propedeutics - horse practical exam Cartes | Quizlet
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
left
from which side do we approach a horse ?
from left side
1. pass lead rope around neck
2. place noseband over horse's nose
3. bring crownpiece (top strap) up behind ears
4. fasten buckle (left side)
how do you put on a headcollar / halter ?
safety knot
what type of knot to tie-up the horse ?

ear twist
skin fold
lip twitch
lifting a limb
rope support
what are the different immobilization methods
horses attitude
signs of pain
anamnesis
what are the first things we need to assess before touching the horse ?
28 - 40 bpm
adult horse - heart rate range ?
10 - 20 rpm
adult horse - respiratory rate range ?
37 - 38.5
adult horse - temperature range ?
80 - 120 bpm
foal - heart rate range ?
24 - 36 rpm
foal - respiratory rate range ?
37.5 - 39
foal - temperature range ?
position
facial symmetry
visible wounds
trauma
abnormal growths
what is the first thing we check when examining the head ?
cranial to caudal
examination of a horse must be done in which order ?
dermatitis
mobility loss
depigmentation
what are we looking for in the examination of external lips ?
lift upper lip
how do we look at the oral mucous membranes ?
capillary refill time
colouration and hydration of mucous membranes
what do we evaluate in the examination of mucous membranes ?
less than 2 seconds
ideal capillary refill time ?
pale pink and moist
ideal mucous membranes ?
use thumb to open bars of the jaw
externalise laterally the tongue
how do we inspect the oral cavity ?
visible wounds
ulcers
colour
movement
smell
what are we looking for in the examination of the tongue ?
physiological / pathological morphological changes that cause damage
(enamel tips, hooks)
what are we looking for in the examination of premolars & molars ?
evaluate correct fusion
(especially foals)
what are we looking for in the examination of palate ?
maxillary artery
facial artery
where can we take the arterial pulse ?
maxillary artery (pulse)
what is being palpated ?
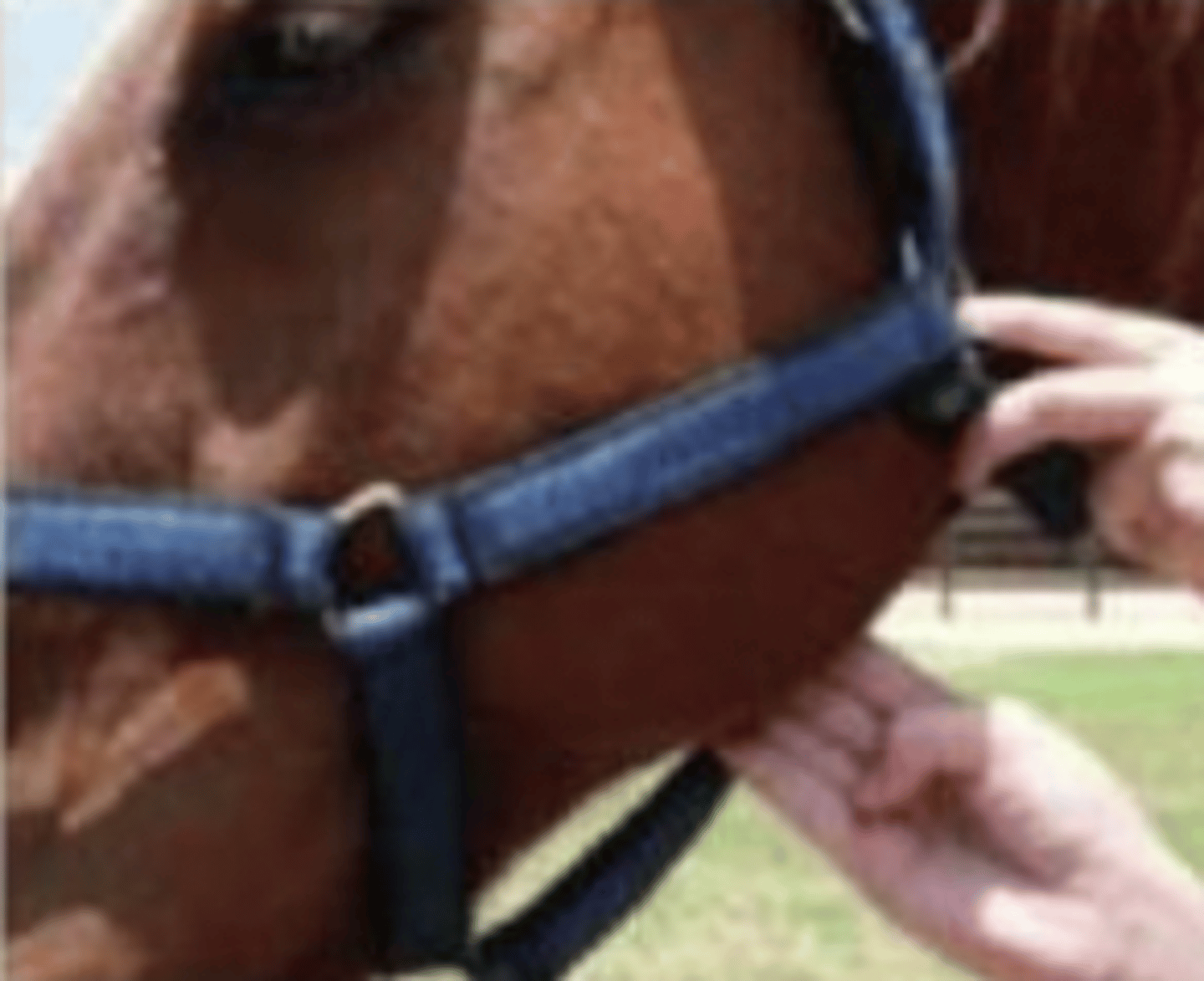

facial artery (pulse)
what is being palpated ?
