life processes CBSE class 10
1/107
Earn XP
Description and Tags
vocab words from life processes class 10 biology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
Life processes
1 - Nutrition
2 - respirations
3 - transportation
4 - excretion
Salivary gland
production of saliva
salivary amylase
an enzyme in the saliva that breaks down some starch into sugar
gastric glands
present in the wall of the stomach, secretes gastric juice
Esophagus
food tube connecting the mouth to the stomach
Pepsin
An enzyme present in gastric juice that breaks down proteins into smaller peptides and amino acids that can be easily absorbed in the small intestine.
Mucus
protects stomach lining from HCL
Exocrine pancreas
produces enzymes used to chemically digest food, especially protein
bile
Breaks big fat globules into smaller globules
Pancreatic juice
consists of pancreatic amylase, trypsin, Lipase
pancreatic amylase
carbohydrate starch into sugar
Trypsin
an enzyme produced by the exocrine pancreas; protein into peptone then amino acid
Lipase
enzyme; fat into fatty acid and glycerol
endocrine pancreas
Makes the hormone insulin, which helps control blood sugar levels
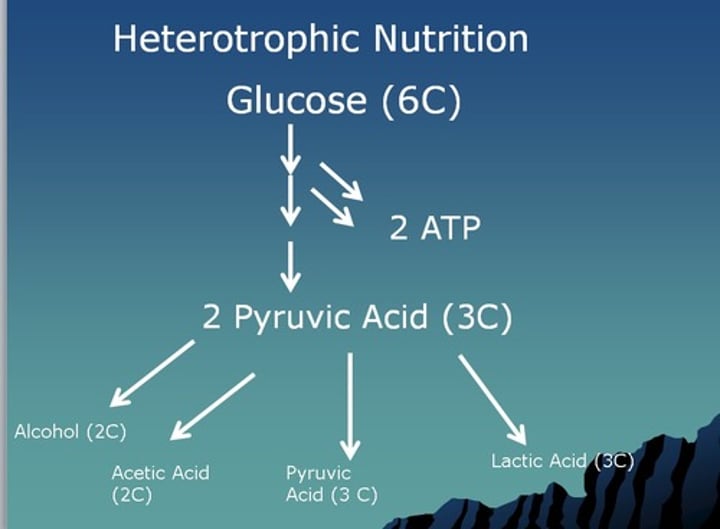
aerobic cellular respiration
Producing ATP with oxygen by breaking down glucose (36-38 ATP); occurs in the mitochondria; complete breakdown of food
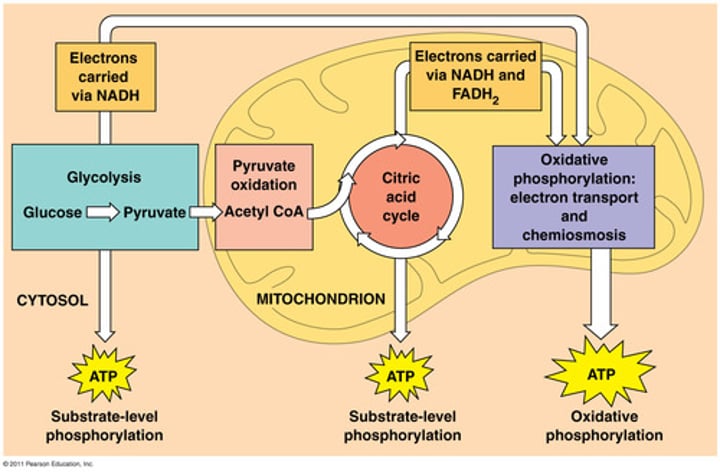
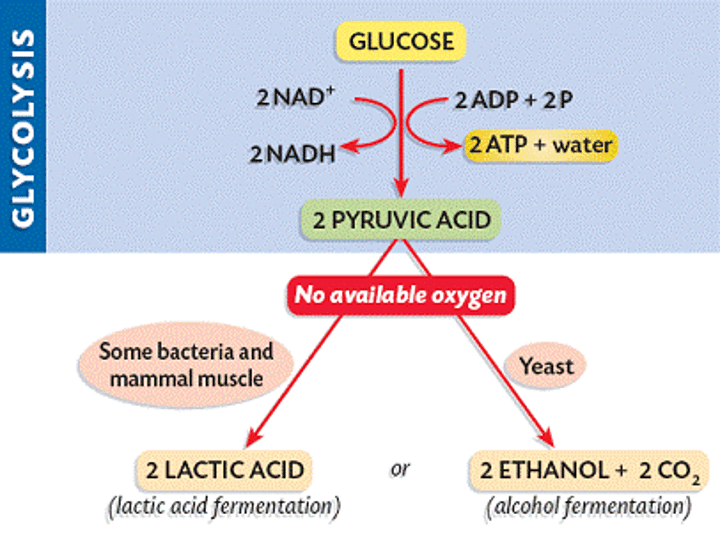
anaerobic respiration
Respiration in the absence of oxygen, releasing small amounts of energy
ATP
Adenosine tri-phosphate
alcoholic fermentation
A process used by yeast cells and some bacteria to produce carbon dioxide and ethyl alcohol
Trachea
windpipe
16–20 C-shaped rings of cartilage
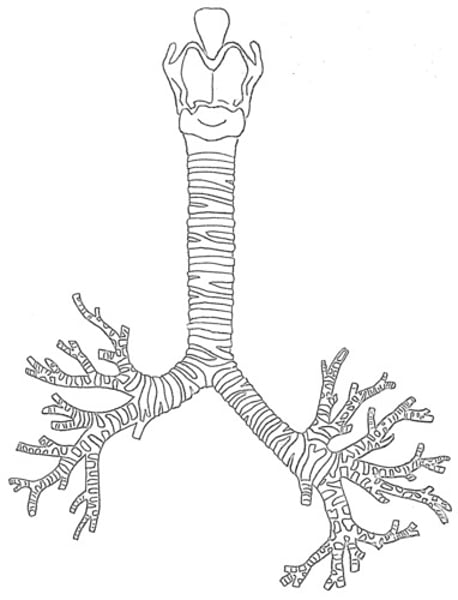
Function of the rings of cartilage in the trachea
support and allow the trachea to move and flex when breathing.
