Wireless Networking New, Installing Networks, Network Documentation, SNMP, DHCP
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
127 Terms
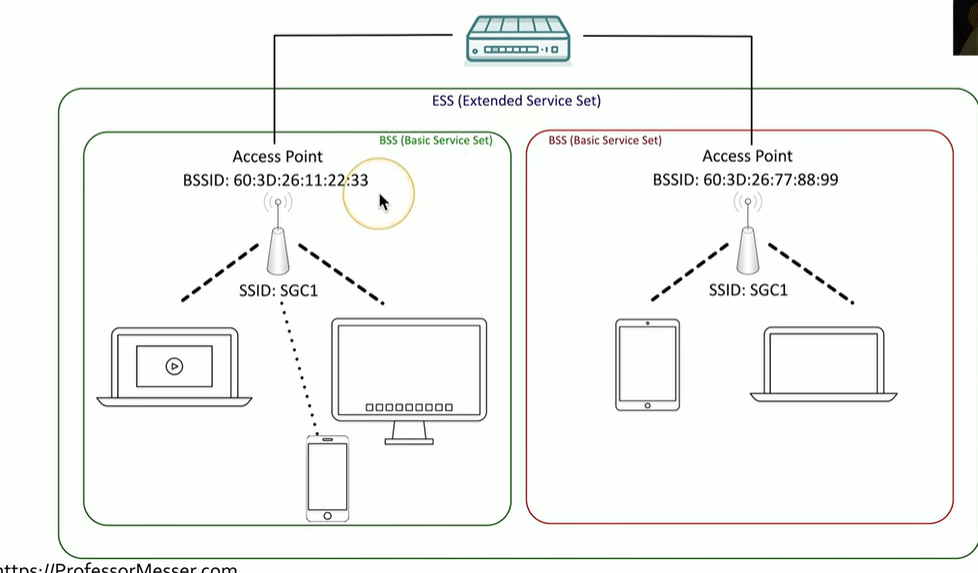
What is Independent Basic Service set (IBSS)? also known as Ad Hoc
Two devices communicate directly to each other using 802.11, without the need of an access point.
What is SSID?
Service Set Identifier
is the name given to a wireless network to distinguish it from others. It allows devices to identify and connect to a specific Wi-Fi network.
There might be multiple access points supporting an SSID, so we need the hardware address of an access point, which is called?
BSSID
Basic Service Set Identifier, which is the MAC address
Real-life example: In a large office building, there may be several access points set up on different floors, all broadcasting the same SSID, like "CompanyWiFi." As you walk around the building, your device automatically connects to the nearest access point with the strongest signal, ensuring a seamless connection without having to manually switch networks. The BSSID of each access point would differ, but they all share the same SSID ("CompanyWiFi").
What is the shared network name across access points called?
ESSID
Extended Service Set Identifier, gives us seamless roaming
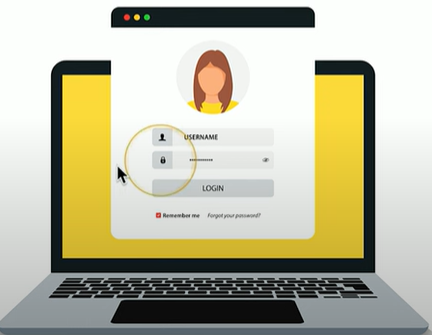
What is a captive portal?
is a web page that users are redirected to when they connect to a public Wi-Fi network. It typically requires users to authenticate (e.g., login, agree to terms)
What is an open system in wireless security modes?
No authentication password is required
What is WPA/2/3-Personal also seen as WPA/2/3-PSK?
are security protocols used to protect Wi-Fi networks. The "PSK" stands for Pre-Shared Key, that everyone uses (256-bit key)
At a coffee shop, customers connect to the "CafeWiFi" network, which uses WPA2-PSK with the password "Cafe123
What is WPA/2/3-Enterprise, also seen as WPA/2/3-802.1X?
Authenticates users individually with an authentication server (etc: RADIUS, LDAP, ETC)
In a corporate office, employees connect to the "OfficeWiFi" network using WPA2-Enterprise with 802.1X authentication. They enter their unique username and password, which are verified by a RADIUS server before granting access to the network.
What are Omnidirectional Antennas?
What does omni mean?
One of the most common, and are included on most access points.
Omni = all
signal is evenly distributed on all sides
but imagine its in the corner of the room, half of it is being wasted for areas where nobody is using the connection..