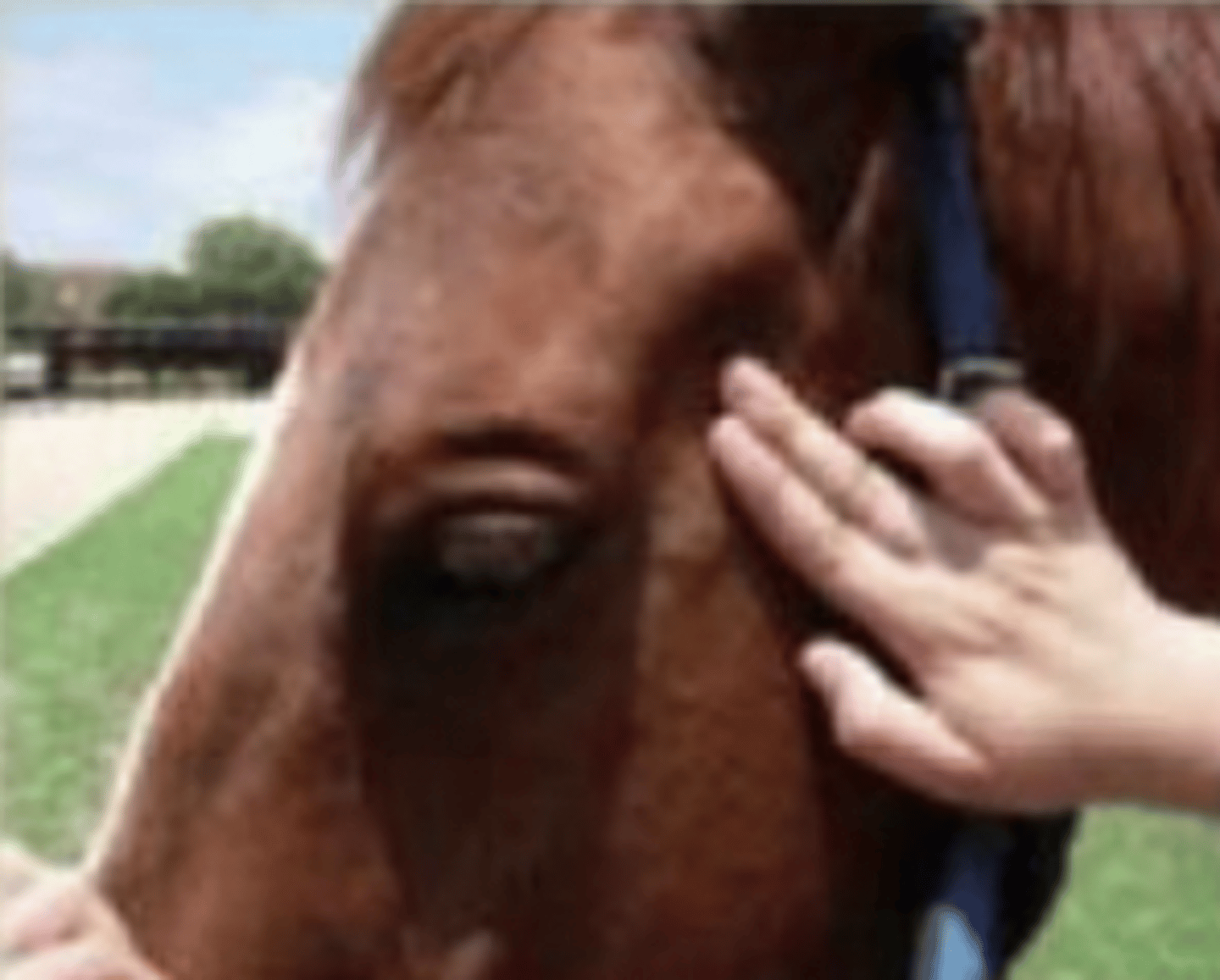

! side of face !
where do we stand when evaluating nostrils ?
hands in front of nostrils (regularity and same flow in both)
how do we assess airflow symmetry ?
airflow symmetry
observe mucosa
response of sensory hairs to tactile stimulus
nasolacrimal duct opening
what is done during nostril examination ?
nasolacrimal duct opening
what is this ?
