AP Psychology Unit 10
5.0(1)Studied by 31 people
Card Sorting
1/84
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:37 AM on 9/23/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
1
New cards
Psychoanalytic Theory
Sigmund Freud proposed that childhood sexuality and unconscious motivations influence personality
2
New cards
Humanistic Approach
Focuses on our inner capacities for growth and selffulfillment (led by Maslow and Rogers).
3
New cards
Personality
a person's characteristic pattern of thinking, feeling and acting
4
New cards
Free Asscociation
(Psychoanalysis) method of exploring the unconscious in which the person relaxes and says whatever comes to mind
5
New cards
Pyschoanalysis
Freud's theory of personality that attributes thoughts and actions to unconscious motives and conflicts
6
New cards
Unconscious
According to Freud, it is the reservoir of mostly unacceptable thoughts, wishes, feelings and memories
7
New cards
Id
The unconscious psychic energy that, according to Freud, strives to satisfy sexual and aggressive drives.
8
New cards
Pleasure Principle
Demands immediate gratification. It is what the Id operates on.
9
New cards
Ego
The conscious "executive" part of personality that, according to Freud, mediates among the demands of the id, superego and reality.
10
New cards
Reality Principle
Satisfying the id's desires in ways that brings long-term pleasure It is what ego operates on.
11
New cards
Superego
Part of personality that, according to Freud, represents the voice of moral compass (conscience) that forces the ego to consider the ideal.
12
New cards
Psychosexual Stages
The childhood stages of development (oral,anal,phallic, latency and genital) where the id's pleasure-seeking energies focus on distinct erogenous zones, according to Freud.
13
New cards
Erogenous Zones
Distinct pleasure-sensitive areas of the body.
14
New cards
Phallic
Only for boys and it is the time that they seek genital stimulation and develop unconscious desires for their mom and jealousy towards Dad.
15
New cards
Oedipus Complex
According to Freud, a boy's sexual desires for mom and jealousy for father.
16
New cards
Oral
(0-18 months) Pleasure centers on the mouth.
17
New cards
Anal
(18-36 months) Pleasure focuses on bowel and bladder elimination;oping with demands for control.
18
New cards
Latency
(6-puberty) Dormant sexual feelings.
19
New cards
Genital
(puberty on) Maturation of sexual interests. Freud thought it was where sexuality re-emerges meaning earlier desires are in the unconscious, superego takes parental values and children begin to agree with same-sex parents.
20
New cards
Identification
According to Freud, process where children incorporate their parents' values into their developing superegos. He also believed that it forms gender identity when it is done with the same sex parent.
21
New cards
Fixation
According to Freud, lingering focus of pleasure-seeking energies at an earlier psychosexual stage, in which conflicts were unresolved.
22
New cards
Repression
Psychoanalytic theory, defense mechanism that banishes anxiety arousing thoughts, feelings and memories from consciousness. Freud thought it was our number one mechanism and that they come out though tongue slips/dreams.
23
New cards
Regression
Psychoanalytic defense mechanism in which an individual faced with anxiety retreats to a more infantile psychosexual stage, where some psychic energy remains fixated.
24
New cards
Reaction Formation
Psychoanalytic defense mechanism which the ego unconsciously switches unacceptable impulses into their opposites. Thus, people may express feelings that are the opposite of their anxiety-arousing unconscious feelings.
25
New cards
Projection
Psychoanalytic defense mechanism by which people disguise their own threatening impulses by attributing them to others.
26
New cards
Rationalization
Psychoanalytic defense mechanism that offers self-justifying explanations in place of the real more threatening, unconscious reasons for one's actions.
27
New cards
Displacement
Psychoanalytic defense mechanism that shifts sexual or aggressive impulses toward a more acceptable or less threatening object or person. as when redirecting anger toward a safer outlet.
28
New cards
Sublimation
Psychoanalytic defense mechanism by which people re-channel their unacceptable impulses into socially approved activities.
