IGCSE Biology (Co-ordinated Sciences Double Award 2024)
1/357
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
358 Terms
excretion
removal of the waste products of metabolism, toxic materials, and substances in excess of requirements
respiration
breakdown of glucose inside cells to give energy
all living things (mrs gren)
Movement, Respiration, Sensitivity, Growth, Reproduction, Excretion, Nutrition
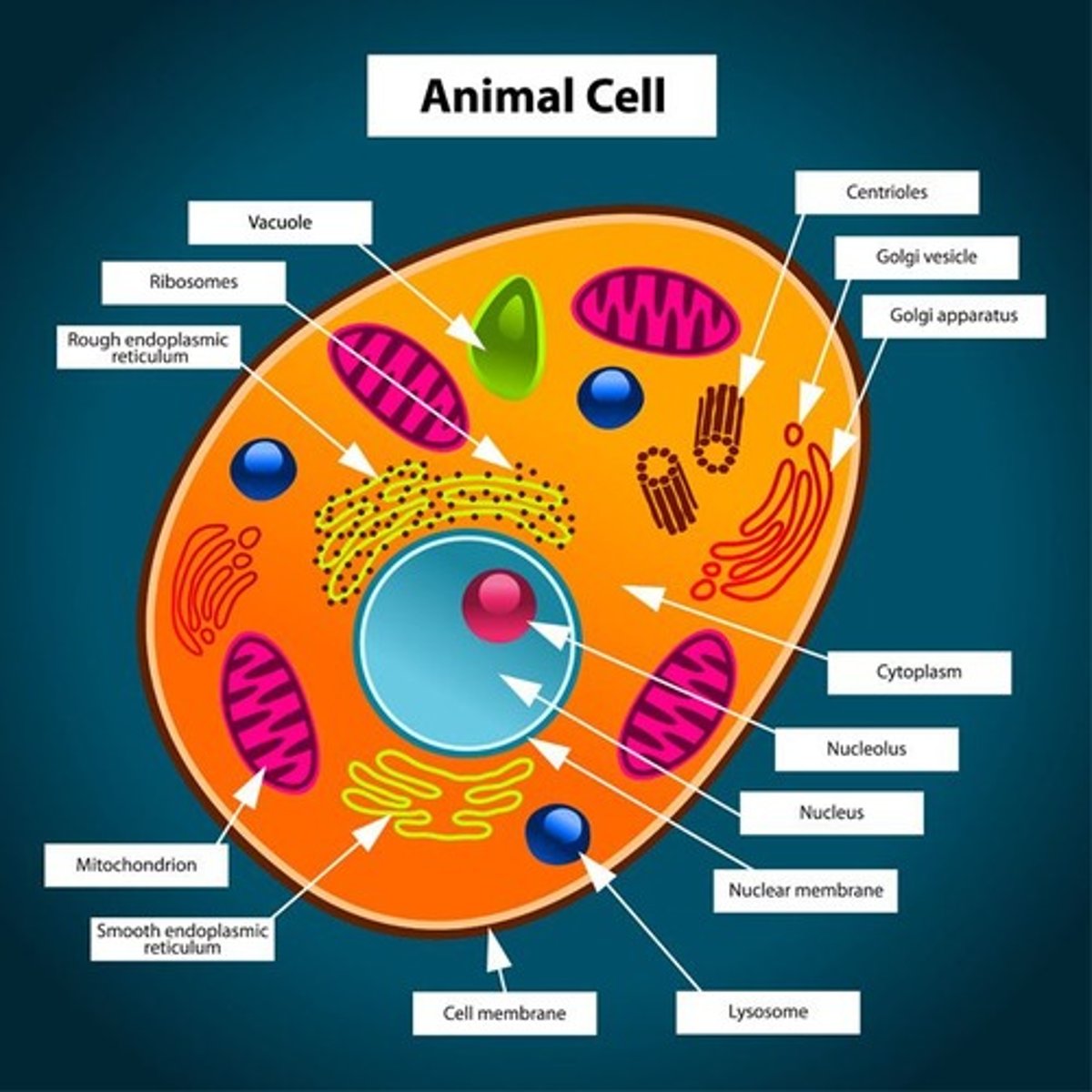
animal cell differences
no cell wall, no chloroplasts, no vacuole, glycogen food storage
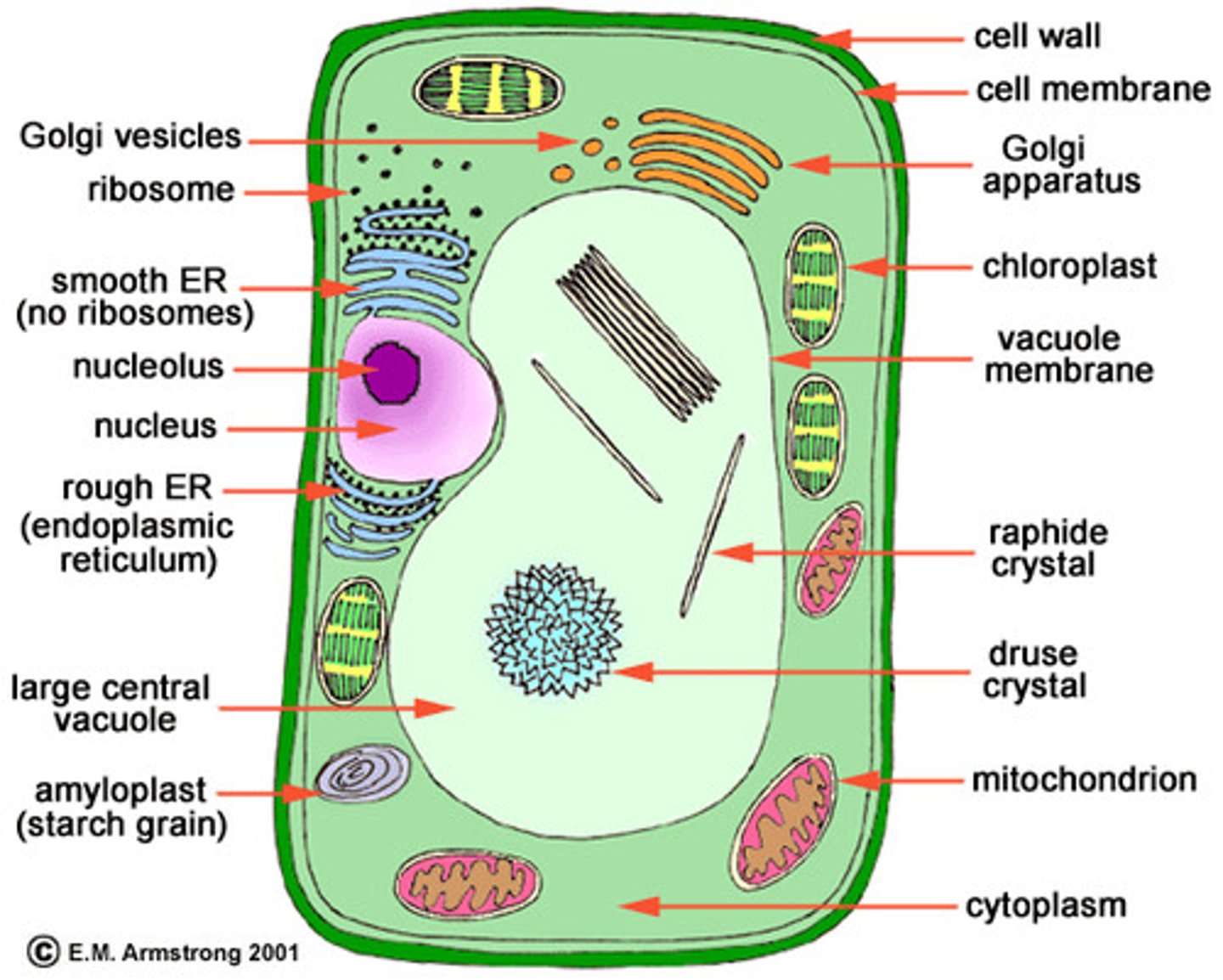
plant cell differences
cell wall, chloroplasts, vacuole, starch food storage
animal cell has
semi permeable cell membrane, cytoplasm, glycogen food store, nucleus
plant cell has
permeable cell wall (glucose fibre), nucleus, cytoplasm, vacuole filled with liquid, chloroplasts (only in green plants), cell membrane, starch grain food storage
animal and plant cells are _______ for the jobs they do
specialized
magnification
size of drawing (mm)/actual size
when you increase the size of something, the surface area
does not increase relative
the bigger an object becomes, the _______surface it has _______
less, relative to its volume
no matter the size of the solid, the substance will _______. That is why cells are _______, so that the _______that is diffusing into them can be _______.
