medical sciences exam 1
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
what are the swallowing stages called?
Pre-oral
Oral preparatory
oral
pharyngeal
oesphageal
what is hyolaryngeal elevation?
the upward and forward movement of the hyoid bone when the swallow repsonse triggers.
what happens in the pre-oral stage of swallowing?
sensory recongnition of food.
what happens in the oral prepatory stage of swallowing?
the food is chewed and organised.
velum is lowered to keep bolus from spilling posteriorly
buccinator tenses to keep food out of lateral sulcus
bolus is mixed with salivia while being chewed
tognue controls bolus and moves it around the oral cavity
rotary movement of jaw
matieral pulled into a cohensive bolus held between hard palate and tongue
what happens in the oral stage of swallowing?
bolus is pushed backwards by stripping movement of tongue
tongue is grooved and so acts as a chute when it moves backwards
the velum is raised to close the nasopharynx
what is the lateral sulcus?
space between teeth and molars where food can gather
What are the 6 stages within the pharyngeal stage?
Hyolarygeal elevation- pulls larynx into a protected postion under the base of the tongue
epiglottis, tue and false vocal folds close
elevation of soft palate (velopharyngeal closure)
The UES relaxes
base of tongue retracts towards posterior pharyngeal wall, pushing bolus backwards
pharyngeal constrictors contract to squeeze bolus downwards
what is the swallow response?
triggers when the bolus touches the sensory recpetors in the anterior palatglossal arches
the sensory nerves relay a signal to the brain stem
the brainstem intiates pharyngeal response
what happens in the oesophageal stage of swallowing?
Begins when bolus reaches the oesophagus
entirely reflexive
bolus is moved down to the stomach by peristalis of the oesophageal wall musculature
what is the oesphagus?
Oesphagus is hollow muscular tube with UES at upper end and LES at entrance to stomach
what are the 3 pharyngeal constrictor muscles?
superior pharyngeal constrictor
middle pharyngeal constrictor
inferior pharyngeal constrictor (lower portion is cricopharyngeus which forms UES)
what is mastication?
chewing- the process of crushing and grinding by the teeth.
how many muscles are involved in chewing?
4
what are the types of muscles in the tongues and how many in each?
intrinsic tongue muscles (entirely in the tongue) X4
Extrinstic tongue muscles (in structures outside the tongue and insert into the tongue) X4
What 2 categories can muscles attached to the hyoid bone and are involved in hypolaryngeal elevation and what do they do?
supra hyoid muscles- pull the hyoid upwards (elevate) and forward (anteriorly)
infra hyoid muscles- below the hyoid that lower (depress) the hyoid and stabilises the movement.
why does the larynx move during hyolaryngeal elevation?
because it is attached to the hyoid bone via muscles.
How does the manidble joint close?
the mandible opens and closes at the temporomandibular joint (TMJ)
the joint allows movement between the temporal bone of the skull and the mandible.
in the TMJ the condylar proccess of the mandible articulates with the temporal bone of the skull
what 4 muscles allow us to masticate and what do they do
Temporalis (elevates and retracts mandible)
massester (elevates mandible and is a powerful biting muscle)
medial pterygoid (elevates mandible, lateral movemrnt for grinding)
lateral pterygoid (protrudes manible, lateral movement for grinding)
What Cranial Nerve is the motor supply of the mastication muscles?
CN V Trigeminal
which 2 muscles allow the jaw to move?
medial pterygoid
lateral pterygoid
What 3 parts can the tongue be split into and how are they each descirbed?
Anterior 2/3rds tongue: in oral cavity, covered in oral muscosa with taste buds (papillae)
Posterior 1/3rd: in orapharynx, smooth nodular surface (lingual tonsils)
lingual fenulum: connects underside of tongie to the floor of the mouth.
what does the lingual frenulum do?
connects the underside of tongue to the floor of mouth
what are the 4 intrinstic tongue muscles and what layer do they make?
inferior longitudinal (lowest layer)
tranverse (middle layer)
vertical (middle layer)
superior longitiudinal (top layer)
how long are the intrstic muscles?
they go the full length of the tongue.
what do the intristic muscles of the tongue do?
move the the tongue tip up/down/side to side
narrow and flatten the tongue
Assit with; elevating, pulling tongue down, retracting.
what are the 4 extrinstic tongue muscles?
Genioglossus
hyoglossus
styloglossus
palatoglossus
What does the genioglossus muscle do and where does it attach?
prime for tongue movement
makes up most of deep bulk of tongue
retracts, protudes, and depresses.
Attachements: inner mandible, fans up and back and forward to insert into the tongue tip and in the hyoid bone.