29
New cards
Denial
Psychoanalytic defense mechanism by which people refuse to believe or even to perceive painful realities.
30
New cards
Collective Unconscious
Carl Jung's concept of a shared, inherited reservoir of memory traces from our species' history.
31
New cards
Projective Tests
A personality test, such as the Rorschach or TAT, that provides ambiguous stimuli designed to trigger projection of one's inner dynamics.
32
New cards
Thematic Appreciation Test
Introduced by Henry Murray, in which people express their inner feelings and interests through the stories they create from ambiguous scenes.
33
New cards
Rorschach Inkblot Test
Introduced by Hermann Rorschach, seeks to identify people's inner feelings by analyzing their interpretations of the blots.
34
New cards
Terror-Management Theory
Death related anxiety, explores people's emotional and behavioral responses to reminders of their impending death.
35
New cards
Self Actualization
According to Maslow, one of the ultimate psych needs that arises after basic physical and psychological needs are met and self-esteem is achieved; the motivation to fulfill one's potential.
36
New cards
Unconditional Positive Regard
According to Rogers, an attitude of total acceptance toward another person.
37
New cards
Self-Concept
Idea that all our thoughts and feelings about ourselves in answer to the question, "who am I."
38
New cards
Trait
A characteristic pattern of behavior or a disposition to feel and act as assessed by self-report inventories and peer reports.
39
New cards
Personality Inventories
A questionnaire (true/false or agree/disagree) which people respond to items designed to gauge a wide range of feelings and behaviors; used to assess selected personality traits.
40
New cards
Minnesota Multiphase Personality Inventory
Most widely researched and clinically used and was developed to identify emotional disorders. Now, it is also used for many other screening purposes.
41
New cards
Empirically Derived Test
A test (such as MMPI) developed by testing a pool of items and then selecting those that discriminate between groups.
42
New cards
Big Five
Conscientiousness, agreeableness, neuroticism, openness and extraversion.
43
New cards
Conscientiousness
Part of big five (organized, careful and disciplined)
44
New cards
Agreeableness
Part of big five (soft-hearted,trusting and helpful)
45
New cards
Neuroticism
Part of big five (emotional stability vs instability)
46
New cards
Extraversion
Part of big five (sociable, fun-loving, affectionate)
47
New cards
Social-Cognitive Perspective
Views behavior as influenced by the interaction between people's traits and their social context.
48
New cards
Reciprocal Determinism
The interacting influences of behavior, internal cognition, and environment.
49
New cards
External Locus of Control
The perception that chance or outside forces beyond your personal control determine your fate.
50
New cards
Internal Locus of Control
The perception that you control your own fate.
51
New cards
Positive Psychology
Aims to discover and promote strengths and virtues that enable individuals and communities to thrive.
52
New cards
Self
Assumed to be the center of personality, the organizer of our thoughts, feelings and actions.
53
New cards
Spotlight Effect
Overestimating other's noticing and evaluating our appearance, performance and blunders.
54
New cards
Self-Serving Bias
A readiness to perceive oneself favorably.
55
New cards
Individualism
Giving priority to one's own goals over group goals and defining one's identity in terms of personal attributes rather than group identifications.
56
New cards
Collectivism
Giving priority to the goals of one's ground defining one's identity accordingly.
57
New cards
Freud Iceberg
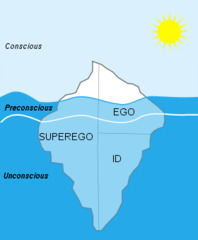
58
New cards
Freudian Slip
When we say the wrong thing out loud, but to Freud, it's the truth surfacing.
59
New cards
Freud Dream Analysis: Manifest Content
What was remembered- it was the censored version of the dream
60
New cards
Freud Dream Analysis: Latent Content
What was not remembered in the dream ( what Freud was interested in the most).
61
New cards
Electra Complex
The Oedipus complex but for girls.
62
New cards
Defense Mechanisms
Emerge when the ego cannot create balance and these are methods that reduce anxiety by distorting reality.
