Lecture 29 - Selenium, Fescue
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Selenium poisoning presents as lots of diseases depending on the__, __,__, and ___.
form of selenium, duration, route of exposure, animal species
True or False? Selenium poisoning only occurs acutely.
False. Selenium poisoning can be BOTH acute and chronic.
What general systems are targeted with acute selenium poisoning?
lung, heart, liver, kidney, less commonly skeletal muscle, nervous (swine only)
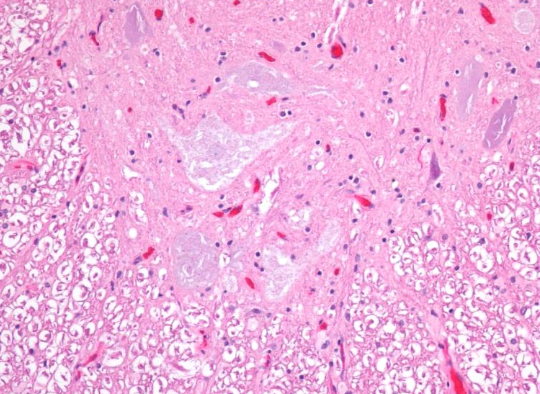
What disease is caused by chronic selenium poisoning?
“bobtailed” disease
If you see this, think ____! (not pathognomic)
selenium poisoning
What are sources of selenium poisoning?
high selenium forages (location driven) areas in WA, ID, MT
selenium supplements (mix, math errors, wrong supplement)
water contamination
Selenium content varies in ___ plants and categorized into ___ and ____.
accumulator,
obligate, facultative
True or False? Obligate accumulator plants accumulate higher amounts of selenium and tends to be more palatable than facultative plants.
False. Obligate plants tends to be LESS palatable, facultative plants passively accumulate selenium and tend to be more palatable.
What species are susceptible to selenium poisoning?
All species, horses most sensitive and primarily LA production animal problem
Clinical signs and lesions will vary between ___ and __ of exposure - it is a ____ problem.
species, duration
multisystemic
What clinical signs and lesions are seen with acute selenium poisoning?
cardiac, lung (liver, kidney, skeletal muscle), neurologic - poliomyelomalacia in swine
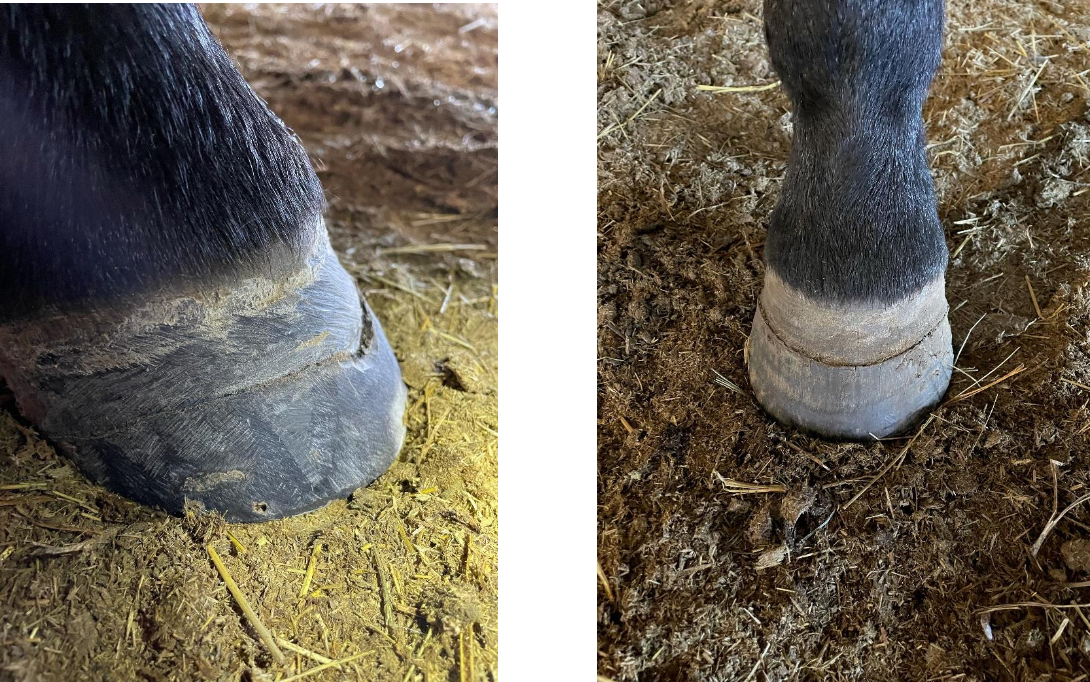
What clinical signs and lesions are seen with chronic selenium poisoning?
lame, rough hair coat, hair loss (mane and tail), anorexia, hoof deformities - circular breaks below coronary band

