Gross Electric Potential
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
what is electodiagnostics?
- a method of medical diagnosis that obtains information about different disease conditions (normal or abnormal)by passively recording the electrical activity (potential difference) of body parts or by measuring their response to external electrical stimuli
what is electodiagnostic examinations a measurement of?
- a measurement of an electrical activity generated by muscles and nerves
what are auditory evoked potential(AEP)?
- auditory signals are transmitted to the ears to detect hearing problems
what is Electroencephalography (EEG)?
- Electrodes (electrical measuring devices) are attached to the scalp to measure brain functions
what is Electromyography (EMG)?
- Surface electrodes are placed on the skin or tiny needle electrodes are inserted into muscle to measure activity in the muscle
what is Nerve conduction studies (NCS)?
- : Electrodes are used to measure activity in the nervesw
what is Somatosensory-evoked potential (SEP)?
- EEG electrodes measure the brain's response to a stimulus applied to the skin
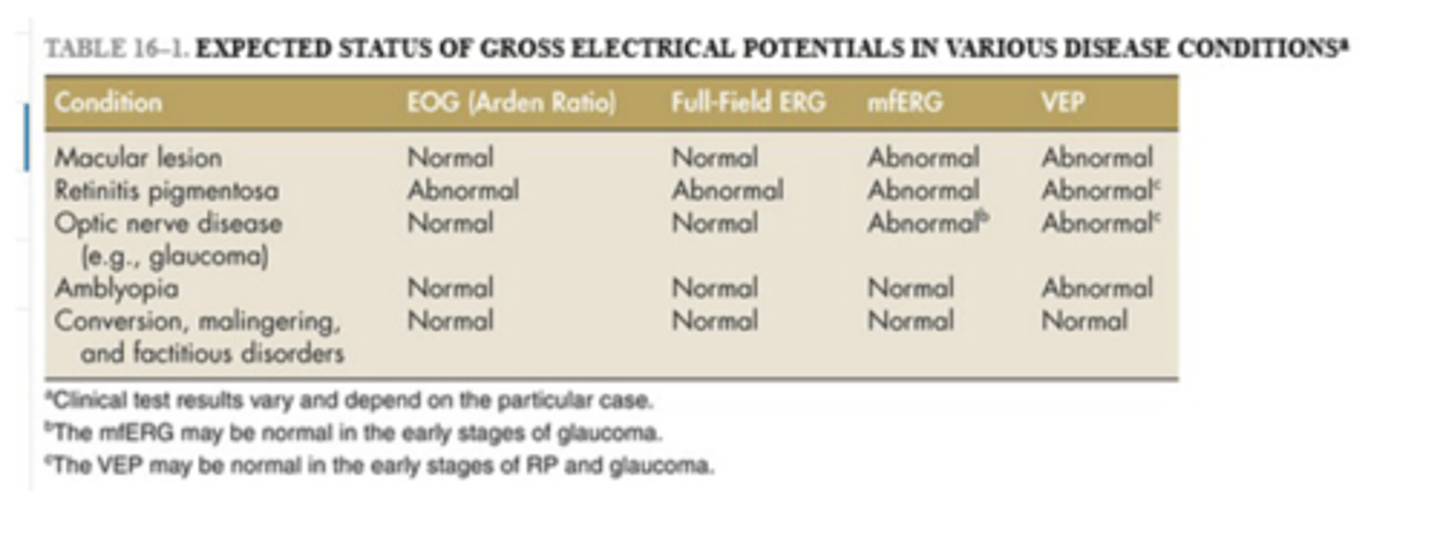
what are the clinical electrodiagnostics tests?
- Electrooculogram (EOG)
• Electroretinogram (ERG)
• Visual Evoked Potential (VEP)
what is an electrooculogram?
- an electrophysiologic test that measures the existing resting electrical potential between the cornea and Bruch's membrane
what does an electrooculogram determine?
