general chemistry 9: solutions
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
A/an [...] is a special type of homogeneous mixture composed of two or more substances
solution
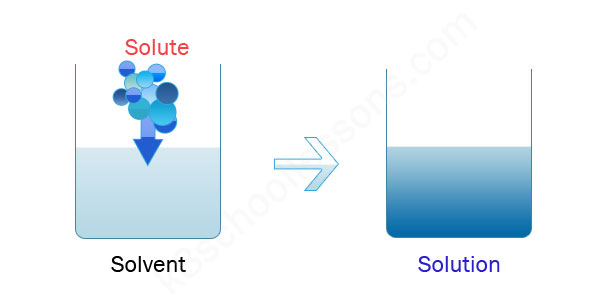
A/an [...] is a liquid that dissolves a solid, liquid or gaseous solute
solvent
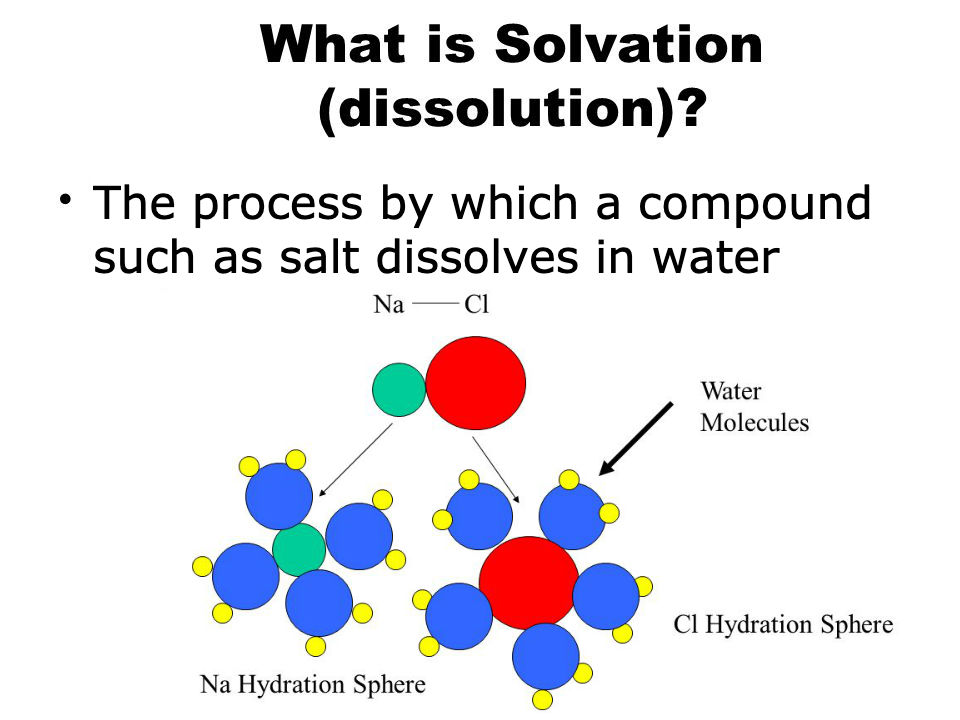
[...] or [...] is the process of dissolving a solute in solvent
solvation or dissolution
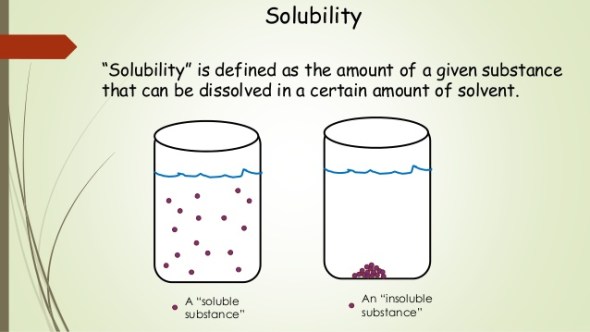
[...] is measured in terms of the maximum amount of solute dissolved in a solvent at equilibrium
solubility
[...] is the number of moles of a substance that can be dissolved per liter of solution before the solution becomes saturated
molar solubility