diffuse at the same rate, so small, oxygen,evenly spread/distributed into the whole cell easily.
as you get a _______ organism/cell, diffusion is made _______
larger, harder/takes longer
cells and multicellular structures have _______ to increase _______ to maximize _______. For example, _______.
specialized structures, surface area, rate of diffusion. Fish gills, leaf is not thick.
osmosis
diffusion of water through a SEMI PERMEABLE MEMBRANE. Osmosis takes place from an area of low solute concentration to high solute concentration (high water potential --> low water potential)
water potential
The ability of the water to move. There is more water leaving high water potential areas.
the water will tend to move until
there are the same number of molecules on both sides.
hypotonic
lower solute concentration
hypertonic
higher solute concentration
isotonic
equal solute concentration
animal cell add to water (ex. red blood cell)
water moves in, cell swells and eventually bursts
animal cell add to strong sucrose solution (ex. red blood cell)
water moves out, cell shrinks, cell deflates, crinkles
plant cell add to water
water moves in, cell swells, cell turgid (full of water). cell will not burst as the cell wall is quite strong
plant cell add to strong sucrose solution
water moves out, vacuole + cytoplasm shrink, cytoplasm comes away from the cell wall. Cell is plasmolysed. Cell wall remains the same/
Plasmolysed plant cell
The cell has lost water and the cytoplasm has shrunk; the membrane has pulled away from the cell wall
when drawing a graph
pay attention to scale on the axis!!! Independent variable on the x axis, dependent variable on the y axis.
autotrophs
organisms that make/produce their own food (like plants)
heterotrophs
organisms that need to eat food (like humans)
fibre is found in
the cell wall
lipids are found in
cell membrane
fats vs oils
fats - found in animals, solid at room temp. oils - found in plants, liquid at room temp.
Monomers
small unit that can join together with other small units to form polymers (larger substances)
Carbohydrates are made of
monosaccharides
proteins are made of
amino acids
main food chemicals are
carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, minerals, vitamins, fibre, water
carbohydrates
provide energy
simple carbohydrates
eg. glucose - sweet and soluble, provide immediate energy
complex carbohydrates
polymers/polysaccharides made from simple sugars. Used as energy store - eg starch, glycogen.
Examples of simple carbohydrates
fruit, vegetables, sugars, milk
Examples of complex carbohydrates
whole wheat bread, pasta, rice, oats, potatoes
lipids
long term energy storage (2x as much as carbs). Used as insulators, used in cell membranes, water proofing (like waxy leaves)
examples of foods containing lipids
margarine, fried food (churros, chips, fries)
proteins
made of long chains of amino acids, used for bodybuilding and repair
there are _______ amino acids. _______ are essential and must be eaten. The rest can be _______.
20, 8, made by the body
examples of proteins
meat and beans
vitamins and minerals
needed in very small amounts, but are essential.
examples of minerals
iron, zinc, calcium, etc.
examples of vitamins
K, B, E, B12, etc.
malnourished
Having a diet that lacks the correct balance; too much or too little of one thing
turgor pressure
The pressure that water molecules exert against the cell wall
Chemical elements that make up carbohydrates, fats, and proteins
oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, (protein: nitrogen too)
starch and glycogen made of
glucose
fats and oils are made of
fatty acids and glycerol
test for starch
add iodine, positive test turns black
test for reducing sugar
add benedict's solution, boil, positive test turns dark orange
test for protein
add biuret solution, positive test turns purple
test for fats and oils
add equal parts ethanol and water, shake well, positive test turns cloudy/white
water is
important as a solvent
Enzymes are a type of ______ called ______ because they are made by ______. They are a type of ______.
catalyst, biological catalysts, living organisms, protein molecule.
substrate
(enzyme specific) something that reacts to make a product
The enzyme has a ______ so that a ______ can fit and carry out its reaction. Each enzyme is specific for one job and can only do ______.
specific shape, specific substrate, one thing
active site
The part of an enzyme where the chemical reaction occurs. Specific to the substrate it catalyses.