- determines function of outer retina and retinal pigment epithelium (RPE)
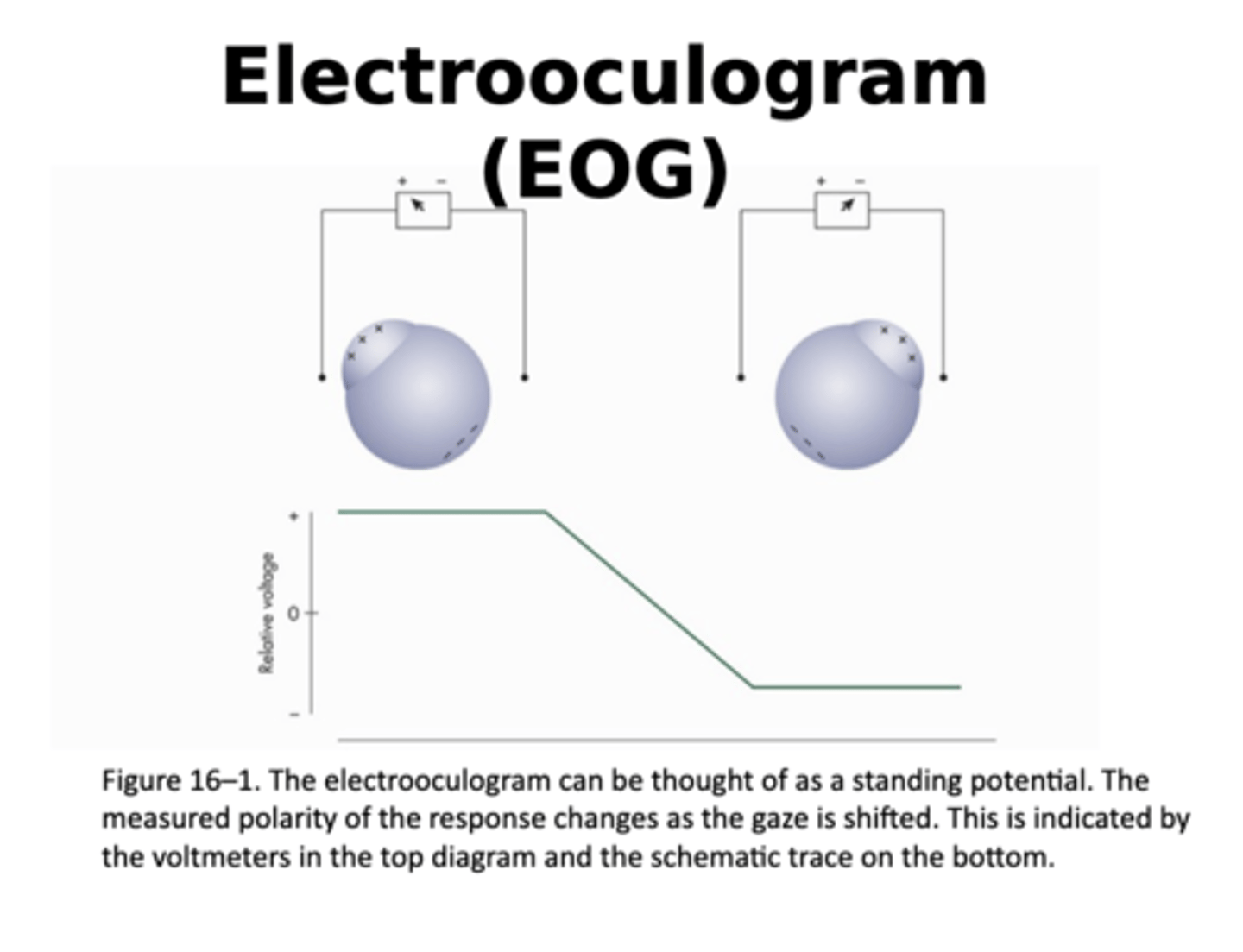
is the electrooculogram larger under light or dark adapted conditions?
- larger under light adapted conditions
when does electrooculogram reach its minimum value?
- It reaches its minimum value (dark trough) after approximately 8 minutes of dark adaptation
when does electooculogram reach its maximum value?
- maximum value (light rise) following approximately 15 minutes of light adaptation
what is the arden ratio?
- The Arden ratio is the ratio of the light rise to the dark trough
- For clinical purposes, it is useful to determine the ratio of the light rise to the dark trough
what AR values are considered to be abnormal?
- AR values lower than approximately165% to 180% are considered abnormal
What is a full-field ERG?
- a retinal potential elicited by a brief flash of light, recommended to be about 5 milliseconds in duration, that evenly illuminates the entire retina
how is a scotopic-dominated ERG obtained?
- obtained by stimulating a dark-adapted retina with a dim, short-wavelength light
how is a photopic-dominated ERG obtained?
- a light-adapted patient is exposed to a relatively bright middle-wavelength stimulus
which kind of ERG is both larger and slower, scotopic or photopic?
