Honors Biology (9) Midterm Vocab- MRS. PEET
1/163
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
164 Terms
Science (1)
An organized way of gathering and analyzing evidence about the natural world. (1)
Observation (1)
The act of noticing and describing events or processes in a careful, orderly way. (1)
Inference (1)
A logical interpretation based on what scientists already know. (1)
Hypothesis (1)
A scientific explanation for a set of observations that can be tested in ways that support or reject it. (1)
Independent Variable (1)
In an experiment, the variable that is manipulated (changed) by the person doing the experiment. (1)
Dependent Variable (1)
In an experiment, the responding variable (the variable that changes in response to changes the person doing the experiment has made) (1)
Control group (1)
In an experiment, the group exposed to the same conditions as the experimental group except for one independent variable. (1)
Data (1)
The information gathered during an experiment. (1)
Theory (1)
A well-tested explanation that unifies a broad range of observations and hypotheses. (1)
Bias (1)
A point of view that is personal rather than scientific. (1)
Biology (1)
The study of life. (1)
Stimulus (1)
A signal to which an organism responds. (1)
DNA (1)
A molecule containing the universal genetic code. (1)
Asexual reproduction (1)
The new organism has a single parent. (1)
Metabolism (1)
The combination of chemical reactions through which an organism builds up or breaks down materials. (1)
Homeostasis (1)
Living things maintaining a relatively stable internal environment. (1)
Biosphere (1)
All of life anywhere on the planet Earth. (1)
Atom (2)
The basic unit of matter. (2)
Electron (2)
A negatively charged particle that has almost no mass located outside the nucleus of the atom in energy levels. (2)
Element (2)
A pure substance made up of only one type of atom. (2)
Isotope (2)
Atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. (2)
Compound (2)
A substance formed when two or more elements combine in definite proportions. (2)
Ionic Bond (2)
A bond formed when electrons are transferred from one atom to another atom. (2)
Ion (2)
An atom that has acquired a charge because it has either gained or lost electrons. (2)
Covalent Bond (2)
A bond formed when two atoms share electrons. (2)
Molecule (2)
The smallest unit of most compounds. (2)
Hydrogen Bond (2)
The attraction between the oppositely charged regions of two different molecules. (2)
Cohesion (2)