How do you diagnose selenium toxicity?
history of exposure - find the source
clinical signs and lesions vary between species, dose, form, duration (heart, lung, liver, kidney, neuro in swine)
analytically
antemortem: whole blood
postmortem: liver, kidney
source (water, feed)
chronic: hair and hoof
What is the treatment for selenium poisoning?
symptomatic and supportive - supplement with S, Mn, Zn if chronic
What is Se deficiency?
aka white muscle disease (cows, goats, sheep, horses) affecting heart, and skeletal muscle in horses causing masseter muscle myopathy
___mining in the Western ___ Formation resulted in what?
Phosphorous, Phosphoria
high selenium

Fescue poisoning is caused by animals eating _____ which contains ____ which is a ____.
tall fescue,
endophyte, mycotoxin
Fescue poisoning is a ___ problem all throughout US and most fesuce is infected. Any feed where infection rate ___% can be problematic.
common,
>5%
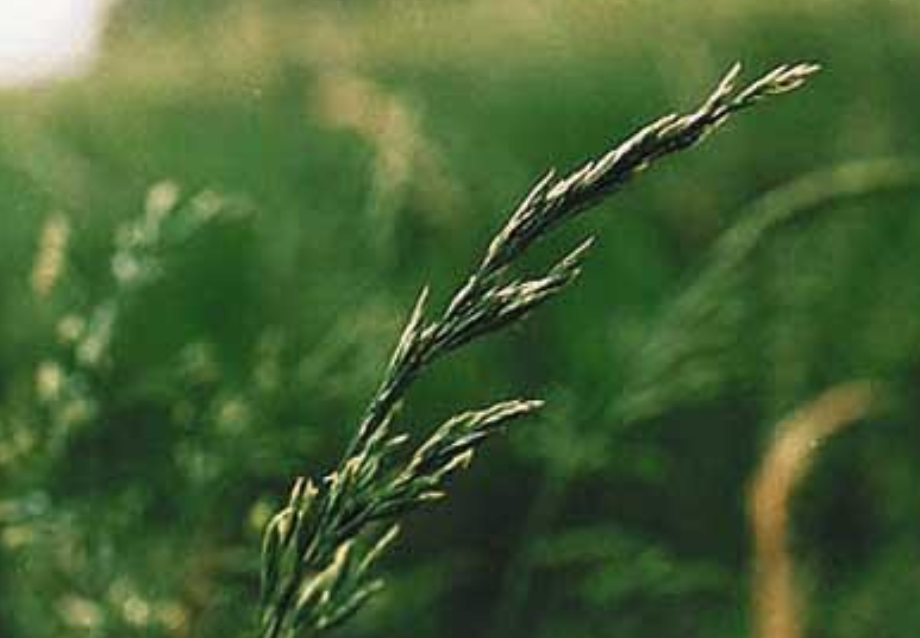

What is the toxin in fescue poisoning?
loline and ergot alkaloids - ergovaline
What is the alkaloid that is tested for fescue?
ergovaline
What is the major mechanism of action of fescue toxicity?
alpha adrenergic receptors → peripheral and other vasoconstriction
D2 dopamine receptors → suppression of prolactin secretion
What are the 3 major clinical diseases from fescue poisoning?
summer slump, fescue foot, reproductive problems
Describe the clinical disease seen in summer with fescue poisoning
summer slump - cattle, vasoconstriction
hyperthermia, decreased feed intake, loss of body weight, poor coat, abortions
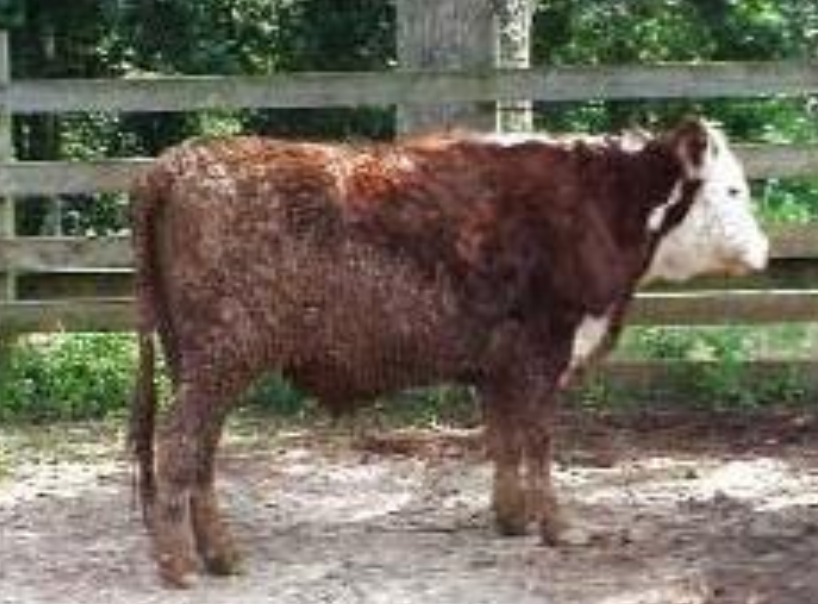

