12.1 - Sustainable energy supply
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Fossil fuels characteristics
Non-renewable
create by the decomposition of plants and animals that have accumulated over millions of years
Oil and gas - they move upwards through porous rock, but can get trapped by impermeable rock and form a reservoir, the hydrocarbons stored can undergo fractional distillation
Coal - Found deep underground, soli, must be mined
Nuclear energy characteristics
Non-renewable
Uranium-235 undergoes fission
Energy is released and used to move a turbine and create heat
Extracted from pit mines, but more of the uranium in isotope 238
Releases no greenhouse gases
Wind energy characteristics
Renewable
Wind moves a turbine, creating kinetic energy which is converted into electricity
Tidal energy characteristics
Renewable
Tidal turbines are used to harness the energy of the waves
Geothermal energy characteristics
Renewable
Used in Iceland
Hot water bought up to the surface from wells, where it has ben heated by magma chambers of volcanoes
This creates steam which creates kinetic energy to be used for electricity
Hydroelectricity characteristics
Renewable
Dams release water down slope, this energy is used to create electricity
Biofuels characteristics
Renewable, but produce greenhouse gases
used in India
It is material from unused plants being burned to create energy, they can also be mixed with gasoline
Solar energy characteristics
Renewable
Suns heat is used to be converted into electricity
can be used on demand in homes
Non-recyclable energy
renewable
Incinerated waste creating heat
which creates energy to be converted into electricity
Energy mix definition
The combination and breakdown of primary energy sources that are used in order to meet energy demand in a certain geographical region
Energy gap definition
The gap between energy supply and demand when the supply is unable to meet the demands of a country so energy must be supplied from a different country
Energy security definition
Where a country can ensure that energy can be supplied at an uninterrupetd rate at and affordable price for everyone
Energy’s importance in development
Allows the world to be connected, which drives globalisation
allows global economies to grow and countries to develop at a faster rate than when energy was first harnessed
Technologies effect on energy demand
Increase in technology e.g. heat engines - made transport energy common
technology needs energy to run - in HICs more devices and tech used
Increases energy demand
Climates effect on energy demand
colder countries need more energy for heating
increases energy demand
Level of development effect on energy demand
More developed a country - the more energy is used as people can afford it
energy demand increases
Energy prices impact on supply and demand
they increased on a global scale
rise in prices made it possible to extract oil from tar sands in canada
Pollution impact on energy supply
LICs/MICs use non renewable energy - economic profit outweighs the pollution
energy production is main cause of global warming
Energy policys impact on energy supply
they are put in place between governemnts and TNCs - help to ensure energy supply isnt getting too expensive
Resource endowments imapct on energy supply
some countries have large natural abundancy to eneergy resources
e.g. China - coal
russia - oil, gas
uk - wind
australia + canada - U-235
countries with little resources have to relay on policies to meet energy demand through trade and globalisation as they cant self produce
Sustainbilitys’s impact on energy supply
some countries cnat supply renewable energy to help environment
they are more expensive to use as a natural energy resource
Climates impact on energy supply
windy climates can use wind power
sunny climates can use solar power
rainy climates can use hydroelectric power
climate dictates what natural renewable resource can be used as a supply
Capitals impact on energy supply
Large investments are needed to produce energy
Power Stations and transport for energy are expensive to build
LICs might not have the money, more reliant on TNCs
technologies impact on energy supply
machines can be used to mine deeper and collect more resources, increases supply
Nuclear power station technology developed to meet demand
hydrogen energy
Can be used as clean energy source - only produces water
can be hard to find sustainably - but can help a low carbon future
Combined heat and power (CHP)
Stops heat being lost while being - 20% cheaper and 80% efficient
excess heat returned to grid by being captured and stored to be used as heating
