Biochemistry--Vitamins, Coenzymes, and Diseases
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Essential Ions
Metal ions involved in enzyme activity. Two categories:
Metaloenzymes: Transition metals (i.e. Fe 2+) that are tightly bound to enzyme and directly participate in enzyme catalysis, usually as part of redox reactions.
Activator Ions (Metal activated enzmes): Loosly bound group 1 & 2 metals that do not directly participate in catalysis, but help align substrates and shield enzyme from charges
Coenzymes
Organic cofactors, usally derived from nutritional vitamins. Two categories:
Cosubstrates (loosely bound), gets altered and then goes on its merry way, e.g. ATP donates a phosphate group then leaves as Adp
Prosthetic Groups (tightly bound), e.g. Heme groups
fat soluable vitamins include
A, D, E, K
Hydrophobic in nature, so dissolve in lipids
Generally stick around much longer than water soluable because harder to excrete
Easier to overdose on than water soluable
Scurvy
A Disease caused by vitamin C deficiency, AKA Ascorbate deficiency
Historically was found in sailors/pirates without access to fresh fruits and vegetables. Solved by citrus rations, i.e. "Limeys"
Symptoms include fatigue, lethergy, anemia, poor wound healing, bleeding; body can't produce new collagen
Beriberi
the thiamin-deficiency disease; characterized by loss of sensation in the hands and feet, muscular weakness, advancing paralysis, and abnormal heart action
Thiamine is coenzyme of citric acid cycle (pyruvate decarboxylase) and also needed to produce neurotransmitters
Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome
Growth Retardation
