Unit 1 Genetics Test Review
1/213
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
214 Terms
Chromosome
a single piece of coiled DNA containing many genes
How Chromosomes Form
a single length of DNA is wrapped many times around histones, and forms nucleosomes
nucleosomes then coil up tightly to create chromatin loops
chromatin loops are then wrapped around each other
Diploid
a pair of each type of chromosome
one pair derived from ovum and the other from the sperm
Haploid
only one copy of every chromosome
n=23
Genes
basic unit of heredity in a living organism
holds information to build and maintain an organism’s cells and pass traits to offspring
a segment of a chromosome that contains the code of a single protein (enzyme). Enzyme then causes a chemical reaction to allow the traits to be shown/expressed
Allele
variation of a gene located at a specific location on a chromosome. Each individual organism has two ______ for each trait, which may be homozygous or heterozygous. _______ are alternate forms of a gene.
Homologous Chromosomes
chromosomes that are paired
are alike with regard to size and position of centromere
have the same genes, but not the same alleles at the same locus or location
Tetrad
pair of homologous chromosomes
chromatids of homologous chromosomes are aligned lengthwise, so that genes of one are adjacent to corresponding genes on the other (total of 4 chromatids)
Synapsis
formation of tetrad
Gamete
specialized sex cell (egg or sperm) that is haploid.
only has half the number of chromosomes
male and female gamete fuse and produce a diploid zygote which develops into a new individual
inheritance
passing genetic information from parent to offspring
Sex Chromosomes
1 pair out of 23 (X & Y) determining individuals sez
Female = XX
Male = XY
Autosomes/Somatic Chromosome
22 pairs out of 23, where it is all chromosomes by sex cells, and it is paired based on similar characteristics
Karyotype
photograph of a particular set of chromosomes for an individual (from largest to smallest & then sex chromosomes)
How are Karyotypes prepared?
a sample of a cell in metaphase is takes, then chromosomes are stained revealing banding patter, and then sorted and paired after
DNA
contains instructions for making proteins within the cell
Double Helix
basic shape of DNA, a double-stranded molecule made of two very long polymers bonded together
Polymer
long molecule made of repeating subunits of monomers (one DNA strand is made of millions of monomers of nucleotides)
Monomer
atoms bonded together to create a larger molecule. many bond together to create various polymers
(nucleotides are ___________ of DNA)
Nucleotides
basic building blocks of DNA & RNA
Parts of Nucleotides
deoxyribose pentose sugar
phosphate group
nitrogenous base
Deoxyribose
sugar in DNA
Ribose
sugar in RNA that is has an additional oxygen as a hydroxyl group in #2 carbon
Phosphate Group
links two sugars together to build polymers
Phosphodiester
joins two sugars via phosphate vertically (joins two nucleotides)
Condensation Reaction
produces H2O when phosphodiester bonds from
Nitrogenous Base
four different nucleotides that make up a DNA polymer
Purine Deoxyribonucleotides
guanine & adenine (have 2 rings)
Pyrimidine Deoxyribonucleotides
thymine & cytosine (have 1 ring)
Uracil
takes the place of thymine in RNA
The Backbone
one strand of DNA made of repeating monomers covalently bonded together
Triplet Code
used to send instructions in the cell: to switch genes on and off to make proteins and enzymes
Hydrogen Bond
holds DNA strands together and is weaker than molecular bonds. Millions in a single molecule cause bases to attract each other.
Complementary Base Pairs
only bonds with each other (A&T or U) (C&G)
Antiparallel
one side up and the other down (in DNA the direction of the phosphate (5’end) on one strand and the hydroxyl (OH 3’end on the other)
DNA Replication
original copy of DNA is unzipped and replicated producing two new identical molecules of DNA
Purpose of DNA Replication
as a cell’s chromosomes are copied for cell division, DNA must be copied too, since DNA makes up chromosomes
instructions for making cell parts are encoded in the DNA so each new cell must get a complete set of the DNA molecules
Unwinding Double Helix
used in DNA replication, where each strand of DNA becomes a new template for a new strand. Each double stranded DNA contains the original copy and one new strand. Parent DNA molecule and two daughter molecules are identical (same nucleotides in same order)
Helicase
enzyme (protein) that breaks the hydrogen bonds between nitrogenous bases to “unzip” or “unwind” the DNA helix. This is the first step in DNA replication
DNA Polymerase
enzyme that moves along the single strands of DNA and helps each free nucleotide bind to a new complementary base to form base pairs. This is the second step to DNA replication and happens as the DNA unzips.
