, regularity, direct & consensual light reflex
Trochlear Nerve
(CN IV) Motor nerve moving the eyeball downward and inward via the superior oblique muscle.
Trigeminal Nerve
(CN V) Mixed nerve providing facial sensation and muscles of mastication.
Assess temporal and masseter
Abducens Nerve
(CN VI) Motor nerve abducting the eye via the lateral rectus muscle.
Facial Nerve
(CN VII) Mixed nerve for facial expression, taste anterior 2/3 tongue, and tear/saliva secretion.
Assess by puffing cheeks and closing eyes tightly shut
Vestibulocochlear (Acoustic) Nerve
(CN VIII) Sensory nerve for hearing and equilibrium.
Assess with whisper test
Glossopharyngeal Nerve
(CN IX) Mixed nerve for taste posterior 1/3 tongue, gag reflex, and swallowing.
Note soft palate & uvula movement as patient says “ahhh”
Note quality of voice
Vagus Nerve
(CN X) Mixed nerve controlling speech, swallowing, heart rate, and GI motility.
Assess patient by asking to swallow a drink of water
Spinal Accessory Nerve
(CN XI) Motor nerve innervating sternomastoid and trapezius for head turn and shoulder shrug.
Assess by shoulder shrugging and neck strength
Hypoglossal Nerve
(CN XII) Motor nerve for tongue movement and articulation.
Assess by sticking tongue out and saying “light tight dynamite”
Snellen chart
Diagnostic for distance visual acuity, 20 ft away
Jaeger chart and Rosenbaum chart
Diagnostic test for near visual acuity, only 14 inches away
20/20
What the patient can see at 20 feet, a normal person could see at 20 feet
20/30 Vision
