Upper Limb Anatomy – Arm, Forearm & Hand
1/126
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Comprehensive Q&A flashcards covering arm, forearm, and hand anatomy: muscles (origins, insertions, actions, innervation), movements, neurovascular supply, clinical correlations, and surface anatomy.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
127 Terms
Which three muscles act as the primary flexors of the arm (at the elbow)?
Biceps brachii, brachialis, and coracobrachialis.
What is the only extensor muscle of the arm?
Triceps brachii.
What are the 6 basic shoulder movements?
Flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, internal (medial) rotation, external (lateral) rotation.
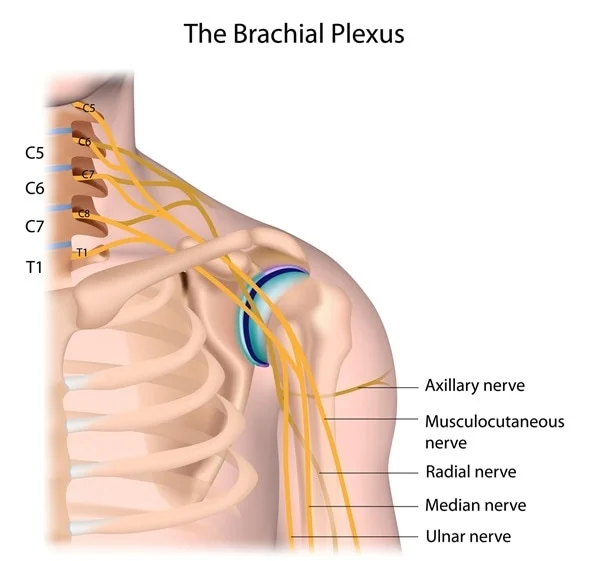
Which three nerves arise directly from the cords of the brachial plexus to supply the arm and forearm?
Musculocutaneous, median, and ulnar nerves (radial and axillary also arise from the plexus).
What are the root levels of the brachial plexus?
C5–T1
Which nerve innervates the biceps brachii?
Musculocutaneous nerve (C5–C6).
What are the origins of the biceps brachii?
Short head – coracoid process of scapula; Long head – supraglenoid tubercle of scapula.
Where does the biceps brachii insert?
Radial tuberosity and bicipital aponeurosis.
Name the three heads of the triceps brachii and their origins.
Long head – infraglenoid tubercle of scapula; Lateral head – posterior humerus; Medial head – posterior humerus.
Where does the triceps brachii insert?
Posterior olecranon process of ulna.
Which nerve supplies the triceps brachii?
Radial nerve (C6–C8).
Main action of the triceps brachii at the elbow?
Extension of the forearm.
Which small muscle assists the triceps in elbow extension and stabilises the elbow joint?
Anconeus.
Which nerve innervates the anconeus muscle?
Radial nerve (C7–T1).
What movement occurs around the trochlea–ulna articulation of the elbow?
Flexion and extension.
Name the primary elbow flexor that acts on the ulna.
Brachialis.
Primary pronators of the forearm?
Pronator teres and pronator quadratus (median nerve).
Primary supinators of the forearm?
Biceps brachii (musculocutaneous) and supinator (radial).
Which nerve is the principal motor nerve of the anterior compartment of the forearm?
Median nerve.
Which two forearm flexor muscles are supplied by the ulnar nerve?
Flexor carpi ulnaris and the ulnar (medial) half of flexor digitorum profundus.
What is ‘Saturday night palsy’ and which nerve is involved?
Compression of the radial nerve causing wrist drop due to loss of extensor function.
Which fracture commonly injures the radial nerve in the arm?
Mid-humeral (spiral) fracture.
Which artery is palpated in the anatomical snuff box?
Radial artery.
Tenderness in the anatomical snuff box suggests fracture of which carpal bone?
Scaphoid.
Name the borders of the cubital fossa.
Superior – line between epicondyles; Medial – pronator teres; Lateral – brachioradialis; Floor – brachialis & supinator.
List the contents of the cubital fossa (lateral → medial).