tracheal rings
allows the trachea to collapse slightly to allow food to pass down the esophagus
prevent the trachea from collapsing and blocking the airway.
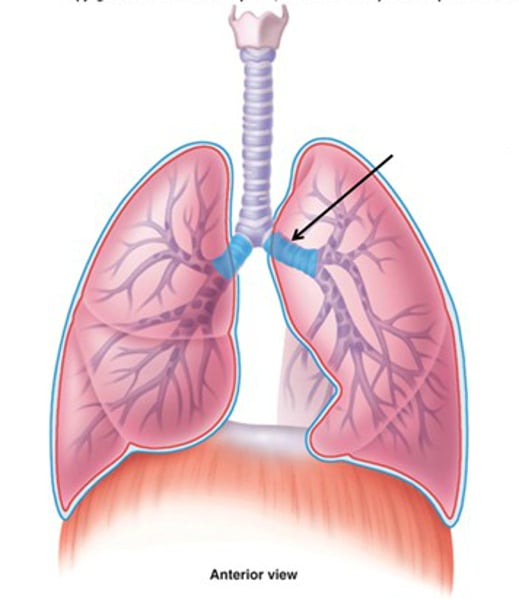
Bronchi
two short branches located at the lower end of the trachea that carry air into the lungs.
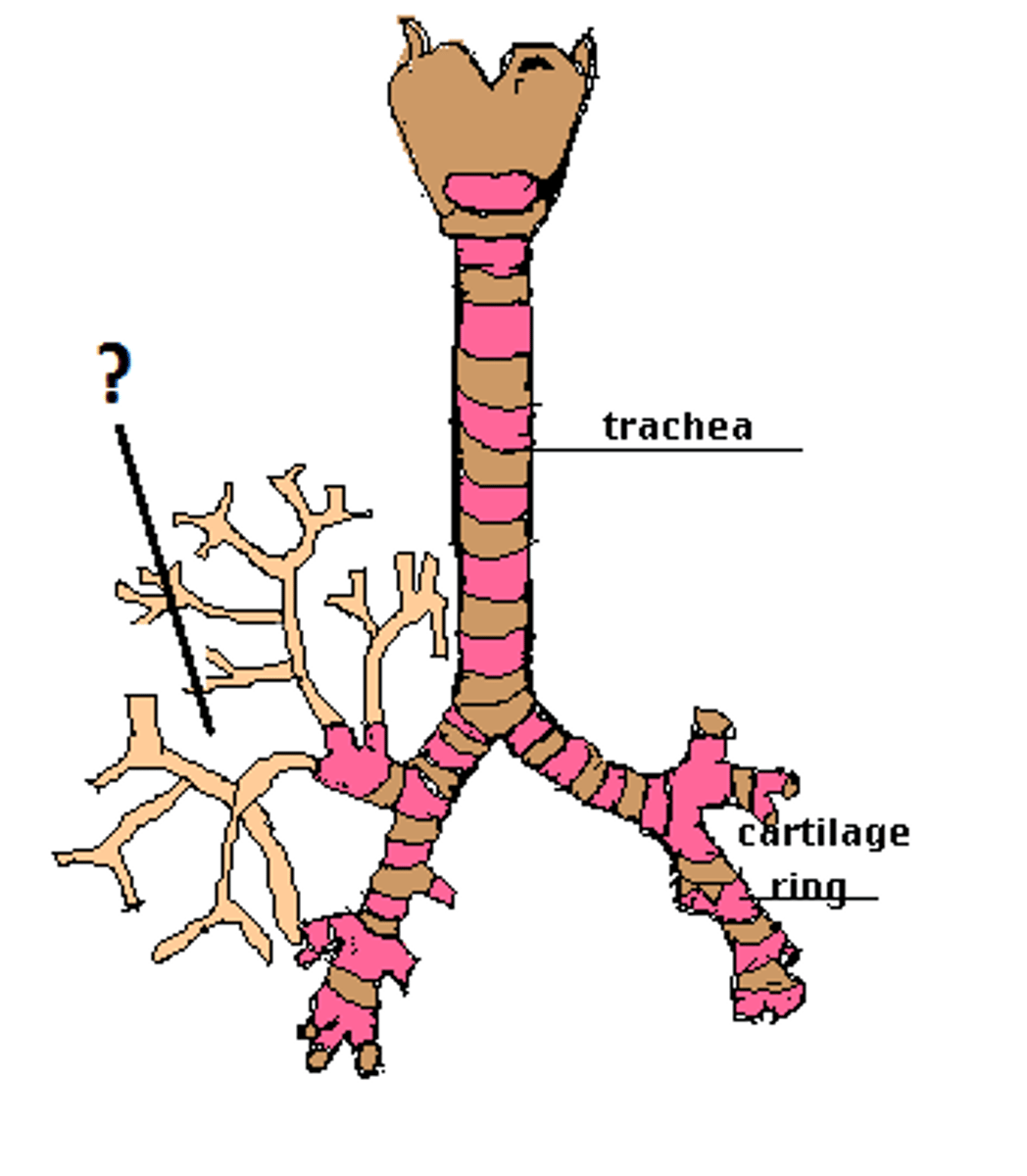
Bronchioles
smallest branches of the bronchi
residual volume
the amount of air left in the lungs after a full exhalation usually 1-1.2L
keeps the lungs from collapsing
Oxyhemoglobin
a bright red substance formed by the combination of hemoglobin with oxygen, present in oxygenated blood.
hemoglobin is also the respiratory pigment in humans
Leukocytes
White blood cells, <1% blood; phagocytosis.
Granulocytes
most common WBC
have little grain-looking things in them
Neutrophil
Eosinophil
Basophil
Neutrophil
phagocytes bacteria (engulfs and destroys/eats foreign substances)
removes cell debris and pathogens (viruses/bacteria)
40-60%
Eosinophil
kills parasitic worms
bilobed nucleus
1-3%
Basophil
releases Histamine and Heparin during alergic reactions
0.4-1%
Histamine
it enlarges blood vessels to improve blood flow (this causes swelling)
Heparin
enzyme that prevents blood from clotting too quickly
help prevent harmful clots from forming in blood vessels.
Agronulocytes
lymphocytes
monocytes
lymphocytes
produced in the bone marrow
goes through a selection process where they learn how to freely attack foreign substances without attacking its own body cells (in the Thymus)
B cells
10%
identifies foreign invaders
produces antibodies
attacks invaders outside the cells
T cells
75%
attacks invaders inside cells
Cytotoxic T cells
Kill cells infected with viruses and bacteria and also destroys tumor cells
Helper T cells
Sends signals which tell other cells in your immune system how to co-ordinate an attack
Regulatory T cells
reduces activity of other T cells when necessary - supress immune response
Monocytes
can leave bloodstream and enter the tissue
phagocytic
dendritic and macrophages cells
Dendritic cells
capture, process, and present antigens to lymphocytes. This initiates and regulates the adaptive immune response
Antibodies
Antibodies are proteins that protect you when an unwanted substance enters your body. Produced by your immune system, antibodies bind to these unwanted substances in order to eliminate them from your system.
antigens
An antigen is a foreign substance that enters your body. This can include bacteria, viruses, fungi, allergens, venom and other various toxins. An antibody is a protein produced by your immune system to attack and fight off these antigens.
Macrophages
plays a role in wound healing and muscle regeneration.
