Chem 2- Hybrid Atomic Orbitals (*exam 1)
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Advanced theories of Covalent Bonding
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
what does the wave function contain information about?
each orbital and the wavelike properties of electrons in an isolated atom
when atoms are bound together in a molecules, the wave functions combine to produce new mathematical descriptions that have different shapes.
what is hybridization?
combining wave functions for atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals that can explain molecular geometry and bonding properties.
what are hybrid orbitals
the orbitals resulting from hybridization
do hybrid orbitals exist in isolated atoms?
no, they are formed ONLY in covalently bonded atoms
are hybrid orbitals shaped similarly to atomic orbitals in isolated atoms?
no, they are shaped VERY differently.
how do you generate a set of hybrid orbitals
combining atomic orbitals
the number of hybrid orbitals in a set is equal to the number of atomic orbitals that were combined to produce the set.
are orbitals in hybrid orbitals equal in shape and energy?
yes
what does the type of hybrid orbitals formed in a bond depend on?
electron-pair geometry as predicted by the VSEPR theory
what kind of bonds do hybrid orbitals make when they overlap?
sigma bonds
what kinds of bonds do unhybridized orbitals form when they overlap?
pi bonds
what is a sp hybrid orbital?
one of a set of two orbitals with a linear arrangement that results from combining one s and one p orbital.
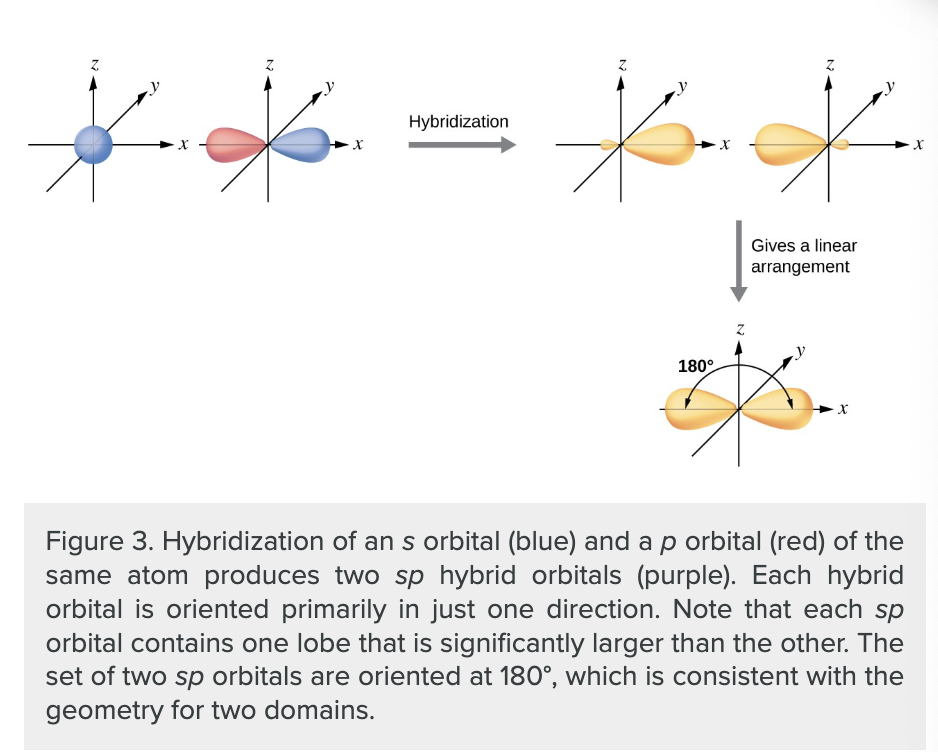
what does the number of atomic orbitals combined always equal?
the number of hybrid orbitals formed.
what gets distributed to the two sp orbitals?
the two electrons previously in the s orbital.
what do energy diagrams represent?
