T19-20: Circulatory Disturbance
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
perfusion disorders
increase in blood volume in tissue
perfusion disorder examples
hyperemia, congestion, hemorrhage
hyperemia is active/passive
active
hyperemia results from
artery dilation from inflammation
hyperemia characteristic
redder tissues
hyperemia example
acne
congestion is active/passive
passive
congestion result from
impaired outflow of venous blood from heart failure
congestion characteristic
blue-red (cyanosis), enlarged organ
hemorrhage
leakage of blood vessel
hemorrhage cause
trauma, atherosclerosis
hemorrhage mechanism
low platelet counts, inflammation
hemorrhage types
hematoma, petechiae, purpura, ecchymosis
hematoma
hemorrhage in soft tissue
petechiae
small hemorrhage
purpura
slightly bigger than petechiae
ecchymosis
hemorrhage of subcutaneous (bruise)
ischemia
deficient blood supply due to blockage
ischemia can cause
hypoxia, malnourishment, waste accumulation
infarction
becoming ischemic necrosis
infarction cause
disrupted artery supply
factors influencing infarction development
anatomy of vascular supply (amount of blood vessel), rate of occlusion, vulnerability to ischemia, blood oxygen content
red (hemorrhagic) infarcts occur when
venous occlusion (congestion) in loose spongy tissue