- scotopic ERG is both larger and slower than photopic
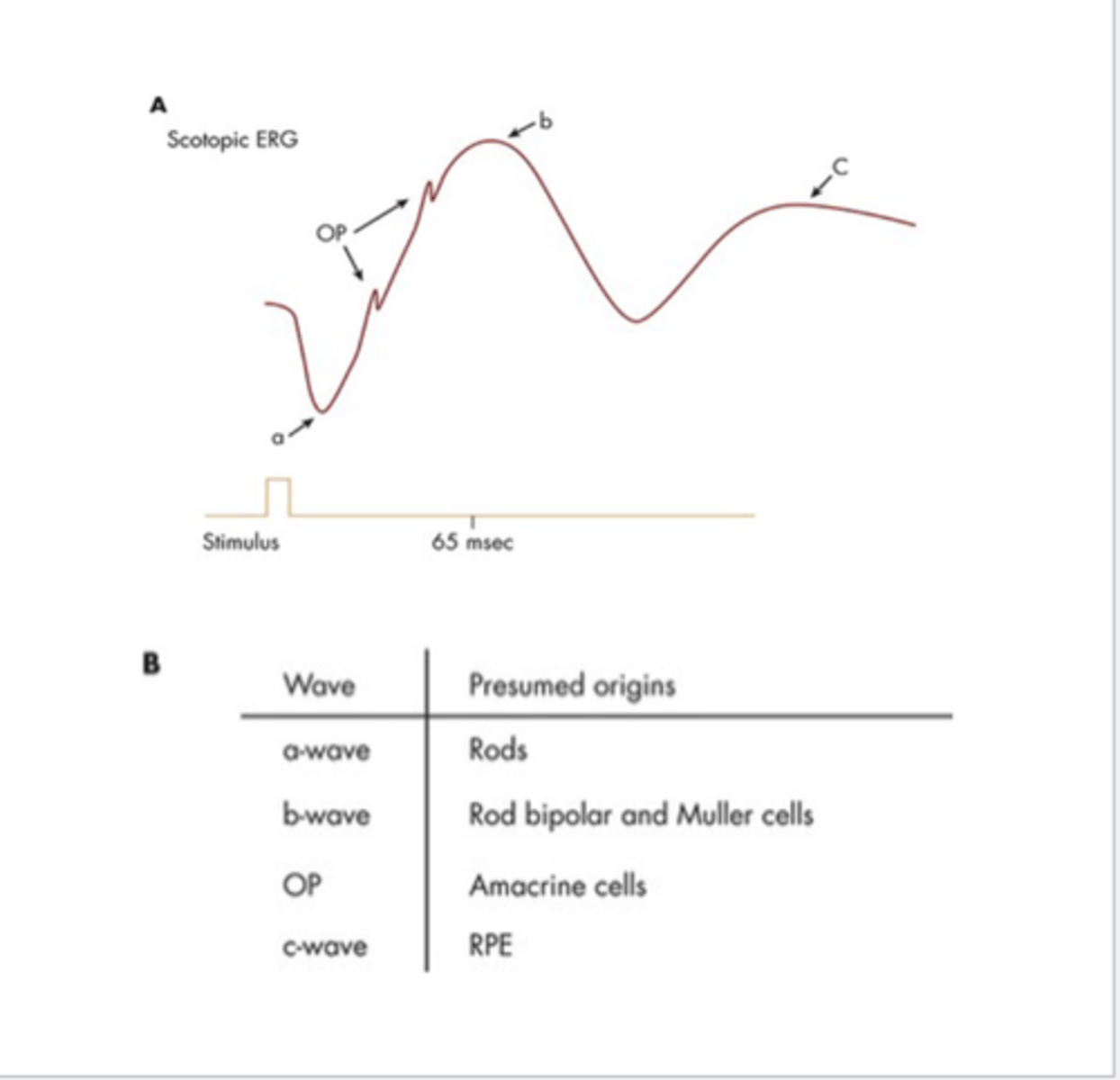
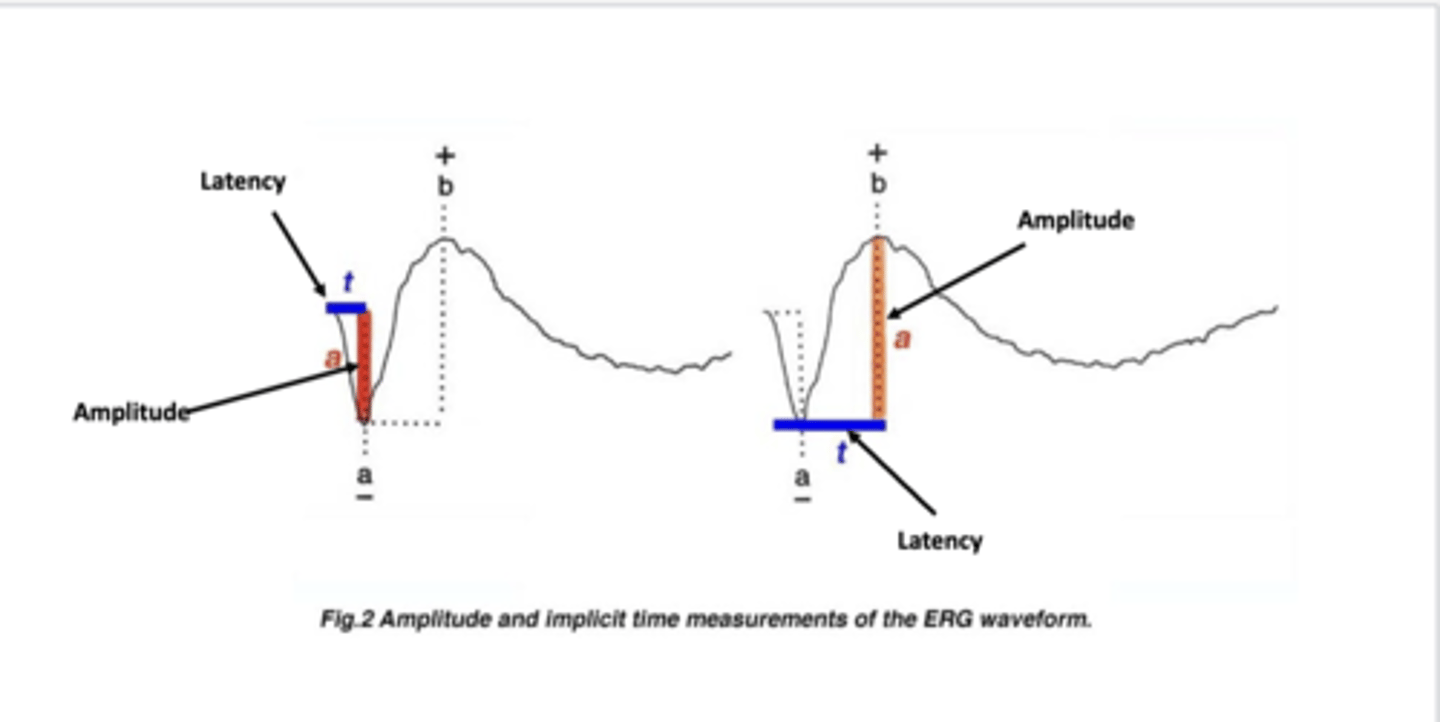
what are the different parts of the scotopic ERG?
