Affinity Chromatography
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What is the purpose of protein purification?
To achieve structure, function, and pharmaceutical application.
What is the first step in protein purification?
Cell lysis, which involves breaking open cells to release proteins.
What methods can be used for cell lysis?
Sonication, enzymatic digestion, or mechanical disruption.
What techniques are used for clarification in protein purification?
Centrifugation or filtration to remove cell debris and insoluble materials.
What methods increase protein concentration during purification?
Ultrafiltration and lyophilization.
What is salting out in protein purification?
A method using ammonium sulfate (NH4SO4) to precipitate proteins.
What techniques are used for intermediate purification?
SDS-PAGE and Western blot.
What are the issues faced during protein purification?
Protein stability, yield vs. purity trade-off, protein aggregation, contaminants, cost and time, and scalability.
What is monitored during protein purification?
SDS-PAGE and protein assay.
What is affinity chromatography?
A technique that separates proteins based on specific interactions between a protein and a ligand immobilized on the chromatography matrix.
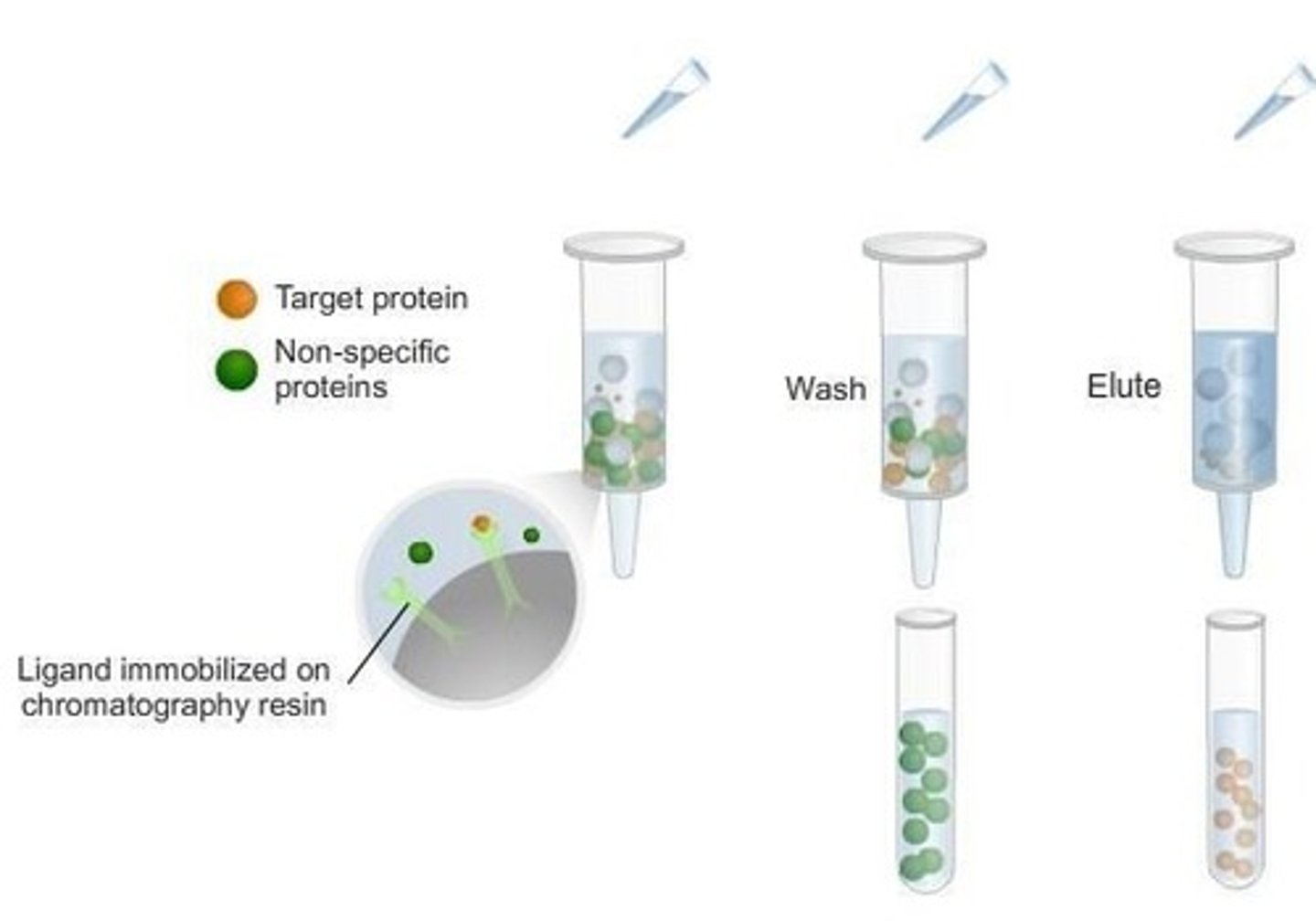
How does affinity chromatography work?
Biological macromolecules interact with immobilized molecules, allowing for selective retention and elution of desired proteins.
What can be used to elute desired proteins in affinity chromatography?
Adding the immobilized molecules, high pH, or increasing ionic strength.
What are some practical considerations for affinity chromatography?
Commercial availability of various affinity chromatography substrates, customization options, and literature support.
What is immuno-affinity chromatography?
A type of affinity chromatography that uses antigen-antibody interactions to purify antibodies.
What is poly (U) chromatography?
