Orgo CH12 In-Class Notes: Amines
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Amines
Amines are organic derivatives of ammonia (NH3 )
Naturally occur in many compounds in palants and animals
Widely used in biologically active pharmaceuticals and illegal substances
Labetalol is a betal-blocker drug that is used for treatment of high blood pressure.
It is formed by an SN2 reaction of an epoxide with a primary amine as the nucleophile.
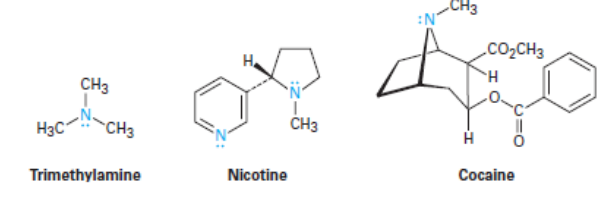
Naming Amines
Amines can either be alkyl-substituted or aryl-substituted
Classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary
Degree of substitution at the NITROGEN!
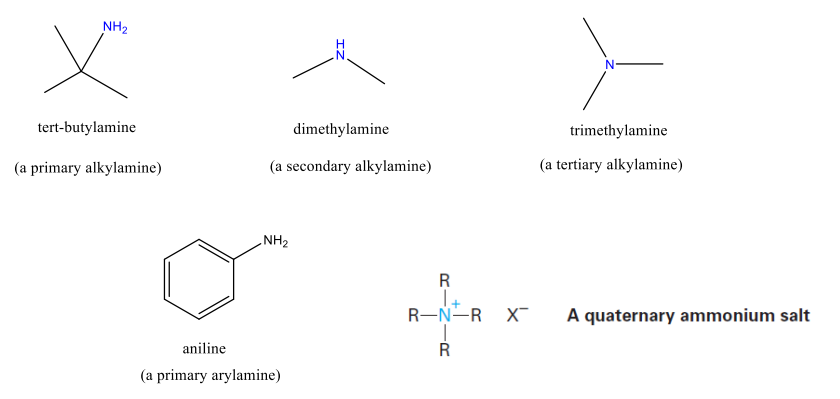
Naming Amines Examples
Parent gets “amine” ending (if highest priority)
If symmetrically substituted, gets named as di or tri, followed by the root, followed by “amine”
If unsymmetrically substituted, the largest group is the parent, and the N-substituents are listed alphabetically
Alcohols, Aldehydes, Ketones, Thiols, Sulfides and Carboxylic acids are all higher priority than amines.
If lower priority, gets names as “amino” group
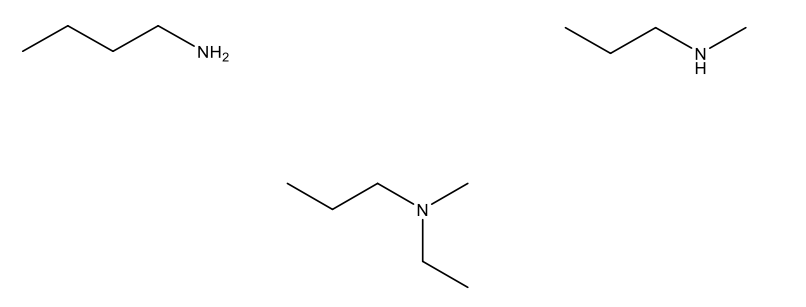
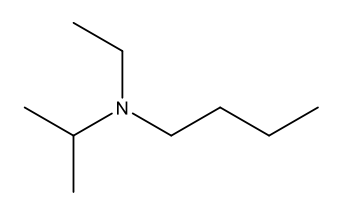
What is the IUPAC name of the following structure?
N-ethyl-N-isopropylbutylamine
Structure and Properties of Amines
sp3 hybridized
Amines with 5 carbons or less are water-soluble • Fish-like odor
Basicity of Amines
Basicity constant (Kb ): the larger the Kb and smaller the pKb , the stronger the base
Alkyl substitutions have little effect on pKb (fall in 3-4 range)
Aryl amines are significantly less basic due to resonance
Aryl amines are less basic than alkyl amines due to the electron delocalization of the lone pair on the nitrogen in the aromatic ring.
Amines are more basic than amides. Amides are nonbasic due to the nitrogen lone-pair electrons shared by orbital overlap with the neighboring carbonylgroup.