Semi-Conservative Model of Replication
one daughter strand is paired with a parent strand, one old one new is __________________
Why new cells are produced
for growth and to replace damaged or old cells, all cells are derived from pre-existing cells
Prokaryotes
organisms whose cells lack a nucleus and other organelles, for ex. bacteria
Eukaryotes
organisms whose cells contain membrane-bound organelles for ex. Animals
Eukaryotic Chromosomes
store genetic information, have between 10-50 chromosomes in their body cells, human body cells have 46 chromosomes (23 pairs)
Chromatin
long uncoiled strand of DNA that takes up less space in a cell. They can’t be seen when cells aren’t dividing.
Histones
a protein which DNA is tightly coiled around to form structures call nucleosomes. Makes mixed up DNA strands into sticks/chromatin
Chromatid
duplicated chromosomes which aren’t held together by the centromere
Centromere
holds sister chromatids together
Asexual Reproduction
a single cell dividing to make 2, identical daughter cells
Sexual Reproduction
involves two cells (egg & sperm) joining to make a new cell (zygote) that is not identical to the original cells
5 Phases of Cell Cycle
Interphase (G1 - primary growth, phase)
(S synthesis; DNA replicated)
(G2 - secondary growth phase)
Mitosis
Cytokinesis
Interphase (G1)
1st growth stage after cell division, Cells mature by making more cytoplasm & organelles, so daughter cells have all organelles, Cell carries on its normal metabolic processes
Interphase (S stage/synthesis)
DNA is copied or replicated
Interphase (G2)
2nd growth stage, occurs after DNA has been copied, all cell structures needed for division are made (ex. Centrioles which move to poles), both organelles & proteins are synthesized
Mitosis/Karyokinesis
Division of the nucleus, only occurs in eukaryotes, has 4 stages, doesn’t occur in some specialized cells such as brain cells
Early Prophase
Chromatin in nucleus condenses to form visible chromosomes (creates absence of space in nucleus), Mitotic spindle forms from fibers in cytoskeleton or centrioles (animal)
Late Prophase
Nuclear membrane & nucleolus are broken down, chromosomes continue condensing & are clearly visible, spindle fibers called kinetochores attach to the centromere of each chromosome (Only called kinetochores only if they grab the centromere of the chromosome called the astor if it doesn't) Spindle finished forming between the poles of the cell
Metaphase
Chromosomes, attached to the kinetochore fibers, move to the center of the cell, chromosomes are now lined up at the equator (or _________ plate), preparing for the actual division of the chromosomes
Anaphase
Occurs rapidly, high forced, sister chromatids are pulled apart to opposite poles of the cell by kinetochore fibers
Telophase
Sister chromatids at opposite poles, Spindle disassembles (disappears), Nuclear envelope (nuclear membrane) forms around each set of sister chromatids, Nucleolus reappears, Cytokinesis occurs, Chromosomes reappear as chromatin
Cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm, Division of the cell into half, in plant cells, cell plate forms at equator to divide cell, In animal cells, cleavage furrow forms to split cell
Daughter Cells of Mitosis
Have the same number of chromosomes as each other and as the parent cell from which they were formed, Identical to each other, but smaller than parent cell, Must grow in size to become mature cells (G1 of Interphase)
Checkpoints in the Cell Cycle
messages sent to the cells nucleus to “divide, or not to divide” at: G1, S Synthesis phase (DNA Replication): cyclins/cyclin dependent kinase signals the division, G2 gap phase 2- cell size/energy reserves are assessed and if all chromosomes have been replicated correctly, M checkpoint (metaphase): spindle checkpoint, are the sister chromatids attached correctly
Meiosis
occurs after interphase to form gametes, starts with 46 double-stranded chromosomes which is 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes. Is called a reduction - division. The original cell is diploid (2n) 4 daughter cells are produced that are haploid (1n)
Meiosis I
homologous chromosomes separate, 23 double stranded chromosomes after division
Meiosis 2
sister chromatids separate (end up with 4 haploid cells), 23 single stranded chromosomes after division
Zygote
a fertilized egg cell - when two haploid (1n) gametes (sperm and egg cell) fuse to form a diploid (2n) zygote. 23 chromosomes from father, 23 from mother
Early Prophase I
chromosomes number doubled, forms homolog pairs
Late Prophase I
the chromosomes condense, crossing over occurs, spindle fibers form, and the nuclear envelope fragments
Metaphase I
homologous pairs of chromosomes align along the equator of the cell, so there are two rows of chromosomes. centromeres are at the opposite sides of the cells, and this is where the mitrotubules attach to the centromere/kinetochore
Anaphase I
homologs separate and move to opposite poles, sister chromatids remain attached at their centromeres. Each copy of chromosomes are on separate sides of the cell. They are not entirely identical, as it’s composed of different characteristics (from paternal or maternal one can have more than the other)
Telophase I
the nuclear envelopes reassemble, spindle disappears, and it now divides the cell into two, as the cells are now haploid
Cytokinesis I/Interkinesis
chromosomes completely uncoil to become chromatin, nuclear membrane completely reforms
Meiosis II
only one homolog of each of the chromosome is present in the cell, and the sister chromatids carry identical genetic information
Interphase II
the cells prepare for division, chromatin begins to coil/condense into chromosomes, however the DNA is not duplicated so it remains a haploid (n)
Prophase II
the nuclear envelope fragments, chromosomes condense, the spindle forms, however there is no crossing over
Metaphase II
chromosomes line up at the center of the cell (no longer in pairs through), independent assortment occurs again of the sister chromatids, and the microtubules attach to the centromere/kinetochore
Anaphase II
the sister chromatids separate and now move to opposite poles of the cell, and continue to be haploid
Telophase II
the nuclear envelope assembles, chromosomes now uncoil, spindle disappears, and now cytokinesis occurs by dividing the cell into two. There is now 4 haploid daughter cells.