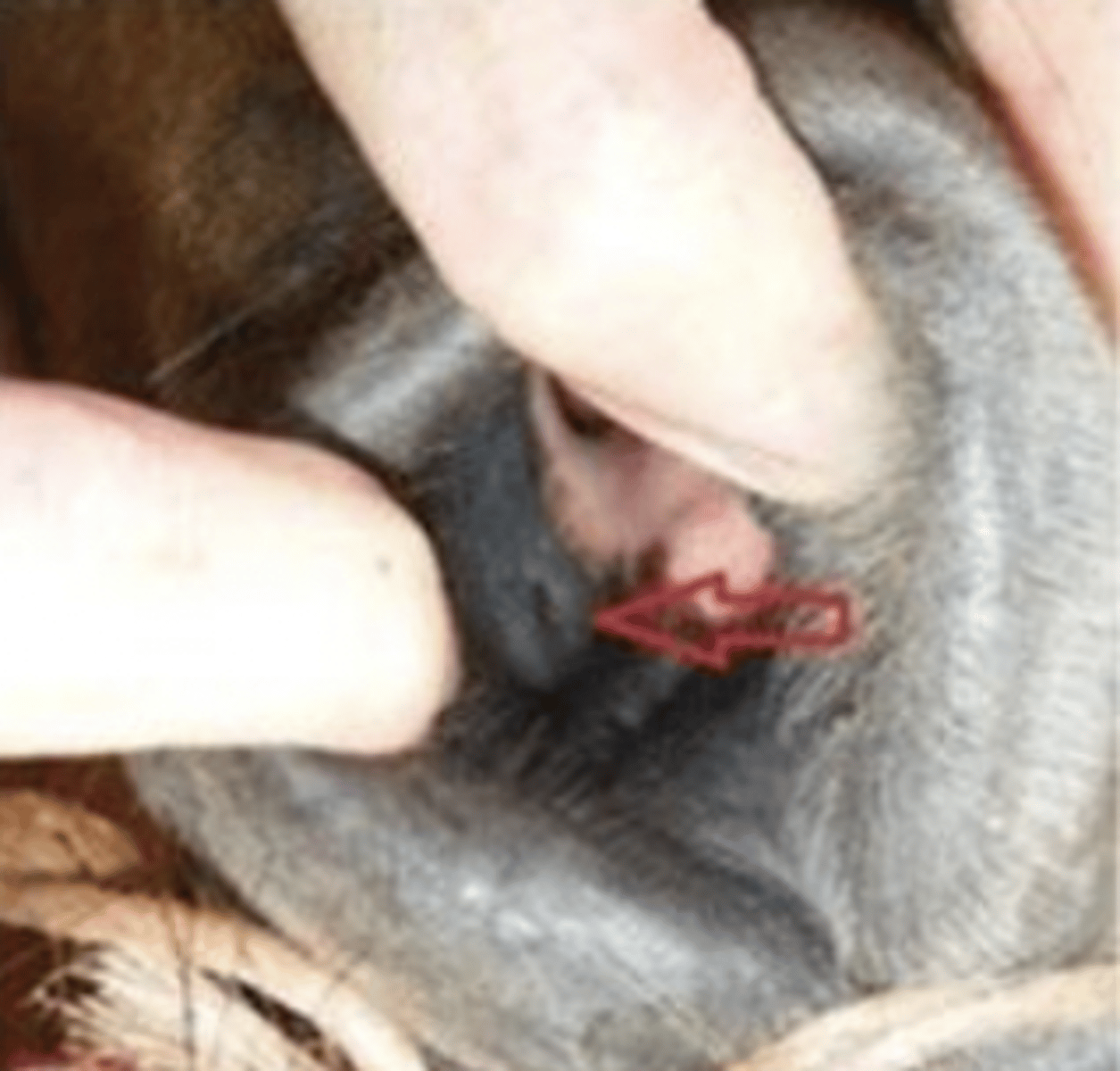
just behind mandible on both sides of neck
where can the parotid gland be palpated ?
submandibular
retropharyngeal
prescapular
precrural
which lymph nodes are palpable on a horse ?
submandibular lymph node
red ?