A method that uses a poly-uridylic acid matrix to purify mRNA.
What is DNA affinity chromatography?
A technique that purifies proteins that bind to single or double-stranded DNA.
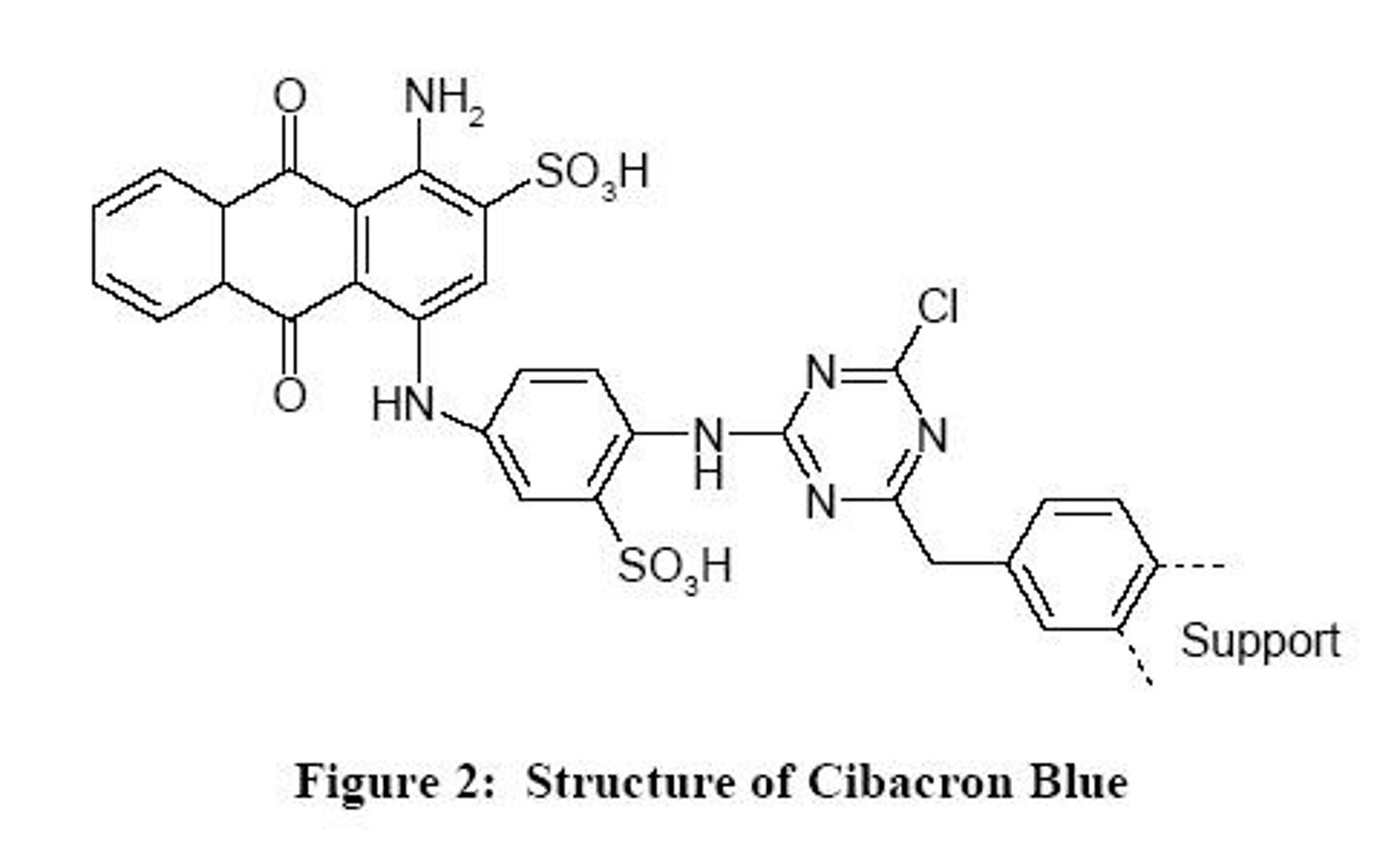
What is dye-binding chromatography?
A method that uses dyes that mimic nucleotides to bind proteins.
What is gene fusion in affinity chromatography?
Infusing the gene encoding the protein of interest with a second gene encoding a purifiable tag.
What is metal chelate chromatography?
A method using immobilized metal ions to purify proteins with histidine tags.
What are the components of the affinity chromatography column material?
Matrix (e.g., agarose, dextran, polyacrylamide) and ligand (chemically bonded group for selective adsorption).
What is the matrix used in the described experiment?
Trisacryl M, a polyacrylamide support.
What ligand is used in the experiment?
Cibacron Blue, which specifically binds to albumin.
What is the purpose of gradient elution in affinity chromatography?
To gradually increase salt concentration, disrupting protein-ligand interactions and eluting the desired protein.
What is the procedure for performing a protein assay?
Label tubes, add samples and protein assay reagent, incubate, and measure absorbance at 660 nm.
What does the elution profile indicate?
The absorbance at 660 nm across different fractions, showing protein presence.
What are the steps involved in the experiment?
Column equilibration, albumin sample loading, gradient salt elution, and protein assay.
What is the significance of maintaining protein stability during purification?
To ensure the protein retains its functionality and does not aggregate.
What trade-off must be managed during protein purification?
The balance between yield (amount of protein) and purity (quality of protein).