Factors effecting energy supply
Social - physical population, what they use energy for, quality of life all effect energy
Economic - LICs may get money for energy infrastructure through FDI inflows, as ability to supply energy relies on development
Political 0 Policies and agreements need to be made to help LIC/MICs get energy from HICs
Environmental - Different energy supplies are sound in different locations e.g. oil rich countries, some countries are resource rich but dont have the devlopment to tap into it
UK’s current energy policy
Creating a British energy firm, standardised government owned energy company, created by taxing oil and gas companies and using the money to create company
Plans for major offshore wind farm expansion - to stop reliance on Russia for energy, as prices have been driven up, creating the cost of living crisis
The company will work with private sectors to develop energy technology
There is a plan to decarbonise electricity by 2030 - and open no new gas or oil fields
Energy demand and supply in the UK
UK does not have energy security - high demand and low supply from within the country
Very reliant on imports from other countries - Russia (using energy as political weapon)
As we tapped into our natural coal resources very early on
There has been increase in use of renewables in recent years from around 2008
Energy Trilemma
The balance between:
energy security - ability to effectively meet current and future energy demand
Energy equity- Accessibility and affordability of energy supply across the popualtion
Environmental sustainability - ability for energy supply to be met using renewable and low carbon sources
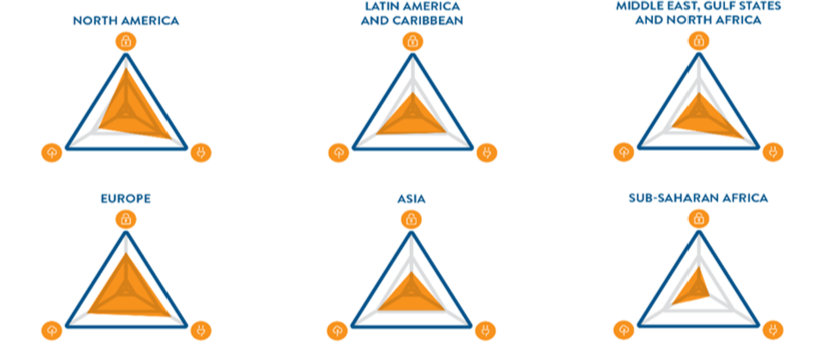
Explanations of energy trilemma
Middle east have large oil reserves, which gives access to energy to people with very little transport cost, which means prices can be lowered and people of all incomes can access the energy
Asian countries are investing into Latin America, providing the infrastructure for hydropower
North America is very self sustaining with energy due to huge oil reserves below the permafrost in Alaska, which is becoming more accessible due to global warming causing the permafrost to melt
Detail is lost in the Trilemma graphs in Asia as the large MICs that are pushing for sustainable energy such as China and India, have their information lost when averaged with the largely populated LICs that are very reliant on non-renewables
Fossil Fuel consumption
Oil is the most used, referred to as liquid gold, worth the most money
Oil is also the only one practical for transport use
peak of oil extraction was 2005, has been decreasing since
MICs and HICs have the most oil consumption, USA, India, China (top 3)
Nuclear energy consumption
Hugh consumption in france, they get most of their resources from Africa, socio-economic impacts (use of child labour)
Very safe, dont produce fossil fuels, but if something goes wrong there will be lasting impacts on humans and environment
Barely used in the southern hemisphere as it is very expensive and infrastructure takes a long time build
Renewable energy consumption
biofuel is most common, as inexpensive and doesnt need much technology
Wind power becoming more common as it becomes cheaper, same for solar panels
Hydropower is being harnessed more, especially in Norway, Nepal and China
Environmental impact of energy production
Lower temporal impact as countries switch to renewables
but only small areas of production affected (e.g. Mississippi coal mines, Chernobyl, Canada tar sands)
Chernobyl - Radiation with 50,000 years impact, creating exclusion zone
Tar sands - causes 3600 tons of Co2, extraction uses water that people could be using
Environmental impact of energy transport
Impact usually due to human error, so more avoidable
As transport becomes more efficient, e.g. using national grid for electricity
e.g. SS Torey Canyon oil spills in Cornwall
oil spill clean up uses harmful chemicals - oil very flammable, releases methane
impacts ecosystems and food chain distribution - e.g. dish soap used to clean animals, goes back into sea, gets ingested by animals
Environmental impacts of energy use
large spatial impact as all countries use energy and all emit greenhouse gases
large temporal impact - as need for energy will increase with popualtion growth
so much co2 in atmosphere that even is emissions stopped temps would still rise
e.g. large industrial use in china - more emissions as less access to renewables
differences in demand between LICs and HICs - so impacts will be different