What is a directional antenna?
Focuses the signal and increased distance in a single direction
focus on transmission and listening

How is antenna performance measured?
in dB
double power every 3dB of gain
What is a yagi antenna?
Type of directional antenna that is very directional and high in gain
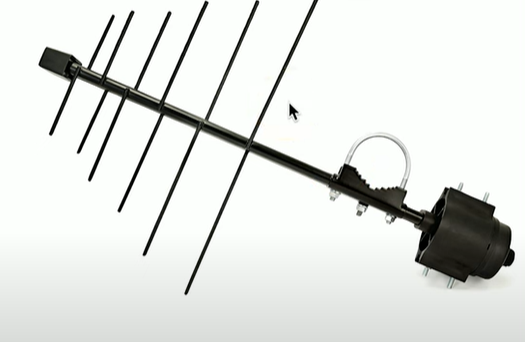
What is a parabolic antenna?
Focuses the single to a single point, good for super long distances

What are autonomous access points?
standalone devices that manage their own configuration and operations without relying on a central controller
access point handles most wireless tasks
In an enterprise, we might be using ______ access points. For what reason?
lightweight
rely on a central switch to manage configuration, security, and traffic management. They are simpler devices, and are cheaper.
allows us to manage and control simultaneously from a single point.
What is the centralized management of all access points called?
Wireless LAN controller
“Single pane of glass”
can deploy new access points
performance and security monitoring
configure and deploy changes
What is WEP?
Wired Equivalent Privacy
One of the first encryption types on networks, found out it has a lot of vulnerabilities so it is not used
What was WEP replaced by?
WPA: Wifi Protected Access, it was a temporary stop gap bridge between WEP and whatever the successor would be.
What was WPA replaced by?
WPA2: Wifi protected Access II (been around since 2004)
CMP (Counter Mode with Cipher Block Chaining Message Authentication Code Protocol) is a security protocol used in WPA2 for encrypting wireless data. It combines AES encryption in counter mode (CCM)
What is the update to WPA2?
WPA3 and GCMP
Includes GCMP block cipher mode which is stronger
What are distribution frames?
Area of the network where you are passively terminating cables
usually includes punch down blocks, and patch panels
Mounted on the wall or flat surfaces, uses a bit of real-estate, often used as a room “Distribution frame room”
What is the main distribution fram (MDF)
The primary distribution frame, the room is referred to as the MDF facility
Termination point for WAN links
good testing point
often the center point

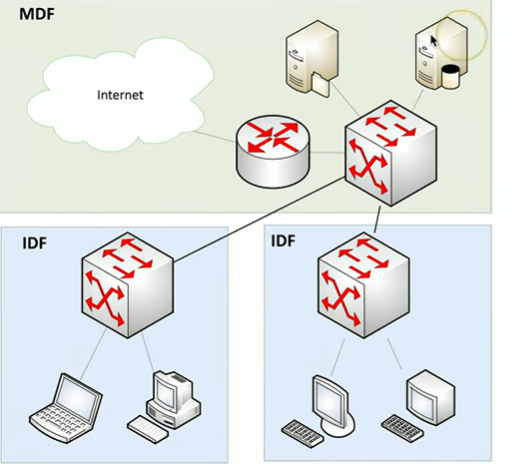
What is an IDF?
Intermediate Distribution Frame
Usually connected to the MDF, but it is an extension of it, often in a different room or building.
What is the standard size for equipment racks? What is a rack unit?
19 inch rack/device width
Height is measured in rack units, 1U = 1.75 inches
A common rack height is 42U
HVAC design/diagram
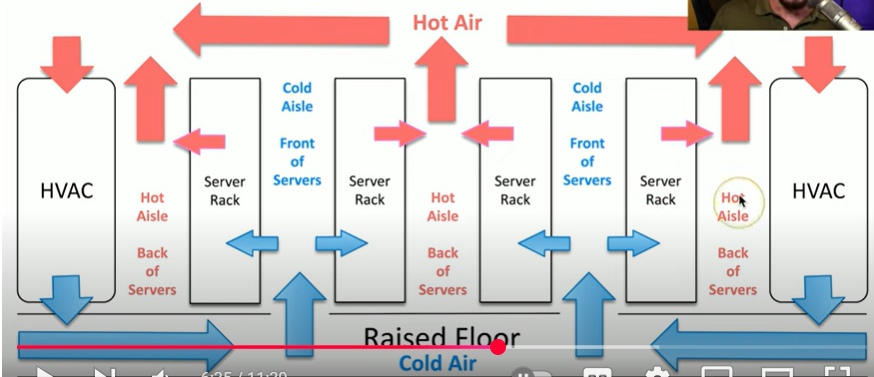
What are hot and cold aisles?