What the patient can see at 20 feet, a normal person could see at 30 feet (patient has worse vision)
Amblyopia
Lazy eyeball
Oh (I)
Olfactory nerve pneumonic
Oh (II)
Optic Nerve pneumonic
Oh (III)
Oculomotor nerve pneumonic
To (IV)
Trochlear nerve pneumonic
Touch (V)
Trigeminal nerve pneumonic
And (VI)
Abducens nerve pneumonic
Feel (VII)
Facial nerve pneumonic
Virgin (VIII)
Vestibulocochlear nerve pneumonic
Girls’ (IX)
Glossopharyngeal nerve pneumonic
Vagina (X)
Vagus nerve pneumonic
Ah (XI)
Accessory (Spinal) nerve pneumonic
Heaven (XII)
Hypoglossal nerve pneumonic
Pneumonic for Types of Cranial Nerves (Sensory, Motor, or Both)
Some Say Marry Money But My Brother Says Big Boobs Matter More
Ptosis
Drooping of the upper eyelid, often due to CN III dysfunction. (Lazy eyelid)
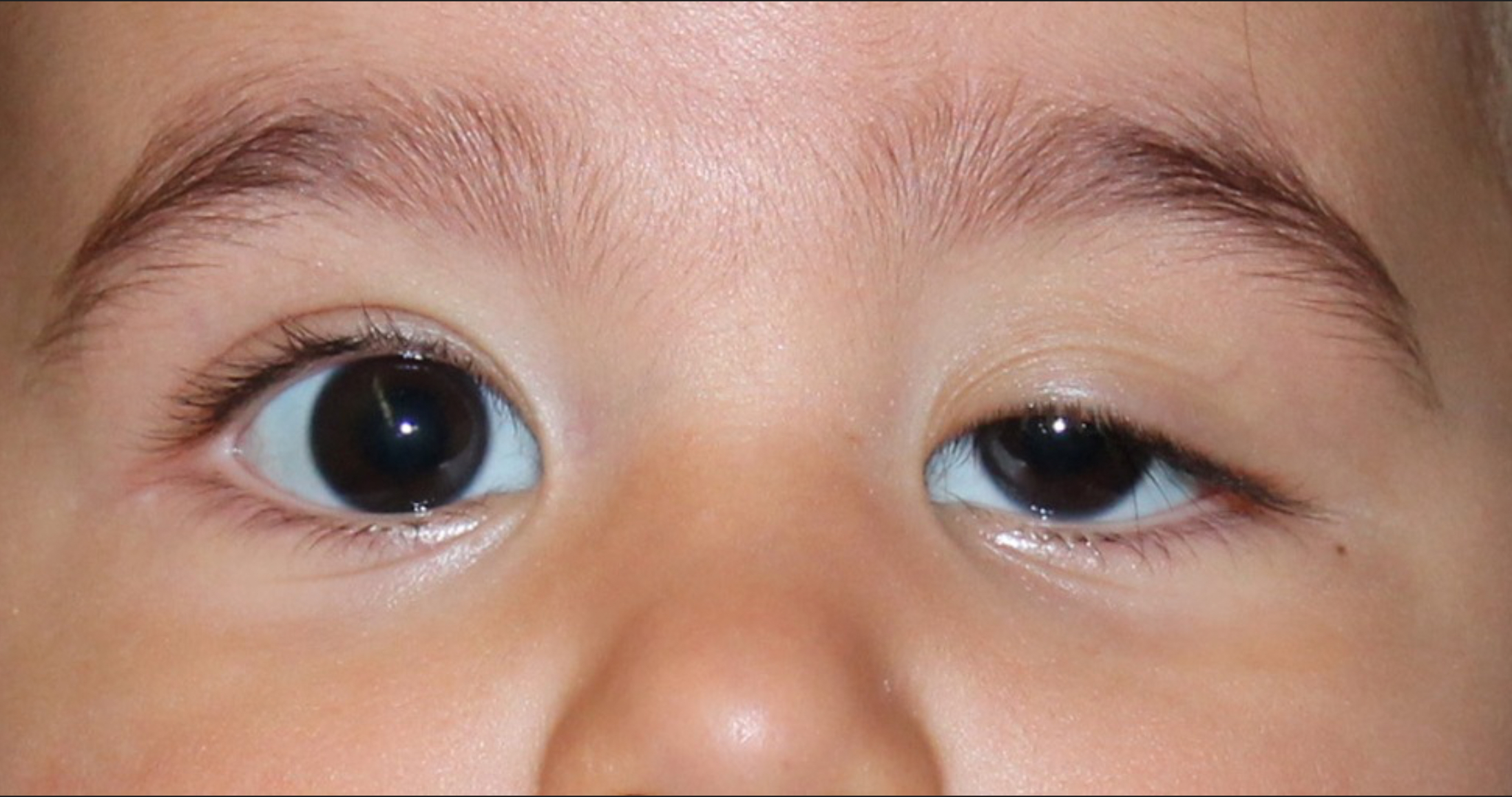
Strabismus
Misalignment of the eyes caused by neuromuscular imbalance (Deviated gaze)

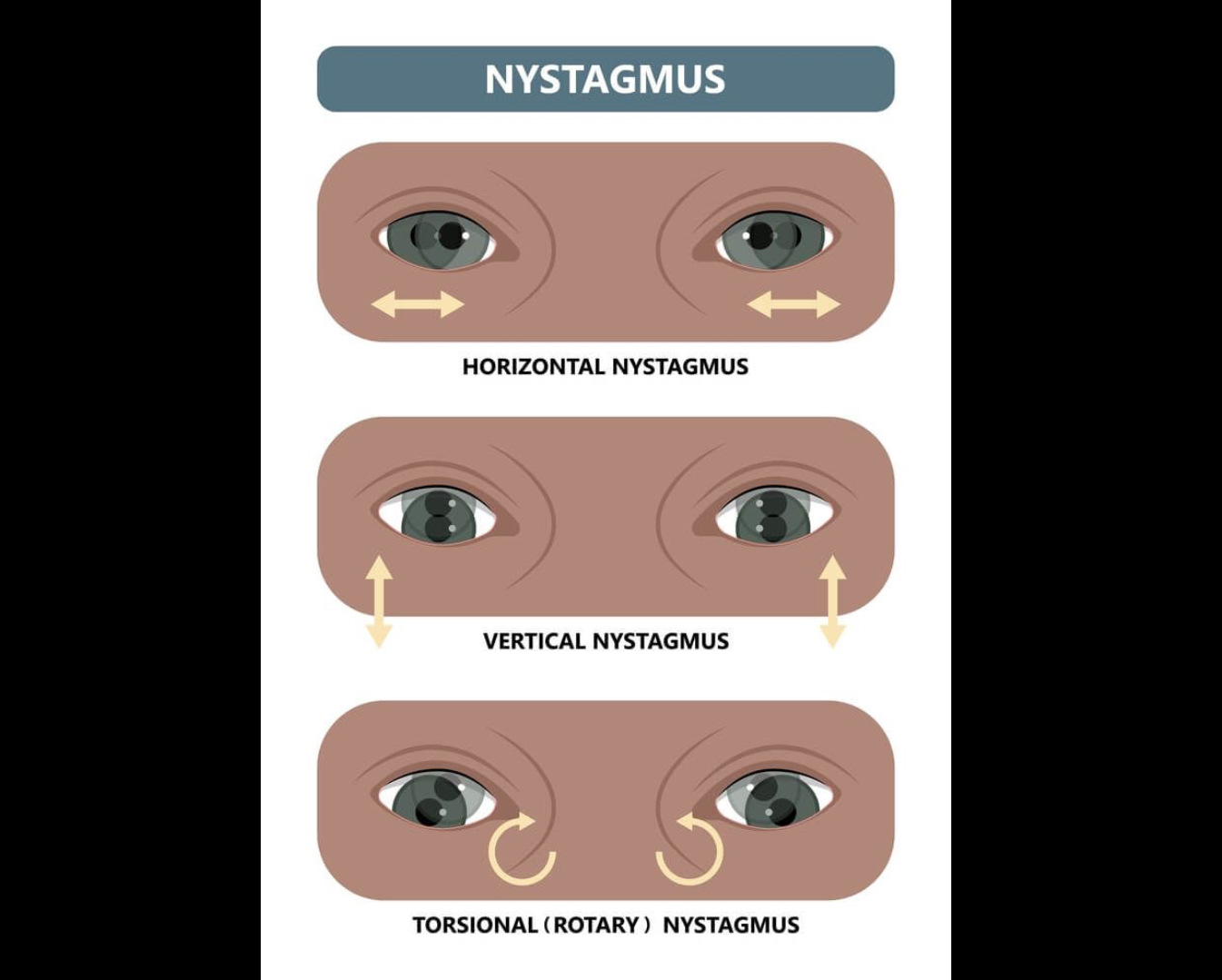
Nystagmus
Involuntary rapid eye movements, may indicate vestibular or cerebellar dysfunction. Alcohol can cause this
Accommodation
Process of the eyes focusing on an object going from far to up close
Anosmia
Loss or absence of the sense of smell.
Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS)
Tool scoring eye opening response, verbal response, and motor responses; 3–15 total; ≤8 suggests coma.
Eye opening must respond to pain, speech, and spontaneous (score to 4)
Motor response must respond to extension, flexion, pain, and verbal command (scores to 6)
Verbal response must respond to being alert and oriented to time and place (scores to 5)
