Proton Beam Therapy
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Name the 4 components of a proton machine.
Proton accelerator
Beam transport system
Gantry
Treatment beam shaping
What can a proton beam accelerator be and where does acceleration happen?
Cyclotron or synchrotron
Acceleration takes Place away from treatment room.
Describe what a cyclotron does.
4m across
Produces one continuous fixed energy proton beam.
Straightforward beam production and application.
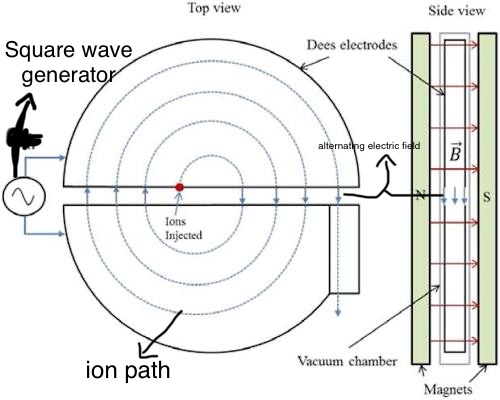
How does a cyclotron work ? (8 steps + image)
Proton starts at centre
Accelerates proton between 2 hollow semicircular cavities (dees)
Dees are opposite each other
Electric field between the 2 dees.
Inside the Dee the proton is steered with an electric field but not accelerated.
Proton is accelerated across the gap between the dees if opposite Dee is negatively charged.
Field alternated between dees to provide acceleration.
Proton spends an equal time in each Dee.
What are some disadvantages to a proton beam therapy machine with a cyclotron?
Cannot directly change energy of particles.
Fixed energy :
High energy initial beam must be produced then degraded to produce energy ranges need for SOBP - inefficient.
More shielding required due to secondary radiation.
Describe what a synchrotron does.
large - 7m across
Produced pulsed beam capable of a range of energies.
High energy possible.
Acceleration more complicated than cyclotron - expensive
What are the disadvantages of using a synchrotron ?
beam currents typically lower than cyclotron - limit dose rates (larger fields )
Long treatment times - inefficient
Describe the role of the beam transport system.
Electromagnetic field focus and transport the proton beam to the room.
Likely one accelerator per centre
Describe the role of the gantry systems.
improve flexibility of beam application + direction
It however weighs a lot (tons)
What are the main 2 methods of beam shaping ?
Passive - developed first, commonly used, reasonably straightforward.
Active - complex, more flexible, more beam conforming.
How does passive beam shaping work ?
Pencil beam from accelerator needs to be spread laterally - double scattering system.
Range shifter modifies beam to desired distal depth of target.
Range modulator spreads out Bragg peak
MLC help conform beam to shape of target.
Compensator shapes dose to distal edge.
Which components are used for passive beam conforming ?
Double scattering system
Range shifter
Range modulator
MLC
Compensator
What are the disadvantages of passive beam shaping?
depth dose tailored to distal end NOIT proximal.
Higher dose region located in normal tissue, proximal target to volume.
Large amount of material in beam increased scatter + nuclear fragments produced.
Describe how active beam shaping works.
Scans pencil beam over treatment field using magnets.
Range sifter used with cyclotron
Tailor dose distribution to irregular shaping (no colls or compensator )
Dose conformal to proximal edge of target volume
Name disadvantage of using active beam shaping.
More technically difficult
More sensitive to organ motion
What are the differences between SCATTERING and SCANNING beam techniques?
Scattering uses specific beam modifying devices whose scanning doesn’t.
Dual scattering generates neutrons whilst scanning produces fewer neutrons.
Scattering can’t IMPT without multiple beams and modifiers whilst scanning can.
In scattering organ motion not as crucial but in scanning it is.
Scattering reduces penetrating power of bema whist in scanning it deeper.
Scattering is simple whilst scanning is complex
Scanning is more conformal.
What are some Dosimetric advantages of protons in the context of paediatrics?
Rapid side fall off beyond SOBP
Conformal to distal edge
Low dose bath minimised
Reduction in secondary tumours
Potentially reduce RT late effects
What are some dosimetric advantages of protons in the context of conformity ?
number of beam entry points kept to a minimum
Usually beam entry positioned :
Shortest path (unless OAR in way)
Avoid distal fall off into OAR
Avoid passing through heterogeneous (not uniform) tissue
What a re some uncertainties of protons ?
we don’t know where in the patient the protons stop.
Stopping power uncertainty ( density of tissue determined in CT)
Range uncertainty caused by tissue inhomogeneity in beam path and taint anatomy/ set up.
What is the effect of patient motion and step up ?
effects dose distribution
Effect worse for spot scanning due to interplay of patient motion/breathing + delivery of each spot.