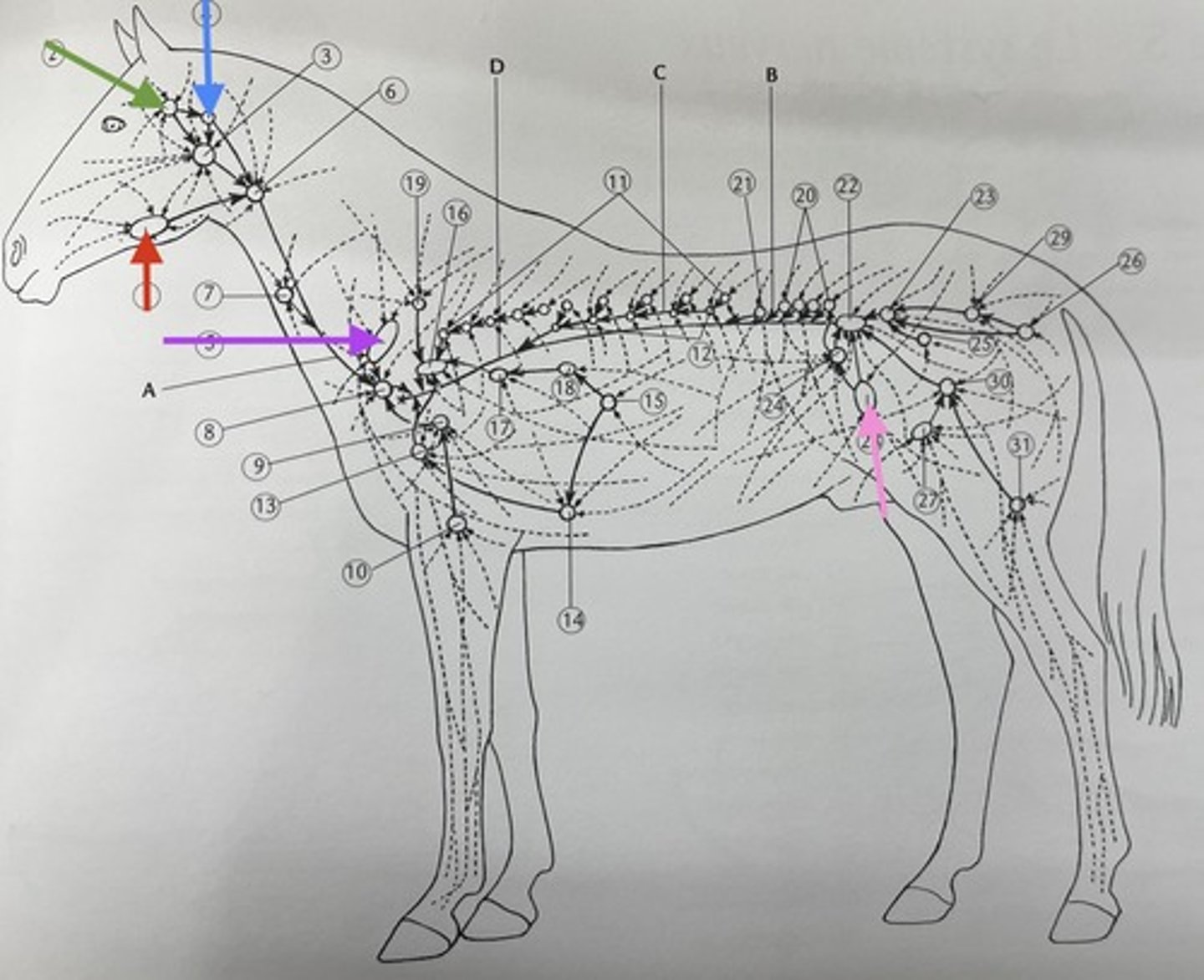
parotid gland
green ?
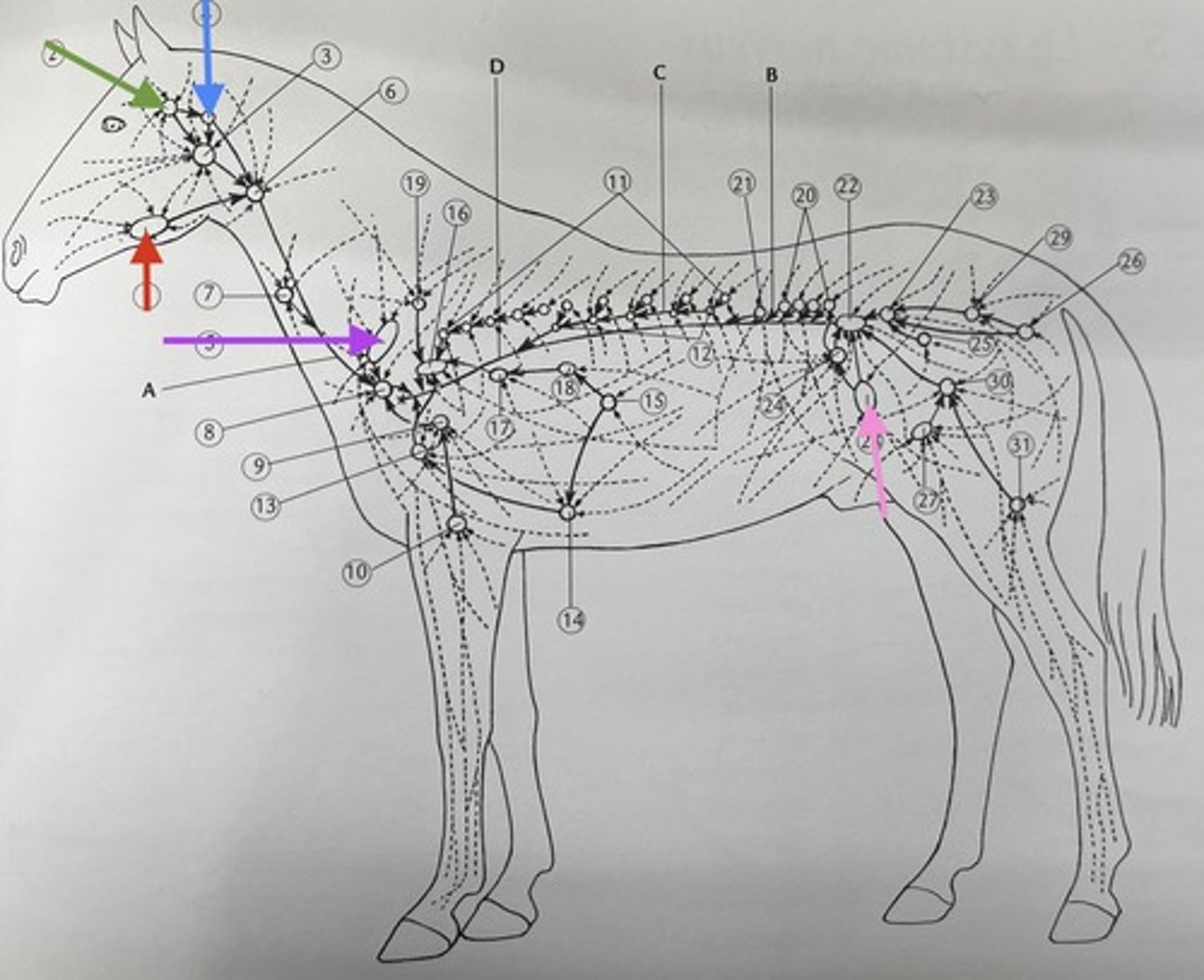