How does an enzyme reaction work?
The substrate fits into the active site of the enzyme. The enzyme causes chemical change in the substrate.
Why, up to a certain point, does increasing the temperature of an enzyme increase the rate of reaction?
the molecules and enzymes increase KE and move around more and faster meaning they are more likely to bump into each other
Why does too hot a temperature cause the rate of reaction to slow and eventually an enzyme to denature?
because it causes the active site to change in shape slightly so it takes longer for the substrate to fit. Eventually, the substrate no longer fits.
optimum temperature
The temperature at which an enzyme is most active
denatured enzyme
An enzyme which no longer functions
effect of cold temperatures on enzymes
Cold temperatures decrease the rate of reaction because molecules are moving slower and are less likely to collide, but cold temperatures do not denature the enzyme, so if the temperature is brought back up, the chemical reaction will speed back up to a normal process.
Effect of pH on enzyme activity
All enzymes work best at optimal pH. above and below the optimal pH the rate of reaction decreases. Extreme pH changes can denature the enzyme.
balanced diet
contains all the nutrients in the right amounts that the body needs (carbohydrates, protein, fats, vitamins + minerals, and fibre)
Vitamin C
from citrus, deficiency scurvy(gums bleed, swollen, tired), helps with repair of body tissue/immune system
Vitamin D
from sunlight/fish oil/red meat, deficiency rickets (leg bones weak and bent), helps with bones and teeth
Iron
from red meat/pulses (lentils, beans, etc.), deficiency anemia (not enough O2 - tired, dizzy) carries O2, needed for hemoglobin
Calcium
from dairy/bones of fish like sardines, deficiency bones and teeth go brittle, helps with bones and teeth
Malnutrition is caused by
unbalanced diet
Kwashiorkor
protein deficiency
Marasmus
lack of energy
digestion
breakdown of large insoluble molecules (eg. protein, starch) into small molecules (eg. glucose, simple sugars) which can be absorbed and moved around the body easily.
ingestion
taking in food
absorption
movement of digested food molecules through the walls of the small intestine and into the bloodstream.
assimilation
movement of digested food molecules into the cells of the body where they are used, becoming part of the cells
egestion
passing out of food molecules that have not been digested as feces through the anus
Egestion vs excretion
excretion is things are chemically changed in the cells but egestion is just passing through (???)
digestion can be ______, eg. teeth, or ______, eg. enzymes
mechanical, chemical
What does saliva do?
Saliva contains the enzyme amylase which breaks down starch and simple sugars (maltose). It also helps food pass into the oesophagus.
What do teeth do?
Teeth break food down to increase surface area. THis makes it easier to swallow and the more surface area, the higher the enzyme activity.
What does the stomach do?
Stomach acid pH 2 helps the enzyme pepsin to break protein into amino acids (optimum pH). It also kills microbes (denatures enzymes).
How does food move down the esophagus?
peristalsis (wave of muscle contractions)
where is bile produced?
the liver
Where is bile stored?
gall bladder and released from the bile duct.
What does bile do?
emulsifies fat (breaks down into smaller droplets) to increase surface area and neutralises mixture of food and gastric juices entering duodenum to provide suitable pH for enzyme activity
What does the small intestine do?
(The small intestine releases amylase) Absorption of food chemicals takes place.
amylase breaks starch down into ______
Protease breaks down protein into ______
Lipase breaks down fats to ______
simple sugars (eg. maltose), amino acids, fatty acids and glycerol
Where do amino acids and glucose go after the small intestine?
blood capillaries
Where do fatty acids and glycerol go after the small intestine?
the lacteals
What are lacteals?
part of the lymph system and drain into the blood
What does the large intestine do?
absorbs water
incisor teeth
cut and bite chunks of food (4 on top, 4 on bottom)
canine teeth
for tearing. Very sharp, pierce food
premolars (bicuspids)
4 of them, for grinding and chewing