AP BIO Unit 1
1/89
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Heyyyyy guysssss ;^
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
-COOH
Carboxyl Group
-NH2
Amino Group
Most diverse; structural, storage, contractive, enzymes, etc.
Proteins
DNA and RNA
Nucleic Acids
-OH
Hydroxyl Group
\
C=O
/
Carbonyl Group
Cholesterol, fats, waxes, and steroids
Lipids
Long-term energy storage, insulation, and building block of hormones
Lipids
Hemoglobin, keratin, and antibodies
Proteins
Fatty acids and glycerol
Lipids
C, H, O, N, S
Proteins
Amino Acids
Proteins
C, H, O, N, P
Nucleic Acids
-OPO3^-2
Phosphate Group
C, H, O, P
Lipids
-SH
Sulfhydryl Group
C, H, O
Carbohydrates
Sugars and Starches
Carbohydrates
Store and share genetic information
Nucleic Acids
Monosaccharides
Carbohydrates
Nucleotides
Nucleic Acids
Cellular energy and support
Carbohydrates
The creation of a new bond by removing a water molecule
Dehydration Synthesis
Breaking of a bond by adding a water molecule
Hydrolysis
Water molecules being attracted to each other
Cohesion
Water molecules being attracted to other molecules
Adhesion
A measure of how hard it is to break the surface of a liquid (caused by cohesion)
Surface Tension
The bonds on the inside of a water molecule
Covalent Bonds
The bonds between water molecules
Hydrogen bonds
Why does water have the temperature moderation ability?
High specific heat and high heat of vaporization
Something doing the dissolving
Solvent
Something being dissolved
Solute
Loves water (polar)
Hydrophilic
Hates water (non-polar)
Hydrophobic
What element is the building block of life?
Carbon
-ose indicates what?
Sugars
-ase indicates what?
Enzymes
How many bonds can Carbon have?
4
What chemical group acts like an acid?
Carboxyl Group
What chemical group acts like a base?
Amino Group
What chemical groups are found in proteins?
Amino Group and Carboxyl Group
Contains only hydrogen and carbon; undergoes reactions that release a lot of energy.
Hydrocarbon
Same molecular formulas with different structures and properties
Isomers
Form the skeleton of most organic molecules
Carbon chains
Name for one “sugar”
MONOsaccharides
Name for two “sugars”
DIsaccharides
Name for many “sugars”
POLYsaccharides
A covalent bond between 2 monosaccharides
Glycosidic Linkage
C6H12O6
Glucose
Unbranched molecule that is the main component of plants’ cell walls
Cellulose
Has a “nitrogen and main” and main component for exoskeletons and fungi cell walls
Chitin
Molecule used to store energy in animal cells
Glycogen
Molecule used to store energy in plant cells
Starch
What does the Methyl Group affect?
Expression of genes
Small; single units that can bond to others to form large chains
Monomer
Larger molecules made of bonded monomers
Polymers
What type of solvent is water?
A universal solvent
What type of solution does water make
Aqueous (aq)
What charge is the oxygen side of water?
Negative
What charge is the hydrogen side of water?