retropharyngeal lymph node
blue ?
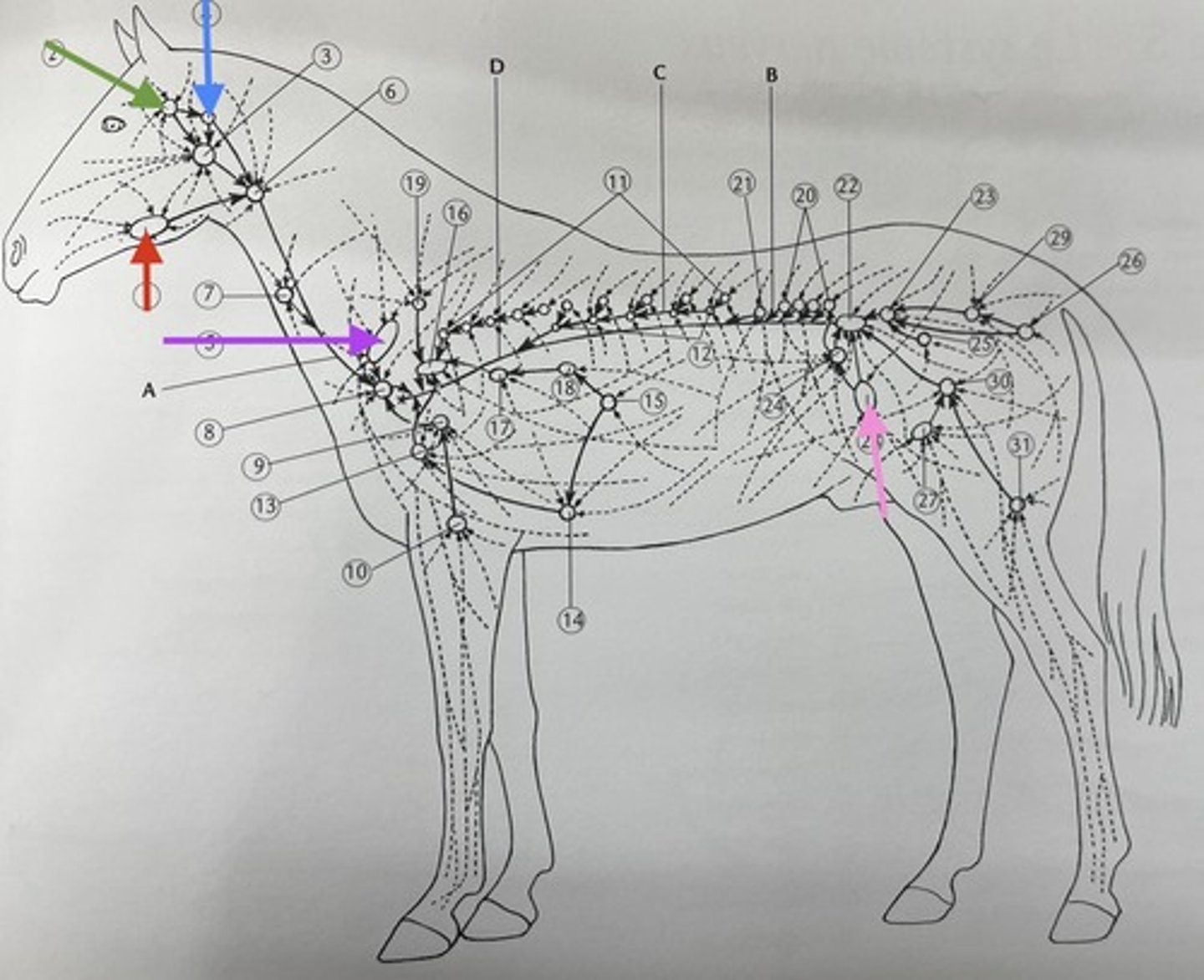
prescapular lymph node
purple ?