Hot and cold aisles help keep servers cool in data centers. Cold aisles blow cool air into servers, while hot aisles push out hot air
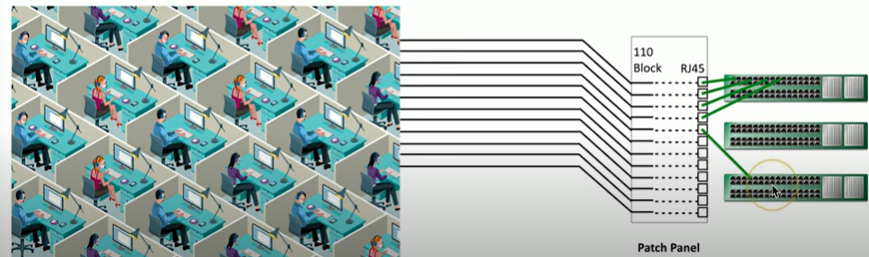
What is a patch panel?
A patch panel is a central hub that organizes and connects network cables in a structured cabling system. It has multiple ports where cables from workstations, switches, and other network devices are terminated.
In terms of safety, what is something you should never do with power?
Never connect yourself to the ground wire of an electrical system
What does AMP mean?
Ampere, the rate of electrons that flow past a point in one second
The diameter of the hose

What is voltage?
Electrical “pressure” pushing the electrons
how open the faucet is
120 volts, 240 volts
What is a Watt?
How much energy is being consumed
Electrical load is measured in watts

How do we calculate the amount of Watts?
Volts * Amps = Watts
120V * 0.5A = 60W
What is alternating Current or AC?
The type of power we usually get from our wall outlets, it is relatively easy to distribute over long distances
Direction of current constantly reverses/changes
Like waves in the ocean. Just as waves move forward and then pull back
What is the frequency cycle of AC in US/Canada
110-120 volts of AC (VAC), 60 hertz
What is DC current?
Direction Current, often used by our electrical components
current moves in one direction, with constant voltage.
Devices commonly use ____ voltage, and most power sources provide ____ voltage.
DC
AC
How do we convert AC voltage to DC voltage?
Using the power supplies in our devices, or sometimes the cord.
What is a UPS?
Uninterruptible Power Supply
short term backup power for blackouts, brownouts, or surges and it will balance out power with its internal batteries.
What is a PDU?
Power Distribution Unit, provides multiple power outlets and are usually in a rack.
allows remote power connection and disconnection, even for specific devices.
What does High humidity cause?
It promotes condensation
What does low humidity promote?
Static discharge
occurs when built-up static electricity suddenly releases, often as a small spark.
According to industry guidelines for data centres, what is the ideal humidity?
40% to 60%
What is the optimal temperature for a datacentre?
64° to 81°F
or
17.7° to 27.2°C
What are fires in data centres treated with?
Intert gases and chemical agents, as water is dangerous with that many electronics.
What is a physical network map?
shows the actual, physical layout of a network, including cables, devices, and connections
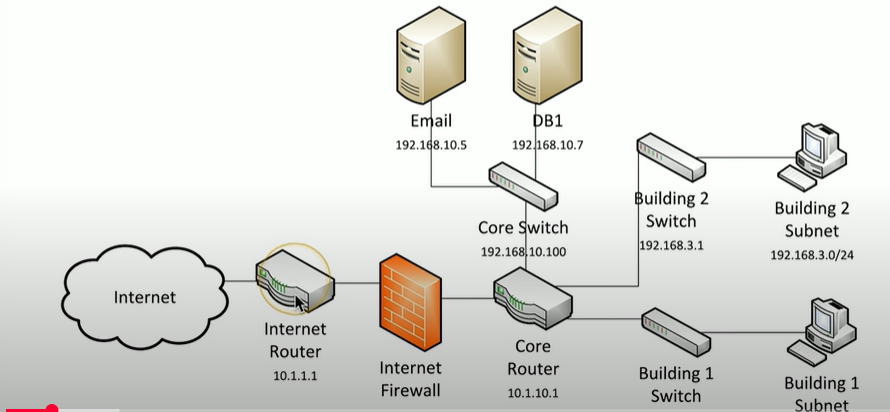
What are logical network maps?