Radial nerve, biceps tendon, brachial artery (splitting into radial & ulnar), median nerve.
Which vein commonly used for venipuncture crosses the cubital fossa?
Median cubital vein.
Main arteries supplying the arm (proximal → distal).
Subclavian, axillary, brachial, (branching into) ulnar and radial arteries.
Which nerve is responsible for elbow extension?
Radial nerve via triceps brachii.
Name the superficial flexor-pronator muscles originating from the medial epicondyle of humerus.
Pronator teres, flexor carpi radialis, palmaris longus, flexor carpi ulnaris.
Intermediate anterior forearm muscle and its main action?
Flexor digitorum superficialis – flexes middle phalanges of digits 2-5 at PIP joints.
Deep anterior forearm muscle that flexes distal phalanges of digits 2-5?
Flexor digitorum profundus.
Which muscle pronates the forearm in the deep anterior layer?
Pronator quadratus.
Prime wrist flexors?
Flexor carpi radialis, flexor carpi ulnaris, palmaris longus, FDS, FDP.
Prime wrist extensors?
Extensor carpi radialis longus, extensor carpi radialis brevis, extensor digitorum.
Which muscle in the posterior forearm flexes the elbow despite being an extensor-compartment muscle?
Brachioradialis.
Origin and insertion of brachioradialis?
Origin – lateral supra-epicondylar ridge of humerus; Insertion – styloid process of radius.
Which nerve innervates all posterior forearm muscles?
Radial nerve (deep branch/posterior interosseous).
Name the three thumb extensor/abductor muscles in the deep posterior forearm.
Abductor pollicis longus, extensor pollicis brevis, extensor pollicis longus.
Which muscle supinates the forearm from the posterior compartment?
Supinator.
Action of extensor indicis?
Extends index finger and assists in wrist extension.
Which two arteries form the superficial palmar arch?
Primarily ulnar artery with contribution from superficial branch of radial artery.
Which arteries form the deep palmar arch?
Primarily deep branch of radial artery with contribution from deep branch of ulnar artery.
What clinical test assesses adequacy of palmar arterial anastomoses?
Allen test.
Which nerve supplies the thenar (thumb) muscles?
Median nerve.
Name the three thenar muscles responsible for thumb opposition.
Abductor pollicis brevis, flexor pollicis brevis, opponens pollicis.
Which nerve innervates most intrinsic hand muscles (hypothenar, interossei, etc.)?
Ulnar nerve.
List the hypothenar muscles.
Abductor digiti minimi, flexor digiti minimi brevis, opponens digiti minimi, (plus palmaris brevis superficially).
Primary action of lumbrical muscles at MCP and IP joints?
Flex MCP joints and extend IP joints (‘bye-bye’ motion).
Innervation split between lumbricals I-II and III-IV?
I & II – median nerve; III & IV – ulnar nerve.
Function of dorsal interossei muscles (DAB)?
Abduct fingers 2-4 from axial line and assist lumbricals.
Function of palmar interossei muscles (PAD)?
Adduct fingers 2, 4, and 5 toward axial line and assist lumbricals.
Which thumb muscle adducts the thumb and what is its innervation?
Adductor pollicis – ulnar nerve.
Main abductors of the wrist (radial deviation).
Extensor carpi radialis longus & brevis, flexor carpi radialis, abductor pollicis longus.
Main adductors of the wrist (ulnar deviation).
Extensor carpi ulnaris and flexor carpi ulnaris.
Which superficial vein runs along the lateral forearm and drains into the axillary vein?
Cephalic vein.
Which superficial vein runs medially and joins the brachial vein to form the axillary vein?
Basilic vein.
Which lymph nodes drain superficial lymphatics of the upper limb?
Epitrochlear and lateral (humeral) axillary nodes.
Dupuytren contracture affects which structure, leading to flexion of digits 4 & 5?
Palmar aponeurosis fibrosis and shortening.
Tenosynovitis refers to inflammation of what structures?
Tendons and synovial sheaths of the digits.
Motor deficits in median nerve injury at the carpal tunnel would primarily affect which hand muscles?