eliminate pathogens and dead cells through phagocytosis
thrombocytes
blood platelets; clothing blood
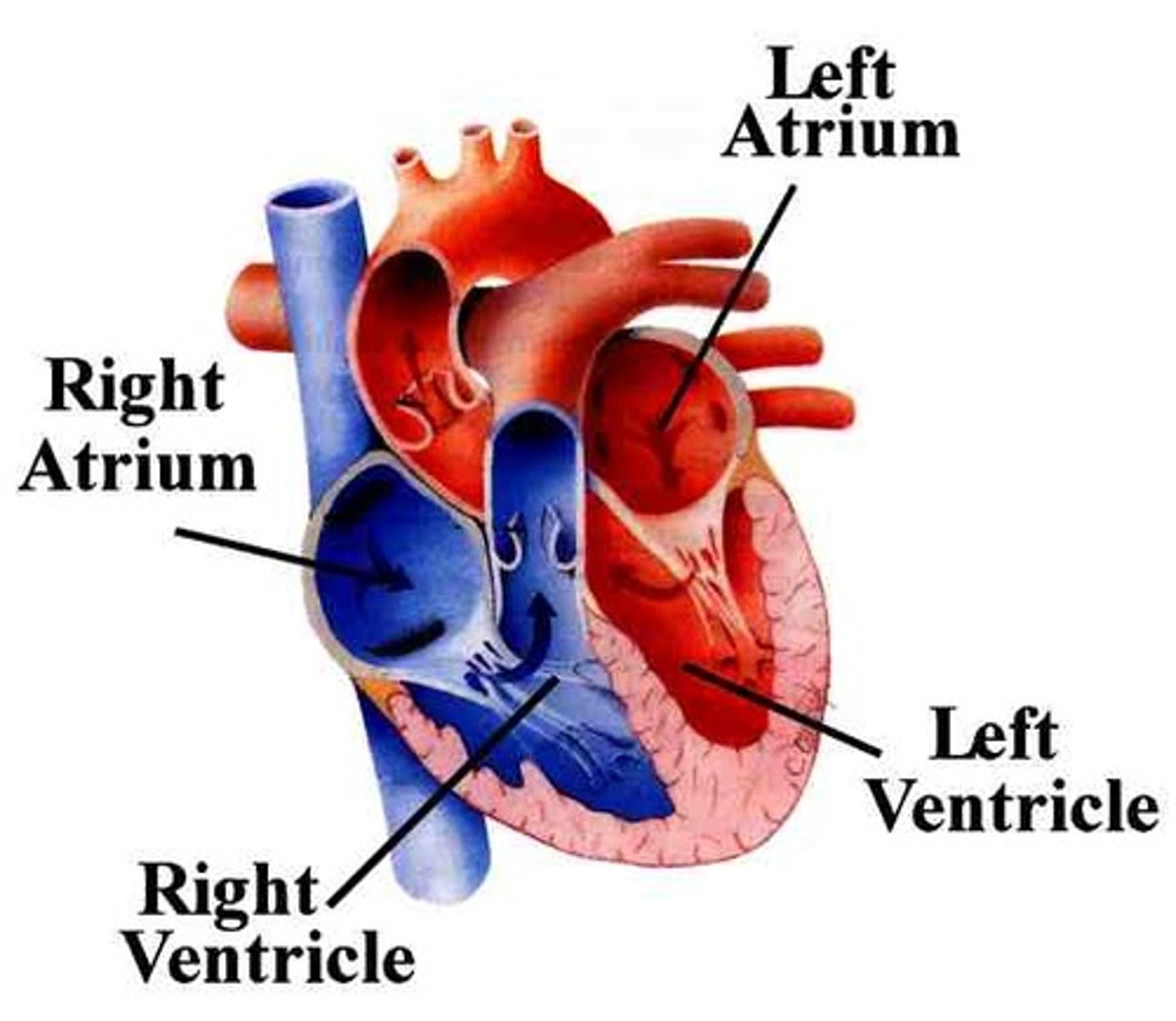
right atrium
the right upper chamber of the heart that receives blood from the venae cavae
right ventricle
pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs
pulmenary artery
The only artery that carries deoxiganted blood; carries it to the lungs for re oxigination and elimination of carbon dioxide
left atrium
Chamber that receives oxygenated blood from the pulmonary veins.
Aorta
Largest artery in the body; distrobutes oxiginated blood from the left ventricle to the rest of the body
Septum
wall dividing two cavities; makes sure substances from the left and right chambers don't mix.
