Hinduism review
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Samsara
reincarnation
process of life, death, and rebirth
What are the key terms in Hinduism?
Atman - the soul
Samsara (reincarnation) - process of life, death, rebirth
Karma - the quality of rebirth is determined by the the moral behavior displayed in the previous life
Moksha (liberation) - breaking the cycle of samsara
Brahman - the ultimate reality
Atman
the soul
karma
the concept that the quality of rebirth is determined by the moral behavior displayed in the previous life
Moksha
liberation
breaking the cycle of samsara
Brahman
the ultimate reality
the universe, the infinite eternal truth
the single binding unity connecting all living things
Dharma
religious law, obligation, and duty governing one’s conduct
live the life that the universe has given you in an honorable way
What does the Dharma wheel symbolize? Where does it appear?
symbol of the continuing motion of the universe, law, and structure
appears in the center of the flag of india
What is the main goal of life in Hinduism?
to escape the cycle of rebirth and death (samsara)
enter into an indescribable state - moksha (liberation)
What happens to someone who has reached moksha?
the ones who reach this sate no longer struggle with the cycle of life and death
this person has united the human soul (atman) with the universal soul (brahman)
What are some basic information about Hinduism (roots, founder, size)?
originated in India
no founder
dates back to 3500 BCE
third largest religion
primarily in India (80% of India practice Hinduism)
What is the worldview/basic principles of Hinduism?
the holy is inside of all of us and in everything
there is no formal organization or leadership
very diverse across India and the world
millions of gods
What does “Hindu” mean?
Indians did not call themselves Hindu until British colonialization
Hindu was a word that derives from Persian, meaning people who lived beyond the Indus River
What is the Hinduist worldview in relation to gods (# of gods)?
polytheistic - many gods (this is how outsiders view Hinduism)
monist - all is ONE; all living things are a part of a supreme reality (Hindus believe this)
monotheistic - one god (many people believe that all Hindu gods are made from one god)
Hinduism encompasses a wide range of beliefs, and while it’s often perceived as polytheistic, it also includes monotheistic, monist, and other perspectives, with many Hindus viewing deities as manifestations of a single, supreme reality.
Who does The Trimurti (Hindu trinity) consist of?
Brahma - creator: responsible for the beginning of the universe and all things within it
Shiva - destroyer: responsible for the end of the universe and the cycle of rebirth
Vishnu - preserver: maintaining the balance + order of the universe
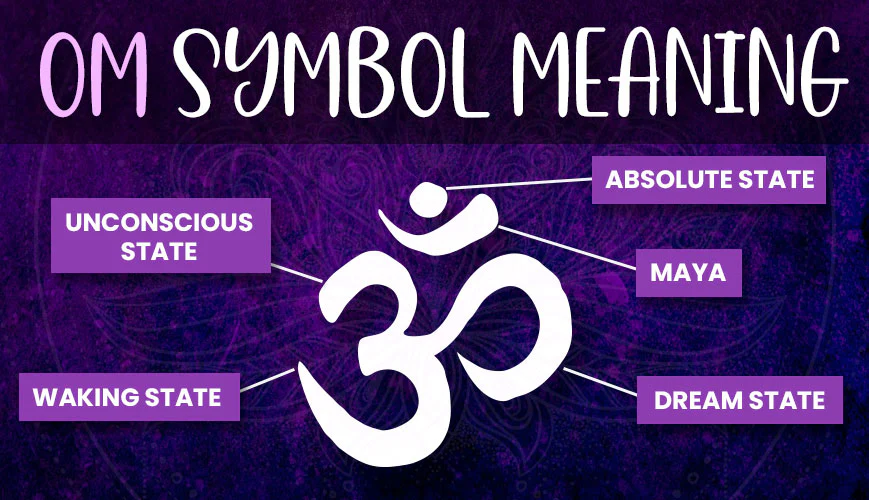
What is the Aum/Om symbol? How is it used?
primordial sound of the universe
chanted to improve physical, mental, and emotional state

What do the parts of the Aum/Om symbol represent?
lower curve: waking state
upper curve: unconscious state
middle curve: dream state
dot: enlightenment
crescent: maya (illusion)
What are the 4 sacred texts in Hinduism?