each orbital by a horizontal line - indicating its energy (1s^x, 2s^x, 2p^x…)
and each electron in the energy level indicated by an arrow
one arrow up to indicate one electron in an orbital
two arrows - one up one down to indicate two electrons of opposite sign
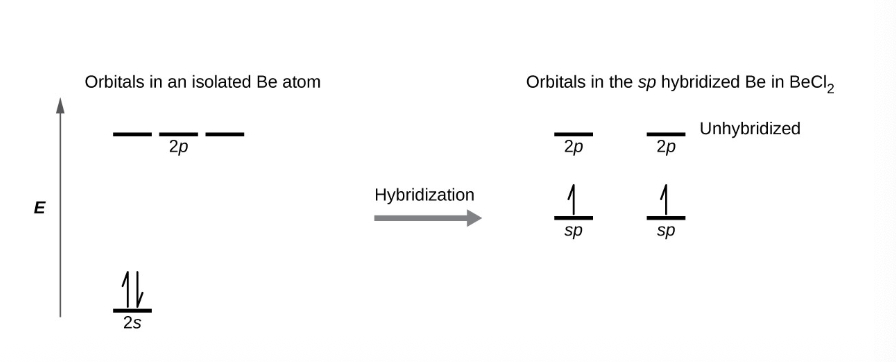
what happens to the valence electrons when atomic orbitals hybridize
they occupy the newly created orbitals
what is sp² hybridization?
mixing one s orbital and two p orbitals to produce three identical hybrid orbitals oriented in a trigonal planar geometry
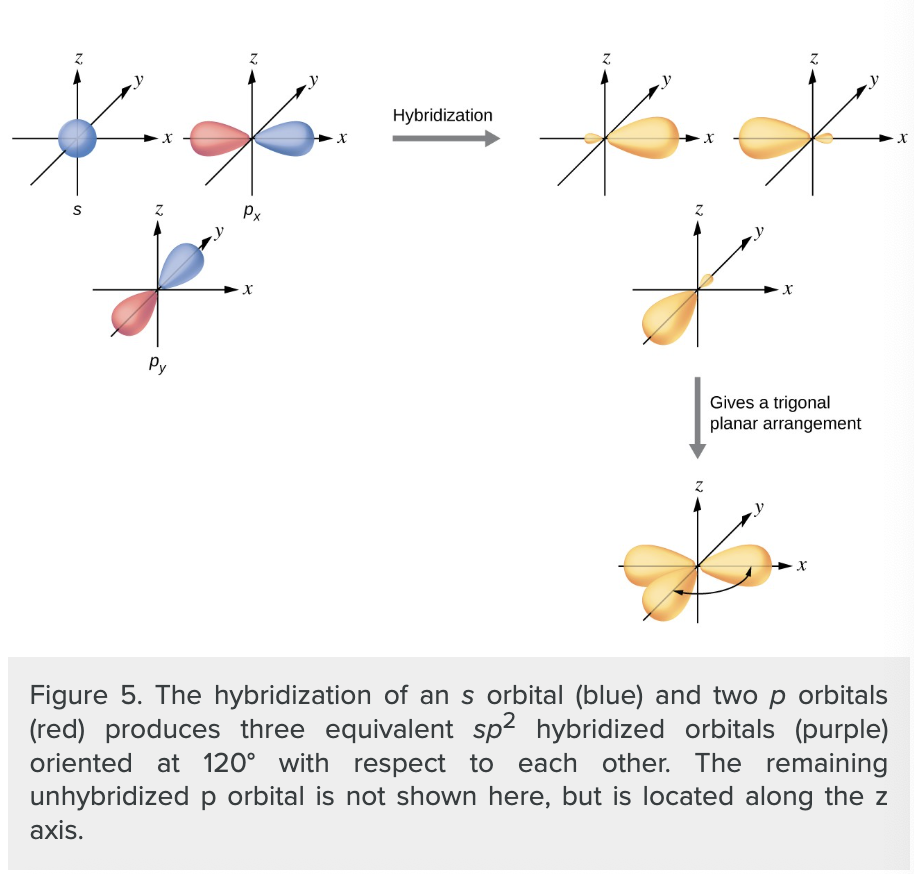
when do we use “thinner” representation of orbital lobes?