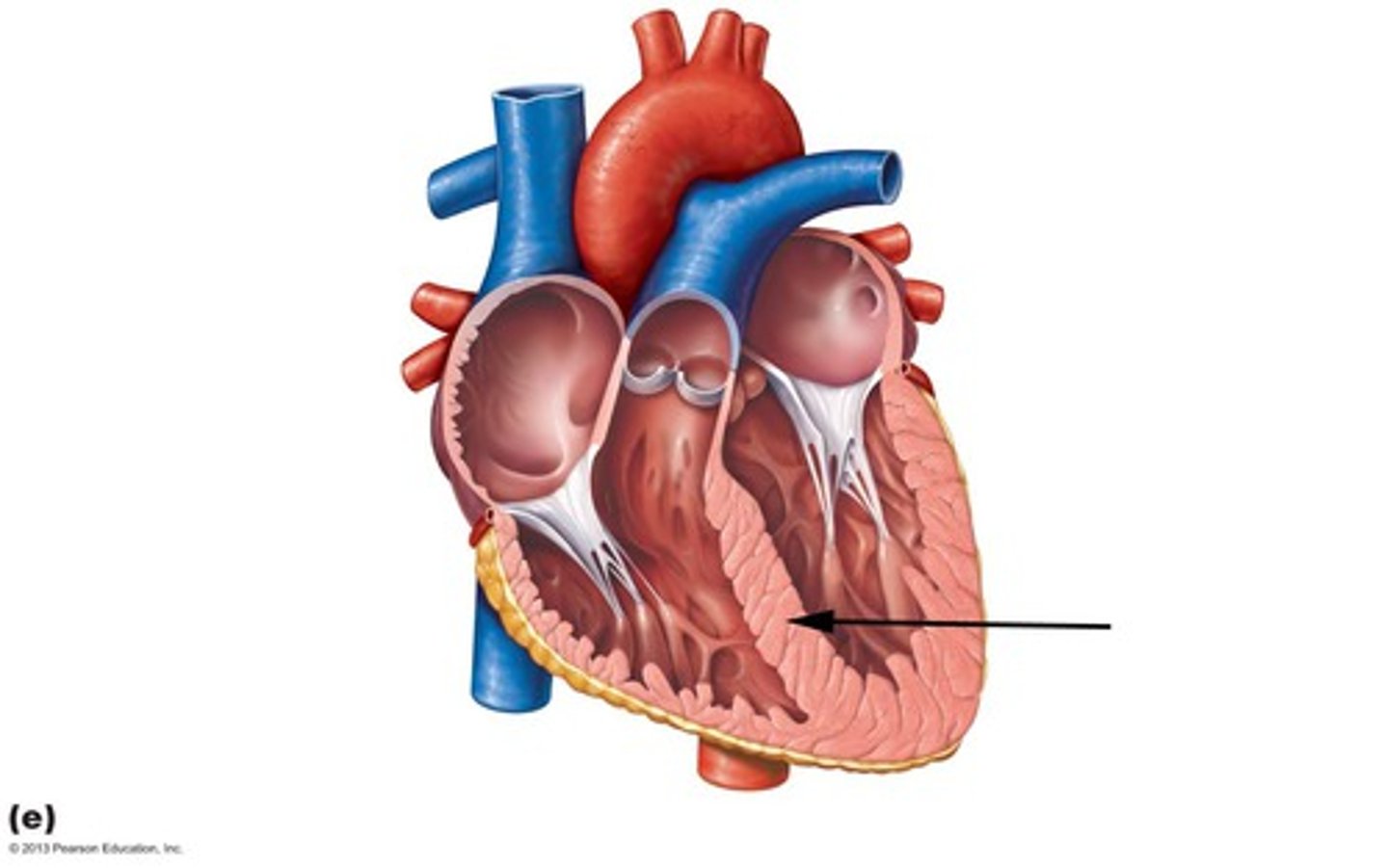
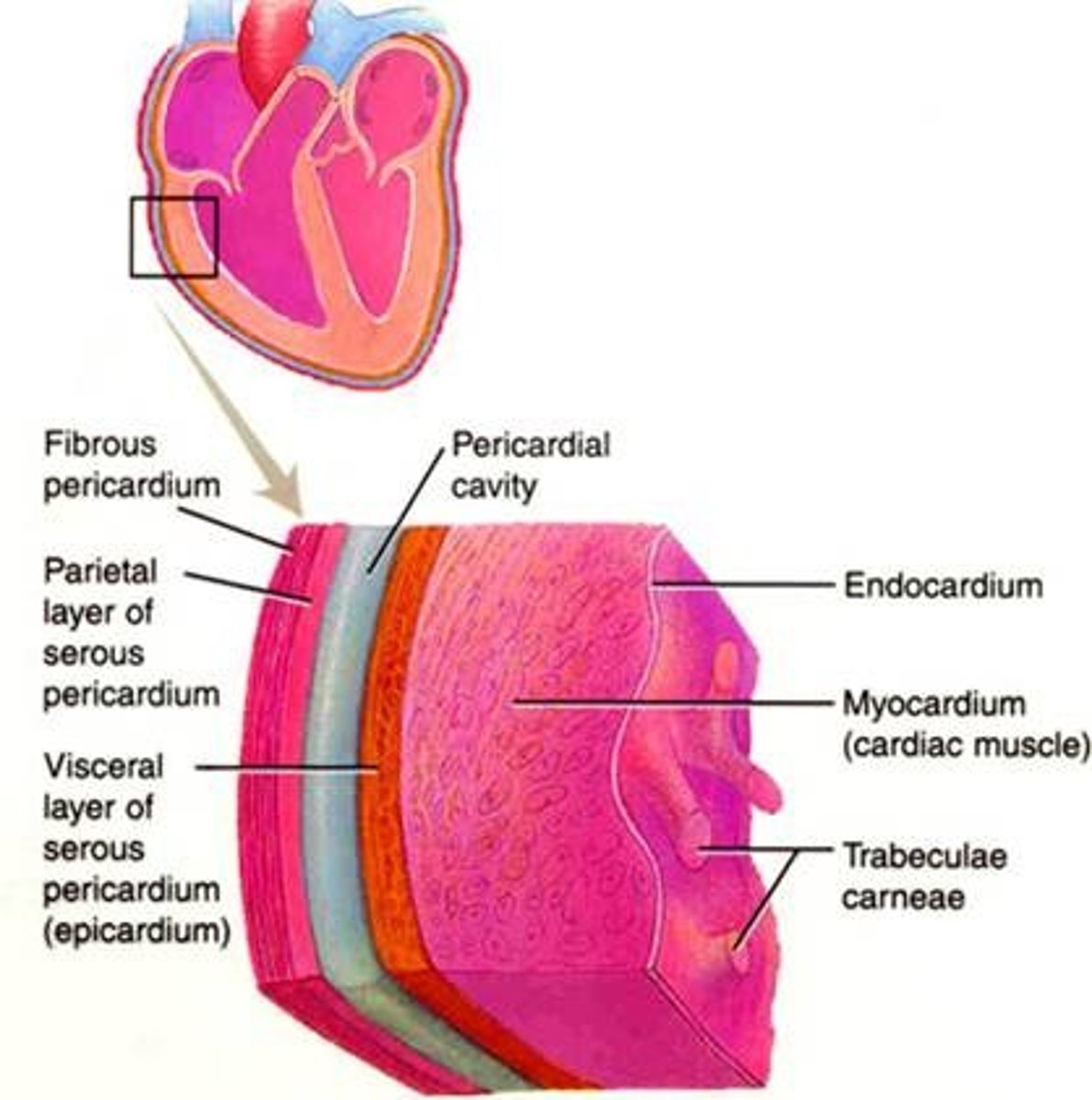
Pericardium layer
outer layer of the heart; protects the heart
Why do ventricles have thicker walls than atriums?
because ventricles have to pump blood into various organs which requires high pressure
double circulation
Blood travels twice through the heart in one cycle. pulmonary circulation and systematic circulation
Pulmonary circulation
Blood from heart to lungs and back to heart
Systematic cirulation
Blood from heart to the body and back to the heart
Single circulation
the blood is pumped to the gills to get oxygenated blood and from there it passes directly to rest of the body. Thus, the blood goes only once through the heart during one cycle of passage through the body. ex) fishes who only have 2 chambers in their heart
Arteries
carry oxygenated blood
walls are thick which enables them to dilate (widen or enlarge)
Capillaries
Microscopic vessel through which exchanges take place between the blood and cells of the body/tissue cells
Their walls are permeable to water and other substances
form connections between veins and arteries
lymph nodes
Bean-shaped filters that cluster along the lymphatic vessels (only one way) of the body. They function as a cleanser of lymph as well as a site of T and B cell activation and contains monocytes
Phloem
Living vascular tissue that carries sugar and organic substances throughout a plant; can go up and down
Why is the transport system in plants slower than of animals?
Because plants are less active than animals so their cells do no need to be supplied with minerals so quickly
Excretion
Process by which metabolic wastes are eliminated from the body