Associated with Riboflavin (B2) Deficiency
Pellagra
the niacin (B3)-deficiency disease, characterized by diarrhea, dermatitis, dementia, and eventually death
Dermititis in Chickens
Pantothenate (B5) Deficiency
Dermititis in Rats
Pyridoxal (B6) Deficiency
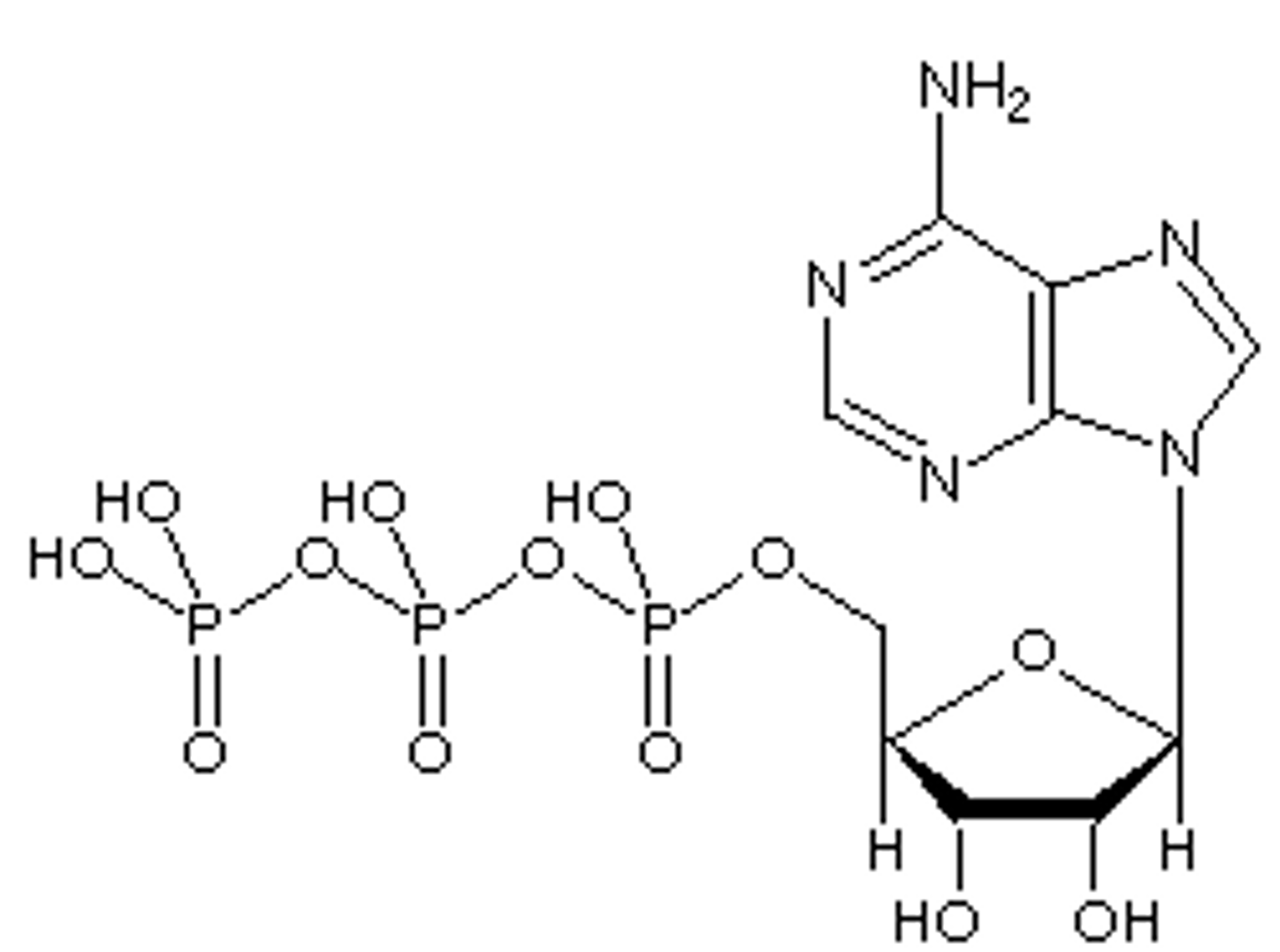
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
Cosubstrate
Donation of Phosphoryl or Nucleotidyl Groups
No Associated Vitamin
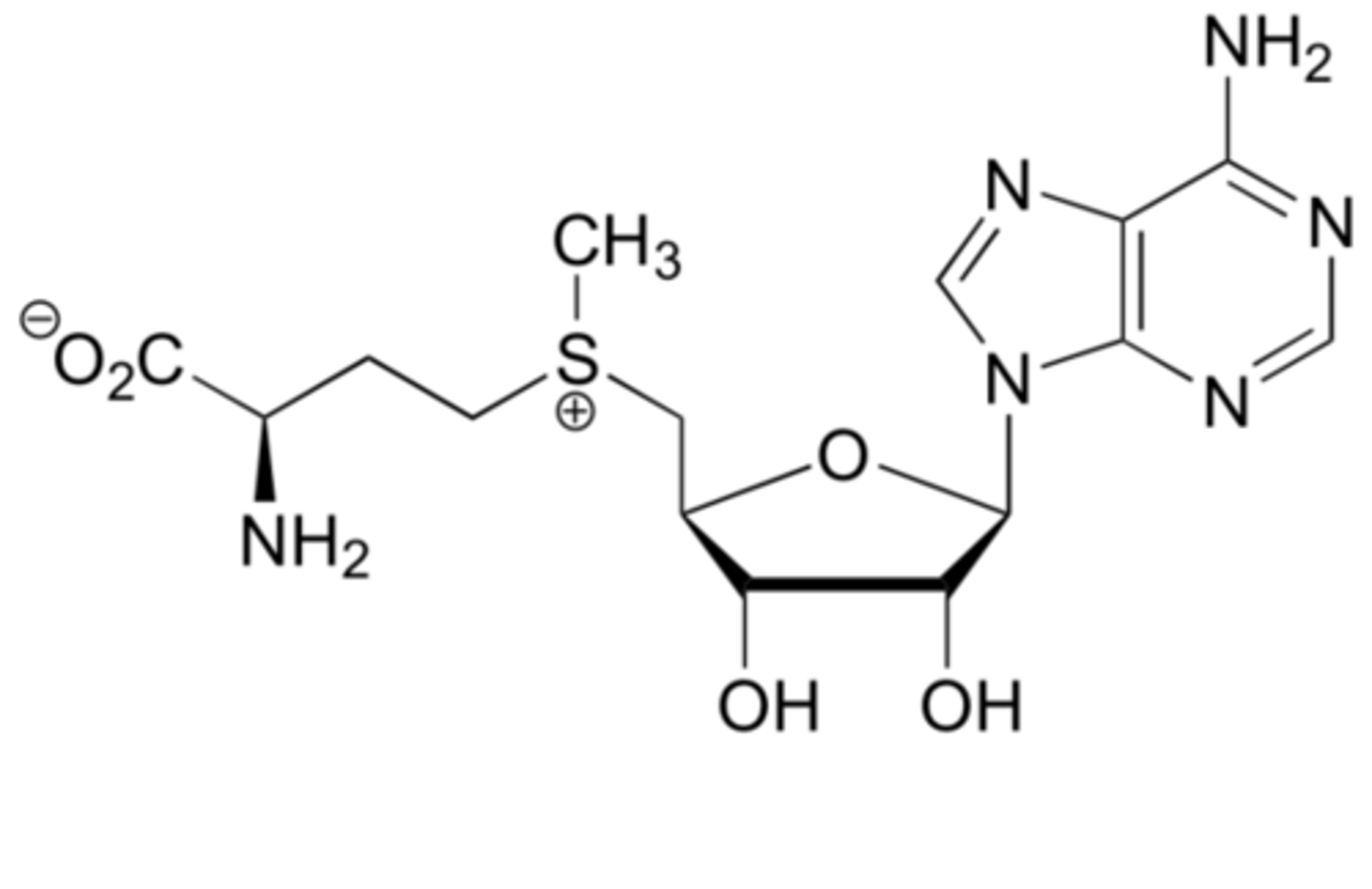
S-adenosylmethionine
Adenosine + Ribose + Mithionine
Co Substrate
Donation of Methyl Group
No associated Vitamin