red infarcts happen in single/dual circulation
dual (in previously congested tissues)
white (anemic) infarcts occur when
arterial occlusions in kidney, spleen, heart due to tissue density limiting blood diffusion
septic infarct
infected infarct
thrombosis
lots of coagulated blood that stick to endothelium
pro-thrombotic
clot too much
anti-thrombotic
no clot
virchow’s triad
abnormalities causing thrombosis: endothelial injury, abnormal blood flow, hypercoagulability
turbulence
blood don’t flow in center
stasis
slow blood flow
atherosclerosis increased risk of thrombosis due to
plug → turbulent and stasis
mitral valve stenosis has increased risk of thrombosis due to
heart valve narrowing → stasis
disseminated intravascular coagulation
widespread thrombosis → cause circulatory insufficiency
arterial thrombosis common causes
atherosclerosis, aneurysm
aneurysm
dilation in one spot → turbulence
main contributor of arterial thrombosis
endothelium damage → procoagulant → platelet aggregate
morphology of arterial thrombosis
lines of zahn
arterial thrombosis leads to
ischemic necrosis, myocardial infarction, embolization
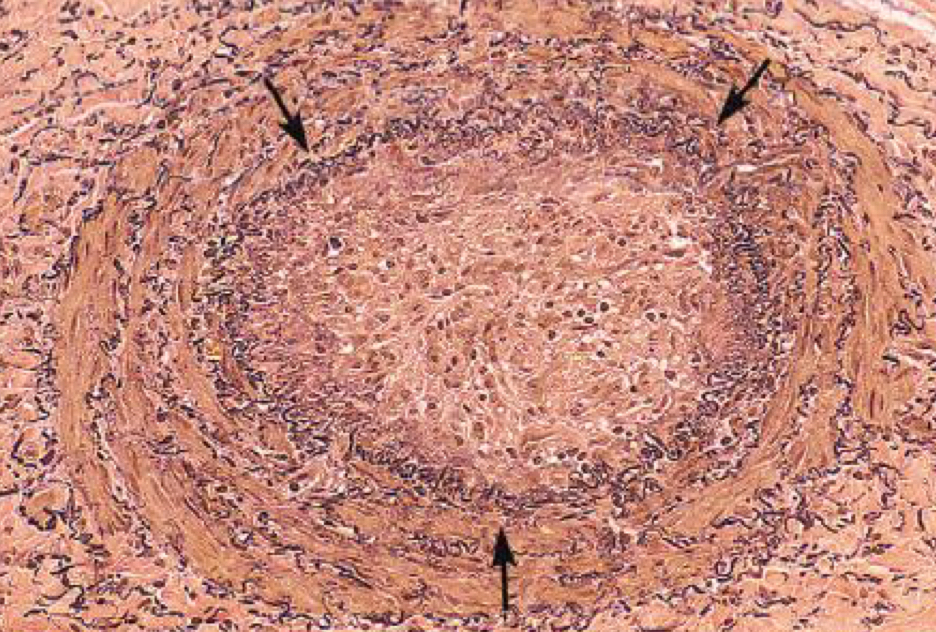
what condition is depicted
arterial thrombosis
mural thrombosis is in
heart chamber, aortic lumen
vegetation
thrombi on heart valves