Name the organs in the excretory system
pair of kidneys, a pair of ureters, urinary bladder and urethra.
Kidney
organ that removes urea, excess water, and other waste products from the blood and passes them to the ureter
Ureters
Two thin tubes which drain out urine from kidney to urinary bladder
Nephron
filtering unit of the kidney
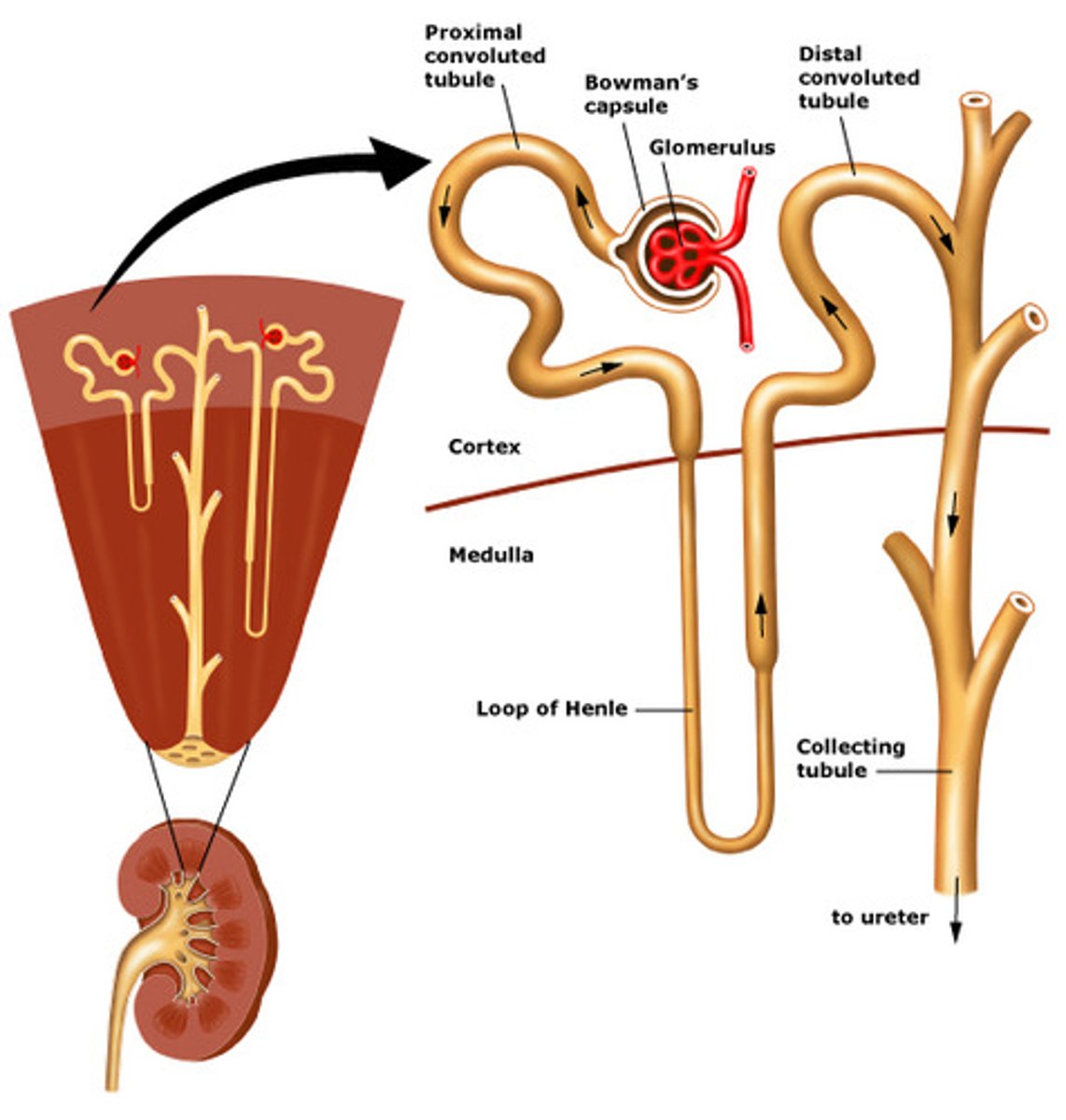
bowmans capsule
Dirty blood enters the bowmans capsule through the renal artery where it gets cleaned and leaves through the renal vein
small molecules pass through its filtration membrane (glomerular filtrate)
Glomerular filtrate
contains water, glucose, salts, urea and metabolic waste; only 1% of this is urine the rest of the 99% gets re-absorbed back into the blood through peritubular capillaries (surround the renal tube)
Tubular secretion
takes place when the glomerular filtrate is being re absorbed back into the blood stream; wastes, drugs from the bloodstream enter the renal tube.
occurs mainly in the renal tubule and the collecting duct of the nephron
collecting duct
collect urine from the nephrons
Autrotrophic nutrition
Organisms make their own form of nutrition from outside sources ex) plants
chemoautotroph
organisms that use chemical reactions to obtain energy (inorganic materials) and synthesize organic compounds from gases like carbon dioxide. They are primary producers in hostile environments, such as deep sea vents.
Photoautotroph
organisms that use light energy from the sun and elements from inorganic compounds to produce organic materials. This process is known as photosynthesis.
Translocation