Attraction between molecules of the same substance. (2)
Adhesion (2)
The attraction between molecules of different substances. (2)
Solution (2)
A mixture where all of the components (parts) are evenly distributed (uniformly spread) throughout the mixture. (2)
Solute (2)
A substance that is being dissolved, it is present in a smaller quantity. (2)
Solvent (2)
The substance that is doing the dissolving, it is present in the larger amount. (2)
Suspension (2)
A mixture of water and undissolved material that is evenly distributed as small particles that do not settle out of the water column. (2)
Acid (2)
Any compound that forms H+ ions in solution. (2)
Base (2)
A compound that produces hydroxide (OH-) in solution. (2)
Buffer (2)
Substances that can react with strong acids or bases in order to prevent sharp changes in pH in a solution. (2)
Monomer (2)
A small unit that joins with other small units to form polymers. (2)
Polymer (2)
Large compound that is made from monomers linked together. (2)
Carbohydrate (2)
Compound containing carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio that is used by living things for energy storage or in some organisms can be used to build structures. (2)
Lipid (2)
A polymer, such as fats and oils, composed of mostly carbon and hydrogen atoms, with less oxygen than other organic compounds. (2)
Nucleic Acid (2)
A polymer, such as DNA or RNA, that contains carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus and that stores cellular/genetic information. (2)
Nucleotide (2)
Contains three parts; a phosphate group, a 5-carbon atom sugar, and a nitrogen base - join/link together to form nucleic acid molecules. (2)
Protein (2)
A polymer that contains nitrogen as well as carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, and that may act as a building material for cells, or may regulate cell processes, or may be involved in immune reactions or may be enzymes. (2)
Amino Acid (2)
Compound with an amino group on one end and a carboxyl group on the other end; building block (monomer) of proteins. (2)
Reactant (2)
An element or compound that enters into a chemical reaction. (2)
Product (2)
An element or compound that forms as a result of a chemical reaction. (2)
Catalyst (2)
Substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction. (2)
Enzyme (2)
A protein that acts as a biological catalyst to speed up a chemical reaction. (2)
Chemical Reaction (2)
A process that changes or transforms one set of chemicals into a new set of chemicals. (2)