Describe the clinical disease seen in winter with fescue poisoning
fescue foot - cattle, vasoconstriction
ischemic necrosis (dry gangrene) of distal extremities, loss of appetite, lameness, inflamed fetlocks, loss of tips of ears and tail, abortions
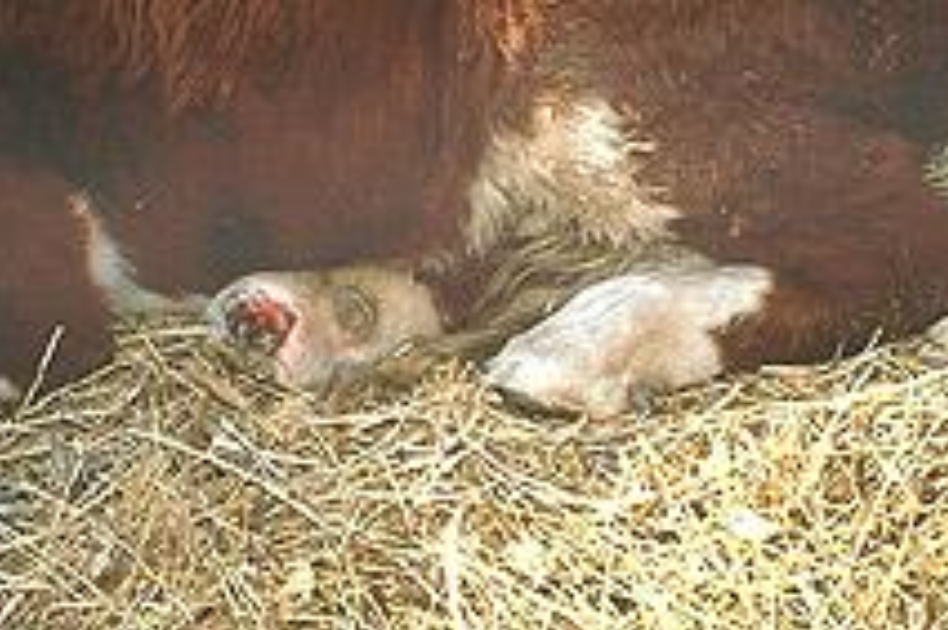

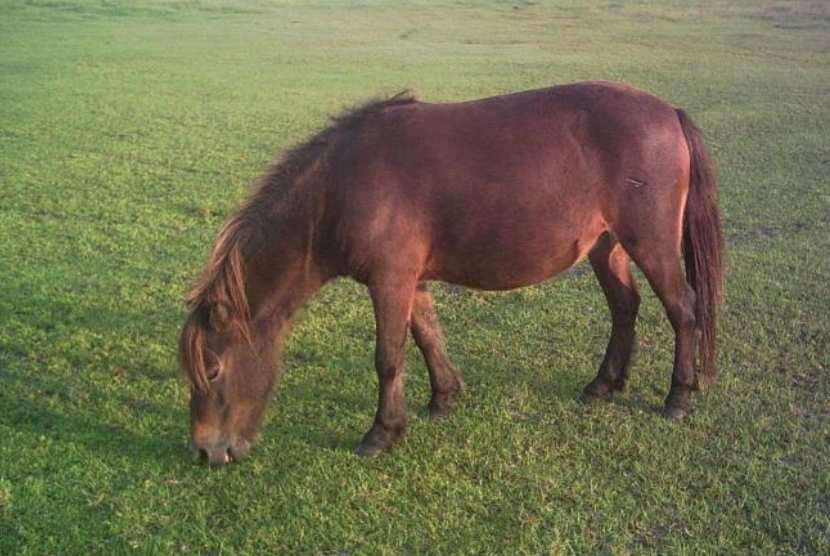
Describe the clinical disease seen all year with fescue poisoning
reproductive problems - horses, cattle, sheep
prolonged gestation, thickened placentas, dystocias, large weak young (dysmature), agalactia, abortions

How do you diagnose fescue poisoning?
three diseases - abortions seen in all 3
ingesting tall fescue - endophyte
test hay for ergovaline // urine testing not common
What is the treatment for fescue poisoning?
symptomatic and supportive,
Domperidone (repro + agalactia).- dopamine antagonist for horses; changes will last as long as horse on fescue; stop exposures last 1-3 months of gestation
prevention is key - may not be cost effective to treat
True or False? Animals with fescue poisoning cannot go to market due to residues.
False. Animals with fescue poisoning have no significant residue issues.