Organic Chem - Arkanes, Arkenes, Arkynes, Aromatic Hydrocarbons
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
organic compounds
All compounds that contains carbon
Various types of compounds ranging from simple carbon chains to more complicated molecules
exceptions to identifying organic compounds
carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, hydrogen cyanide (HCN)
sys for naming organic compounds developed by
IUPAC (Union of Pure & Applied Chemistry)
international
general naming compounds rules
identify the homologous series it belongs to
identify the longest chain → provides “root” of compound name which is the ending
identify the substituants and branches
number in such a way that makes the branch w the first ordered letter in the alphabet have the lowest number possible
you are to indicate where each substituent is w its number
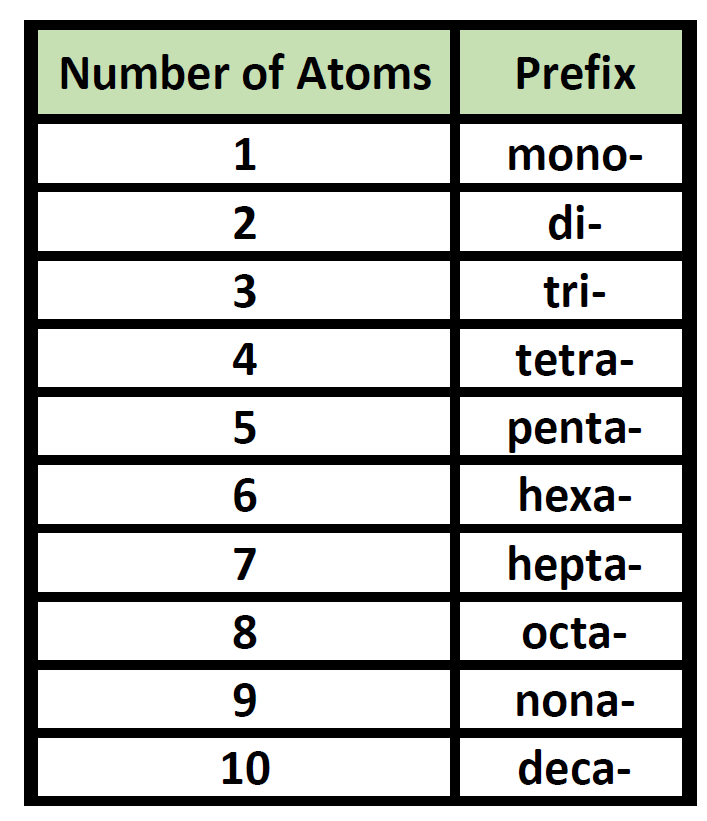
if there are multiple of a substituent, you must use number prefixes (di, tri, etc)
branches should be listed in alphabetical order
homologous series
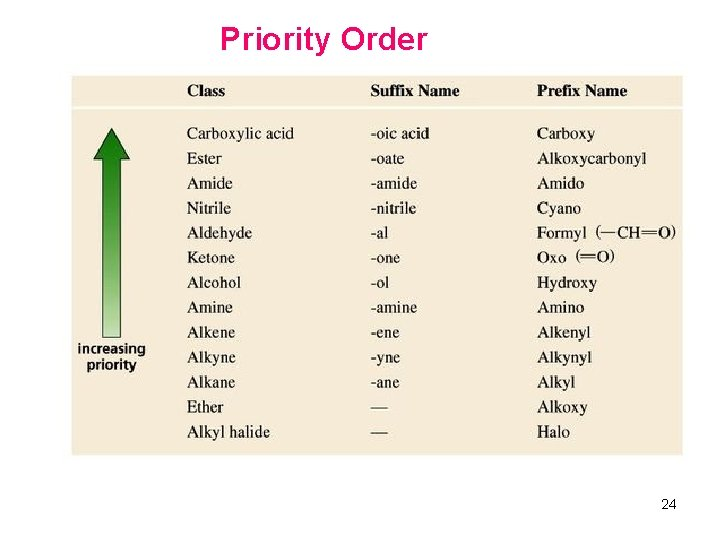
series of compounds with the same functional group → use order of priority (A functional group is the reactive part of the molecule that affects the compounds chemistry)
as well as the functional group, all homologous series:
Can be represented by a general formula
Differ from their neighbour by CH2
Have varying physical properties
highest priority means
it is numbered the lowest
is the ending of the name
hydrocarbons
Organic compounds that contain only hydrogen and carbon
hydrocarbons are divided into
aliphatics (linear), alicyclics (rings), and aromatics (benzene)
aliphatics are divided into
alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes
alkanes
simple hydrocarbons with only single bonds between the carbon atoms
also known as a saturated hydrocarbon
general formula for alkane
C(n)H(2n+2) → two hydrogens for each carbon and hydrogens at the ends
each alkane is named by adding _____ to the appropriate prefix which is det by
-ane; # of carbons
roots prefixes
meth-
eth-
prop-
but-
pent-
hex-
hept-
oct-
non-
dec-
the parent chain is the
longest continuous chain, can be counted from any dir
anything attached to the parent chain is called a
branch or substituant
if it is a carbon branch, it uses the same root prefixes but ends in “-yl”