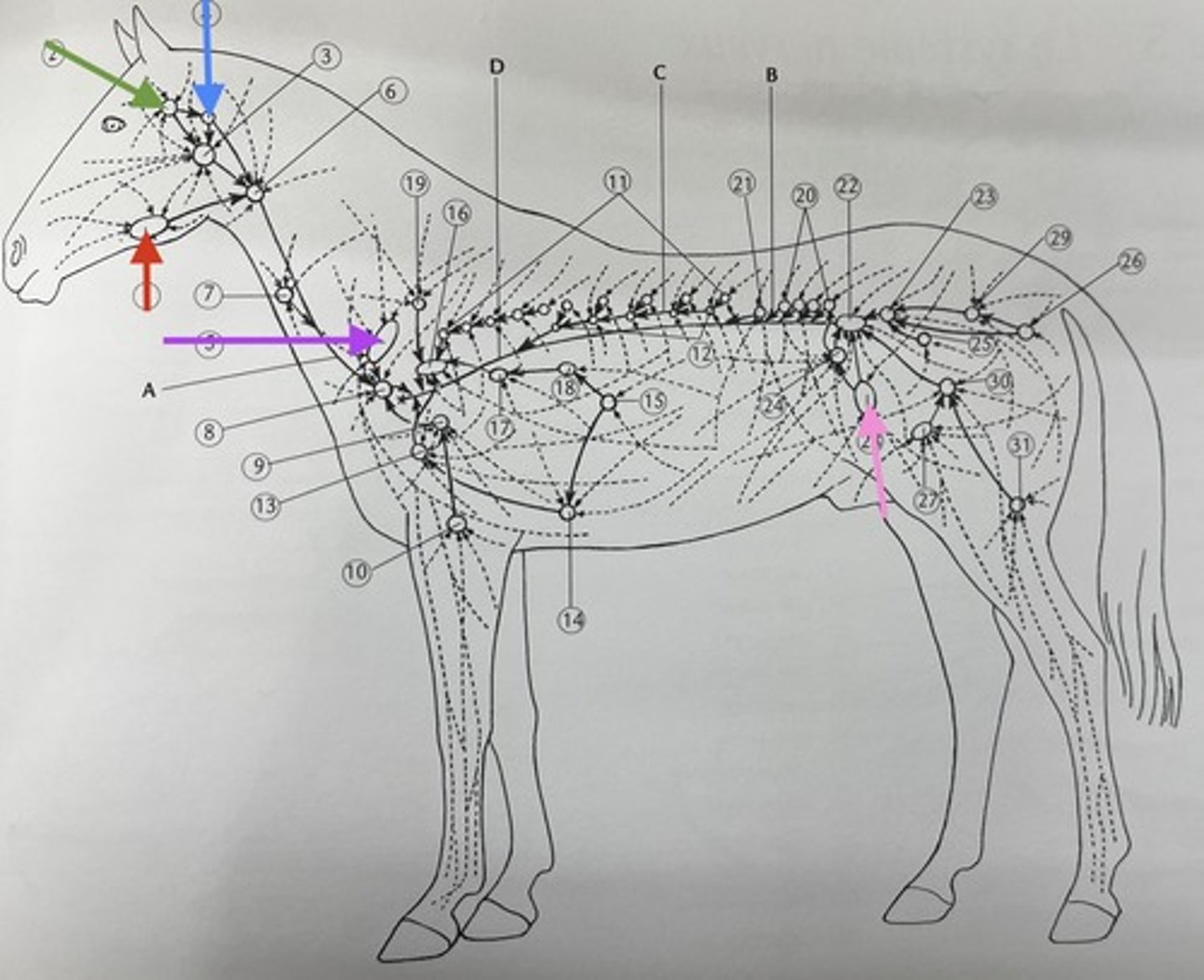
precrural lymph node
pink ?
symmetry
what are we looking for when INSPECTING the sinuses ?
heat
pain
fluctuation
instability
changes in consistency
what are we looking for when PALPATING the sinuses ?
frontal sinus (upper forehead)
maxillary sinus (cranial to molar teeth)
where do we PERCUSS the sinuses ?