Activation Energy (2)
Energy needed to get a reaction started. (2)
Substrate (2)
The reactants of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction. (2)
Active Site (2)
The location on an enzyme where the substrates bind to the enzyme - its shape is complementary to the shape of the substrate. (2)
Ecology (3)
The scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment. (3)
Population (3)
An assemblage of individuals that belong to the same species and live in the same area. (3)
Community (3)
An assemblage of different populations that live together in an area. (3)
Ecosystem (3)
All the organisms that live in a particular place, together with their physical environment. (3)
Biome (3)
A group of ecosystems that have similar climates and organisms. (3)
Biotic Factor
Any living part of an environment. (3)
Abiotic Factor (3)
Any nonliving part of an environment. (3)
Climate (3)
The average conditions of temperature and precipitation over a long period of time in an area. (3)
Weather (3)
The day to day condition of the Earth's atmosphere. (3)
Greenhouse effect (3)
Gases in the atmosphere that trap heat in the Earth's atmosphere. (3)
Latitude (3)
A measure of how far north or south of the equator a point on the Earth's surface is. (3)
Winds and Ocean Currents (3)
A major factor in transporting heat energy across the globe. (3)
Canopy (3)
The dense, leafy covering formed by tall trees. (3)
Understory (3)
The shaded area just below the canopy that is characterized by shorter trees and vines. (3)
Humus (3)
Material formed from decaying leaves and other organic matter. (3)
Taiga (3)
Dense forests of conifers along the northern edge of the temperate zone; also called boreal forests. (3)
Permafrost (3)
A layer of permanently frozen subsoil found in the tundra. (3)
Photic Zone (3)
The area of the water column that receives sunlight. (3)
Aphotic Zone (3)
The area of the water column that receives sunlight. (3)
Plankton (3)
Organisms that are suspended in the water and are pushed around by the water. (3)
Wetland (3)
An ecosystem where water either covers the soil or is present at or near the surface for at least part of the year. (3)
Estuary (3)
A wetland formed where a river meets the sea. (3)
Autotrophs (4-5)
Organisms that can capture energy from sunlight or chemicals and use that energy to produce food. (4-5)
Photosynthesis (4-5)
The process in which autotrophs capture light energy and use it to convert carbon dioxide and water into oxygen and sugars. (4-5)