A/an [...] has a metal ion at its center with a number of other molecules or ions surrounding it
complex ion
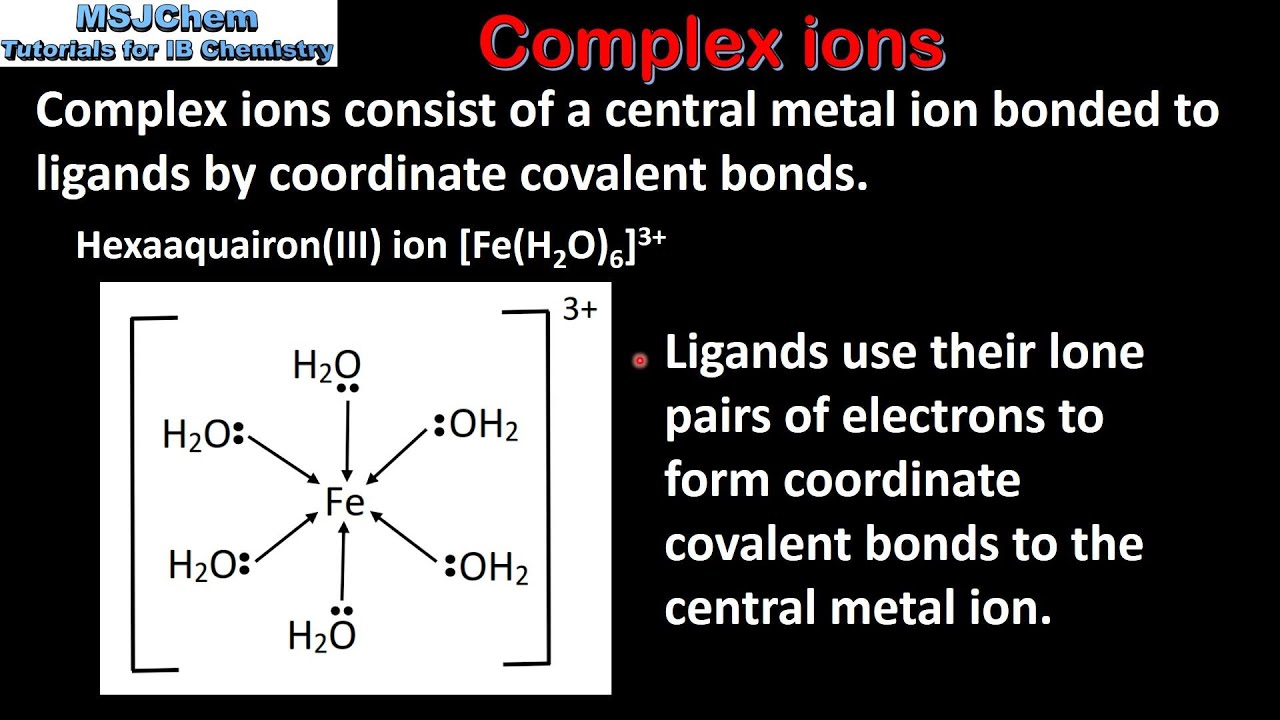
Polar molecules are [hydro...]
Nonpolar molecules are [hydro...]
polar = hydrophilic
nonpolar = hydrophobic
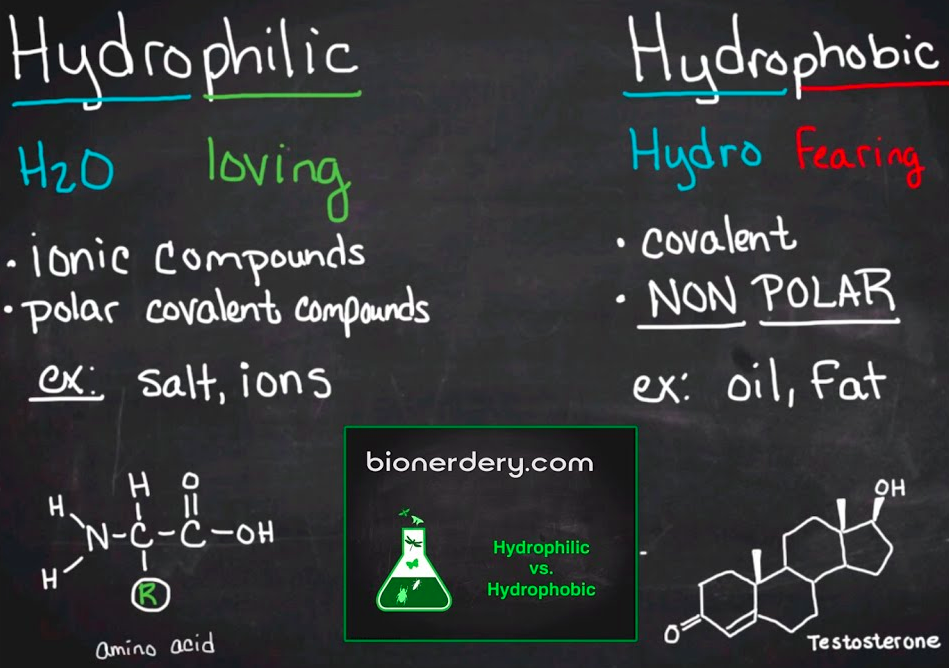
In a 1 molar solution, normality can be thought of as the [...]
number of protons a molecule of acid can release in solution
for example, each molecule of H2SO4 can release two protons in solutions so its normality is 2