- a-wave: presumed origin rods
- b-wave: presumed origin rod, bipolar, muller cells
- OP wave: presumed origin amacrine cells
- c-wave: RPE
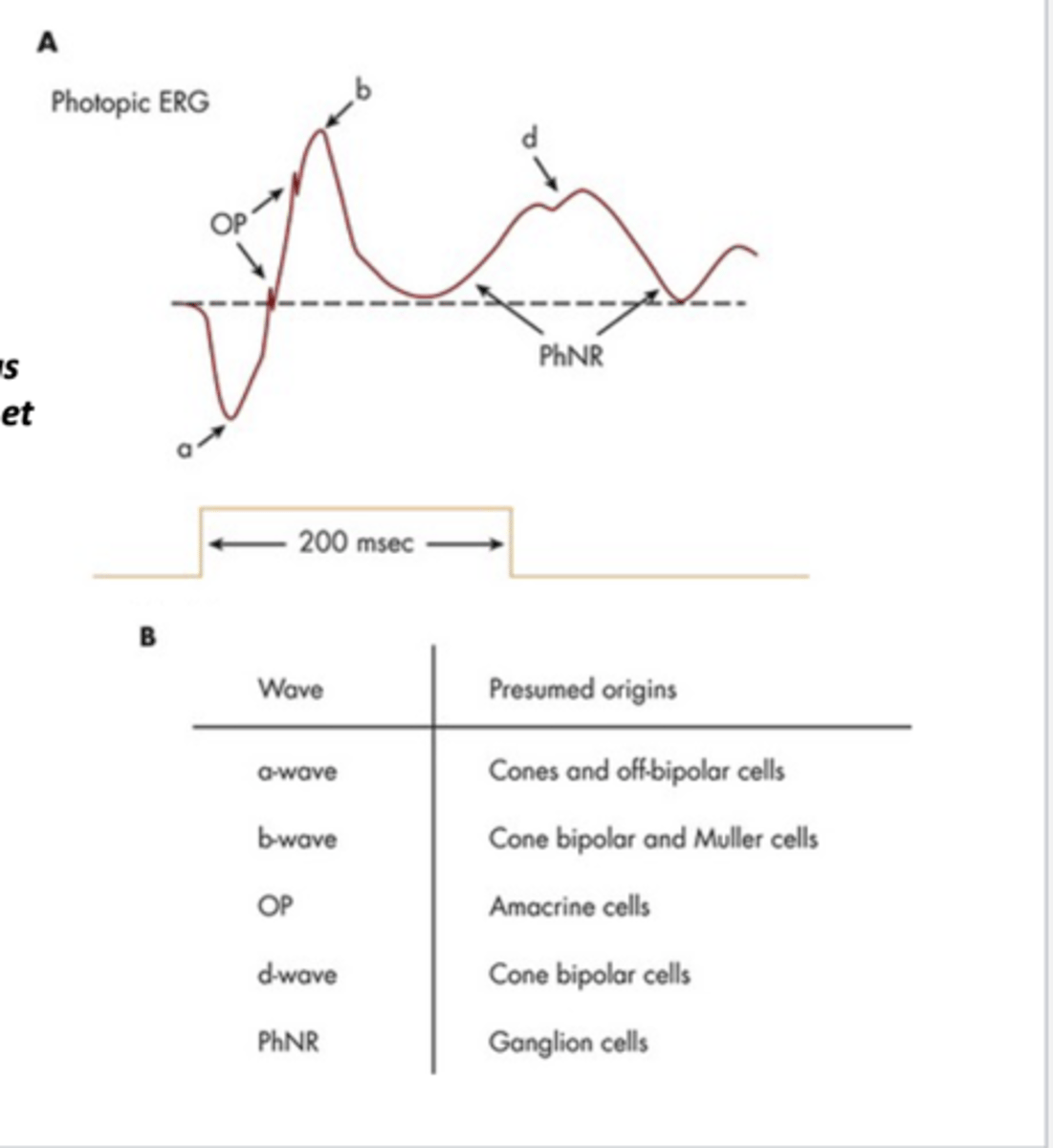
what are the different part of the photopic ERG?
