6.1.1 - Aromatic Compounds
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
a) What are the two different models of Benzene?
Kekule
Delocalised Pi System
Brief description of Benzene?
C6H6
Cyclic
Planar
Lone electrons from p orbitals form a pi system = delocalised ring
Which is able to form due to C-C being all the same bond length
b) What are the differences between Kekule model and delocalised system?
Kekule:
Alternating single and double bonds
Pi bonds are localised
Delocalised:
Pi bonds are delocalised
P orbitals overlap
Carbon - Carbon bond lengths are the same
Enthalpy change of hydrogenation is less exothermic tha regular alkenes
Explain why Benzene is resistant to reactions?
Too stable
Requires catalysts
c) What is the name of these benzenes if they have an additional NO2/ OH/ BR/ 2 CH3/ NH2 groups?
Nitrobenzene
Phenol
Bromobeneze
1,2 - dimethylbenzene
Phenylamine
d) Why doesn’t Benzene undergo electrophilic addition what happens instead?
EA will disrupt the ring so it undergoes electrophilic substitution
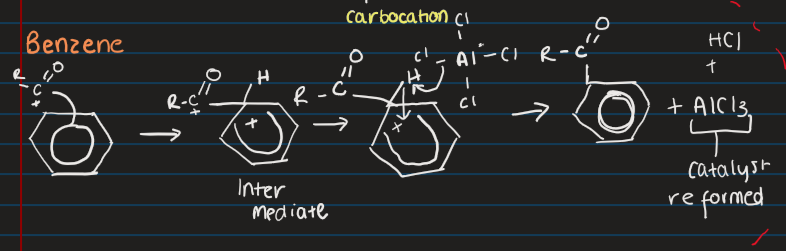
What is the Friedel Craft Acylation?
Adds an acyl group to allow benzene to be weaker for substitution
Requires halogen carrier to act as a catalyst
What does a halogen carrier and acyl chloride form together?
Carbocation
What is the general mechanism for Acylation
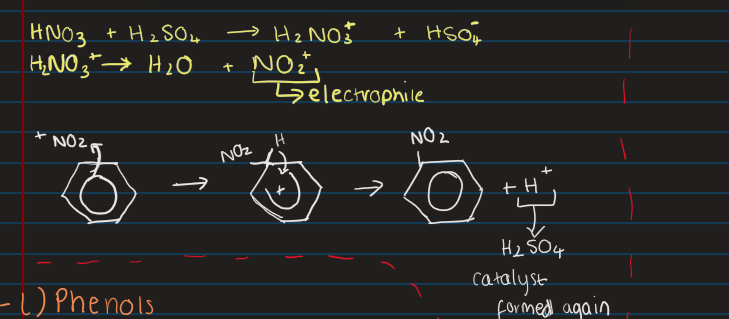
What conditions does nitration occur?
55 degrees celcuis
Must react sulfuric acid and nitric aid to form electrophile
Draw the mechanism of nitration of benzene?
h) What is a phenol?
Weak acid
Why is phenol more reactive benzene?
Phenol has a higher electron density
Due to hydroxyl group (OH)
O contains lone pair of electrons in p orbital - overlaps with delocalised ring
So electron density increasing making it more susceptible to attack from electrophile
What are electron withdrawing groups?
Withdraw electron density from carbon 3 and 5
Where electrophiles are more likely to attack
Examples: NO2
What is an electron donating groups?
Donate electrons increasing electron density at carbon 2,4,6
Example: NH2,OH
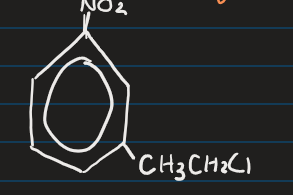
Example: Predict reaction between nitrobenzene and chloroethane using AlCl2 as a catalyst?
When phenols react with alkalis what do they form?
Salt + Water