Na+, K+, NH4+, and NO3- are [sometimes or always] soluble
always soluble

Cl-, Br-, and I- are [...] except with Pb2+, Hg22+, and Ag+
soluble

SO42- is [...] except with Ca2+, Sr2+, Ba2+, Pb2+, Hg22+, and Ag+
soluble

S2- is [...] except with Na+, K+, NH4+, Mg2+, Ca2+, Sr2+, and Ba2+
insoluble

O2- is [...] except with Na+, K+, Sr2+, and Ba2+
insoluble

OH- is [...] except with Na+, K+, Ca2+, Sr2+, and Ba2+
insoluble

CrO4- is [...] except with Na+, K+, NH4+, and Mg2+
insoluble

PO43- and CO32- are [...] except with Na+, K+, and NH4+
insoluble

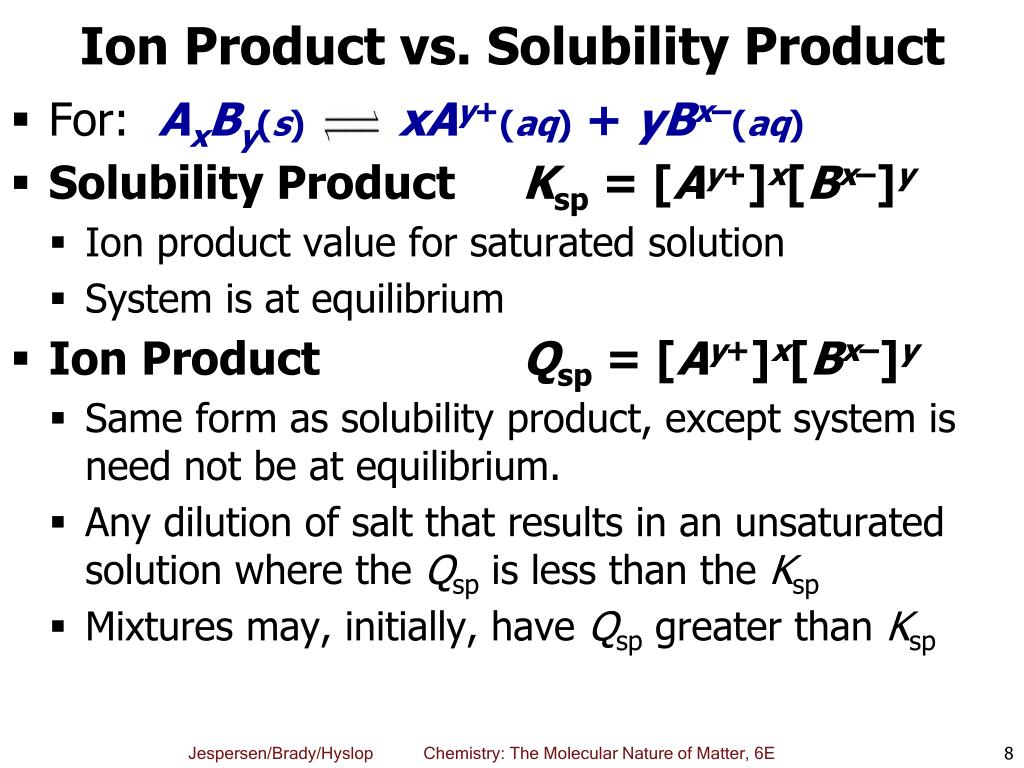
Ksp is the [...] for a reaction that consists of a solid dissolving in a solution
equilibrium constant
the equlibrium constant for a regular chemcial reaction is abbreviated keq
Give the solubility product constant for the following chemical equation:
BaSO4(s) ⇌ Ba2+(aq) + SO42-(aq)
Ksp = [...]
Ksp = [Ba2+][SO42-]