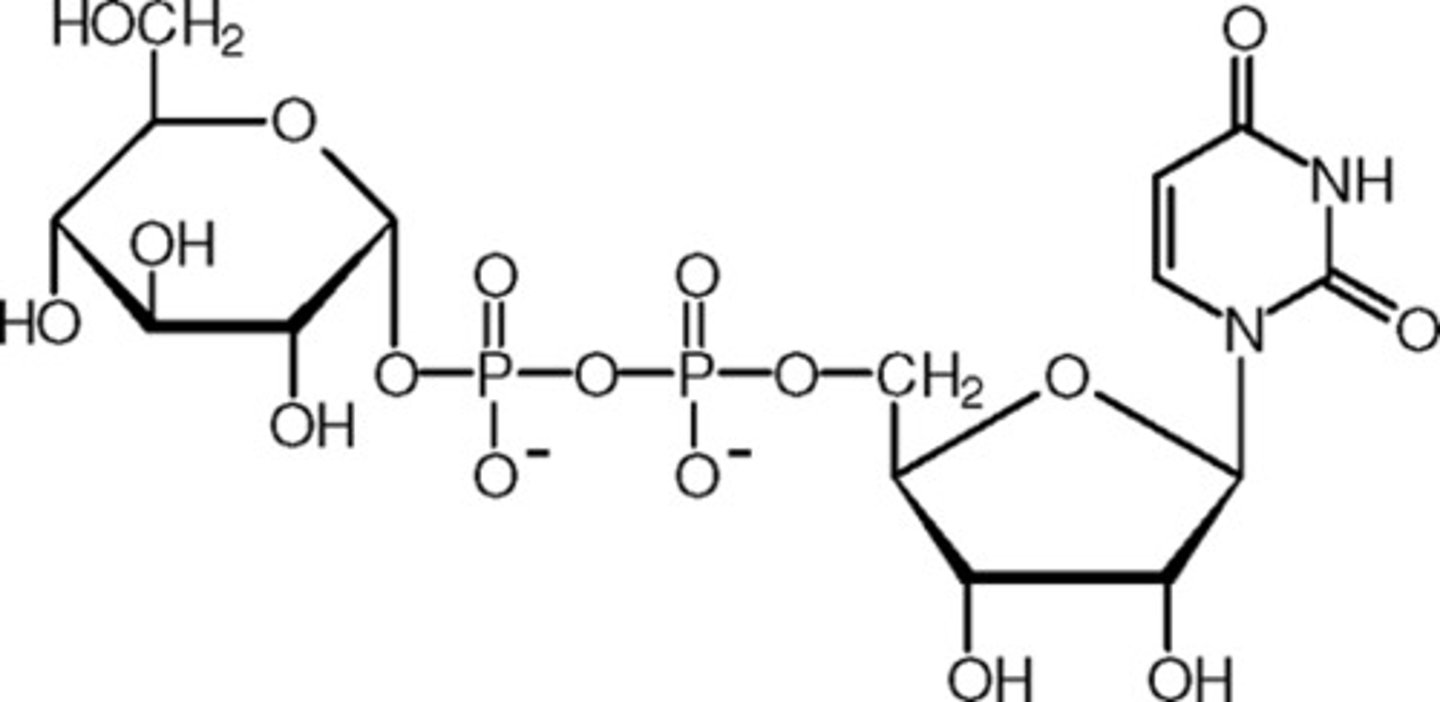
Uridine diphosphate glucose
Uracil + 2 Phosphates + Glucose
Cosubstrate
Transfer of Glycosyl groups
No Associated Vitamin
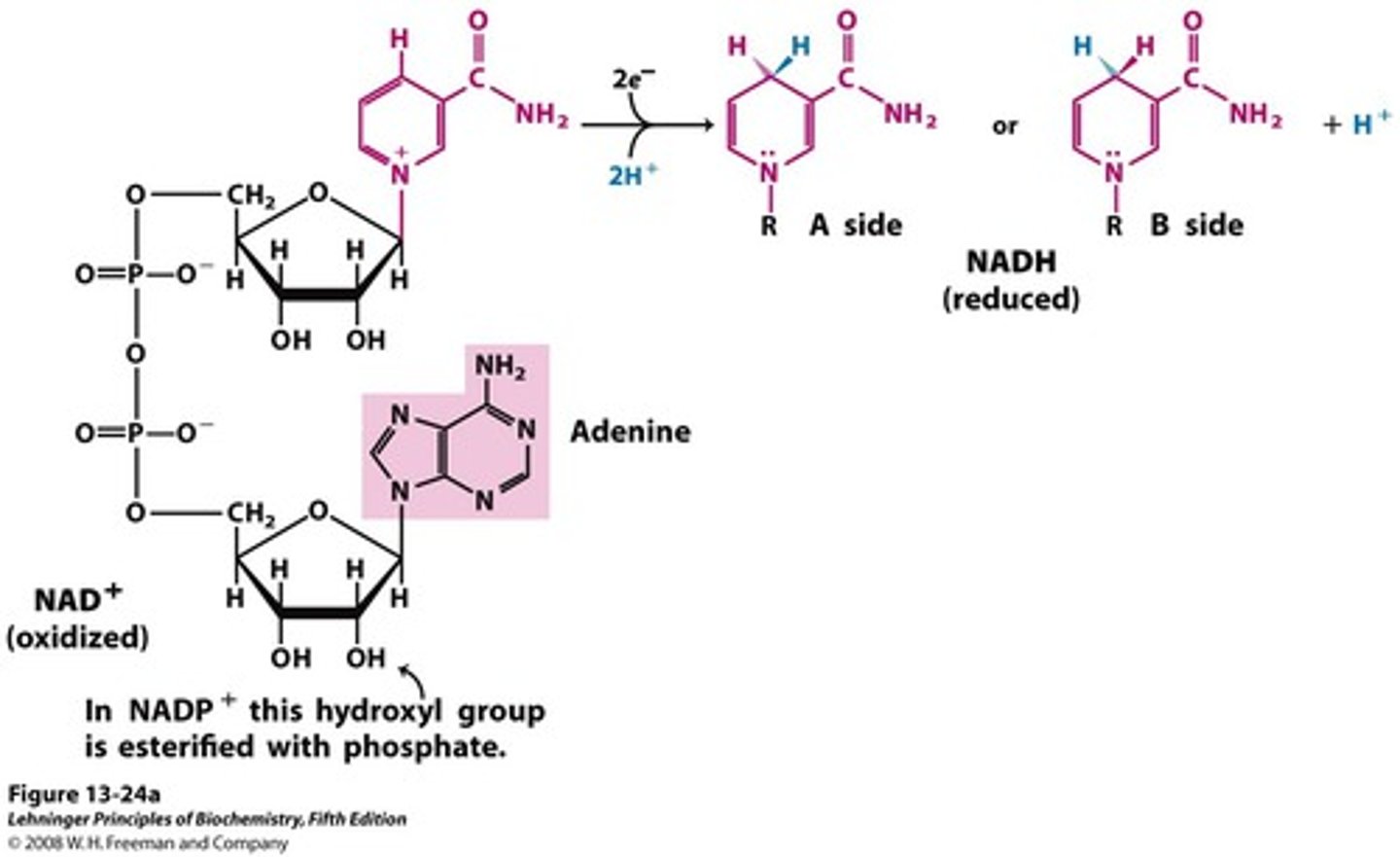
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+)
&
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide Phosphate (NADP+)
Adenine + Ribose + 2 Phosphates + Ribose + Nicotinamide
Cosubstrate
Redox reactions involving 2 electron transfer; Glycolysis and TCA--Give e- to electron transport chain
Source is Vitamin B3 / Niacin