Higher level view of connectivity, where it is focused on how the entire network is connected rather than individual cables
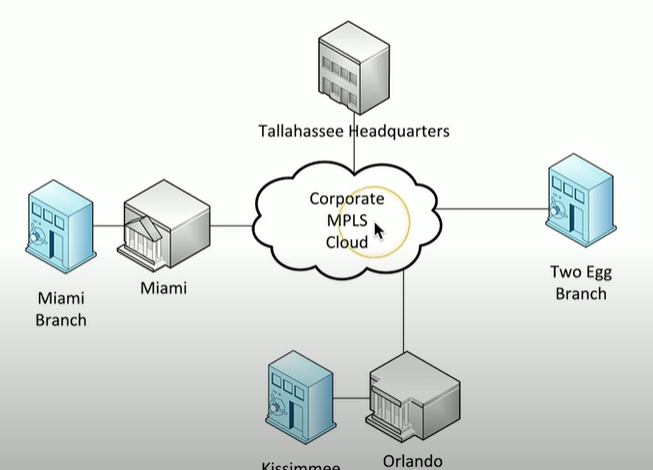
What are logical network maps good for?
If you are planning for additional locations installations
What is a rack diagram?
A rack diagram is a visual representation of how network and server equipment is arranged in a rack. It shows the physical placement of devices like servers, switches, and patch panels.
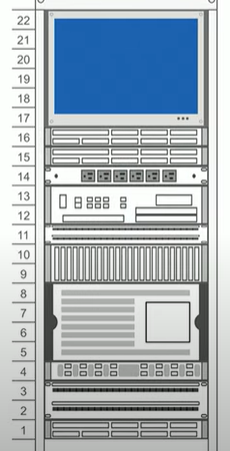
Why do we need rack diagrams?
A network admin may never walk into a data centre, because physical access is often limited. So the diagram is there to guide them remotely.
What are cable maps and diagrams?
visually represent how cables are routed and connected within a network. They help identify which cables go where
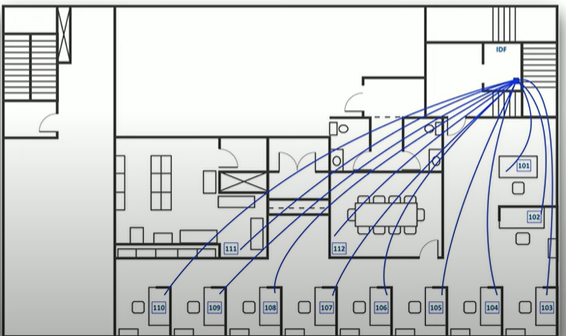
What is a network diagram?
A network diagram is a visual representation of a network’s devices, connections, and topology, with layer 1,2 and 3.
What is asset management?
Labelling assets brought into an organization (laptops, desktops, server, routers, etc)
tag can be associated with support tickets with a device make and model
What is an asset database?
A central asset tracking system, used by different parts of the organization.
warranty status
licensing and renewals
What does IPAM stand for, and what is it?
IP Address Management
the process of tracking, managing, and organizing IP addresses in a network, as well as configuring DHCP
What is an SLA or service level agreement?
contract between a service provider and a customer that defines the expected level of service, including uptime guarantees, response times, and performance metrics
“no more than 4 hours of unscheduled downtime for internet”
What are site surveys?
assessing and analyzing a physical location. It involves evaluating factors like signal strength, coverage area, potential obstacles
What is EOL?
End of Life
the point when a product or service is no longer supported or sold by the manufacturer. For IT hardware or software, this MAY mean no more updates or patches.
What is EOS?
End of Service
refers to the point when a manufacturer stops providing official support, including updates, patches, and troubleshooting assistance for a product.
EOS happens after EOL
What is firmware?
Firmware is specialized software embedded in hardware devices that controls and manages their functionality.
etc printers
What is decommissioning?
refers to the process of retiring or removing IT equipment, software, or infrastructure from active service. This involves safely disconnecting, erasing data, and disposing of or recycling the hardware
some data cannot be destroyed for legal reasons, so you might have to consider offsite storage.
What is change management?
the process of planning, implementing, and overseeing changes in IT systems or infrastructure to minimize disruption and ensure smooth transitions
most companies have policies regarding frequency, duration and installation process.