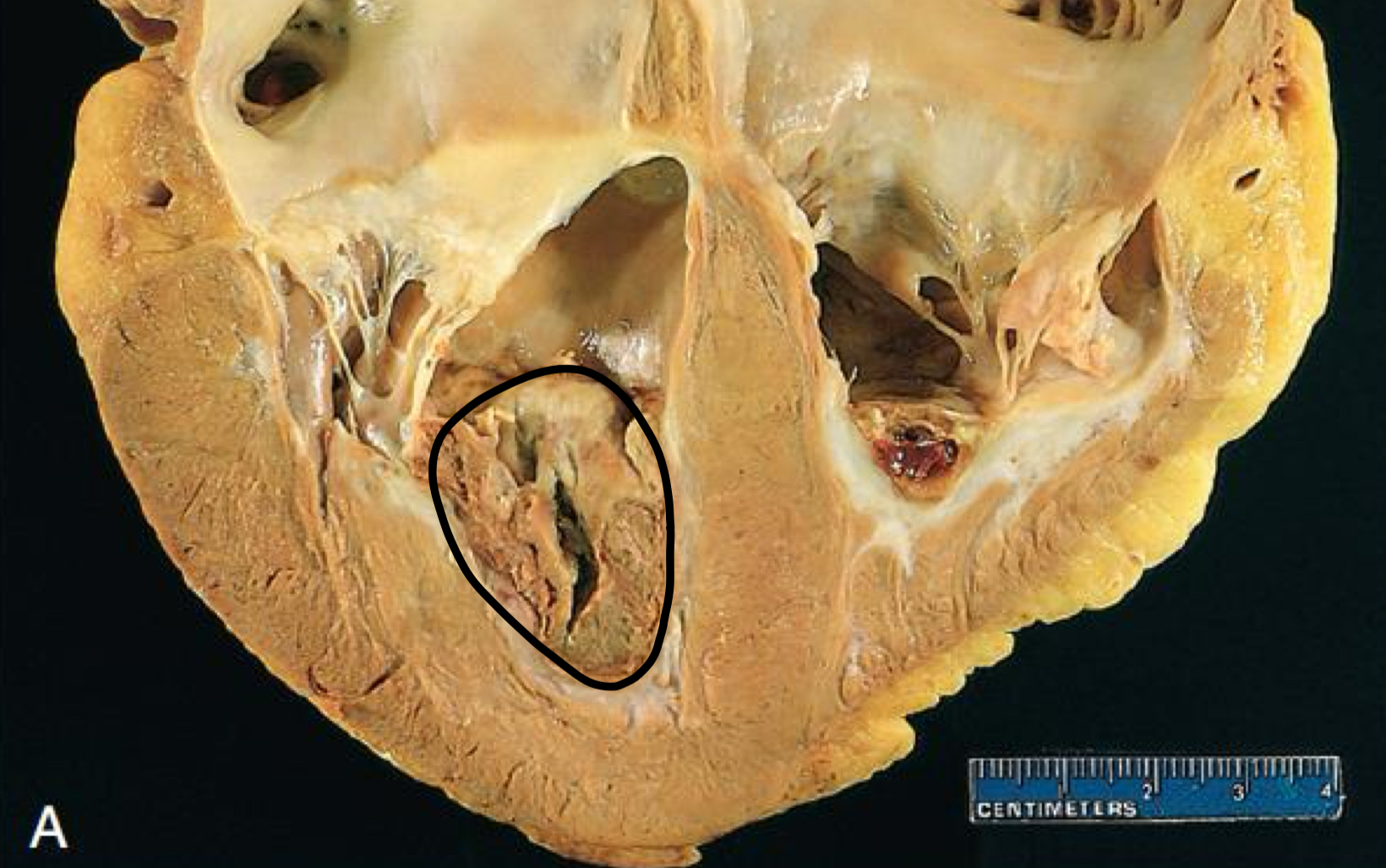
what is circled
thrombus
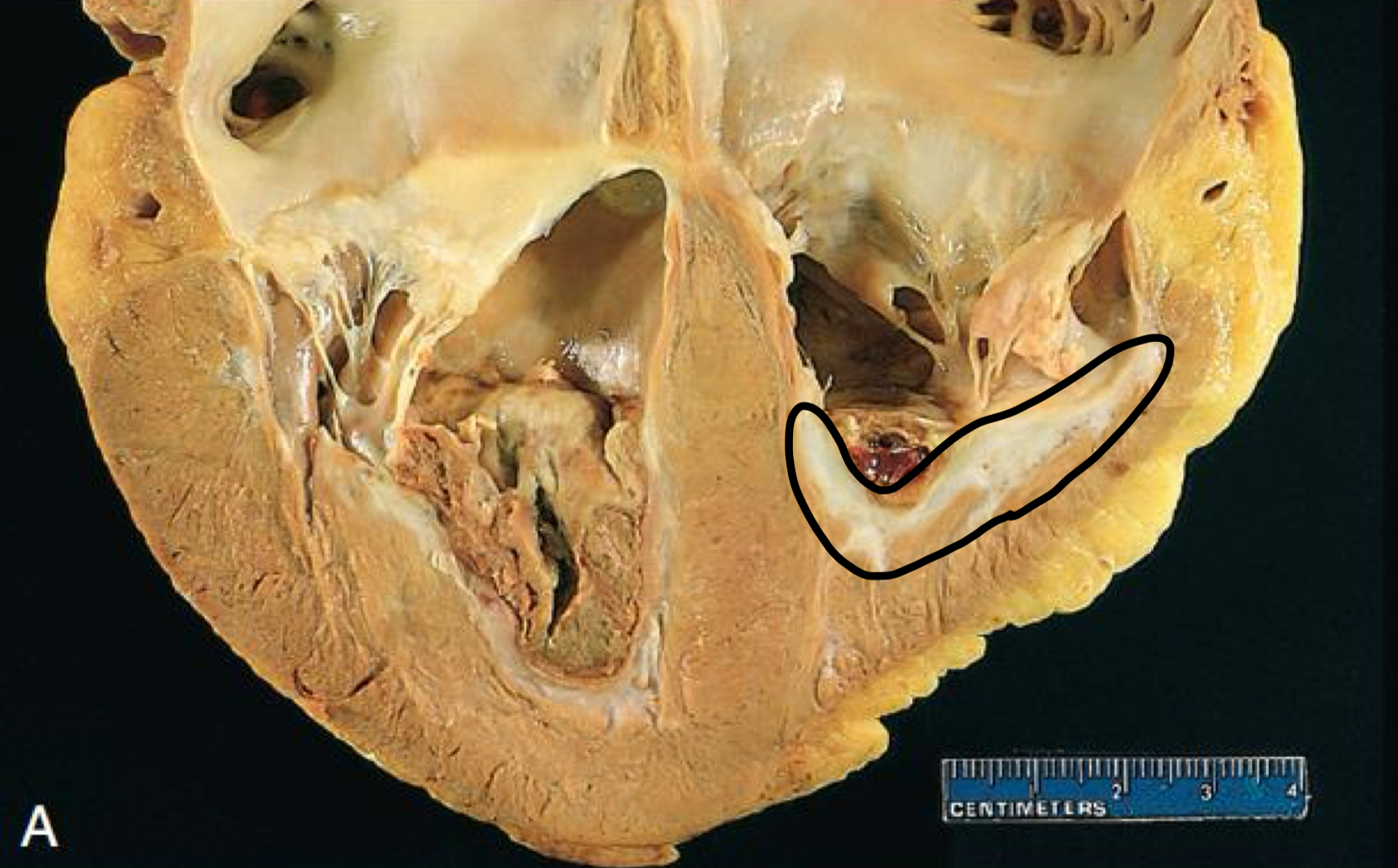
what is circled
infarct
venous thrombosis aka
phlebothrombosis
venous thrombosis is common in
deep vein of leg (DVT)
main contributor to venous thrombosis
stasis
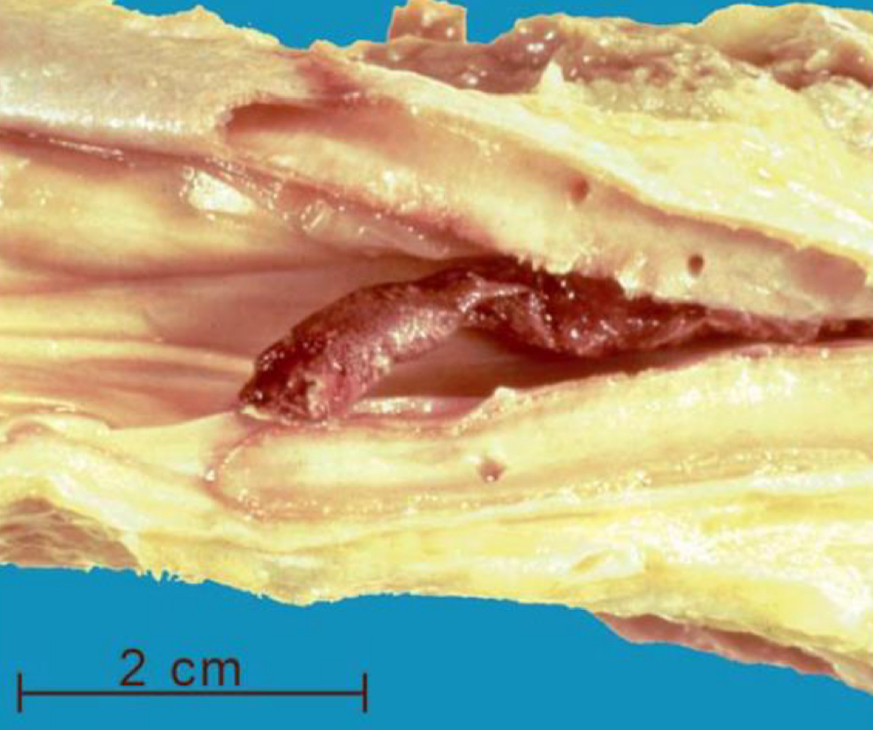
what is depicted
venous thrombosis
venous thrombosis can lead to
congestion, edema, DVT, embolization
thrombus fates
dissolute/resolution, organization, propagation, thromboembolism, recanalization
organization
create blood vessel in thrombus
propagation
increased size due to more platelet → increased risk
recanalization
restore blood flow
embolism
embolus passage through blood vessel that can lodge and obstruct lumen
consequences of embolism
ischemic necrosis
pulmonary embolism main cause
DVT
pulmonary embolism happens in _______ patients
bed-ridden
saddle embolus
big → sudden death
systemic embolism mostly from
intracardiac mural thrombi lodged in artery
embolism in end arteries
infarction
consequences of fat and marrow embolism
respiratory failure
fat and marrow embolism cause
tissue or skeletal injury
air embolism happens due to
neck wounds or vein puncture in surgery
large air embolism
hypoxia
decompression sickness
gas expand if come up too fast
consequence of air embolism
ischemic injury
