Coag exam review
1/145
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
146 Terms
what is virchows triad
components of blood
vessel structure
blood flow
endothelium prevents clots
secreting substances to keep plt from sticking
makes thrombomodulin
released t-pa
heparan sulfate
first response to injury
vasoconstriction
damaged endothelium is clot inducing
exposure of collagen receptors to trigger plt adhesion
TXA2 released to activate plts
Weibel-palade bodies release vWF
Tissue factor is released
PAI- 1,2,3,4 released to limit fibrinolysis
Plt maturation sequence
megakaryoblast
promegakaryocyte
megakaryocyte
Plt
life span of plt is
7-10 days
what organ holds 1/3 of all plts
spleen
normal range of plts
150-400 ×103
what are the 4 zones of plts
peripheral
structural
organelle zone
membranous
peripheral zone is
the outer part of the plt F3
structural zone manages
the shape changeand aggregation of platelets.
organelle zone manages
the release of granules
The membranous zone manages the
chemicals released from the plt
Alpha granules contain
PF4
PDGF
Beta thromboglobulin
coag factors
dense bodies contain
storage pool ADP and Ca+
serotonin
PDGF does what
starts wound repair
PF4 does what
neutralizes heparin
Beta thromboglobulin
neutralizes heparin
What is the process of aggregation
collagen is exposed on endothelial
vWF binds subendothelium
plt binds to GP1b/IX (adhesion)
exposing GPIIb/IIIa on plts and chemicals released from granules (activation)
These receptors bind fibrinogen which creates a plt to plt bridges (aggregation)
A stimulating chemical is called a
agonist
Dense bodies release
ADP and Ca+
AP binds to plt membrane, activates enzymes releasing…
Arachidonic acid
The next enzyme released after arachidonic acid is
cyclooxygenase
cyclooxygenase converts arahidonic acid to
Thromboxane A2
What does thromboxane A2 do
amplifies aggregation
What inactivates thromboxane A2 throught the binding of arachidonic acid
ASA, Aspirin
bleeding due to plts primary first step
family history is first step
primary hemostasis symptoms
epistaxis
mucous membranes
external skin
How to screen for primary hemostasis
plt function, plt count
what are 4 primary hemostasis disorders
hereditary hemorrhagic telangiatasia
osteogenesis imperfecta
Marfans
Ehlers danlos
what is a common defect in primary hemostasis disorders
abnormal or no collagen leading to no plt adhesion
low plts is
thrombocytopenia
decreased production of plts is seen in
aplastic
myelophthisic
acute leukemia
myelodysplastic
megaloblastic anemia
chemotherapy/radiation
Acute ITP is in what populaion
kids post viral
How is acute ITP treated
it usually self resolves in 1 month to 6 weeks
Chronic ITP is in what population
women of child bearing age
what is the treatment for chronic ITP
steroids and splenectomy
HIT antibodies are made against
Plt factor 4 complex
Non immune mechanisms that cause destruction of plts are
TTP
HUS
DIC
TTP is triggered by what and what are the coag tests results?
AdamsTS13 deficiency
normal PT, aPTT and D-Dimer
HUS is triggered by what and what are the coag tests results?
e.coli infection
normal PT, PTT, ad D-dimer
DIC is triggered by what and what are the coag tests results?
sepsis, OB complications, leukemia or trauma
prolonged PT, aPTT and elevated D-dimer
What shows abnormal with Epi but normal with ADP
aspirin is present
What shows a abnormal epi and ADP?
von willibrands disease or bernard solier or plavicks syndrome or platelet function defects.