What is Configuration management?
is the process of systematically handling changes to IT systems, ensuring that hardware, software, and network configurations are documented, consistent, and properly controlled
What is production configuration?
refers to the specific setup and settings of IT systems, networks, and infrastructure that are used in the live, operational environment
everyone uses this config
What is a backup configuration?
refers to the settings and strategies used to ensure data is regularly copied and stored for recovery in case of system failure
What is a snapshot of a VM?
point-in-time copy of the VM's state, including its disk, memory, and settings. It allows you to preserve the current state of the VM so you can restore it to that exact configuration later,
What is a baseline/golden configuration?
is the standard or reference configuration for a system, device, or network that represents its optimal, secure, and stable state
(a template/ideal setup)
What does SNMP stand for?
Simple Network Management Protocol
What is SNMP?
Designed to provide a management interface for devices, and SNMP queries those devices.
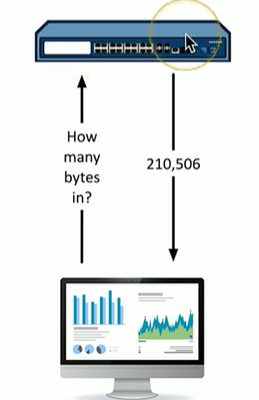
What port does SNMP use to poll devices?
SNMP uses UDP port 161 for communication between network devices and management systems.
What is the MIB in SNMP?
Management Information Base
database or collection of standardized information and objects that SNMP-managed devices use to store and organize data
What are the different versions of SNMP?
SNMP V1: The original with structured tables, and in the clear
SNMP v2c: a good upgrade, data type enhancements, bulk transfers, but still in-the-clear
SNMP v3: The new standard, has message integrity, authentication, and encryption
What are SNMP OIDs?
(Object Identifiers) are unique identifiers used to reference specific objects or variables in the Management Information Base
1.3.6.1.2.1.11.28.0 etc
Like library book catalog numbers. Just as each book in a library has a unique catalog number that helps you find it, each OID uniquely identifies a specific piece of information (like device stats) within the MIB
What is a MIB walker?
is a tool or software that allows you to traverse and explore the MIB (Management Information Base) of an SNMP-enabled device. It sends SNMP requests to the device to retrieve various data objects and their value
What is an SNMP trap?
An SNMP trap is an unsolicited notification sent by an SNMP-enabled device to an SNMP manager to alert it about specific events or issues, such as system failures, threshold breaches, or device status changes. Unlike regular SNMP queries, traps are sent automatically by the device without the need for the manager to request them.
What port does an SNMP trap use?
udp/162
What are community strings for SNMP authentication?
simple text-based authentication credentials used in SNMP to control access to a device's MIB. There are typically two types: read-only (RO), which allows the SNMP manager to view the data, and read-write (RW), which allows the manager to both view and modify the device's settings.
in SNMP v3, we use a password and username → safer and better.
Imagine you're the manager of a warehouse (SNMP manager) that oversees many shelves (SNMP-enabled devices).
You can regularly ask for updates on the stock levels (SNMP queries), but if something unexpected happens (like a shelf breaking or running low on inventory), the shelves can automatically send you an alert (SNMP trap) to notify you, without you having to check on them.
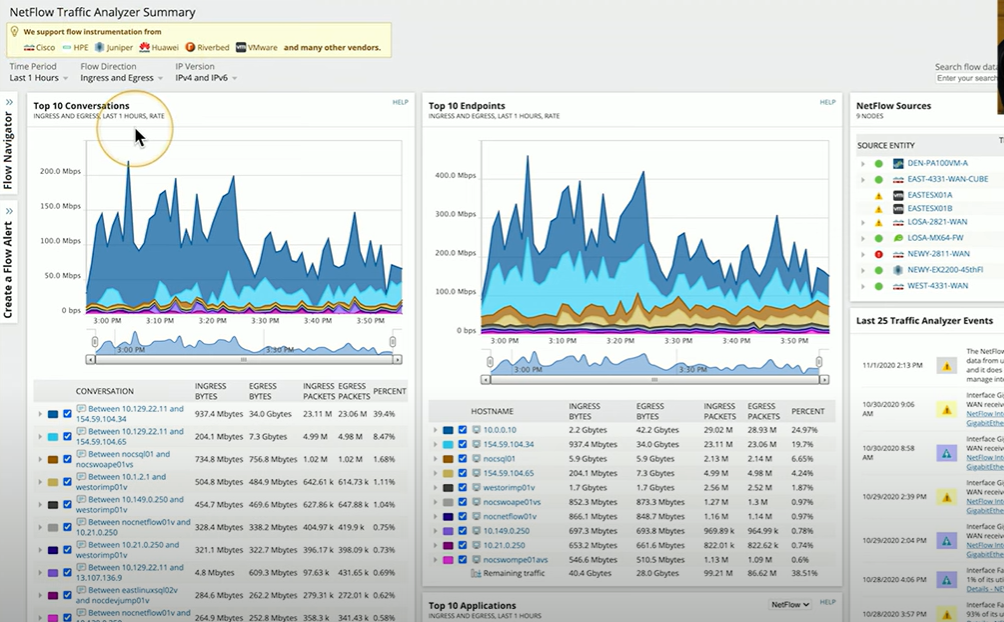
What is Net Flow?