![<p><span>K</span><sub>sp</sub><span> = </span><span style="color: mediumseagreen"><strong>[Ba<sup>2+</sup>][SO<sub>4</sub><sup>2-</sup>]</strong></span></p><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/2d5897a9-442b-4405-8fd4-eb9bbf53b032.jpg)
Qsp is the [...] for a reaction that consists of a solid dissolving in a solution
reaction quotient
the reaction quotient for a regular chemical reaction is abbreviated Qc
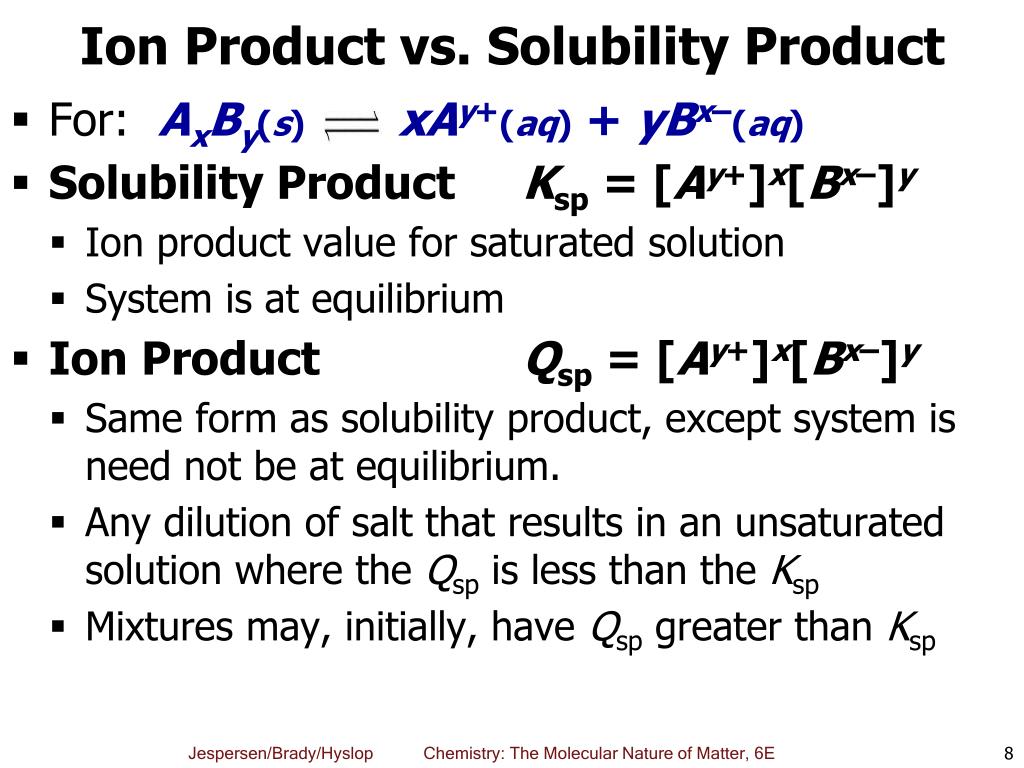
If Qsp is [less than, greater than, or equal to] Ksp then the solution is unsaturated so no precipitate will form
less than

If Qsp is [less than, greater than, or equal to] Ksp then the solution is saturated and at equilibrium so no precipitate will form
equal to

If Qsp is [less than, greater than, or equal to] Ksp then the solution is supersaturated so a precipitate will form
greater

The common ion effect causes solubility to[increase or decrease]when adding like ions
decrease