The Bhagavad Gita: most ancient and well-known text
The Four Vedas: oldest texts (2500 years old)
The Upanishads: philosophical texts
Puranas: ancient stories centered around the Trimurti (Brahma, Vishnu, Shiva)
What is The Bhagavad Gita?
most ancient and well-known text
What is The Four Vedas?
oldest texts (2500 years old)
What are the Upanishads?
philosophical texts
What are the Puranas?
ancient stories centered around the Trimurti (Brahma, Vishnu, Shiva)
What is the mandir?
home for the gods
Hindu temple: place of worship
What to do when visiting a Hindu temple?
ring a bell: let the gods know you came to worship them
perform a puja: sit in front of the gods, make an offering and pray
circling the statues of gods
shiva linga: ritual
What are the main parts of a mandir?
inner shrine
bell
arthi
What is the shrine? What is its purpose?
sacred center of the Mandir
found in most Hindu households
Where the Murti is kept
What is the Murti?
sacred image of a deity
helps Hindus to develop and express their relationship to the deity
an access point to the deities
What is the puja? Where can it be done?
a ritual of worship and devotion (of the Sacred image)
can be done both in the Mandir and at home
involves:
bathing and dressing the deity
offering of food
followed by the arthi
What is the arti? How is it done?
performed multiple times each day
offering light to the gods (in a clockwise motion)
other items include incense, flowers, water
lamp and other items are passed around amongst the congregation
often accompanied by singing
all stand out of respect
What are the three main types of festivals celebrated in Hinduism?
Celebrating a significant event in the life of a deity (e.g.: Diwali)
Celebrating a significant event in the life of a holy person (e.g.: the birthday of a particular guru)
Seasonal festivities or customs (e.g.: spring festivals like Holi)
What is Diwali?
most well known festival in Hinduism
also known as: festival of lights
recounts the stories from the Ramayana
tells the story of Rama and Sita
What is the story of Ramayana (Rama and Sita) behind Diwali?
Hindu deities: Rama + Sita
Rama is sent away to a far-off country by his father
Rama leaves with his wife Sita
Sita gets kidnapped by a wicked demon: Ravana
The monkey god, Hanuman, helps Rama save Sita and kill Ravana so they can return home
good vs. evil
lamps were lit to guide Rama and Sita home
why Hindus light diya lamps during Diwali today
What is the caste system?
an important part of Hinduism
castes: social classes into which a person is born and lives their entire life
if a person has a good karma, they may be reincarnated into a higher caste
When was the caste system outlawed?
since 1950
Caste
from the Portuguese word ‘casta’
means race
Aryans
ruling groups in India
1500-500 BCE
Dravidians
group of people ruled by the Aryans
Varna
‘colour’
Jati
lineage or kinship group
What is the origin of the caste system?
date back to >3000 years ago with the Rig Veda
helped the ruling Aryans keep the Dravidians under control
maintained social harmony + cohesion
How was each caste determined?
each caste was determined by heritage
dharma: fulfill the expectations for people in your caste
What are the different castes?
Bhramin: priests, academics
Kshatryia: warriors, kings
Vaishya: merchants, landowners
Sudra: commoners, peasants, servants
Untouchables: outcast—out of caste, street sweepers, latrine cleaners
Untouchables
Panchama: those who fall outside the four classes
to be treated with charity but not to touch
recently referred to themselves as dalits (the oppressed)
What was the controversy surrounding the caste system?
poor treatment of the lower castes
the lowest of castes are shunned from society
movement in the 20th century to dismantle the caste system
outlawed in 1950, but very little change
social and economic pressure in globalized world eroding the caste system