Flavin mononucleotide (FMN)
&
Flavin Adenin Dinucleotide (FAD)
Prosthetic Group
Redox Reactions Involving 1-2 e- transfers
Source is Vitamin B2 / Riboflavin
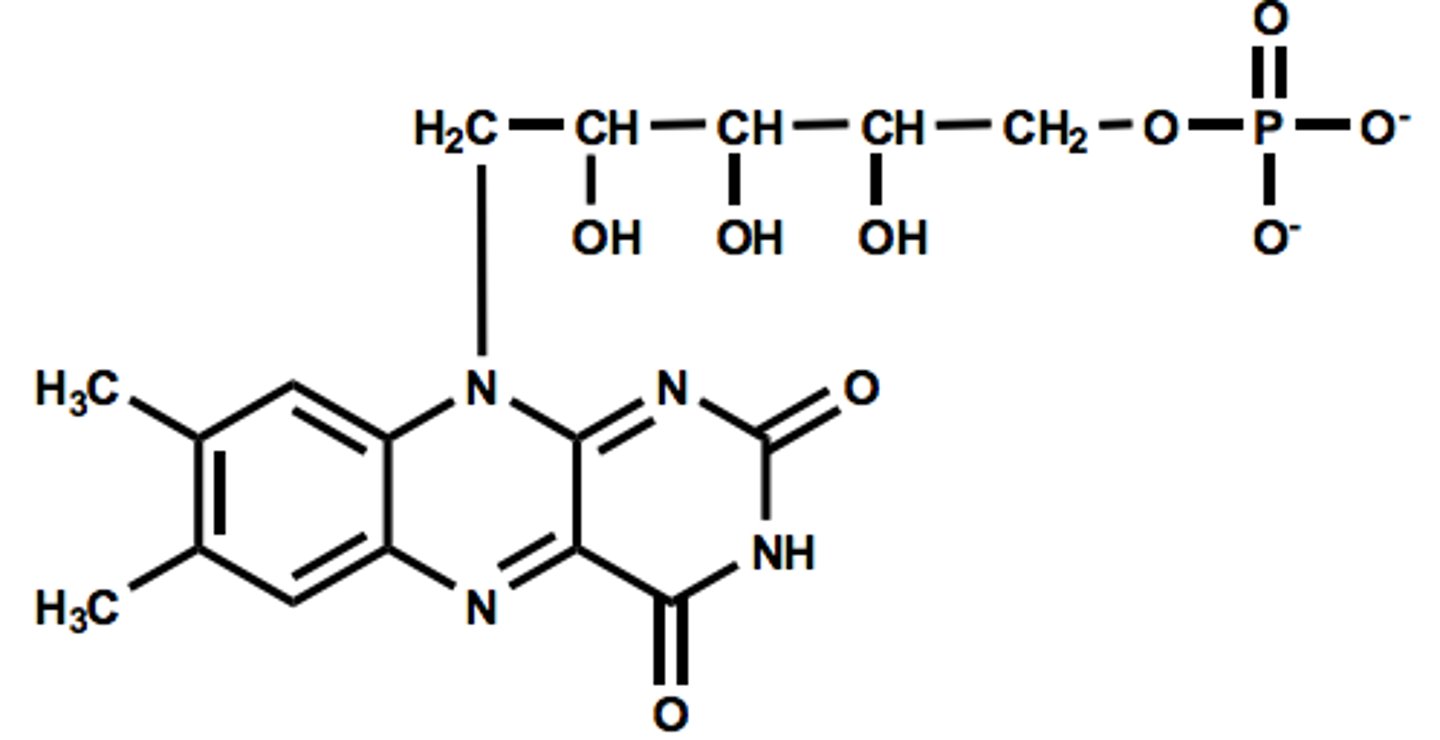
Coenzyme A (Acetyl COA)
Cosubstrate
Transfers Acyl Groups
Source is Vitamin B5 / Pantothenate
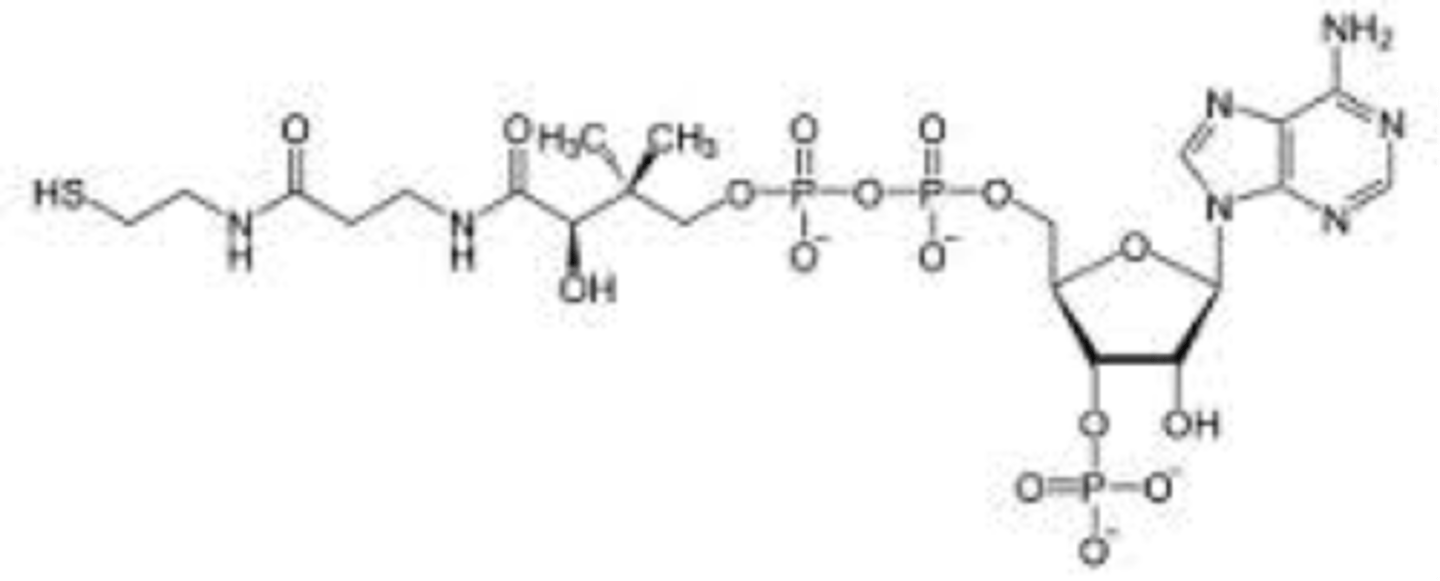
Thiamine Pyrophosphate (TPP)
Prosthetic Group
Transfer of multi-carbon fragments containing a carbonyl group
Source is Vitamin B1 / Thiamine
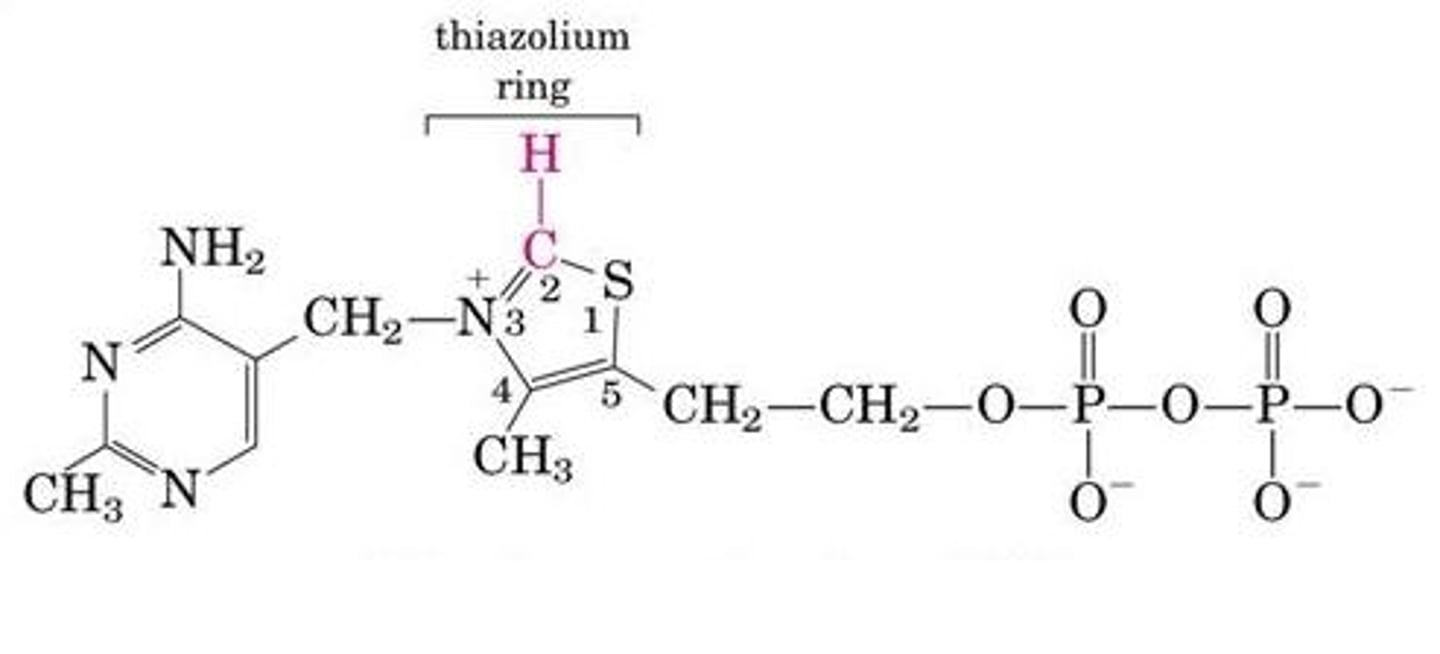
pyridoxal phosphate
Prosthetic Group