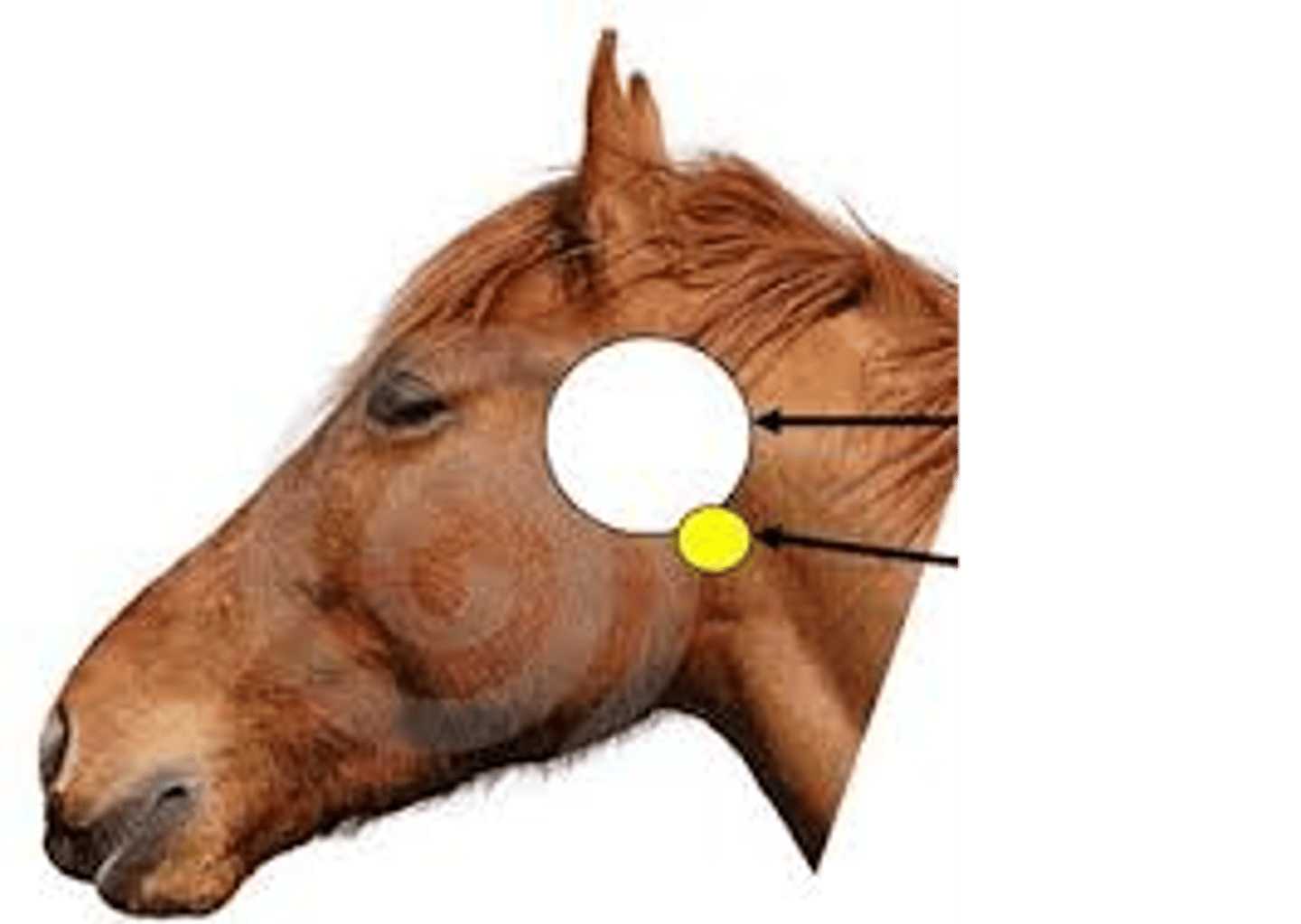
guttural pouch
white circle ?

sliding eyelids laterally
how do we evaluate the conjunctival mucosa ?
dorsal margin of the iris
location of corpora nigra ?
block and filter sunlight
aid pupil constriction
improve depth perception
function of corpora nigra ?
medial corner of the eye
location of nasolacrimal duct ?
gentle tactile stimuli on sensory hairs/eyelashes
what is the palpebral reflex ?
trigeminal nerve (V)
facial nerve (VII)
which nerves are being evaluated in the palpebral reflex ?
a quick movement towards the eye
what is the menace response ?
optic nerve (II)
facial nerve (VII)
which nerves are being evaluated in the menace response ?
exerting pressure at base of ear -> crackling = otitis
what is the click test ?
skin tent
jugular fill/emptying time
how do we assess horses hydration ?
nostril movement
flank movement
tracheal auscultation
how can we determine respiratory rate in a horse ?
in 3 points : proximal, middle, distal
how do we auscultate the trachea ?