What does the hyoglossus muscle do and where does it attach?
attaches: from the hyoid bone to sides of tongue
pulls the side of the tongue down
What does the styloglossus muscle do and where does it attach?
attaches: from styloid proccess of skulls to inferior sides of tongue
moves tongue back and up
What does the palatoglossus muscle do and where does it attach?
attaches- from soft palate to sides of posterior tongue and muscles of anterior faucial arches (palatglossal arches)
elevates the tongue and depresses the soft palate
What Cranial nerves supply motor to the tongue?
Hypoglossals nerve (CNXII) provides motor supply to all muscles
except for palatoglossal CN X vagus and CN XI accessory
Why is it an issue if the CN responsible of sensory supply to the tongue are damaged?
if your tongue is numb you will find speech difficult, as you cannot sense where the tongue is.
could burn tongue on drinks
might not swallow effectively cannot feel where the bolus is.
Which cranial nerves are involved in sensory supply to the tongue?
sensation in 2/3rds tongue, CN V trigeminal
taste in anteior 2/3rds CN VII facial nerve
taste and sensation in posterior 1/3rd CN IX glossopharyngeal nerve
which spinal nerves are involved in propicoception of tongue?
cervical spinal nerves C1-4
what cranial nerve and spinal nerve supplys the thyrohyoid muscle?
CN XII Hypoglossal
Spinal nerve C1
what cranial nerve and spinal nerves supplys the sternothyroid muscle?
CN XII Hypoglossal
Spinal nerves C1, C2, C3
What spinal nerves supply the sternohyoid omohyoid?
Spinal nerves C1-C3
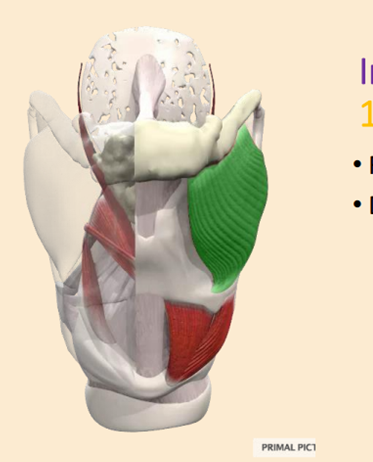
Tell me about the nerve supply to the thyroid and its role
CNXII Hypoglossal
C1 cevical spinal nerve 1
depresses the hyoid or elevates layrnx
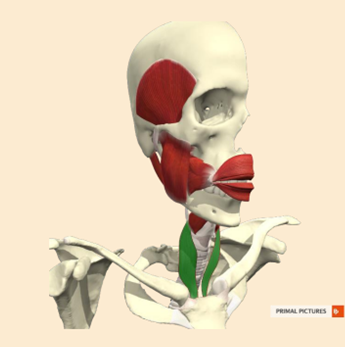
Tell me about the nerve supply to the Sternothyroid and its role
CNXII hypoglossal
C1 and C2 cervical spinal nerves
sternum (breast bone) and clavical (collarbone) to the hyoid bone
depresses the hyoid bone after swallowing
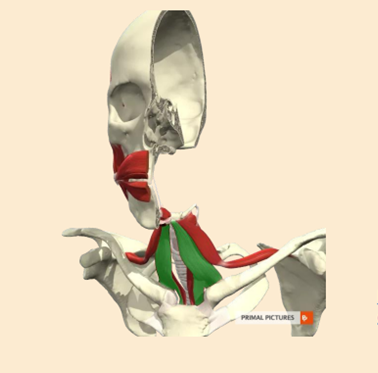
Tell me about the nerve supply to the Sternohyoid and its role
CN XIII hypglossal
cervical spinal nerves 1,2,3
From the sternum (breast bone) and clavicle (collar bone) to the hyoid bone
depresses the hyoid bone after swallowing.
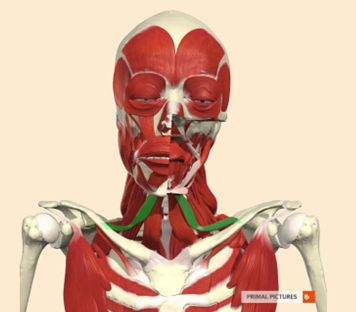
tell me about the omohyoid
2 muscle bellies that are connected by tendon
from scapula (shoulder) bone to hyoid bone
depresses hyoid after swallowing
What are the 6 suprahyoids?
Genioglossus
Hyoglossus
Diagastric
Stylohyoid
Mylohyoid
Genionhyoid
what can the muscles involved with hylaryngeal elevation be broken into and what are their function?
supra-hyoid muscles- that pull the hyoid upwards (elevate) and forwards (anteriorly)
Infra-hyoid muscles- below the hyoid that lower (depress) the hyoid and stablise the movement.
What cranial nerve supplys the Genigoglossus suprahyoid, where is it and what does it do?
CN XII Hypoglossal
Inner mandible to tongue and hyoid
Elevates hyoid (and moves tongue as an extrinxtic tongue muscle)
What cranial nerve supplys the hyoglossus suprahyoid, where is it and what does it do?