network monitoring protocol developed by Cisco that collects and analyzes network traffic data. It captures metadata about IP traffic flows, such as source/destination IPs, ports, protocols, and volume
What is a protocol analyzer?
is a tool used to capture, inspect, and analyze network traffic and frames to diagnose issues, monitor performance, and detect security threats. It examines network packets at various protocol layers
etc: Wireshark
Troubleshooting begins with a:
baseline
troubling shooting starts with a blank slate, and a baseline can add context.
What does SIEM stand for?
Security Information and Event Management) is a system that collects, analyzes, and correlates security logs and event data
What is syslog?
The standard for message logging, usually a central logging collector and it is integrated into the SIEM.
each log entry is labeled and has a facility code (program that created the log)
no matter the company or device, syslog is consistent.
What does a SIEM do?
Logs security events and information, can also give real time security alerts and warnings.
Has long term storage for advanced reporting features
What is API integration?
Allows us to have a central management station directly communicate to a switch, router, firewall etc, instead of having to manual use the command line and SSH consoles
automation
What is port mirroring?
is a network feature that copies traffic from one or more switch ports to another port for monitoring and analysis.
What is an LLDP?
Link Layer Discovery Protocol
helps network devices identify and share information with directly connected devices. It’s used for mapping networks, troubleshooting, and managing connections
What is availability monitoring?
Tells us if the the network is up or down
the most important statistic
Can create alerts and alarms
Every device has a ____________
configuration
IP addresses, security settings, port configs
most devices allow the configs to be downloaded or uploaded
What is configuration monitoring?
tracks and records changes to device and system settings to ensure compliance, security, and stability.
often apart of a larger management system or central console
What is a DRP?
Disaster Recovery Plan
A detailed plan for resuming operations after a disaster.
What is an RTO?
Recovery Time Objective
How quickly we can get up back and running after an outage
getting back to a particular service level in a certain time frame
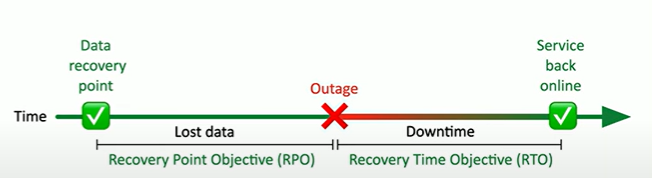
What is an RPO?
Recovery Point Objective
How much time did we loss due to that outage?
the maximum acceptable data loss measured in time before a disruption occurs
How do we define the RPO?
defined by balancing business impact, data criticality, and backup frequency
etc: patient records: less than an hour
while a website update can be 1-4 hours
What does MTTR mean?
Mean Time to Repair
the average time required to fix the issue, this is the time from the point of failure, to full functionality.
What does MTBF mean?
is the average time a system or device operates before failing
predict the time between outages
useful because if a MTBF of a router is 20 years, you can just get one backup instead of 2 or 3…
What is Site Resiliency?
The ability of an organization to maintain operations during a site failure by using backup locations
making sure the other site has hardware, resources etc
What is a cold site?
a backup location with no active equipment or data but ready to be set up in the event of a disaster

What is a hot site?
An exact replica of your site (or close as possible)
same hardware, that is constantly updated
Software and apps updated
A quick switch from primary site to hot site
What is a warm site?
In the middle of a hot a cold site, just enough to get going
big room with rack space, and you bring the hardware, or there could be some.
What are tabletop exercises?
discussion-based simulations where team members review and walk through emergency scenarios or response plans without actual physical deployment