whenever the true view is too crowded to easily visualize.
how many regions of electron density does a central atom need to be surrounded by to be sp² hybridized
three regions of electron density
(includes molecules with a lone pair on the central atom OR molecules with two single bonds and a double bond connected to the central atom)
what is sp³ hybridization?
the mixing one s orbital and all three p orbitals
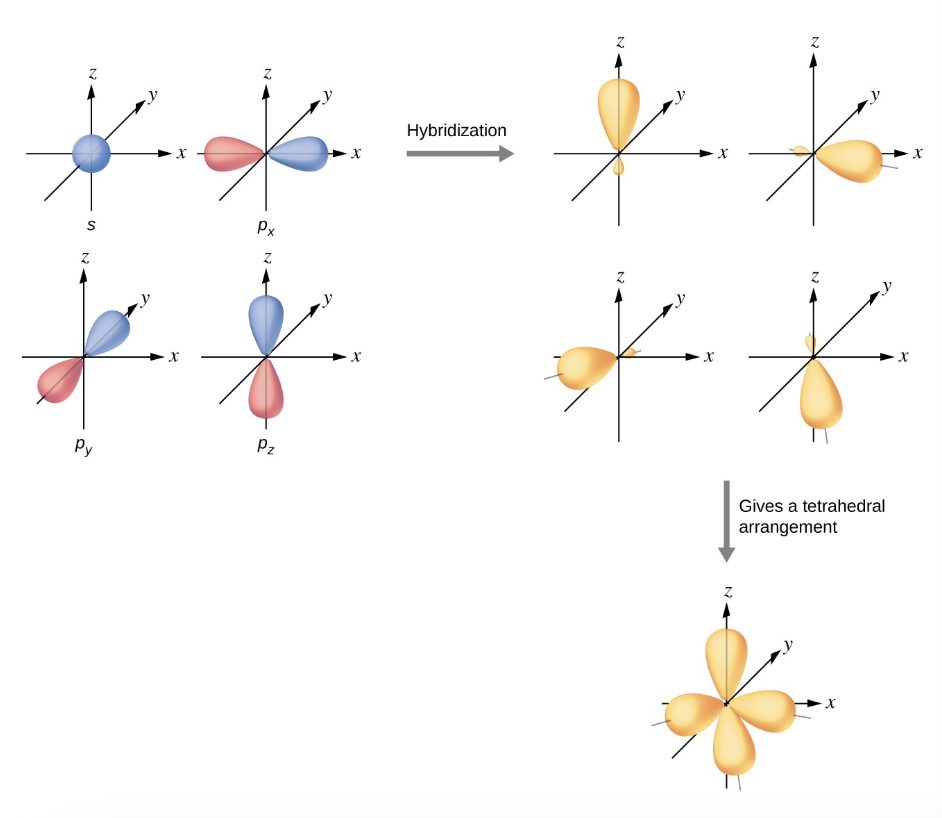
can an sp³ hybrid orbital hold a lone pair of electrons?
no
what is a sp³d hybrid orbital?