Cytokinesis II
produces 4 haploid daughter cells
Results of Meiosis
the gametes (egg & sperm) form, as four of the haploid cells contain one copy of each chromosome. there is one allele for each gene, and it contains different combinations of alleles for different genes along the chromosome
Gametogenesis
gamete formation
Spermatogenesis
production of sperm
meiosis takes place in testes
begins with diploid cell called a spermatogonium
Oogenesis
production of eggs
meiosis takes place in the ovaries
begins with a diploid cell called an oogonium
Oogonia reproduces by mitosis, then oocyte begin meiosis but stops at prophase 1 till meiosis 1 continues for the cell each month beginning at puberty. Creating an unequal division of cytoplasm (a polar body and a visible egg)
Gamete formation in animals
Meiosis in mammals differs drastically between males & females
two types of ____________ in humans
Spermatogenesis
Oogenesis
Spermatogonium (pl: Spermatogonia)
a diploid that starts spermatogenesis
_____________ reproduces by mitosis and resulting cells undergo meiosis
1 _____________ produces 4 sperm
Polar Body
created during oogenesis and will eventually degenerate
Oogonium (pl: Oogonia)
a diploid cell that starts oogenesis
_________ reproduces by mitosis, then begins meiosis but stops at prophase 1
Major differences between Spermatogenesis & Oogenesis
cytokinesis is unequal among daughter cells during __________
at birth, the ovaries contain all the cells it will ever have that will develop into eggs
sperm continue to develop by meiosis throughout the male reproductive years
__________ has a long resting period after prophase 1 until hormones activate them
Why is cytokinesis is unequal during oogenesis
ensures only one zygote is formed during fertilization
more nutrients given to 1 egg to ensure survival or zygote
more than one zygote means nutrients are divided (increases chance of health complications)
400,000 - 500,000 eggs
all the cells in the ovaries that will ever develop into eggs
only 400 will mature and become eggs
each egg will complete division process upon puberty one at a time
Fraternal Twins
When more than 1 egg is released and both are fertilized (diff DNA)
Identical Twins
A single zygote divides into two separate bodies (genetically identical)
Importance of Meiosis
provides a vast amount of genetic variation
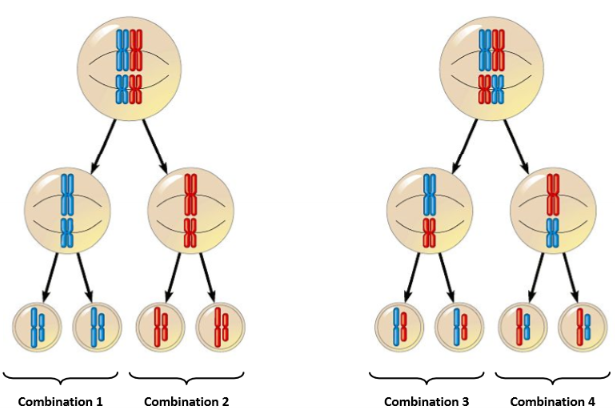
Independent Assortment
How pairs orient themselves in Metaphase1 and Metaphase2 will determine their variance (diff combos of chromosomes). In Anaphase1 homologs pairs independently separate, in Anaphase2 sister chromatids independently separate.
2n
2n
number of genetically distinct gametes that can be produced from a diploid cell during independent assortment
n = number of chromosome pairs
In humans 223 = 8,388,608
Crossing Over
In prophase1 chromosomes exchange DNA by ________ each other
occurs in several points along non-sister chromatids
result: chromosomes have genes form maternal & paternal origin
bonds holding DNA together are broken & reformed (might not reform correctly)
Errors Cause by Changes in Chromosome Structure
Deletion, Duplication, Inversion & Translocation
Deletion
a piece of the chromosome deleted/lost
missing gene = info form making vital proteins missing
can be caused by: viruses, irradiation, chemicals