- a-wave: presumed origin cones and off-bipolar cells
- b-wave: presumed origin cone bipolar and muller cells
- OP wave: presumed origin amacrine cells
- d-wave: presumed origin cone bipolar cells
- PhNR wave: presumed origin ganglion cells
what conditions are the photopic negative response (PhNR) decreased in?
- The photopic negative response (PhNR), which has its origins in ganglion cells, is decreased in glaucoma and multiple sclerosis
how does glaucoma treatment affect PhNR?
- glaucoma treatment that lower IOP has been demonstrated to increase PhNR
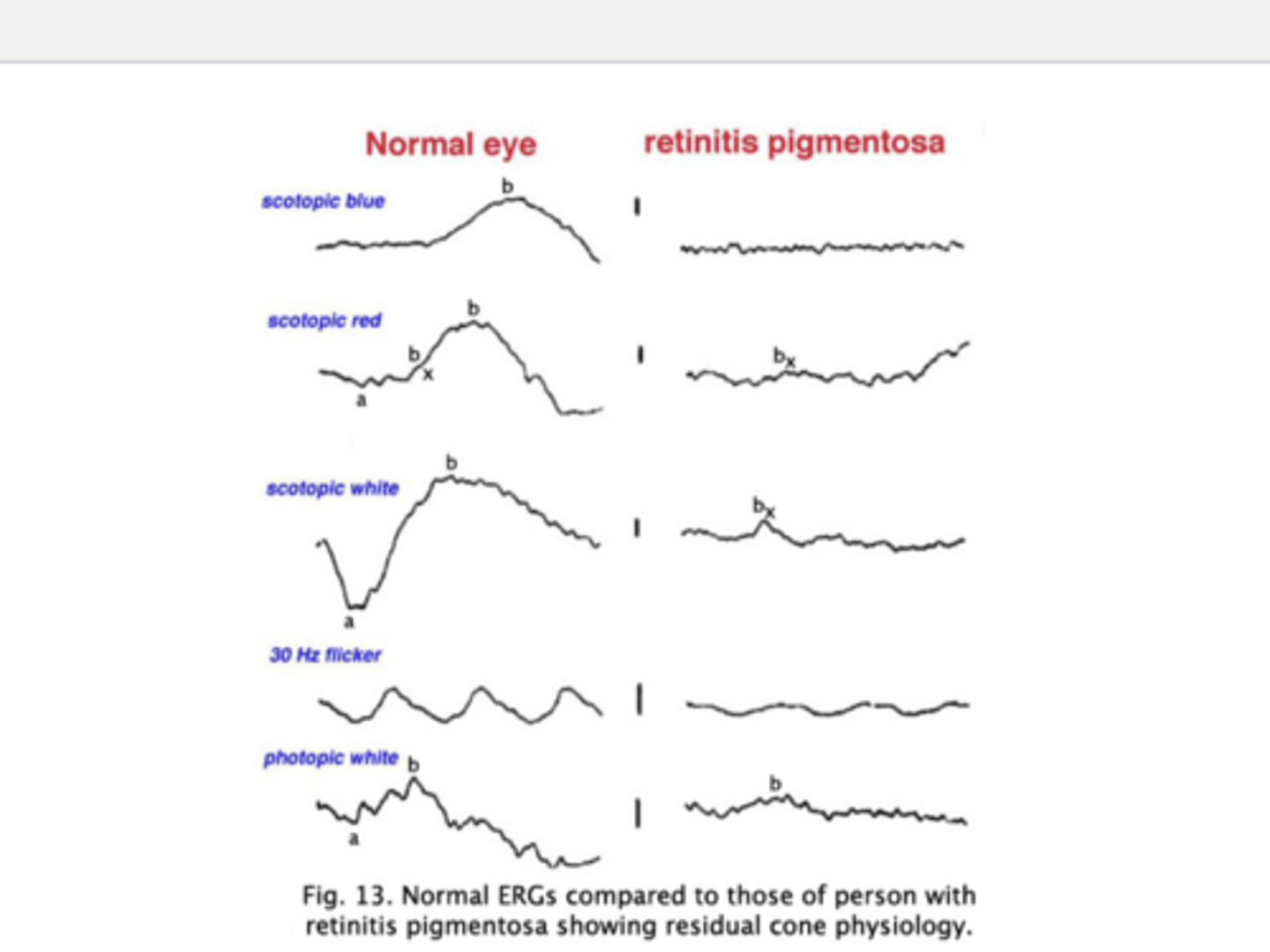
how is pattern ERG obtained?
- s obtained with a temporally modulated patterned stimulus whose average spatial luminance remains constant
• A grating or, more commonly, a checker board pattern is used • Stimulus conditions are photopic.
does PERG have same or different retinal origins?