63
New cards
Neo-Freudian
Accepted id, ego, superego, that personality was defined in childhood and in the unconscious. Differed by increasing the role of the conscious and decreasing the roles of sex and violence.
64
New cards
Adler and Horney
Believed that a child's social, not sexual, struggles define their personality formation.
65
New cards
Inferiority Complex
According to Alder, it occurs when we fail to overcome struggles as kids.
66
New cards
Carl jung
Believed in collective unconscious, focused on different people's myths, religions and symbolic images and his ideas are not accepted anymore.
67
New cards
Two theories for Traumatic Experiences
1. Are too bad to deal with so we push them into our unconscious. (Freud would lean in this direction)
2. Are seared into our memories, never to be forgotten. History has shown that more often than not, this is the case.
2. Are seared into our memories, never to be forgotten. History has shown that more often than not, this is the case.
68
New cards
False Consensus Effect
The tendency to overestimate how much others share out beliefs.
69
New cards
Abraham Maslow
Said people are motivated by hierarchy of needs and seek self-actualization-that is to reach one's full potential.
70
New cards
Maslow's Needs
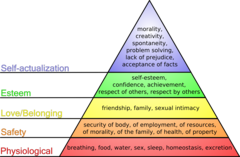
71
New cards
Carl Rogers
(Agreed with Maslow) believed that people are basically good and unless stopped, would move toward self-actualization.
72
New cards
Roger's 3 Needed Parts For Self-Actualization
1. Genuineness-person must be honest with him/herself and not put up fronts
2. Acceptance- a person must accept others and ourselves for who we are... Must give unconditional regard
3. Empathy-person should share another's feelings
2. Acceptance- a person must accept others and ourselves for who we are... Must give unconditional regard
3. Empathy-person should share another's feelings
73
New cards
Trait Perspective
Started by Gordon Allport, it focused on the describing the person, rather than why people behaved a certain way.
74
New cards
Myers-Briggs Type Indicator
Questionnaire that sorts people into Carl Jung's personality types ( asks questions like "Do you like routines or spontaneity?")
75
New cards
Eysenck Test
Test that rates people on a circular scale, meaning, it measures how much a person is intro vs extroverted and how emotionally un vs emotionally stable they are.
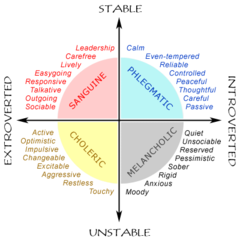
76
New cards
Person Situation Controversy
Asks " whats more important, me as I am or me as other see me?"
77
New cards
Do psychologists believe believe that people's traits tend to change?
No. Most believe that our traits tend to be stable and if change does occur that it is very minimal.
78
New cards
Biopsychosocial
Approach that personality is influenced by our bodies, minds and interactions with our surroundings.
79
New cards
Who started the Social Cognitive Perspective?
Albert Bandura
80
New cards
Social Cognitive Specific Beliefs
1. we learn behaviors by conditioning or watching others
2. what we think about a situation also matters (cog. part)
3. Three things interact with one another...
-Our behavior
-internal cognitive faster (out thinking)
-Environment
2. what we think about a situation also matters (cog. part)
3. Three things interact with one another...
-Our behavior
-internal cognitive faster (out thinking)
-Environment
81
New cards
Personal Control
Whether we feel we are in control or are controlled by external factors.
82
New cards
Two Ways to Study Personal Control
1. correlating people's feelings of control with their achievements and behaviors
2. experiments where researchers alter a person's control level then measure the feeling of control
2. experiments where researchers alter a person's control level then measure the feeling of control
83
New cards
Two theories of Personal Control by Rotter
External and Internal Locus of control.
84
New cards
Defensive self-esteem
Focuses on defending yourself and correlates with aggression and antisocial behavior.
85
New cards
Secure Self esteem
Esteem that is not as dependent on outside factors, but more on internal factors like being secure with yourself for who you are.