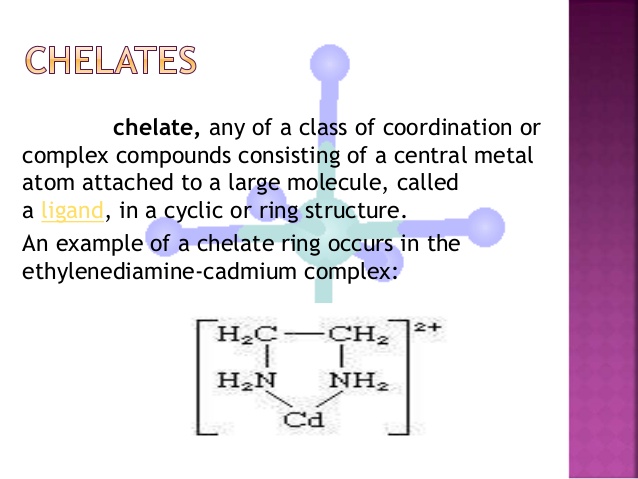
A/an [...] is a compound with a central cation bonded to the same ligand in multiple places
chelate
[...] are physical properties of solutions that depend on the concentration of dissolved particles but not on their chemical identity
colligative properties

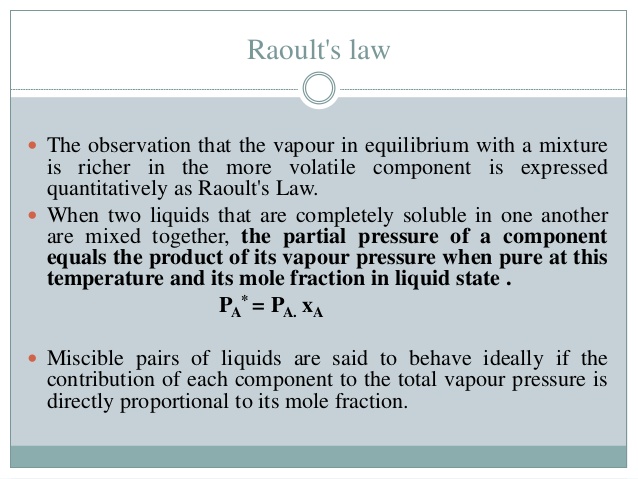
Raoult's law states that the vapor pressure of a solution is equal to [...]
the sum of the vapor pressure of each volatile component multiplied by the mole fraction of that component in the solution
raoult law can be used to calculate the molecular mass of an unknown solute
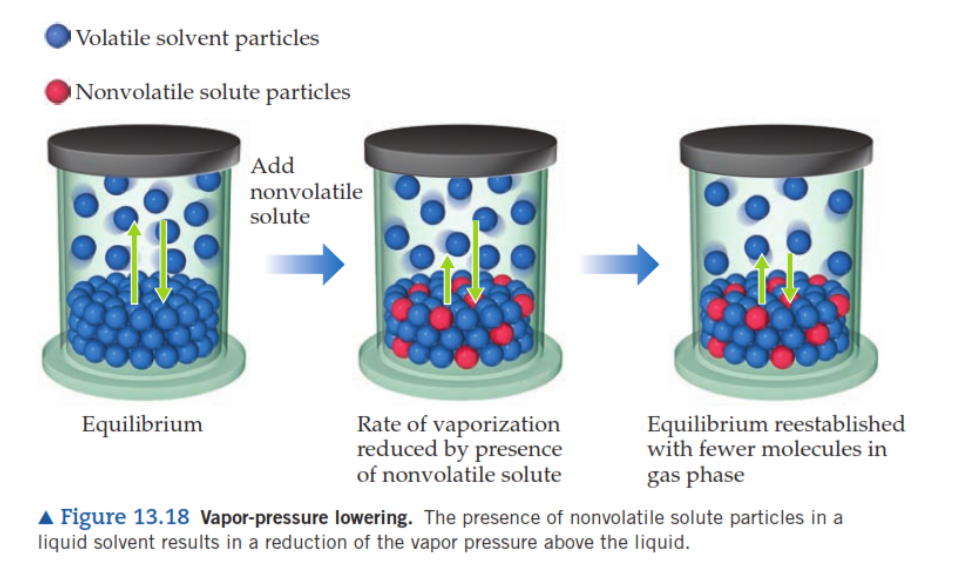
The presence of nonvolatile solute particles in a liquid solvent results in a/an [increase or reduction] of the vapor pressure above a liquid
reduction
[...] is the number of individual particles in solution
osmolarity