- different
what may PERG be helpful in doing?
- The inner retina, particularly retinal ganglion cells, may play a role in its genesis
• The PERG may be helpful in the assessment of inner retinal function
• PERGs can be abnormal in early glaucoma
what is Vision Evoked Potential (VEP)?
- VEP refers to an electrical signal generated over the primary visual cortex (V1) in response to a time-locked visual stimulus
- Objective, rapid, repeatable, and non-invasive method to assess functionality and integrity of the retinal and early-afferent, visuo-cortical pathways
- This technique has proven to be beneficial for special populations (e.g.,infants and young children, non-verbal patients, cognitively-impaired patients), as well as acquired brain injury
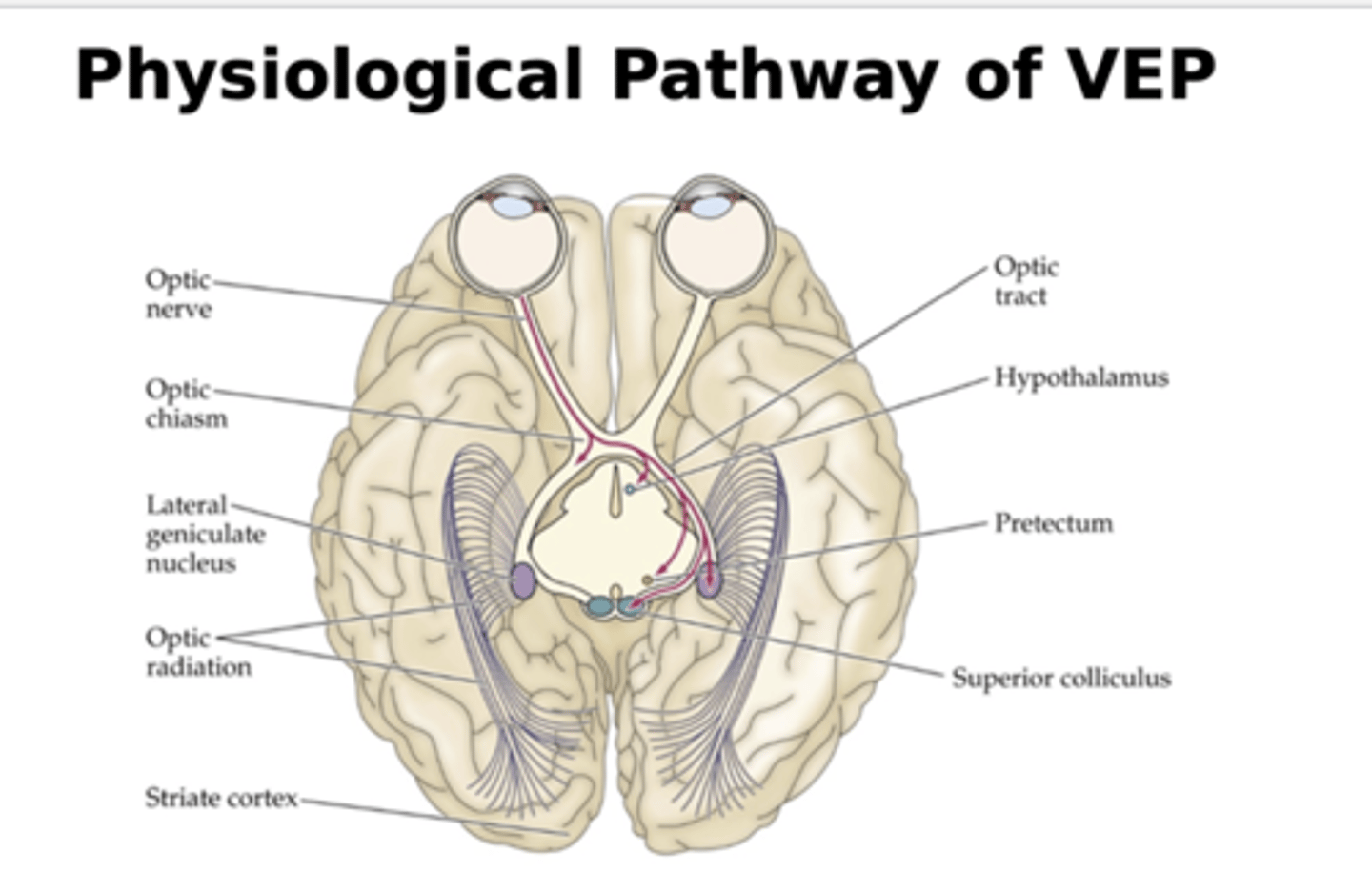
what is the physiological pathway of VEP?
- 3 categories of ganglion cells (Magno, Parvo, Konio)
- they send info from retinal ganglion cells to LGN to primary visual cortex to elicit VEP response
what is the M pathway believed to be responsible for?
- carries info from the large ganglion cells
- the mediation of information regarding movement of objects, high temporal frequencies, low spatial frequencies and very low contrast targets
- what is the P pathway believed to be responsible for?