the process of moving materials from the leaves to other parts of a plant. (photosynthesis) This process occurs in the phloem, which is a vascular tissue.
Transpiration
process of loss of water as vapour from aerial parts of plants
The evaporation of water during transpiration provide cooling effect to the leaves.
The water stream moving upwards carries dissolved minerals with it. Transpiration also helps in distributing these minerals throughout the plant.
The absorbed water is transported from roots to leaves through xylem vessels which is greatly influenced by transpiration pull.
During the daytime, water and minerals travel faster through xylem as compared to the night why?
because during daytime the rate or transpiration is higher
Heterotrophic nutrition
organisms depend on other organisms for food ex) humans and animals
holozoic nutrition
digestion of food; absorbtion; assimilation of food ex) amoebae, humans
parasitic nutrition
organism obtains food from hosts body without killing the host ex) lice
Saprophytic nutrition
feed on dead decaying matter ex) bacteria or fungus
different steps involved in nutrition in Amoeba
1- ingestion, amoeba ingests food using its finger like projections and makes a pear like shape called pseudopodia
2- digestion, food is engulfed with a little surrounding water forming a food vacuole; the food is digested with food enzymes inside the vacuole
3- diffusion, food is absorbed directly into the amoeba
4- assimilation, food gives energy and growth of the amoeba
5- Egestion- When considerable amount of undigested food collects inside Amoeba then its cell membrane ruptures at any place to throw out this undigested food.
Pseudopodia
A cellular extension of amoeboid cells used in moving and feeding.