although the chains appear to be straight or 2D, there’s acc a _____ angle b/w each carbon
109.5 deg
general naming rules
numbers & groups should be separated w a hyphen until it is the last listed group, which sticks to the root
numbers for the same group are separated w a comma
no line diagram for
methane or ethane
when halogens are attached as a branch, their names are turned into
flourine → flouro
chlorine → chloro
and so on
cylic alkanes
otherwise known as cycloalkanes
when carbon atoms join to make a circle/ a closed loop
naming them is jus cyclo-root prefix-ane if it is the main chain
cyclo-rootprefix-yl if it is branch
simplest cycloalkane
Cyclopropane w three carbons
general formula of cyclic alkanes
C(n)H(2n)
structural isomers
Hydrocarbons with 4 or more carbons in the main chain can have structural isomers, depending on where the alkyl group is located
diff variations → they would have the same chem formula (same number of carbons and hydrogens) but their structure is different (arranged differently)
properties of alkanes
only intermolecular force present is London dispersion forces
low boiling and melting pt
boiling pts are related to the length of the chain → longer the chain, higher the b pt
common rxns of alkanes
do not react with acids, bases, or strong oxidizing agents
combustion is the main rxn
smaller alkanes are highly flammable
but longer chains are difficult to ignite
alkyl halide
halogen as a substituent group (branch)
substituent group
anything that replaces a hydrogen in a hydrocarbon chain
complete rxn vs incomplete
insufficient oxygen for incomplete, results in some carbon (soot)
numerical prefixes
unsaturated hydrocarbons
hydrocarbon containing either double or triple carbon-carbon bonds
types of unsaturated hydrocarbons
alkenes and alkynes
order of priority
pay special attention to the alkanes stuff
alkenes
contains at least one double bond
alkynes
contains at least one triple bond
general formula for alkenes
C(n)H(2n)
general formula for alkynes
C(n)H(2n-2)
naming alkenes and alkynes
mult double or triple bonds must have numerical prefixes (diene, triene, triyne) and the locations must be indicated before the “ene” or “yne”
the first carbon atom involved in a mult bond must have the lowest number (see order of priority)
