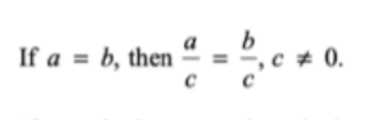Honors Geometry Vocabulary
1/232
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
233 Terms
Symmetry
a geometric characteristic of both nature and art.
Reflectional symetry
a design has reflectional symmetry if you can fold it along a line of symmetry so that all the points on one side of the line exactly coincide with all the points on the other side of the line.
Rotational symmetry
A design has rotational symmetry if it can be rotated around a central point by a certain angle and appear unchanged.
bilateral symmetry
an object with only one line of symmetry.
Segment
A part of a line that is bounded by two distinct endpoints.
Ray
A ray is bound by an endpoint on one side and extends infinitely in the other direction.
Oposite rays
Two collinear rays that extend infinitely oposite directions along a line.
Intersection
2 or mere geometric figures intersect when they have one or more points in common.
Ruler postulate
the points on a line can be matched one to one with real numbers. The real number that corresponds to a point is the coordinate of the point. The distance between points A and B, written as AB, is the absolute value of the difference of the coordinates of A and B.
Construction
a construction is a geometric drawing that uses a limited set of tools, usually a compass and a straightedge.
Congruent segments
line segments that have the same length are called congruent segments.
Segment addition postulate
when three points are collinear, you can say that one point is between the other two.
Segment addition postulate formula
AC = AB + BC
Polygon
a closed plane figure formed by three or more line segments called sides b
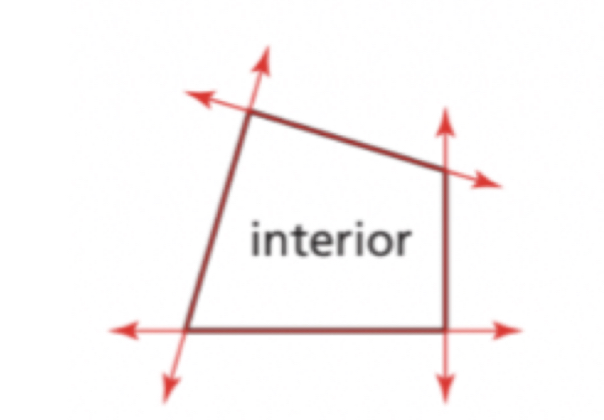
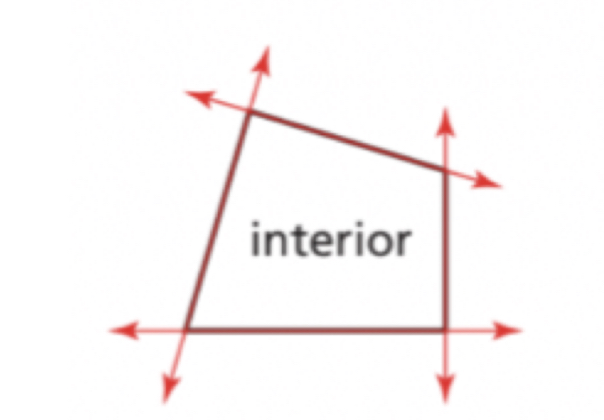
Convex polygon
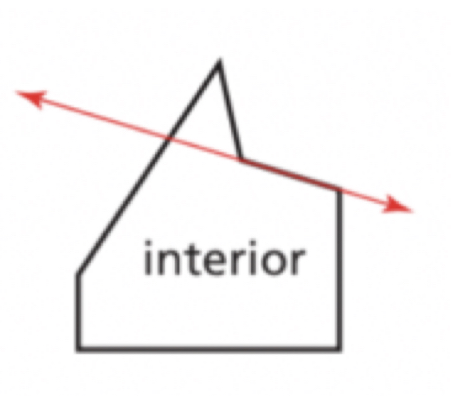
Concave polygon
Convex
a polygon is convex when no line that contains a side of the polygon contains a point in the interior of the polygon.
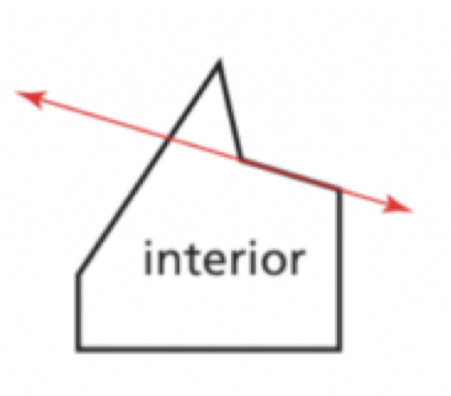
Concave
A polygon is concave when one or more line that contains a side of the polygon contains a point in the interior of the polygon.
Radical expression
an expresion that contains a radical.
Rationalizing the denominator
When a radical is in the denominator of a fraction, you can multiply the fraction by an appropriate form of 1 to eliminate the radical from the denominator.
Conjugates
are used to simplify radical expressions that contain a sum or difference involving square roots or radicals in the denominator.
Like radicals
radicals with the same index and radicand. These can be added and subtracted the same way like terms are combined by using the Distribution Property.
Midpoints
a point that decides the segment into 2 congruent segments
Segment bisector
A point, line, line segment, or plane that intersects the segment at its midpoint.
