Lesson 2.9: Pure Competition and Monopolies
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards made from a presentation segment created as a lesson on pure competition and monopolies.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
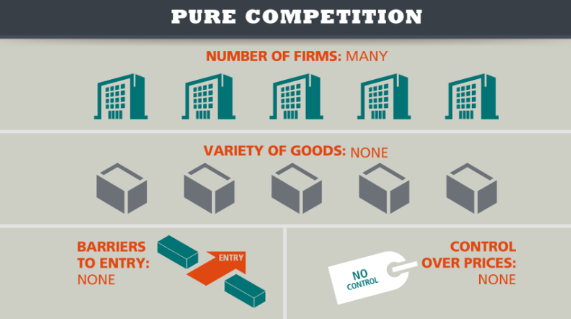
Pure competition
A market structure where:
There is a large number of firms
There is one main, same product
There is little price control in the market
The market is in equilibrium
Imperfect competition
A market structure that fails to meet the conditions of perfect competition
Commodity
A product that is considered the same no matter who sells it
Barrier to entry
Any factor that makes it difficult for a new form to enter a market
Can lead to imperfect competition
Includes start-up costs and technology
Start-up costs
The expenses a new business must pay before it can begin to produce or sell goods
Higher amounts can make it difficult for new firms to enter the market, leading to imperfect competition
Can include complex or expensive technology
Perfect competition
A market where all transactions are efficient as competition keeps prices and production costs low through resource maximization and proper market valuation
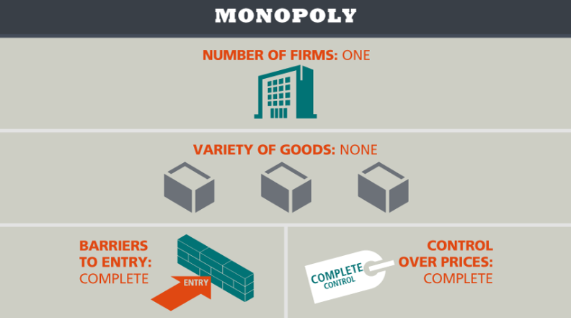
Monopoly
A market in which a single seller dominates
Can be legalized, as is the case for governments allowing drug development companies to accrue more revenue
Has usually one firm, no variety, controlled prices, and high barriers to entry
Natural monopoly
A market that runs most efficiently when one large firm suppplies all output
Adding more firms will drive down the price of both firms’ products, eventually leading both to an inability to pay their initial costs
Seen with residential water companies having only one network connected to each house in an area
Government monopoly
A monopoly created or sanctioned by the government
Patents and franchises are included in this category
Patent
A license that gives the inventor of a new product the exclusive right to sell it for a specific period of time

Franchise
A contract that gives a single firm the right to sell its goods within an exclusive market
Price discrimination
The division of consumers into groups based on how much they will pay for a good
Market power
The ability of a company to control prices and total market output
Patent
A governmentally-granted exclusive right to sell a new good or service for a particular period of time
License
A permit to operate a business, especially where scarce resources are involved
Monopolist’s Dilemma
Situation where a producer with complete control of a good has to set price and production at equilibrium
More production will lead to lower prices and thus falling revenue
Less production will lead to higher prices and thus lost potential revenue
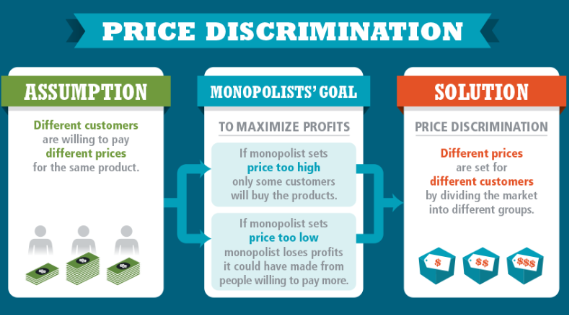
Price discrimination
Practice where a monopolist may be able to divide consumers into two or more groups and charge a different price to each group for more revenue
Requires significant market power, distinct customer groups, and difficult resellability