when you have a double bond b/w carbons, you
cannot rotate the atoms around that bond.
so you have two poss ways to lay out the atoms surrounding the double bond
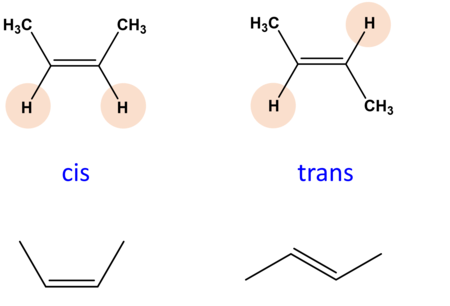
stereoisomers
when the molecules have the same chemical formula and structural backbone but have a different arrangement of atoms.
types of isomers
Cis isomers
Trans isomers
Trans isomers
have the same groups located on opposite sides of the double bond
e formation
cis isomers
have the same groups located on opposite sides of the double bond.
z formation
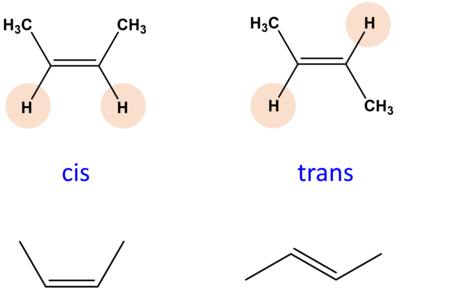
when naming, cis or trans appears right before
the ENTIRE name of the alkene or alkyne
cis-
trans- (use a hyphen)
reactions of alkenes
Addition Reactions (breaking of the double bond)
types of addition reactions (alkenes)
Halogenation (adding halides)
Hydrogenation (adding hydrogen)
Hydrohalogenation (adding hydrogen halides)
Hydration (adding water)
halogenation
alkene + halogen → haloalkane
Hydrogenation
alkene + hydrogen → alkane
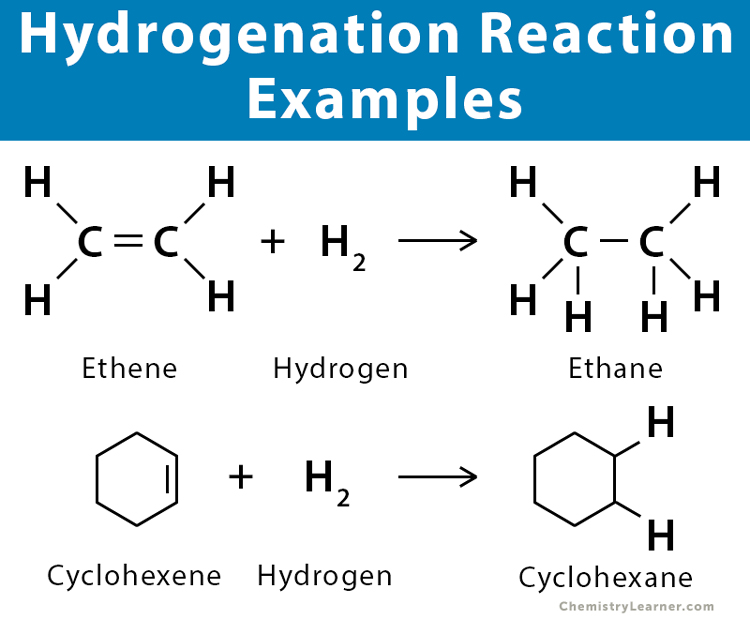
Hydrohalogenation
alkene + hydrogen halide → haloalkane
Hydration
alkene + water → alcohol (water is separated into H and OH)
Markovnikov’s Rule
states that the hydrogen is added to the carbon with the most hydrogen atoms originally bonded to it
Hydrohalogenation and hydration follows this rule
reactions of alkynes
Addition Reactions (breaking of the multiple bond)
types of addition rxns (alkynes)
Halogenation (adding halides (like bromine))
Halogenation (alkyne)
alkyne + 2 halogens → haloalkane
alkyne + 1 halogen → haloalkene
Aromatic Hydrocarbons
An UNSATURATED hydrocarbon that has a ring structure and a bonding arrangement that causes it to be chemically stable
what is the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon
benzene (C6H6)
structure of benzene
Benzene appears to have 3 double bonds, each spaced by a single bond
The reality is that these bonds all measure out at equal length.
actual double bonds would measure shorter.
this means they are not true double bonds
benzene can be represented in 2 ways (see picture)
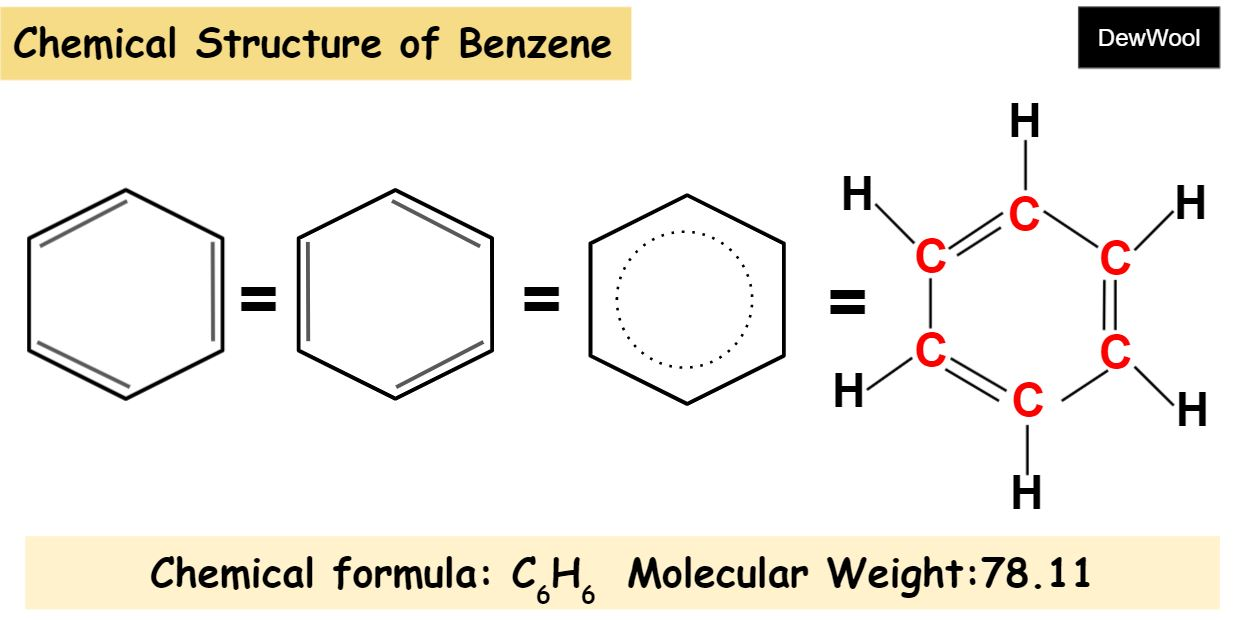
if the main branch is a benzene
the root is benzene
if benzene is a branch
it is called a PHENYL
alkyl halides
when a halogen is attached to a carbon chain