Transfer of Groups to and from amino acids
Source is Vitamin B6 / Pyridoxine
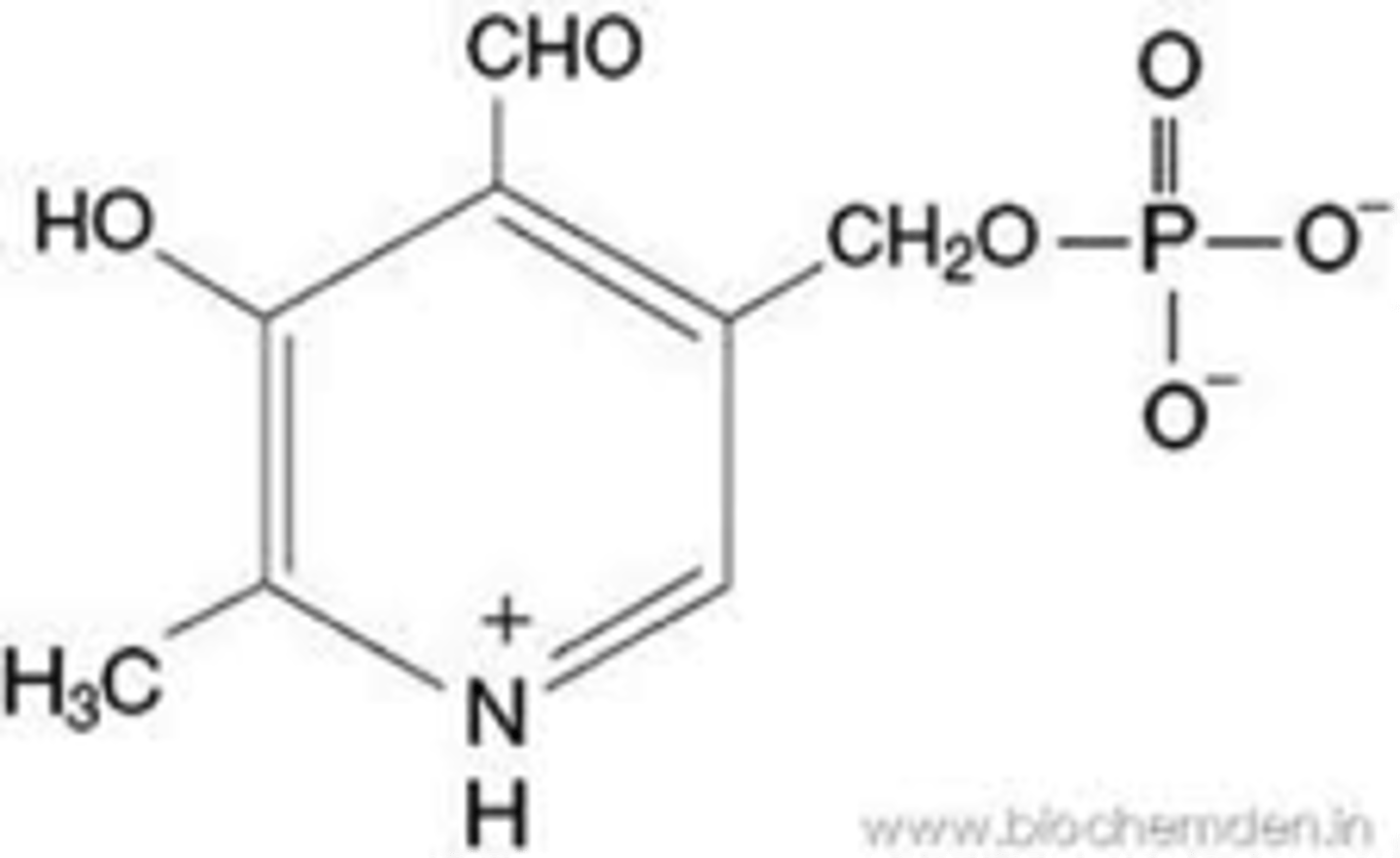
Biotin
Prosthetic Group
ATP-Dependent carboxylation of substrates or transfer of carboyl groups between substrates
Source: Vitamin B7 / Biotin
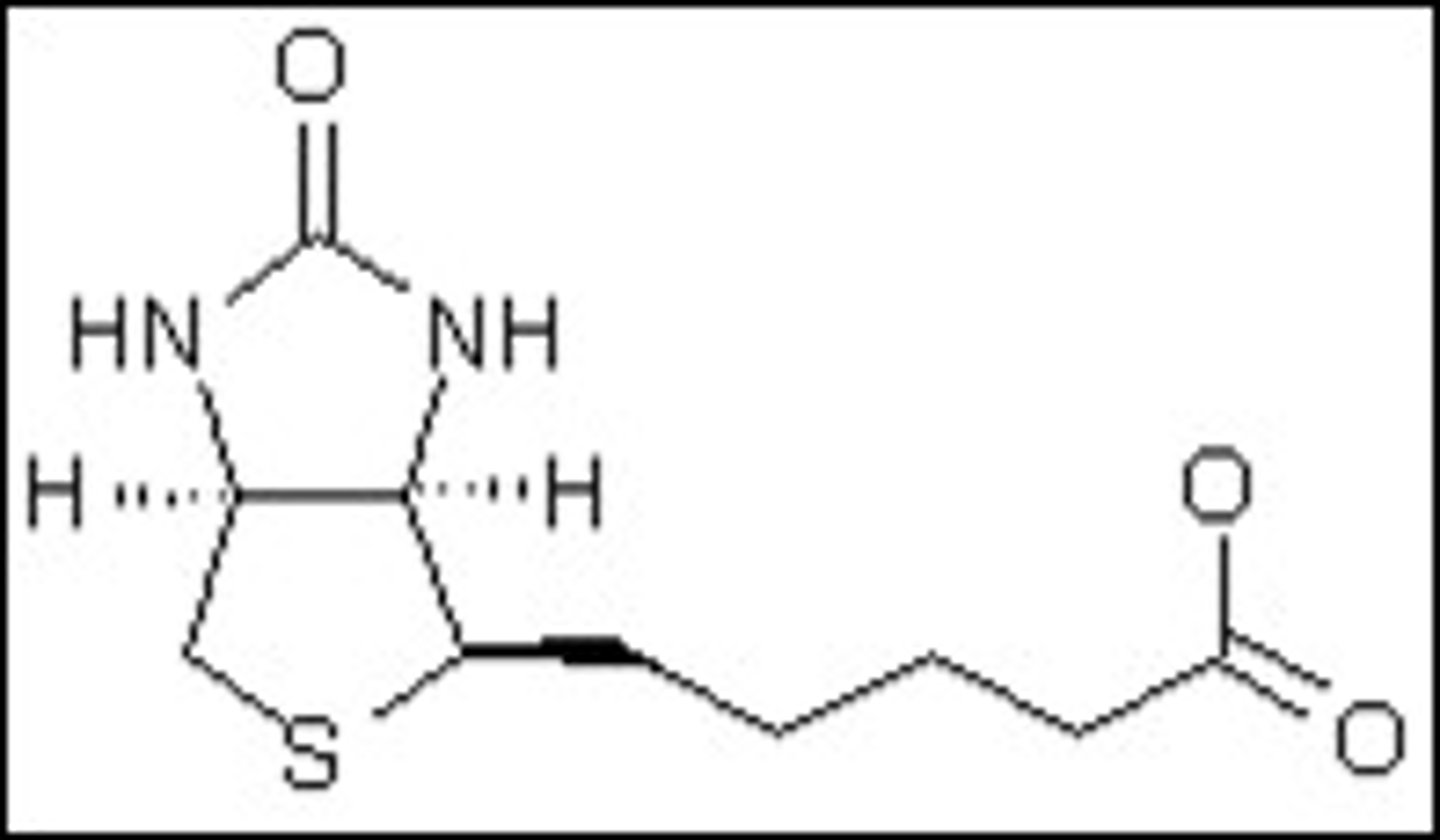
Tetrahydrofolate
Cosubstrate
Transfer 1-carbon groups, e.g. the methylation of DNA
Source: Folate
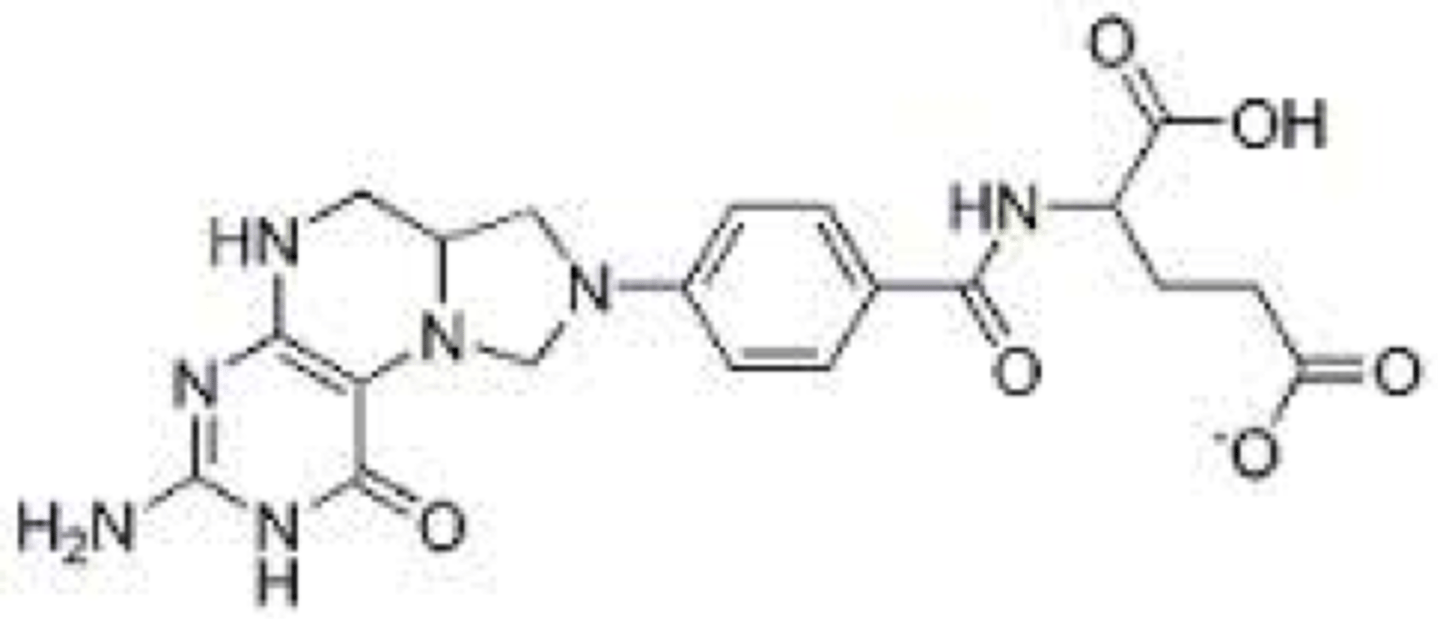
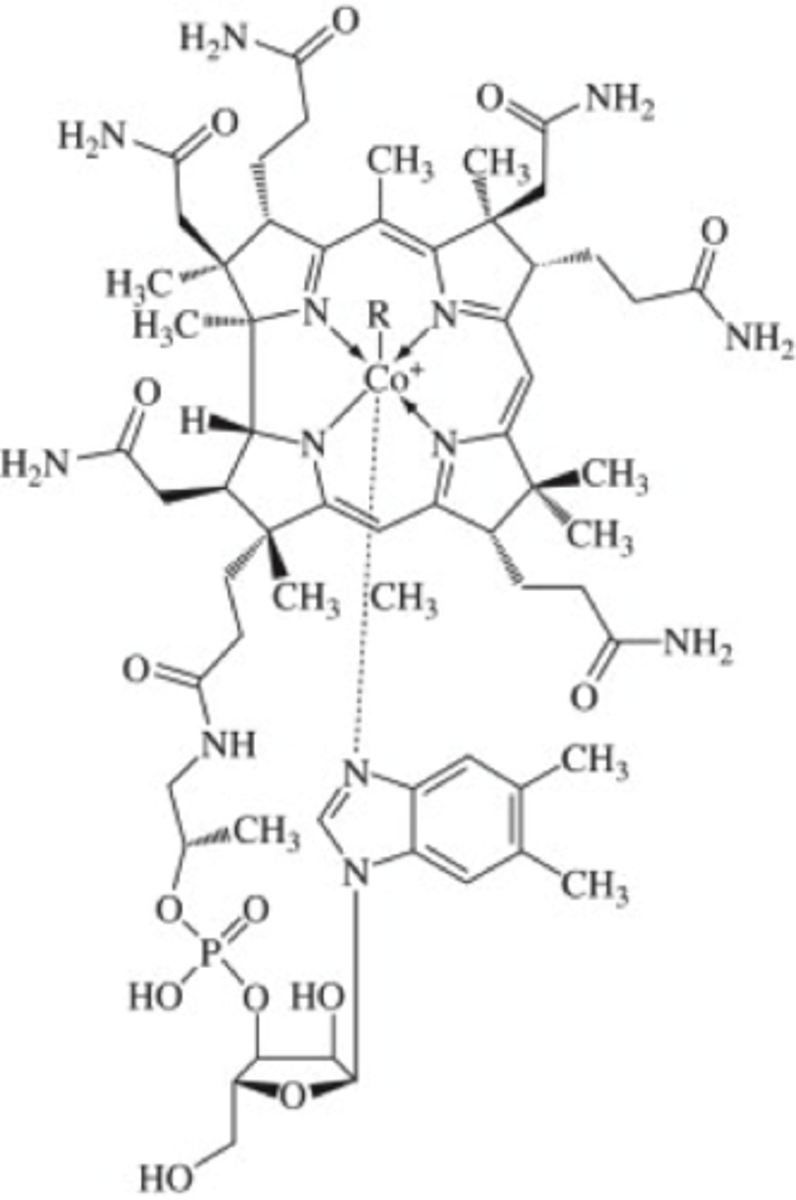
Cobalamin
Prosthetic Group
Intramolecular rearrangements, transfer of methyl groups.