Romberg Test
Balance assessment with patient standing eyes closed; sway indicates cerebellar or proprioceptive loss.
Rapid Alternating Movements (RAM)
Cerebellar test requiring quick alternating hand or finger motions.
Finger-to-Nose Test
Coordination test where patient touches nose then examiner’s finger repeatedly.
Spinothalamic Tract
Anterolateral pathway carrying pain, temperature, and crude touch sensations.
Posterior (Dorsal) Column Tract
Sensory pathway for vibration, position sense, and fine touch.
Stereognosis
Ability to recognize an object by touch alone.
Graphesthesia
Ability to identify traced numbers or letters on the skin.
Two-Point Discrimination
Minimum distance at which two tactile points are felt separately.
Deep Tendon Reflex (DTR)
Involuntary contraction of a muscle after tendon is stretched; graded 0–4+.
Plantar Reflex
Superficial reflex where foot stimulation normally causes toe flexion; Babinski sign is abnormal in adults.
Biceps Reflex
DTR causing elbow flexion when biceps tendon is tapped.
Decorticate Rigidity
Abnormal flexed posture indicating corticospinal tract damage above the brainstem. (Arms and wrists are flexed)
Decerebrate Rigidity
Abnormal extended posture indicating brainstem lesion below red nucleus. (Arms are extended, forearm is pronated, and wrist is flexed)
PERRLA
Pupils Equal, Round, Reactive to Light and Accommodation; normal pupillary response.
Ataxia
Unsteady, staggering gait or incoordination due to cerebellar dysfunction.
Kinesthesia
Sense of joint position and movement.