Endocrine Glands & Dysfunction: The Thyroid Gland (cont.)
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Week 7: Tuesday, October 7th: Review & Midterm Exam 1; Thursday, October 9th: Endocrine Glands & Dysfunction: The Thyroid Gland (cont.)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
the following are _______ effects of the thyroid gland:
metabolism of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins
basal metabolic rate
temperature
growth and nature
physiological
effector organs of the hypothalamus, which all have thyroid receptors, are:
bones, the brain, nerves, the heart, and body cells
pressure on the eyes that causes bulging, and excessive thyroid hormone in the blood describes _______
exophthalmos
_______ is also known as hypothyroidism, and has the following characteristics:
1. metabolic dysregulation
an auto immune disease
High basal metabolic rate (BMR)
Increased sweating
Weight loss
Graves’s disease
_______ is also known as hyperthyroidism, and has the following characteristics:
1. Still causes goiter
metabolic dysregulation
low basal metabolic rate (BMR)
Decreased sweating
Weight gain
Hashimoto’s disease
in 1814, Gay-Lussac discovered that _______ deficiency caused goiter, so he fed those with the disease seaweed and marine products
iodine (I2)
in 1895, Kocher found high amounts of iodine (I2) in the _______
thyroid gland
in 1918, Kendall found and named _______, which has four iodine atoms bound to a tyrosine
thyroxine/tetraiodothyronine (T4)
in 1952, Gross and Pitt-Rivers found and named _______, a more active form of thyroid hormones that has three iodine atoms bound to a tyrosine
triiodothyronine (T3)
_______ can remove iodine form tetraiodothyronine (T4) to create triiodothyronine (T3)
ionodases
the thyrid gland developed from the embyro’s _______
digestive tube
true or false: if the thyroid gland weighs more than 20g, this indicates a thyroid disease
true
the thyriod gland communicates and delivers hormones via
large sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves, and blood and lymph
_______ are special cuboidal/columnar epithelia cells in the thyroid gnad that make T3 and T4
thryoid follicles
the lumen around each thyroid follice cell is filled with a glycoprotein colloid called _______
thyrogobulin (TG)
_______ produce calcitonin, which is involvedin calcium homeostasis
parafollicular c cells
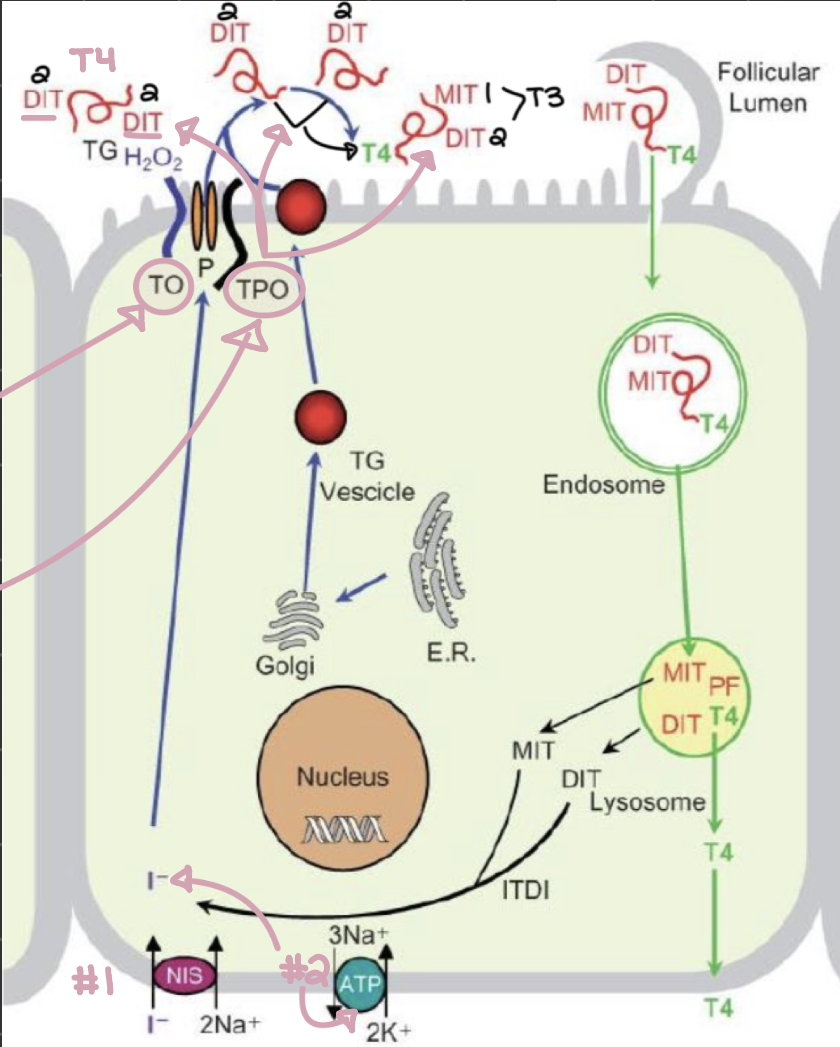
describe the process of thyroid hormome secretion, starting with iodide entering the cell
iodide (I-) enters the cell bound to 2 Na+
The cell charge changes once I- enters, Na+ out, and K+ in
I- is oxidized by thyrooxidase (TO) to become I²
thyroid peroxidase (TPO) attaches I² to Thyroglobulin (TG)
triiodothyronine (T3) and tetraiodothyronine (T4) are produced from diiodotyrosine (DIT) and monoiodotyrosine (MIT)
thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) binds to these cells to release triiodothyronine (T3) and tetraiodothyronine (T4)