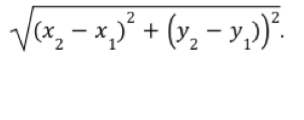
Distance formula
Midpoint Formula
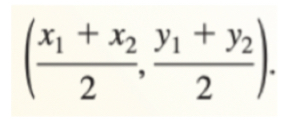
Angle
A set of points consisting of two different rays that have the same endpoint, called a vertex. The rays are the sides.
Interior of the angle
The region that contains all the points between the sides of the angle.
Exterior of the angle
The region that contains all the points outside the sides of the angle.
Protractor postulate
The measure of an angle is equal to the absolute value of the difference between the real numbers matched with the two rays of the angle on a protractor.
Acute angle
Angle measures greater than 0˚ and less than 90˚.
Right angle
Measures 90˚.
Obtuse angle
Measures greater than 90˚ and less than 180˚.
Strait angle
Measures 180˚.
Angle addition postulate
m<abc = m<abm + m<mbc
Angle bisector
A ray that divides an angle into two congruent angles.
Complementary angles
Two positive angles whose measures have a sum of 90˚.
Supplementary angles
Two positive angles whose measures have a sum of 180˚.
Adjacent angles
Two angles that share a common vertex and side, but have no common interior points.
Linear pair
Two supplementary adjacent angles.
Vertical angles
Two angles whose sides form two pairs of oposite rays.
What you can conclude from a diagram.
• all points shown are coplanar
• points on a line are collinear
• a point that appears to be between two points is between two points
• lines that apear to intersect at a point intersect at a point
• angles that appear adjacent are adjacent
• angles that appear to be straight angles are straight angles
• a point that appears to be in the interior of an angle is in the interior of the angle
Regular polygons
Polygons with equal side lengths and equal angle measures
Trapezoid
A quadrilateral with exactly one set of parallel lines
Kite
Quadrilateral with two pairs of consecutive congruent sides
Parallelogram
Quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel sides
Rhombus
Equilateral parallelogram
Rectangle
Equiangular parallelogram
Square
Regular quadrilateral
Circle
The set of points in a plane a given distance from a given point
Radius
Distance between a point in the circle and the center point
Chord
A line segment whose endpoints lie on the circle
Diameter
The longest chord in a circle
Tangent
A line that intersects a circle at exactly one point
Congruent circles
Two or more circles with the same radius
Concentric circles
Two or more coplanar circles that share a center point
A circle is ________ about a polygon if and only if it passes through each vertex of the polygon. (The polygon is _________ in the circle)
Circumscribed, inscribed
A circle is __________ in a polygon if and only if it touches each side of the polygon at exactly one point. (The polygon is __________ about the circle)
Inscribed, circumscribed
Arc of a circle
Two points on a circle and a continuous part of the circle between the two points.
Semicircle
An arc of a circle whose endpoints are the endpoints of a diameter. It is named with three points.
Minor arc
An arc of a circle that is smaller than a semicircle.
Major arc
An arc of a circle that is bigger than a semicircle
Cylinder
Solid consisting of two congruent, parallel circular bases and the segments with an endpoint on each circle that are parallel to the segment between the centers of the circles.
Prism
A polyhedron with two congruent, parallel bases connected by lateral faces that are parallelograms
Sphere
The set of all points in space a given distance from a given point
Cone
A solid consisting of a circular base, a point nit in the plane of the circle, and all points on line segments connecting that point to points on the circle
Pyramid
A polyhedron consisting of a polygon base and triangular lateral faces that share a common vertex
Hemisphere
Half a sphere
What you cannot conclude from a diagram.
• unmarked lines are congruent
• unmarked angles are congruent
• angles that look like right angles are right angles
Space
The set of all points. Including those in the third dimension
Rigid transformations
A motion that produces a congruent image to the original image
Translation
• A slide
• a rigid motion
Rotation
• A turn
• a rigid motion
Reflection
• a flip
• a rigid motion
Deductive reasoning
Uses the laws of logic to find a true conclusion from two true premises
Law of syllogism

Conditional statement
A logical statement that has two parts, a hypothesis p, and a conclusion q. The statement is written if p then q.
Negation
The opposite of the original statement. The symbol is ~
Converse
Exchange the hypothesis and conclusion of a conditional statement
Inverse
The negation of the hypothesis and the conclusion
Contra positive
The inverse of the converse
Equivalent statements
When two statements are both true or both false

Perpendicular lines
Two lines that intersect to form a right angle
Biconditional statement
A statement that contains the phrase “if and only if”
Truth table
Used to determine the conditions under which a conditional statement is true
Counterexample
A specific case for which the conjecture is false
Law of detachment
If the hypothesis of a true conditional statement is true, then the conclusion is also true
Inductive reasoning
A way to write a conjecture based on a pattern found in specific cases
Two point postulate
Through any two points, there exists exactly one line.
Line-point postulate
A line contains at least two points
Line intersection postulate
If two lines intersect, then their intersection is exactly one point
Three point postulate
Through any three noncollinear points, there exists exactly one plane
Plane-point postulate
A plane contains at least three noncollinear points
Plane-line postulate
If two points lie in a plane, then their intersection line containing them lies in the plane
Plane intersection postulate
If two planes intersect, then their intersection is a line.
Line perpendicular to a plane
A line is ___________________ if and only if the line intersects the plane in a point and is perpendicular to every line in the plane that intersects it at that point.
Additional property of equality
If a = b, then a + c = b+c
Subtraction property of equality
If a=b, then a - c = b - c
Multiplication property of equality
If a = b, then a • c = b • c, c ≠ 0
Division property of equality