Source; Vitamin B12 / Cobalamin
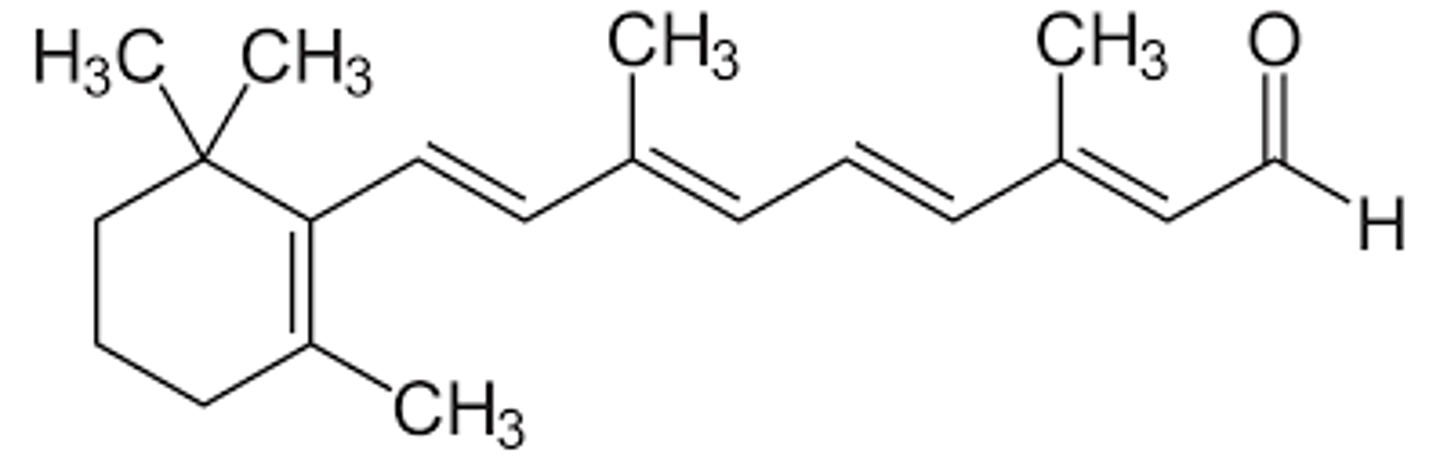
Retinal
Prosthetic Group
Essential for Vision
Source: Vitamin A
Vitamin K
Prosthetic Group
Carboxylation of some glutamate residues; clotting factors
Source: Vitamin K
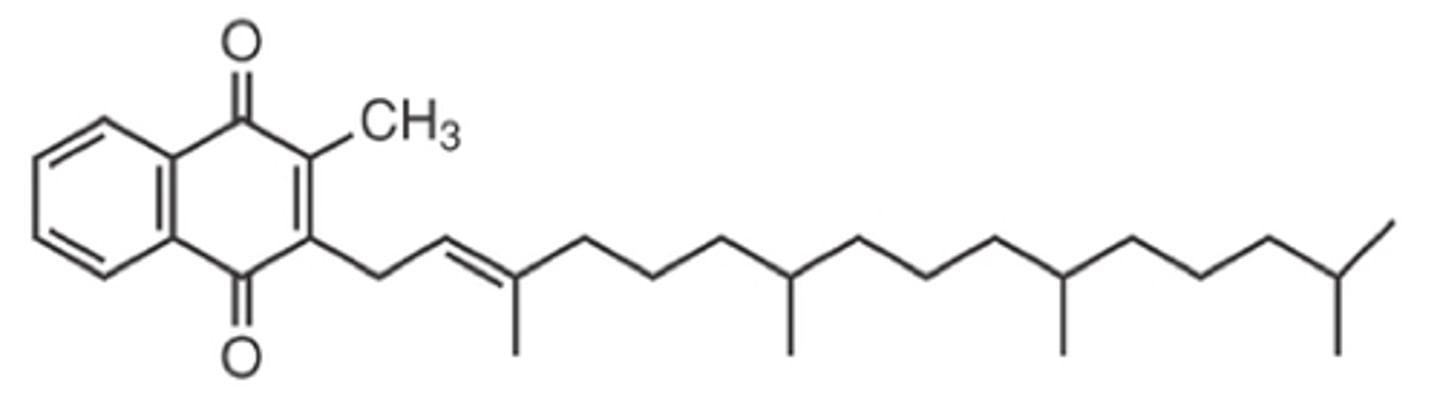
Ubiquinone (coenzyme Q)
Cosubstrate
Lipid-Soluable Electron Carrier
No Vitamin Source
Heme group
Prosthetic Group
Electron Transfer
No Vitamin Source