- carries information from smaller retinal ganglion cells
- considered to be the main carrier of high contrast, color information and high spatial frequency information, especially at lower temporal frequency
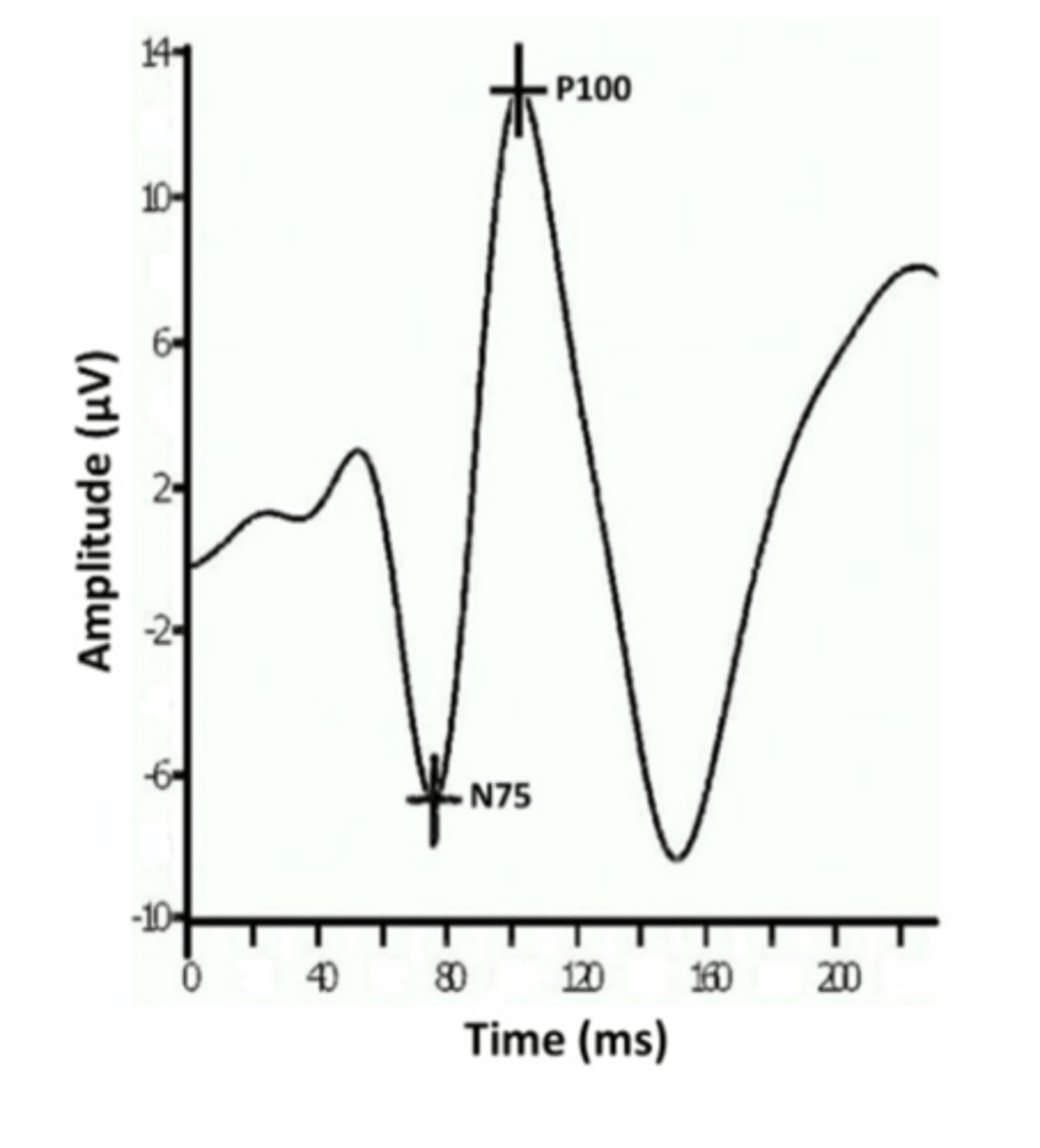
what are the two response components of VEP waveform?
- two components: N75 and P100
what is N75?
- reflects the negative peak occurring approximately 75msec after stimulus onset
what is P100?
- reflects the positive peak occurring approximately 100 msec after stimulus onset
what is the VEP amplitude?
- The N75-P100 (peak-to-trough) difference
what is VEP latency?