Chemosythesis (4-5)
The process in which autotrophs use chemical energy to produce carbohydrates. (4-5)
Heterotroph (4-5)
Organisms that rely on other organisms that they eat for their energy and food. (4-5)
Herbivores (4-5)
Organisms that obtain energy by eating only producers - i.e. cows. (4-5)
Carnivores (4-5)
Organisms that eat only other consumers - i.e. wolves. (4-5)
Omnivores (4-5)
Organisms that eat both producers and consumers - i.e. bears. (4-5)
Detrivores (4-5)
Organisms that break down organic matter - i.e. fungi. (4-5)
Decomposer (4-5)
Organisms that feed on dead/decaying matter - i.e. earthworms. (4-5)
Scavenger (4-5)
Organisms that consume the carcasses of other consumers. (4-5)
Food Chain (4-5)
A series of events in which one organism eats another and obtains energy. (4-5)
Food Web (4-5)
A community of organisms where there are several interrelated food chains. (4-5)
Phytoplankton (4-5)
Microscopic, free-floating, autotrophic organisms that function as producers in aquatic ecosystems. (4-5)
Zooplankton (4-5)
Tiny floating organisms that are either small animals or protozoa. (4-5)
Trophic Level (4-5)
Each step in a food chain or food web. (4-5)
Ecological Pyramid (4-5)
A diagram that shows the biomass of organisms at each trophic level. (4-5)
Biomass (4-5)
A measure of the total dry mass of organisms within a particular region. (4-5)
Nitrogen Fixation (4-5)
Bacteria convert nitrogen gas from the atmosphere into ammonia that can be used by producers and other organisms. (4-5)
10 % RULE (4-5)
An organism only obtains ------ percent of the energy from the organism that it ate. (4-5)
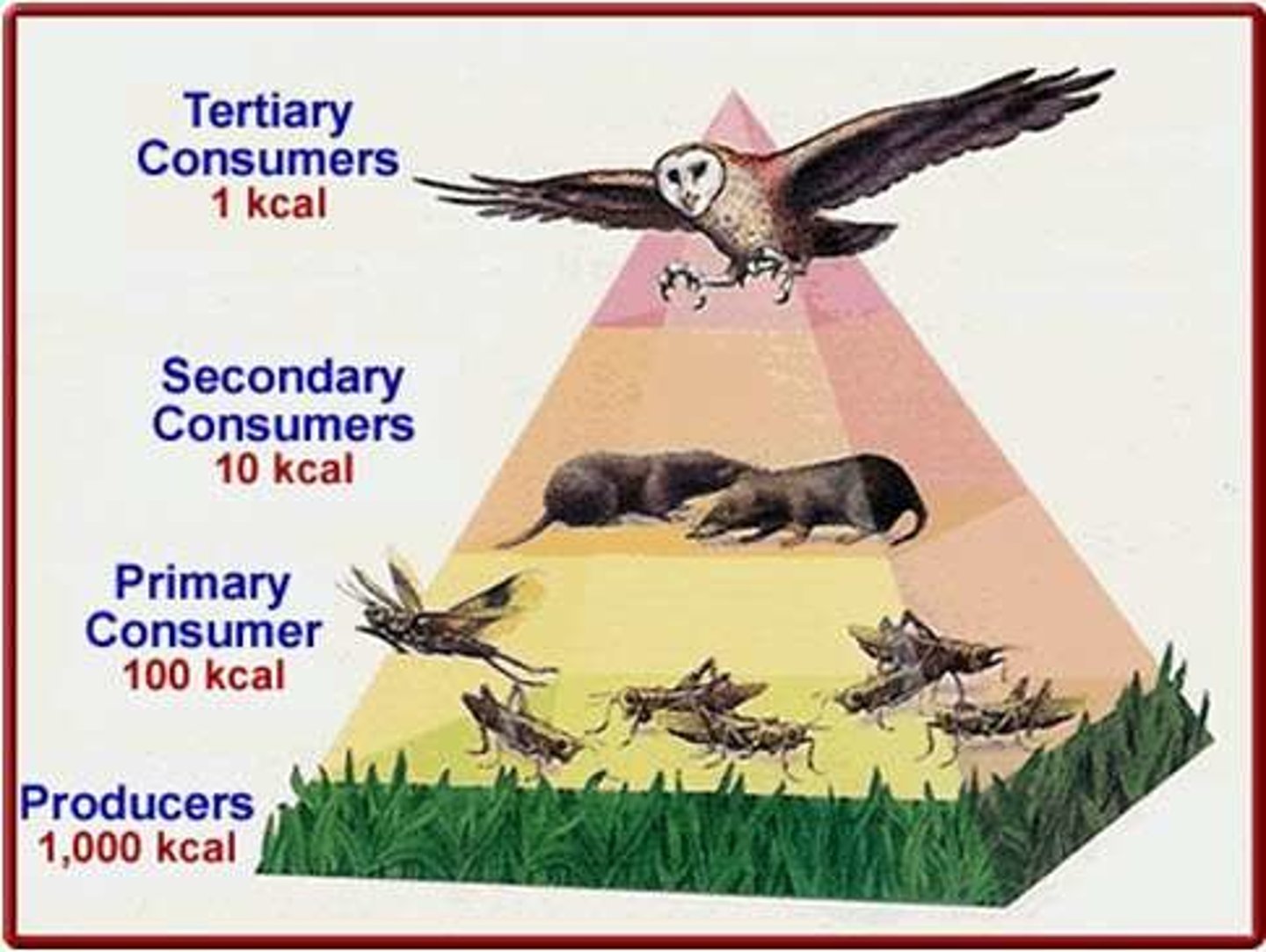
Pyramid of Energy (4-5)
A pyramid that shows the total amount of energy available at each trophic level. (4-5)
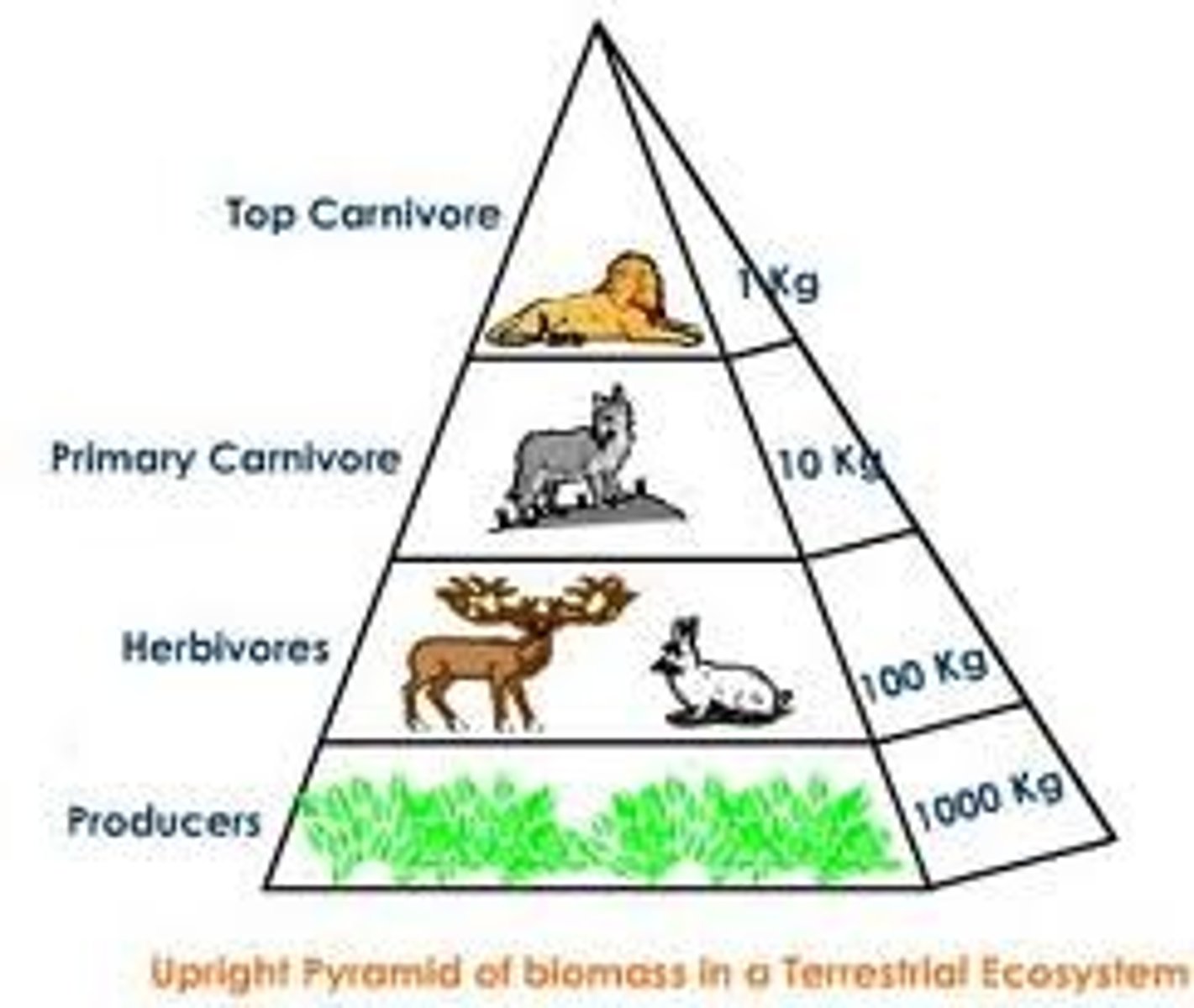
Pyramid of Biomass (4-5)
A pyramid that illustrates the total mass of all the organisms in a trophic level. (4-5)
Pyramid of Numbers (4-5)
Representation of the number of individual organisms in each trophic level of an ecosystem. (4-5)
Biogeochemical Cycle (4-5)
Cycle by which chemicals circulate through an ecosystem using biotic and abiotic components. (4-5)
Nutrient (4-5)
Compounds in food that the body requires for proper growth, maintenance, and functioning. (4-5)
Denitrification (4-5)
Conversion of nitrates into nitrogen gas. (4-5)
Limiting Nutrient (4-5)
A nutrient that, in short supply, can limit the productivity of an ecosystem (4-5)