Positive
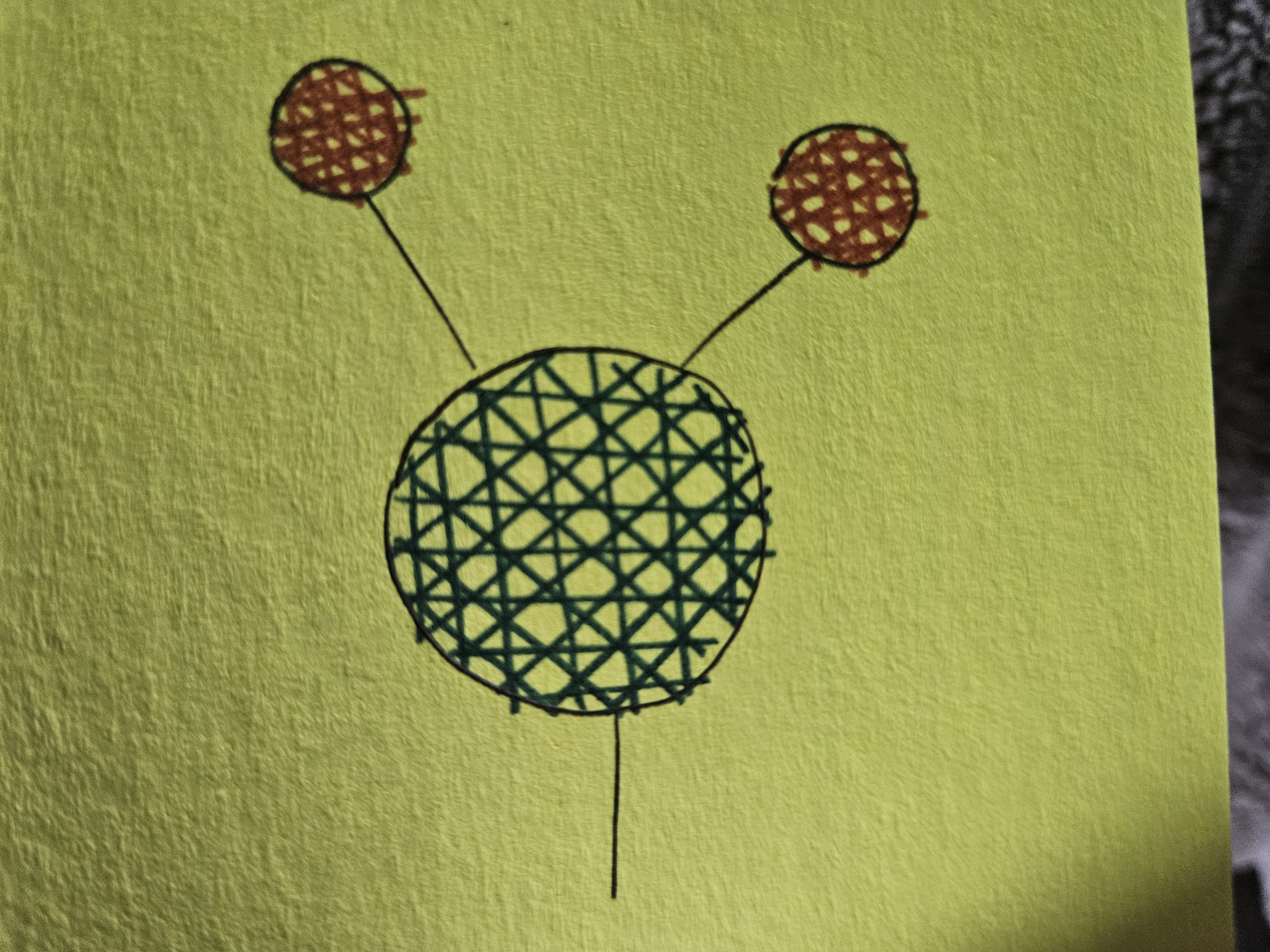
Amino Group
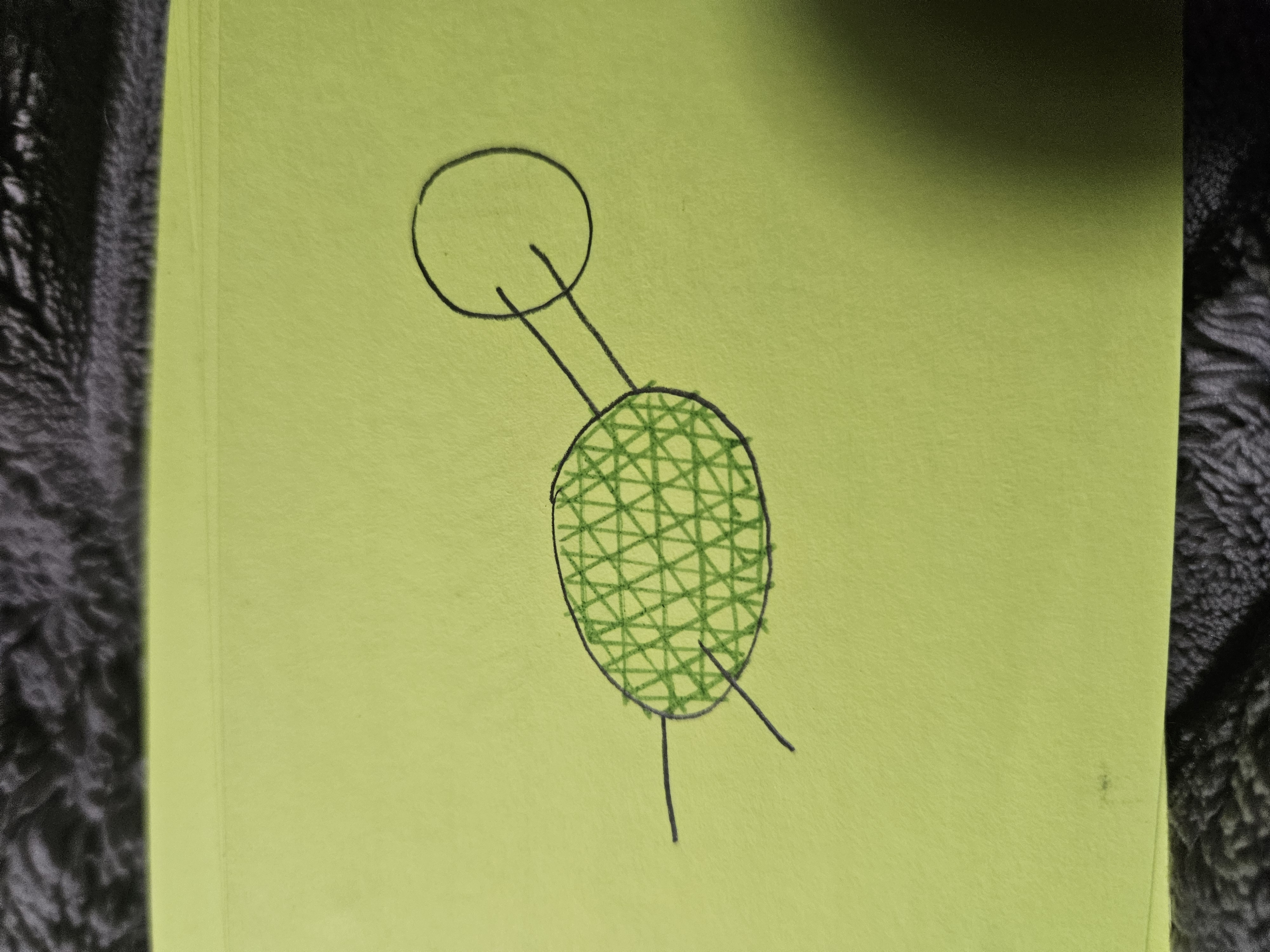
Carbonyl Group
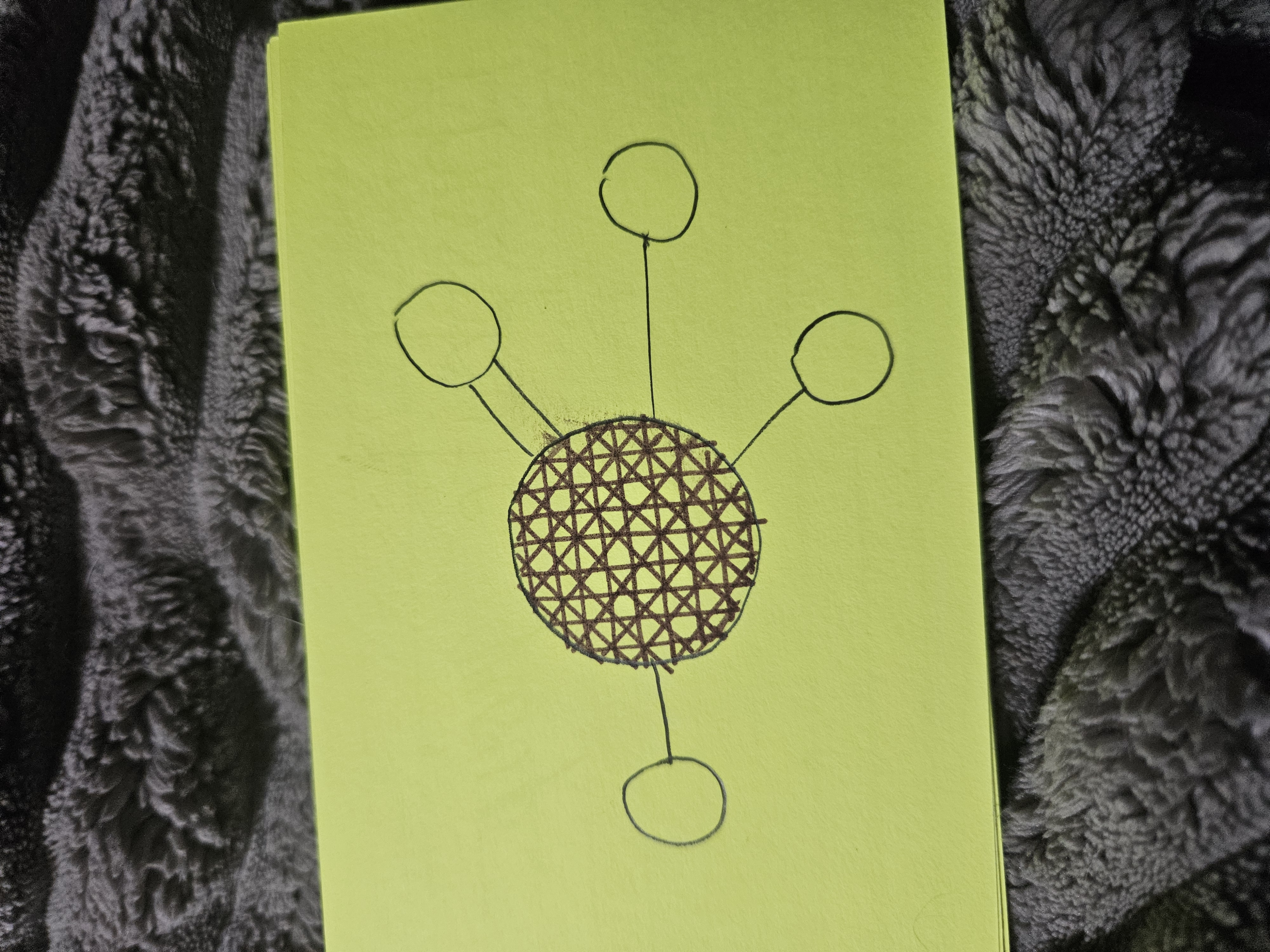

Phosphate Group
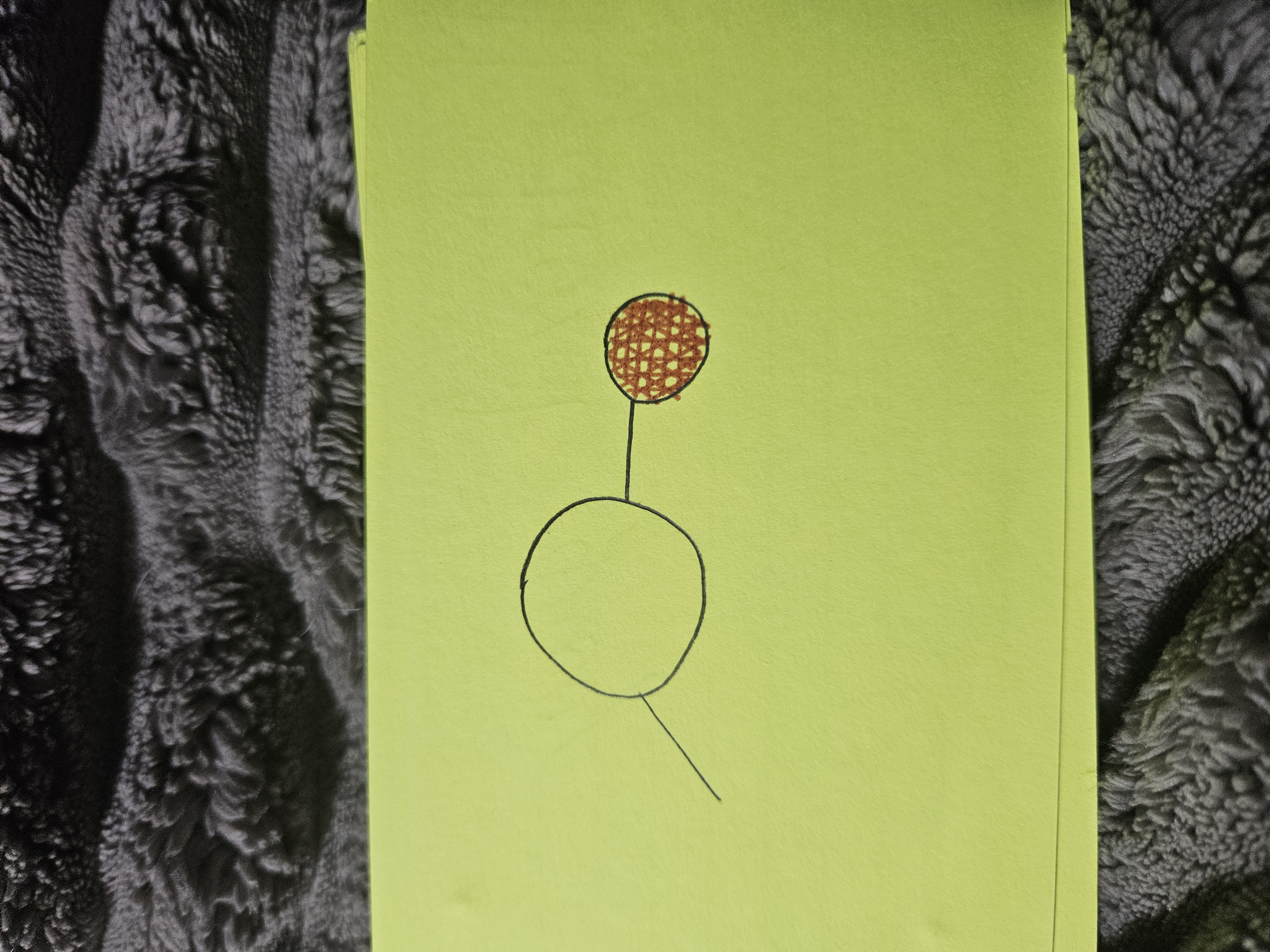

Hydroxyl Group
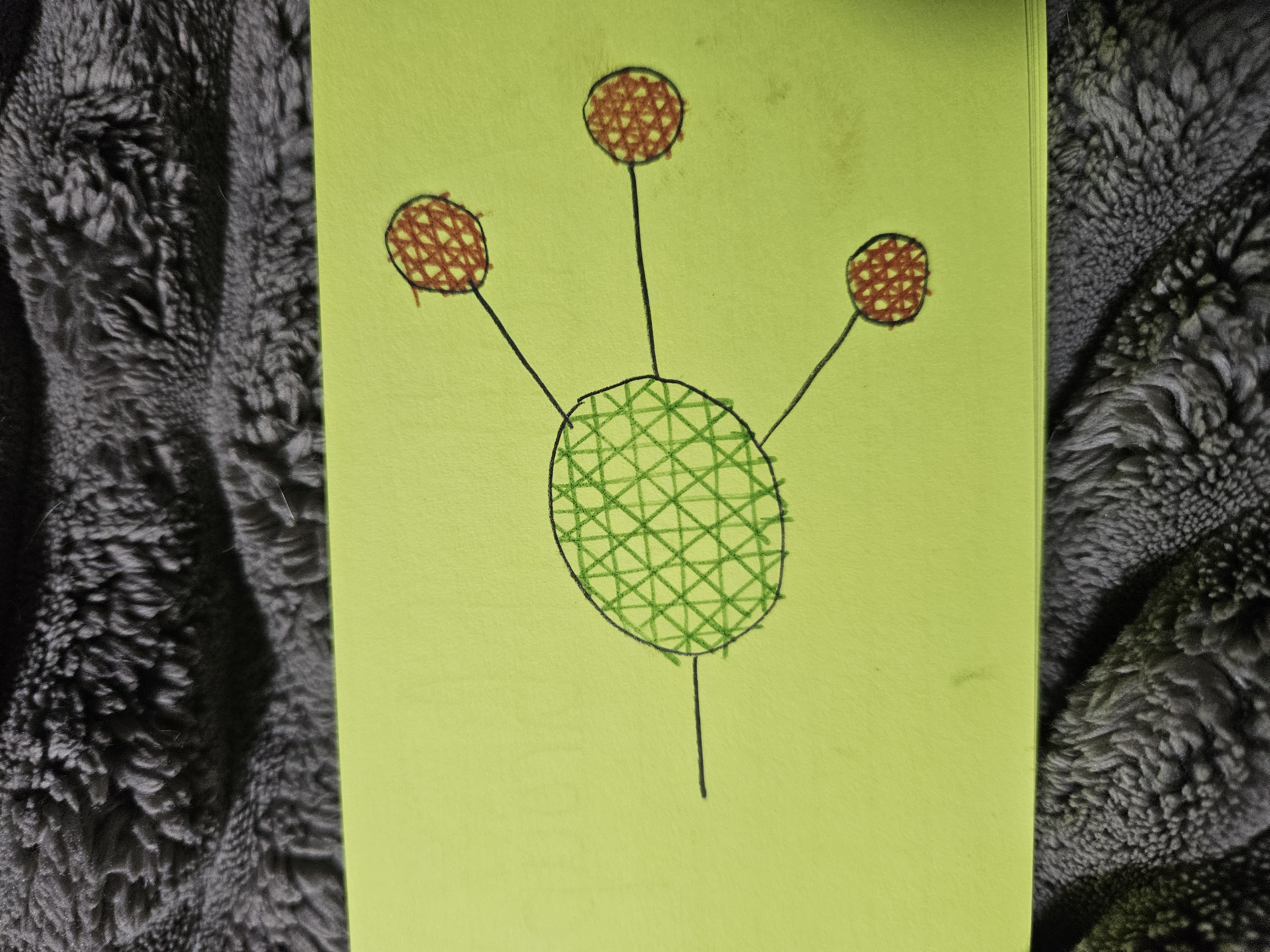