one of a set of 5 orbitals with a trigonal bipyramidal arrangement that results from comining one s three p and one d orbital
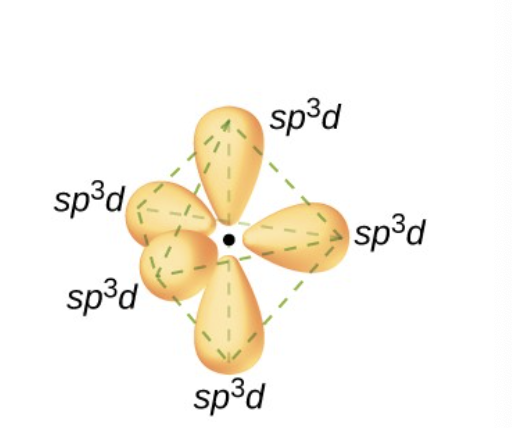
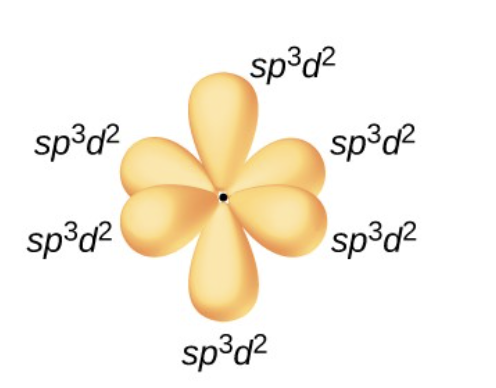
what is a sp³d² hybrid orbital?
one of a set of six orbitals with an octahedral arrangement that results from combining one s three p and two d orbitals
how do we determine the hybridization of an atom?
we base it on the number of regions of electron density that surround it
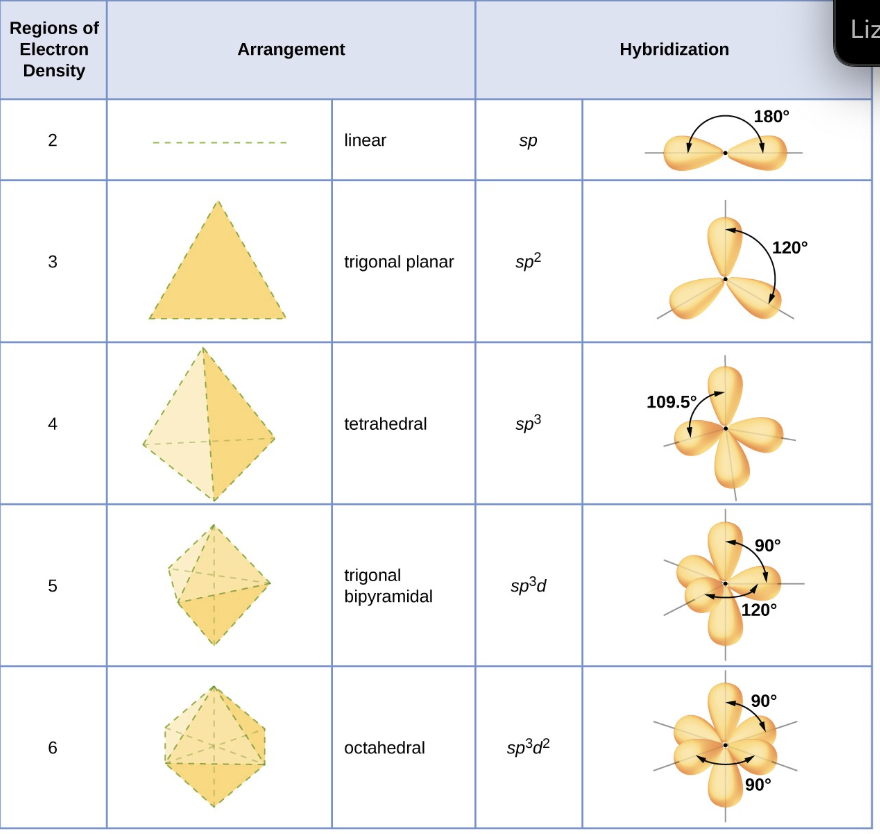
what are the guidelines to find the hybridization of a central atom?
1) determine the lewis structure of the molecule
2) determine the number of regions of electron density around an atom using VSEPR theory, in which single bonds, multiple bonds, radicals, and lone pairs each count as one region
3) assign the set of hybridized orbitals that corresponds the the geometry.