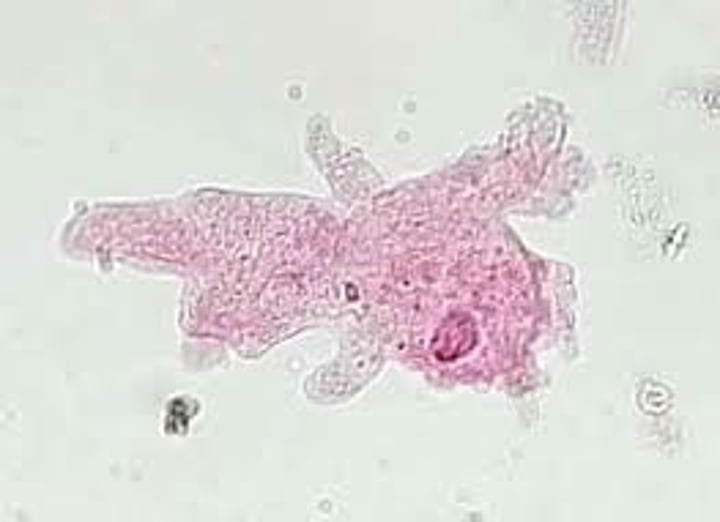
phagocytosis
cell englulfs and internalizes large particles such as bacteria by extending its membrane around them
peristalic movement
a muscle contraction and expansions of gut muscles (esophagus, stomach, and intestines.) that moves food in the correct direction
alimentary canal
The digestive tract is a long tube of organs that carries food throughout the body, from the mouth to the anus including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines)
HCL
hydrochloric acid, acid in the stomach that kills germs in the food
HCl makes medium acidic for the activation of an enzyme pepsin.
Sphinctter muscles
stomach contains 4 sphincter muscles which are circular muscles that expand and contract to control the in and out of the food.
Villi
Fingerlike extensions of the intestinal mucosa that increase the surface area for absorption - absorbs food, supplies absorbed food to blood vessels)
Why is small intestine in herbivores longer than in carnivores?
Due to the cellulose in plants that herbivores eat. Cellulose takes a longer to be digested by our digestive organs, thus they have longer small intestine that carnivores who feed on flesh, which does not have cellulose.
Assimilation
is making food part of a cell which occurs after absorption
lactic acid fermentation
the chemical breakdown of carbohydrates that produces lactic acid as the main end product
Alveoli
Terminal air sacs that constitute the gas exchange surface of the lungs.
increase surface area for exchange of gases
thin walls and a network of capillaries
Rate of breathing in aquatic organisms is much faster than that in terrestrial organisms. Give reasons.
Aquatic animals obtain oxygen from water present in the dissolved form through their gills. The amount of dissolved oxygen is quite small as compared to the amount of oxygen in the air.
Therefore, to obtain required oxygen from water, aquatic animals have to breathe much faster than the terrestrial organisms.
plasma
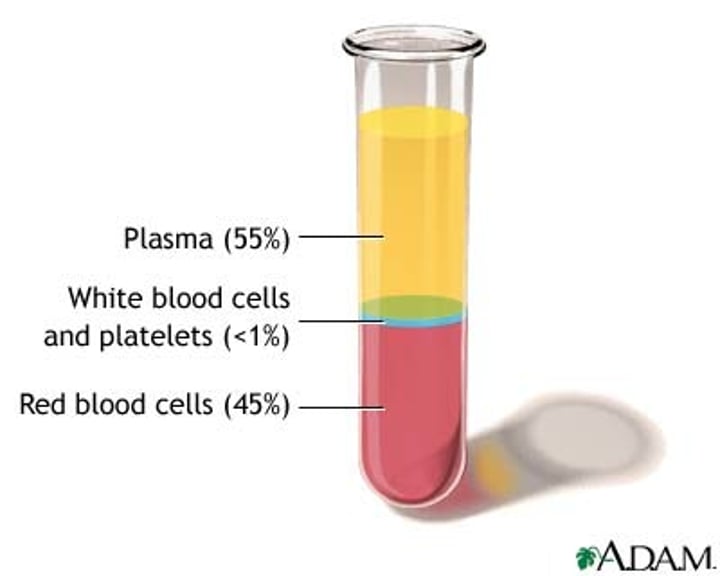
Erythrocytes
Red blood cells that transport oxygen; no nucleus or organelles
Vena cave
a large vein carrying deoxygenated blood into the heart; largest vein in the body
valve
structure in veins or in the heart that temporarily closes an opening so that blood flows in only one direction
4 Valves in the heart - Pulmonary valve, tricuspid valve, Mitral valve, Aortic valve
Tricuspid valve
valve that separates the right atrium and ventricle
blood passes through this valve when going to the right ventricle from the right atrium
Pulmonary valve
blood passes through this valve from the right ventricle to pulmonary arteries
Mitral valve
Blood enters the left atrium and passes thorugh this valve to the left ventricle