Methyl Group
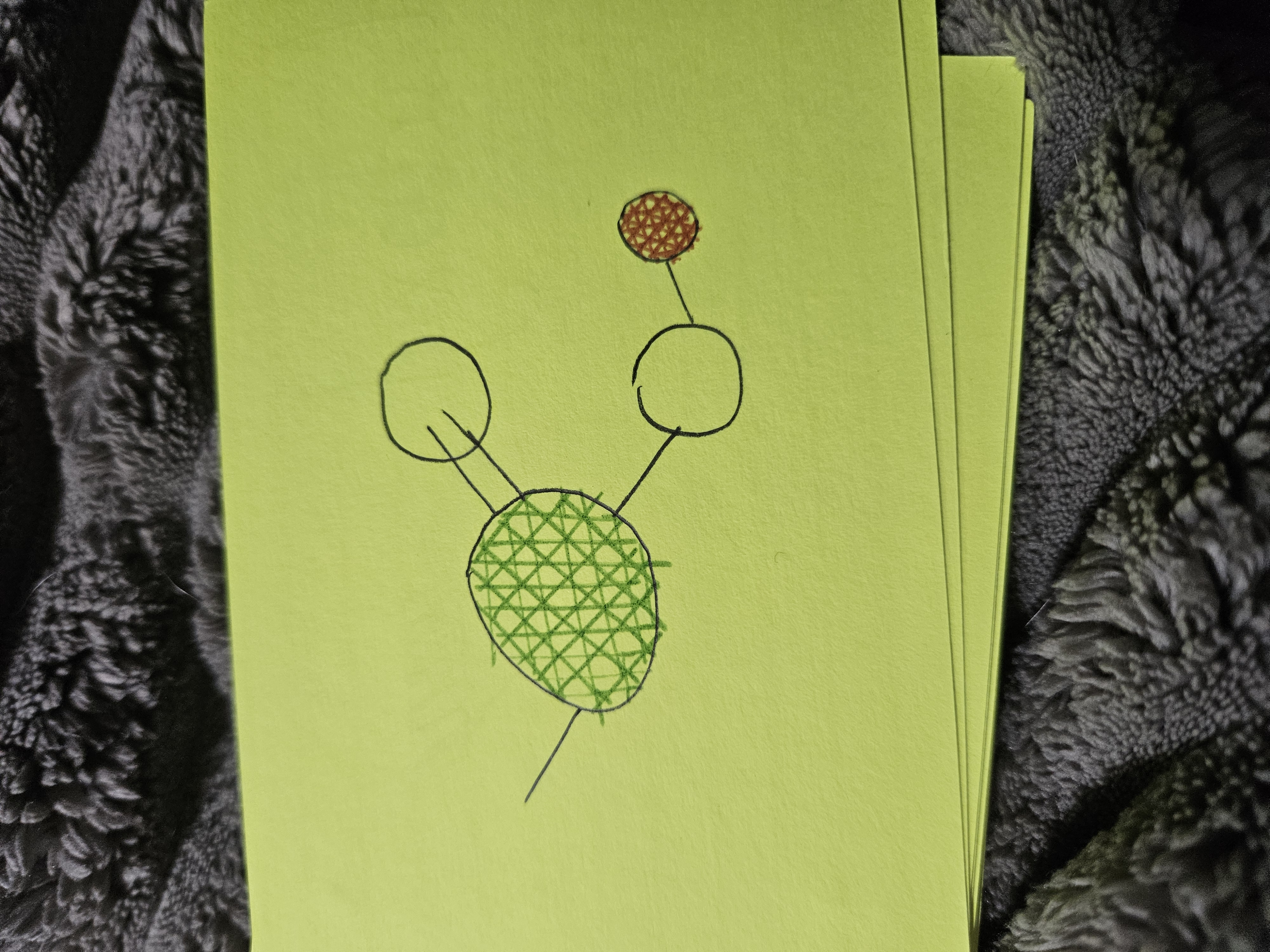

Carboxyl Group
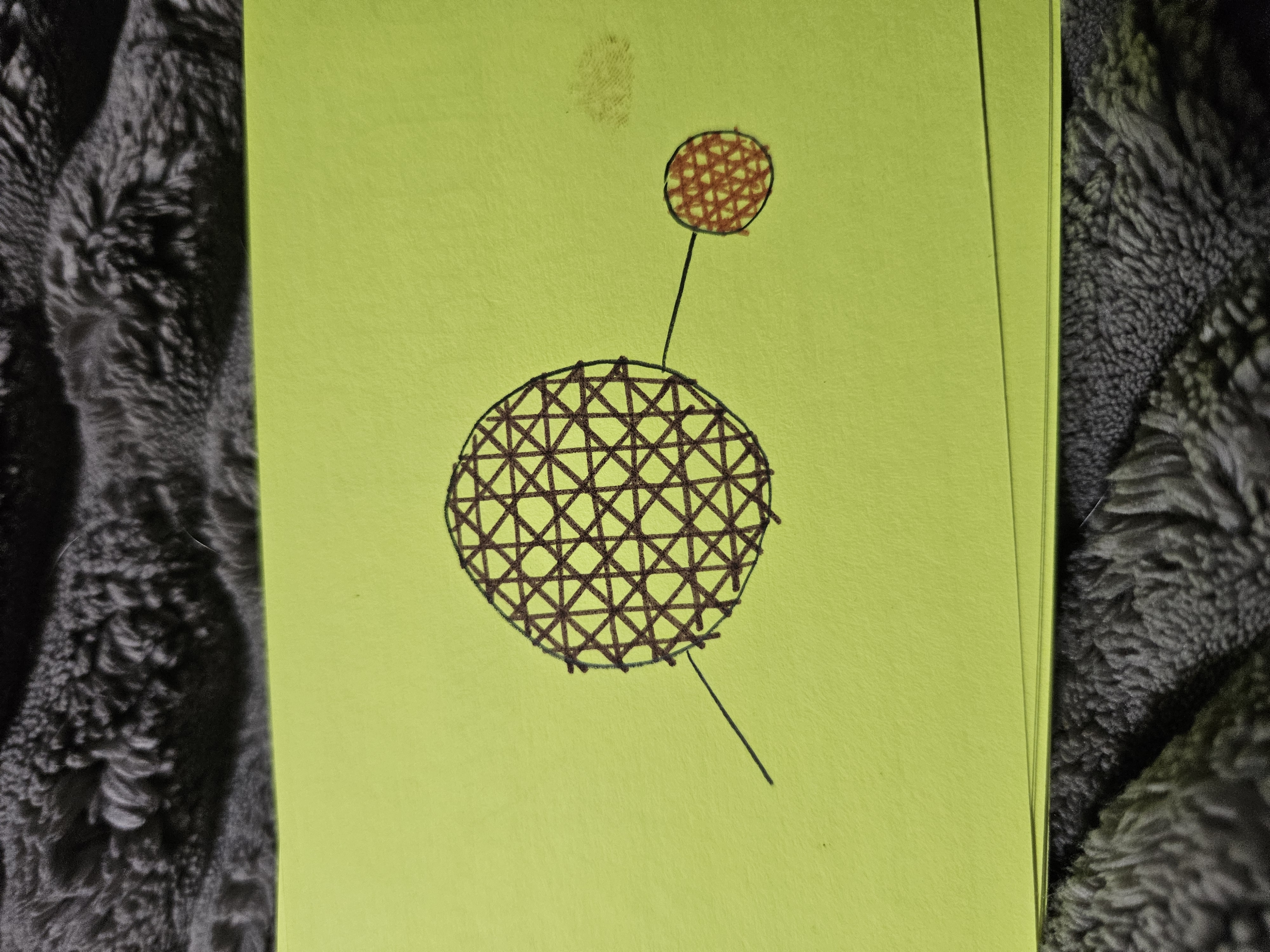

Sulfhydryl Group
-CH3
Methyl Group
The only biomolecule that doesn’t have true monomers
Lipids
Bonds between fats
Ester Linkage