- defined "as the time from the stimulus onset to the largest amplitude of a positive(P100) and/or negative peak (N75)"
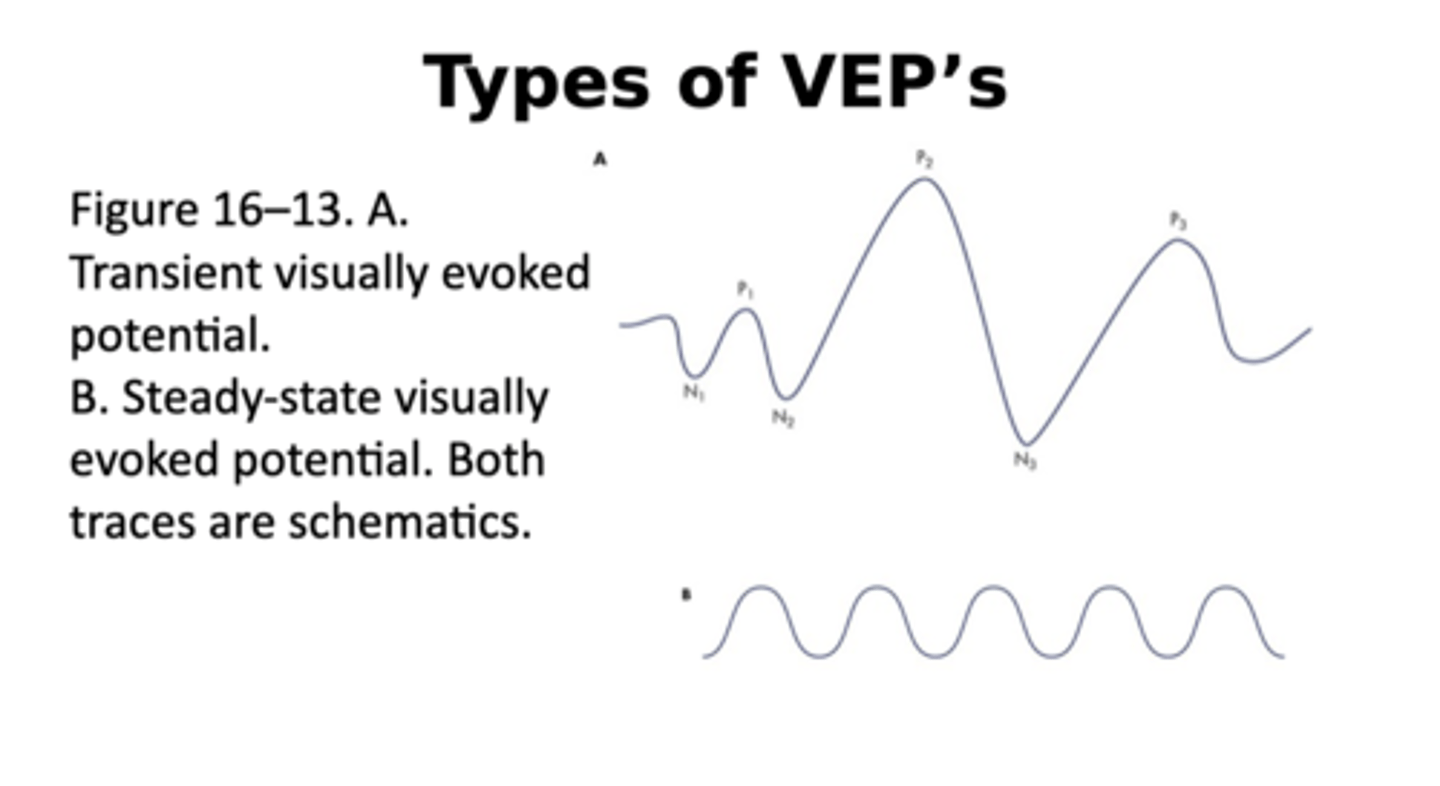
how are the stimulus arrangement used in mfERGs compared to mfVEP?
- they are similar
- Comparable to an mfERG, the mfVEP shows VEPs for many different retinal loci.
• Interestingly, the mfVEP elicited by a given stimulus location is enhanced when the subject attends to this location
what is the amplitude of VEP for given spatial frequency proportional to?
- proportional to the stimulus contrast
- threshold contrast is obtained by extrapolation(dashed line) from data obtained at higher contrast levels
what is the amplitude of the pattern electroretinogram proportional to?
- proportional to the surface area of the retina stimulated.
- Reducing the stimulus size in half, as is done toelicit the bottom two PERG traces, reduces the PERG amplitude in half.
- It does not make any difference that one stimulus is foveal and the other is parafoveal.
- For the visually evoked potential (VEP), however, the surface area of the stimulated retina is not the critical issue.
- The VEP is a foveal response; consequently, a parafoveal stimulus does not elicit a significant response. (Note that the amplitudes of the PERG and VEP have been equated in this figure for illustrative purposes
- The amplitude of the PERG is actually considerably greater than the VEP.)
what can VEP be used to assist in the diagnosis of?
- multiple sclerosis, a demyelinating disease that can cause optic neuritis
- During bouts of optic neuritis, the myelin sheath and axons of the optic nerve are damaged, resulting in reduced saltatory conduction velocity along the optic nerve
-
is optic neuritis in MS unilateral or bilateral?
- The condition is typically unilateral and may result in increased VEP latency for the affected eye relative to the unaffected eye
does latency in optic neuritis persist?
- VA generally improves as the optic neuritis is resolved, but the increased latency does not