The cardiac cycle
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
That happens in systole and diastole
Systole : heart chambers contract and heart pumps the blood
Diastole: heart chambers relax and the heart fills
Where is the SA node found?
Near the opening of the superior vena cava
What causes the A and C wave
A: increase in atrial pressure
C: mitral valve closes
What causes V wave?
Atrial pressure increasing due to blood from pulmonary vein
What causes the X descent and dichrotic notch?
X descent: atrial pressure initially decreases as atrial base is being pulled down as the ventricles contract
Dichrotic notch: Aortic valve closes
Stroke volume =
End diastolic volume - end systolic volume
What is the EDV and ESV ?
EDV: volume of blood in the ventricle just before contracting (how full it is at the end of diastole)
ESV:the lowest volume of blood in the ventricle during the cardiac cycle (how much blood is left over after a contraction)
What factors can increase the heart rate (positive chronotropic)
sympathetic nervous system
Hormones (T3,T4)
Increases Ca²+ levels
What factors can decrease the heart rate (negative chronotropic)
parasympathetic nervous system
Decrease in K+ levels
Decrease in Ca2+ levels
How do chemoteceptors cause an increase in heart rate?
** found in the middle all of the aorta and carotid artery
respiration causes an increase in CO2 → decrease in pH
Increase frequency of impulses sent to the medulla via the SNS
Increase of impulses sent to the SAN
How do baroreceprtoes cause an decrease heart rate?
** found in the wall of the aorta ans carotid artery
Receptors stretch with increased bp
Send more impulses to the medulla via PSNS
less frequency of impulses to the SAN
What is the order of conduction in the heart?
SA node
AV node
Common bundle
Bundle (bundle of his)
Purkinje fibres
What is stoke volume affected by?
preload
Contractility
Afterload
What is preload?
Amount of stretch of ventricles in diastole
** increases stroke volume
What is preload affected by?
Heart contacts → increased venous return → increase in EDV → increases preload
Respiratory pump: increases thoracic volume → decreased pressure + decreases abdominal volume → increases pressure : blood flows high to low pressure
Venous tone
Gravity decreases preload
What is frank atsrlings law of contractility?
The more the heart stretches the more it contracts (as the heart fills and stretches the harder it pumps our blood)
What factors increases contractility ?
sympathetic nervous system (noradrenaline)
Hormones (T3/4, glucagon)
Drugs
What factors decrease contractility ?
beta blockers
Calcium channel blockers
High K+/ Na+/ H+
What is afterload?
The amount of resistance needed to be overcome by the ventricles to pump blood to the aorta
** decreases SV
What increases after load?
semilunar valve damage
Increased vascular resistance
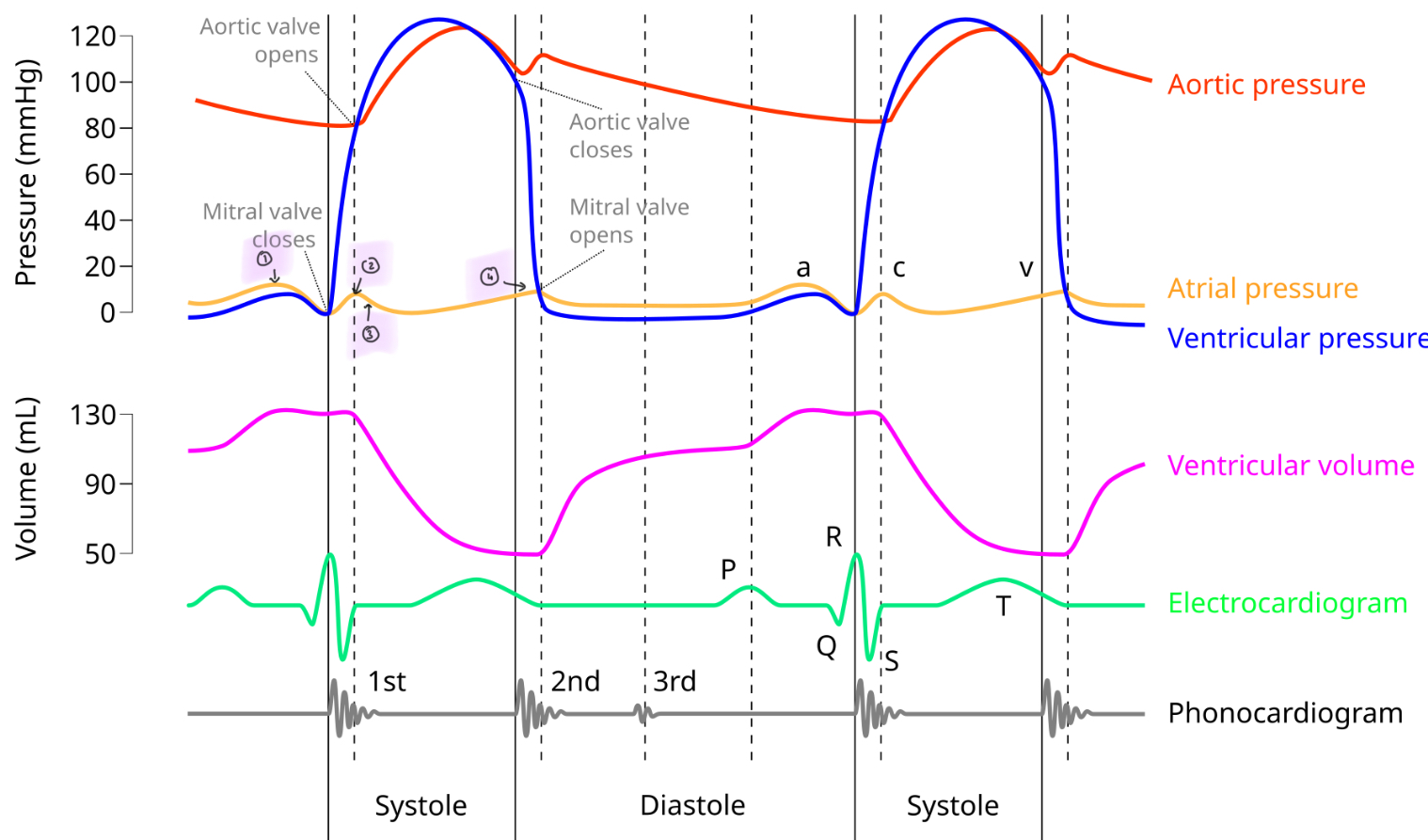
A wave
C wave
X descent
V wave
In what order do the valves open and close?
Mitral valve closes
Aortic valve opens
Aortic valve closes
Mitral valve opens
The cardiac cycle
atrial systole: atria contract → arial pressure > ventricular → the mitral valve opens remaining blood flows into the ventricle (ESV)
Isovolumetric contraction: ventricles contract → ventricular pressure > atrial → mitral valve closes → S1 sound
Ejection stage: ventricular pressure > pressure in aortic → aortic valve opens
Isovolumetric relaxation: ventricular presure < aortic → aortic valve closes → S2 sound
Atrial systole/Ventricular diastole: atria fills → atrial pressure > venticular → mitral valve opens and the ventricles start to fill