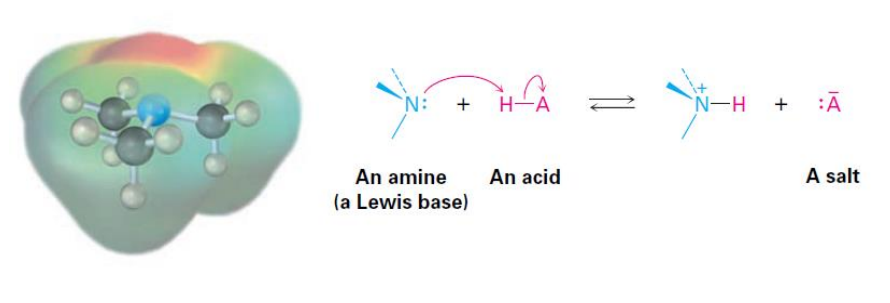
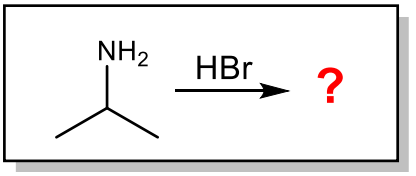
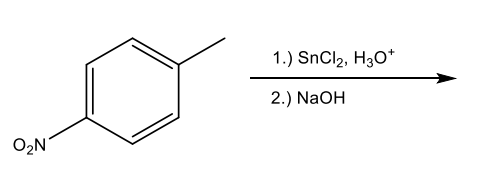
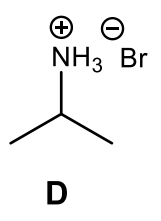
What is the major organic product of the following reaction?
Synthesis of Amines
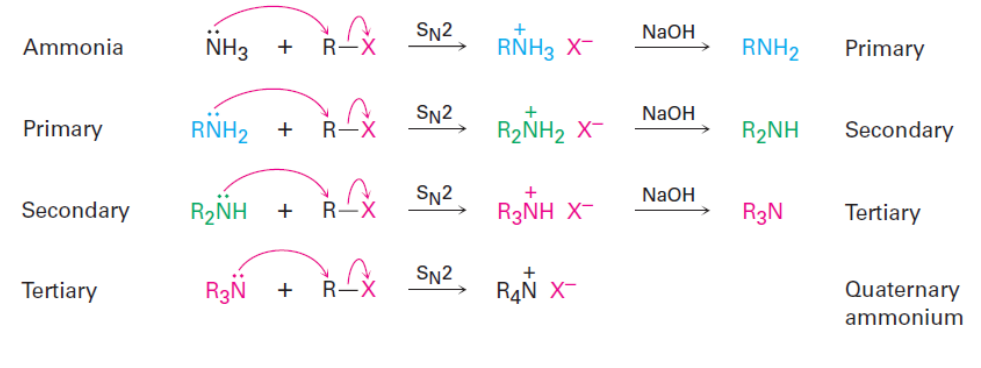
SN2 Reactions
Nitrogen containing compounds can be synthesized by reaction of azide ions (N3 - ) or cyanide ions (NC- ) with alkyl halides via an SN2 reaction.
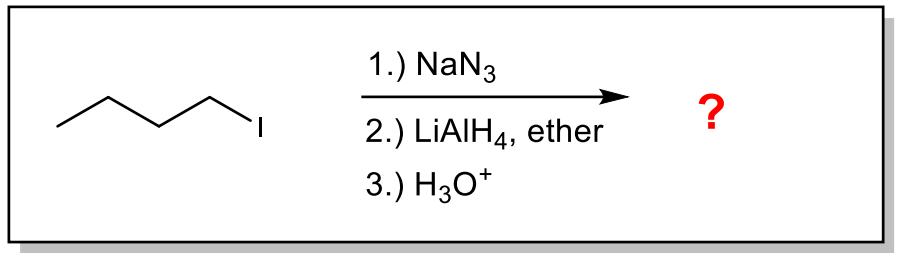
Give the IUPAC name of the major organic product of the following reaction
butylamine
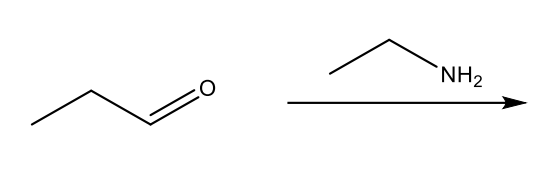
Reaction of Amines: Imine Formation
The reaction of amines with aldehydes or ketones to form imines, characterized by the replacement of the carbonyl oxygen with a nitrogen-based group.
Reductive Amination of Aldehydes and Ketones
A method to form amines by reacting aldehydes or ketones with amines in the presence of reducing agents, resulting in the addition of an amine group and the reduction of the carbonyl.
Reduction of Nitrobenzene (Specifically for nitro groups on arenes (benzenes))
The chemical process where nitro groups on benzene derivatives are converted to amines through the use of reducing agents, typically involving catalytic hydrogenation or chemical reducing agents.