what test is used for P2Y12 ADP inhibition
Verify Now
Glanzmanns thrombasthenia defect
2b-3a receptor
Bernard-Soulier syndrome defect
1b9 receptor
von willebrands disease defect is
von willebrands factor
storage pool disorders (including aspirin) defect
lack of granule release
Plt aggregation results for Bernard-Soulier Syndrome abnormal results in
Ristocetin and Ristocetin/normal plasma as it's missing the 1b9 receptor on the plt

Plt aggregation results for von willebrands disease abnormal results are
only ristocetin because the factor is added back into the mix during the mixing study

plt aggregation results for Glanzmanns that are abnormal
ADP (flat lines)
Epinephrine
collagen
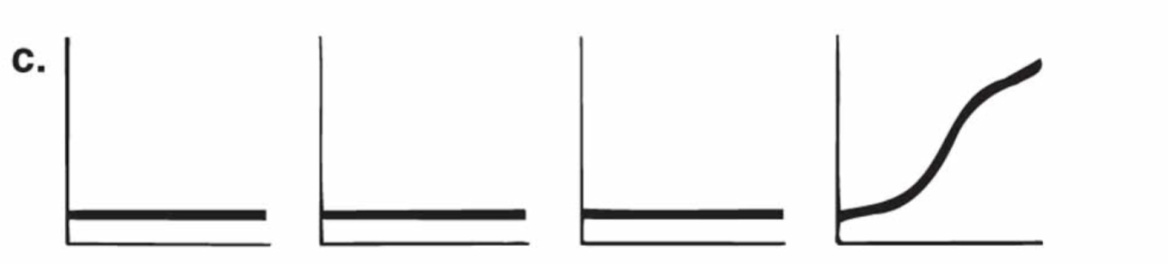
Plt aggregation results for storage pool disorders and aspirin
APD- normal
Epinephrine- normal
Collagen- normal
Ristocetin- normal
Arachidonic acid- abnormal
Extrinsic factor uses what factors and test
7, 10, 5,2,1
PT
Intrinsic factors uses what factors and what test
12,11,9,8,10,5,2,1
PTT
Common pathway uses what factors and test
10,5,2,1
PT/PTT
Contact factors
12, 11,HMWK, prekalikrein
Vit K dependent factors
2,7,9,10
Fibrinogen group cofactors
8,5,fibrinogen, 13
Process of fibrinogen to fibrin
cleavage of A and B fibrinopeptides
fibrin monomer is formed
fibrin monomers polymerize
F13 and ca+ creates cross links
Secondary hemostasis shows bleeding symptoms in what way
deep tissue bleeding and bleeding in the joints
deficiencies in clotting proteins are known as
hemophilias
inheritance pattern for vWF
Dominant
inheritance for 8 and 9 def.
x-linked
how do blood groups play a roll in VW disease
type O has lower amounts and type A and B have high amounts
vW factor binds to
Plt GP1B/IX and promotes adhesion to subendothelial collagen
how does VW disease affect secondary hemostasis
it complexs with factor 8, 1:1, extending factor 8’s half life
vonwillebrands disease is tested for via what tests
ADAMSTS-13
vWF multimer analysis
vWF activity
antigen
what is the treatment for VW disease
DVADP nose spray
hemophilia A
fator 8 def.
hemophilia B
factor 9 def.
severe hemophilia is
1% or less of factor
moderate hemophilia
1-6% of fractor
Mild hemophilia
6-40% of factor
Treatment to X-linked hemophilias
recombinant factor
inhibitors in X linked hemophilia
Factor9 autoantibodies
contact factors in recessive disorders are what and have what symptoms
11,12, prekalikrein, HMWK
have no bleeding
hemophilia C is a deficiency in
Factor 11
Parahemophilia has a deficiency
factor 5 deficiency
what are the recessive hemophilia disorders
contact factors
hemophilia C
parahemophilia
fibrinogendef. /dysfibrinogen
factor 13
severe hemophilia has what symptoms
spontaneous joint bleeding
spontaneous deep tissue/brain bleed
moderate hemophilia has what symptoms
bleeding at circumcision
excess bleeding after surgery and minor injuries
mild hemophilia symptoms
often goes undetected until excess bleeding after surgery
if a specimen is underfilled what would the PT be
long
over filled specimen for PT
short/increase in clots
hemolyzed samples have a
short PT/PTT
patients with hct of >55% have a
long PT/PTT
clotted samples have a
>100 PT and >200 PTT
how do you store a sample for coag
double spin to remove plts; freeze in -70C
Prothrombin time reagents
thromboplastin (TF/Cl2)
CaCl2
sources for prothrombin
human brain/placenta
rabbit brain
recombinant
sensitivity of prothrombin time measured by
ISI
closer to 1 is more sensitive
Protime used to monitor
coumadin
what is the specimen stability for a PT
24hrs
What is the therapeutic range for INR
2-3
What is the bedside version of PT
whole blood INR
PTT measures what pathway
intrinsic
what are the reagents for PTT
PTT reagent (phospholipids/ativators)
CaCl
What is the stability of PTT and why
4hrs because the plt neutralize PF4
PTT is used to screen
any factor but 7