CN XII Hypoglossus
from hyoid bone to sides of tongue
elevates the hyoid (and depresses tongue asan extrinstic tongue muscle).
What cranial nerve and spinal nerves supply the geniohyoid suprahyoid, where is it and what does it do?
CN XII Hypoglossal
cervical spinal nerve 1
inner mandible to hyoid
elevates hyoid
What cranial nerve supplys the Mylohyoid suprahyoid, where is it and what does it do?
CN V Trigeminal
inner mandible to hyoid
elevates hyoid
What cranial nerve and cervical spinal nerve supplys the Geniohyoid suprahyoid, where is it and what does it do?
CN XIII Hypoglossal
Cervical nerve 1
inner mandible
elevates hyoid
What cranial nerve supplys the stylohyoid suprahyoid, where is it and what does it do?
CN VII facial
form styloid proccess of temporarl bone to hyoid bone
elevates the hyoid bone (a draws it backwards)
What cranial nerve supplys the diagstric suprahyoid, where is it and what does it do?
2 bellies (sections) anterior and posterior
anterior digastric: CN V Trigeminal, inner manidble to hyoid tendon
posterior diagstric: CN VII facial, hyoid tendon to mastoid proccess
what is the palatoglossal arch also called?
anterior faucial arch/pillar
What is the labial (anterior) sulcus
between teeth and inner lip where food can gather
What is velopharyngeal closure?
The velum raises to close against the posterior pharyngeal wall when we swallow.
Where are the palatine tonsils?
Between the palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal arches
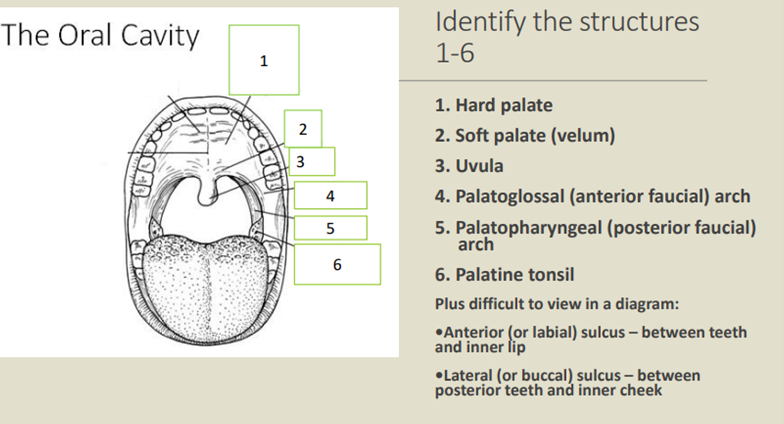
What are the 5 muscles of the soft palate?
Palatoglossus
Palatopharyngeus
Levator veli palatini
Tensor veli palatini
What is the role of the palatoglossus?
pulls soft palate down
or tongue upwards and backwards.

what does the palatopharyngeus do?
pull soft palate down
tongue upwards and backwards
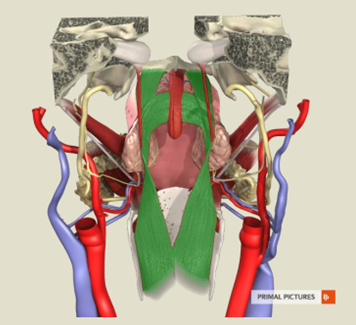
What does the levator veli palatini do?
bulk of velum
lifts the soft palate
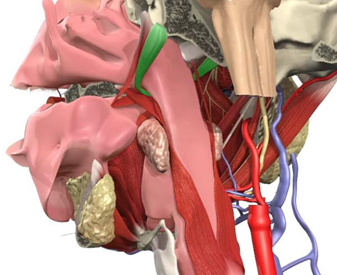
what does the tensor veli palatini does?
tenses the soft palate
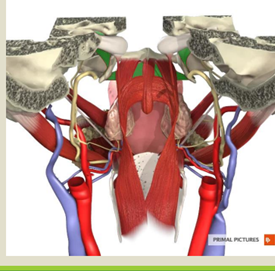
what does the musculus uvulae do?
small muscle that adds lift to the velum to tighten the velopharyngeal contact.
Which cranial nerve provides the majority of the nerve supply to the salivary glands and stimulates the production of salvia?
Facial CN VII
What are the key salivary glands?
Partoid
Submandibular (below the mandible)
Sublingual (under tongue)
The salivary glands come in….
3 pairs- left and right.
Tell me about the motor supply to the soft palate.
motor nerve supply is through vagus CN X
Except tensor veli palatini which has motor supply from trigeminal CN V
which CN provides the sensory supply to the inside of cheeks, hard palate, and floor of mouth
CN V trigeminal
Which CN provides sensory supply to the faucial arches and palatine tonsils
CN IX glossopharyngeal