Thenar muscles and first two lumbricals.
Which nerve is called the ‘nerve of fine movements’ of the hand?
Ulnar nerve.
What forms the lateral and medial boundaries of the anatomical snuff box?
Lateral – tendons of abductor pollicis longus & extensor pollicis brevis; Medial – tendon of extensor pollicis longus.
Name two carpal bones forming the floor of the anatomical snuff box.
Scaphoid and trapezium.
Where is the radial pulse commonly palpated in the wrist?
Just lateral to flexor carpi radialis tendon (anterior distal radius).
Which nerve is most at risk in a supracondylar fracture of the humerus?
Median nerve.
What movement at the thumb involves medial rotation at the 1st carpometacarpal joint?
Opposition, performed by opponens pollicis.
Which muscle flexes the interphalangeal joint of the thumb?
Flexor pollicis longus.
What is the insertion of flexor carpi ulnaris?
Pisiform, hook of hamate, and base of 5th metacarpal.
Which nerve provides sensation to the lateral dorsum of the hand?
Superficial branch of the radial nerve.
Which cutaneous nerve supplies the medial forearm?
Medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve (from brachial plexus).
Name the tendon that forms the medial border of the anatomical snuff box and can be palpated when extending the thumb.
Extensor pollicis longus tendon.
At what angle is full elbow flexion achieved?
Approximately 140°.
Normal forearm pronation and supination range?
About 80° each direction.
Which muscle is considered a flexor of the forearm yet located in the extensor compartment?
Brachioradialis.
What passes through the carpal tunnel along with the median nerve?
Tendons of flexor digitorum superficialis, flexor digitorum profundus, and flexor pollicis longus.
Which artery travels with the ulnar nerve superficial to the flexor retinaculum within the ulnar (Guyon’s) canal?
Ulnar artery.
In wrist drop, which action is lost due to radial nerve paralysis?
Extension of the wrist and hand.
Which muscle originates from the lateral epicondyle and inserts into the extensor expansion of the 5th digit?
Extensor digiti minimi.
Which superficial posterior forearm muscle inserts at the base of the 5th metacarpal and adducts the wrist?
Extensor carpi ulnaris.
What is the innervation of flexor carpi radialis and its main action?
Median nerve; flexes and abducts the wrist.
Which hand muscle wrinkles the skin of the hypothenar eminence?
Palmaris brevis (ulnar nerve).
Which nerve passes through the supinator muscle, potentially compressed in ‘radial tunnel’ syndrome?
Deep branch of radial nerve (posterior interosseous).
Which intrinsic hand muscles are bipennate?
Lumbricals III & IV and all dorsal interossei.
How many dorsal interossei muscles are there and what is their mnemonic?
'DAB' – 4 Dorsal interossei Abduct.
How many palmar interossei muscles exist and what is their mnemonic?
'PAD' – 3 Palmar interossei Adduct.
What structure prevents bow-stringing of extensor tendons on the dorsum of the wrist?
Extensor retinaculum.
Which muscle assists in abduction of the ulna during pronation?
Anconeus.
What are the 4 movements of the forearm?
Flexion, extension, supination, pronation
Anterior forearm muscle groups movement?
Flexors
Posterior forearm muscle groups movement
Extensors
Flexion/extension of the forearm at the elbow joint occurs through the _____.
Trochlea
What muscles are the forearm flexors?
Biceps brachial, brachialis, brachioradialis
What muscles are the forearm extensors?
Triceps and aconeus
Pronation/supination of the forearm at the elbow joint occurs through the _________.
Capitulum of the humerus
What muscles are the pronators of the forearm at the elbow joint?
Pronator teres (short and long heads), pronator quadratus
What muscles are the supinators of the forearm at the elbow joint?
Supinator and biceps brachii
What are the 5 nerves of the brachial plexus?
Axillary, musculocutaneous, radial, median, ulnar
What nerve is responsible for flexion of the forearm?
Musculocutaneous, radial and median nerves
What nerve is responsible for extension of the forearm?
Radial