Only single bonds between carbons; animal fats (more solid at room temp)
Saturated Fats
At least one double bond between carbons; plant fats (more liquid at room temp)
Unsaturated Fats
Precursor to all other steroids
Cholesterol
What structure does a steroid have?
4 Fused Rings
A molecule with a polar and non-polar region
Amphipathic
Main component of a cell membrane with polar heads and non polar tails
Phospholipid bilayer
Made of a phosphate group and a 5-carbon sugar
DNA backbone
Cytosine, Thymine, and Uracil
Pyrimidines
Adenine and guanine
Purines
When is uracil used?
In RNA, paired with adenine
How many bonds do A-T have?
2
How many bonds does G-C have?
3
What bonds do nitrogen bases use?
Hydrogen bonds
What directions do DNA strands point to?
Opposite 5’-3’ directions. ANTIPARALLEL
How many R-groups are there?
~20
The sequence of amino acids determined by inherited genetic information.
Primary Structure
The formation of alpha-helix or beta-sheets and hydrogen bonds between different amino acids.
Secondary Structure
The overall shape of a polypeptides resulting from the R-group interactions. Includes: H-bonds, ionic bonds, and hydrophobic interactions.
Tertiary Structure
Results when 2 or more polypeptide chains interact/combine EX: hemoglobin
Quaternary Structure
What determines function?
SHAPE