amniotic fluid embolism consequences
pulmonary emboli
capillary hydrostatic pressure
fluid → outside
plasma oncotic/osmotic pressure
inside push on wall
interstitial hydrostatic pressure
outside push in
interstitial oncotic/osmotic pressure
outside push out
net filtration formula
force favoring filtration - force oppose
positive net filtration means
fluid move out
plasma oncotic pressure is decreased when
albumin is decreased
edema
excess fluid accumulation in interstitial space
edema is caused by
too much force favoring filtration
effusion
accumulation in body cavity
causes of edema
increased hydrostatic pressure, decreased plasma oncotic pressure, lymphatic obstruction, sodium retention, inflammation
inflammation increases/decreases vascular permeability
increases
clinical symptoms of edema
swelling, pitting
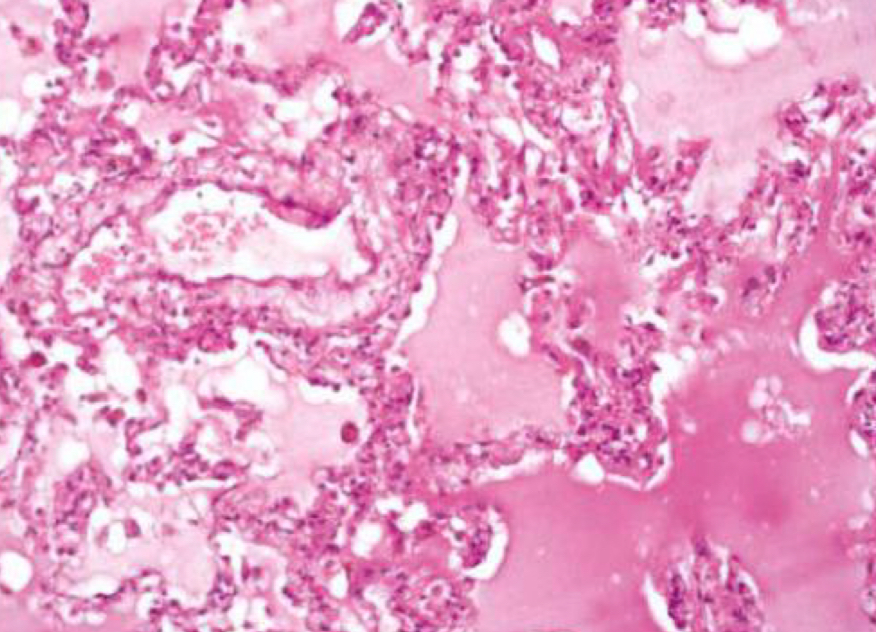
what condition is depicted
pulmonary edema (alveoli shouldn’t be pink)
dehydration leads to
hypernatremia
shock
systemic hypoperfusion from decreased cardiac output by ineffective circulating blood
cardiogenic shock
heart failure
hypovolemic
decreased intravascular volume
septic shock
infection
septic infection leads to
DIC, hypoperfusion, organ disfunction
shock consequences
decrease blood volume, increased vasodilation, increased permeability