5 intercostal points per side:
3 dorsal
2 ventral
Normal = quiet sounds (sometimes masked by gut sounds)
lung auscultation on a horse ?
slap shoulder -> to generate abduction reflex of laryngeal cartilage
what is a slap test ?
left side - 5th ICS
placement for ausculation of mitral valve ?
left side - 4th ICS
placement for ausculation of aortic valve ?
left side - 3rd ICS
placement for ausculation of pulmonic valve ?
right side - 4th ICS
placement for ausculation of tricupsid valve ?
right dorsal quadrant (borborygmi)
placement for auscultation of ileocecal valve ?
right dorsal
left dorsal
right ventral
left ventral
what are the 4 quadrants for abdomen ausculation ?
6-8 bowel movements per minute
normal intestinal motility ?
stand on side, lateralize tail
insert thermometer diagonally
proper technique to take horses temperature ?
standing laterally, facing caudal
proper technique to lift limbs ?
hoof tester
what tool is being used ?

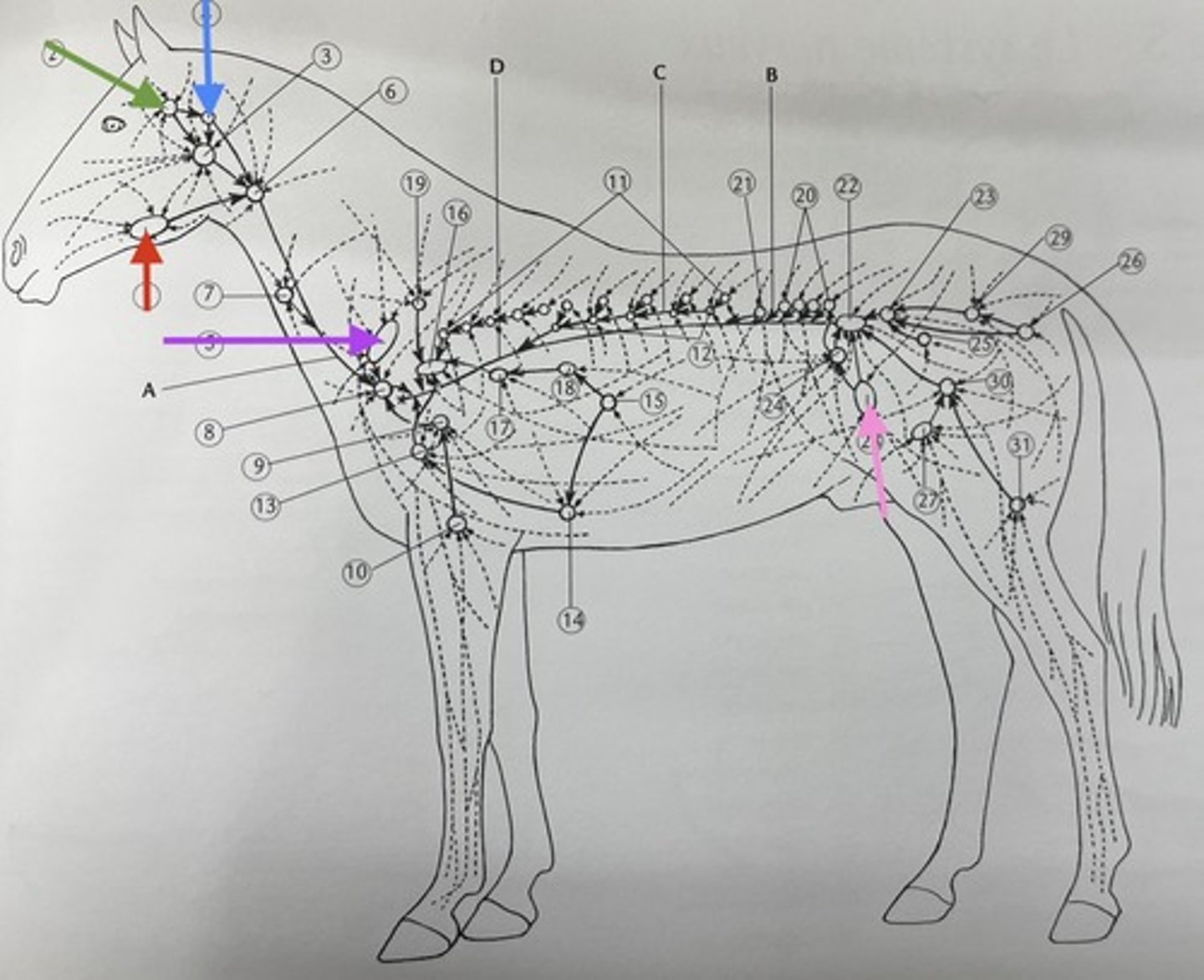
accessory carpal bone
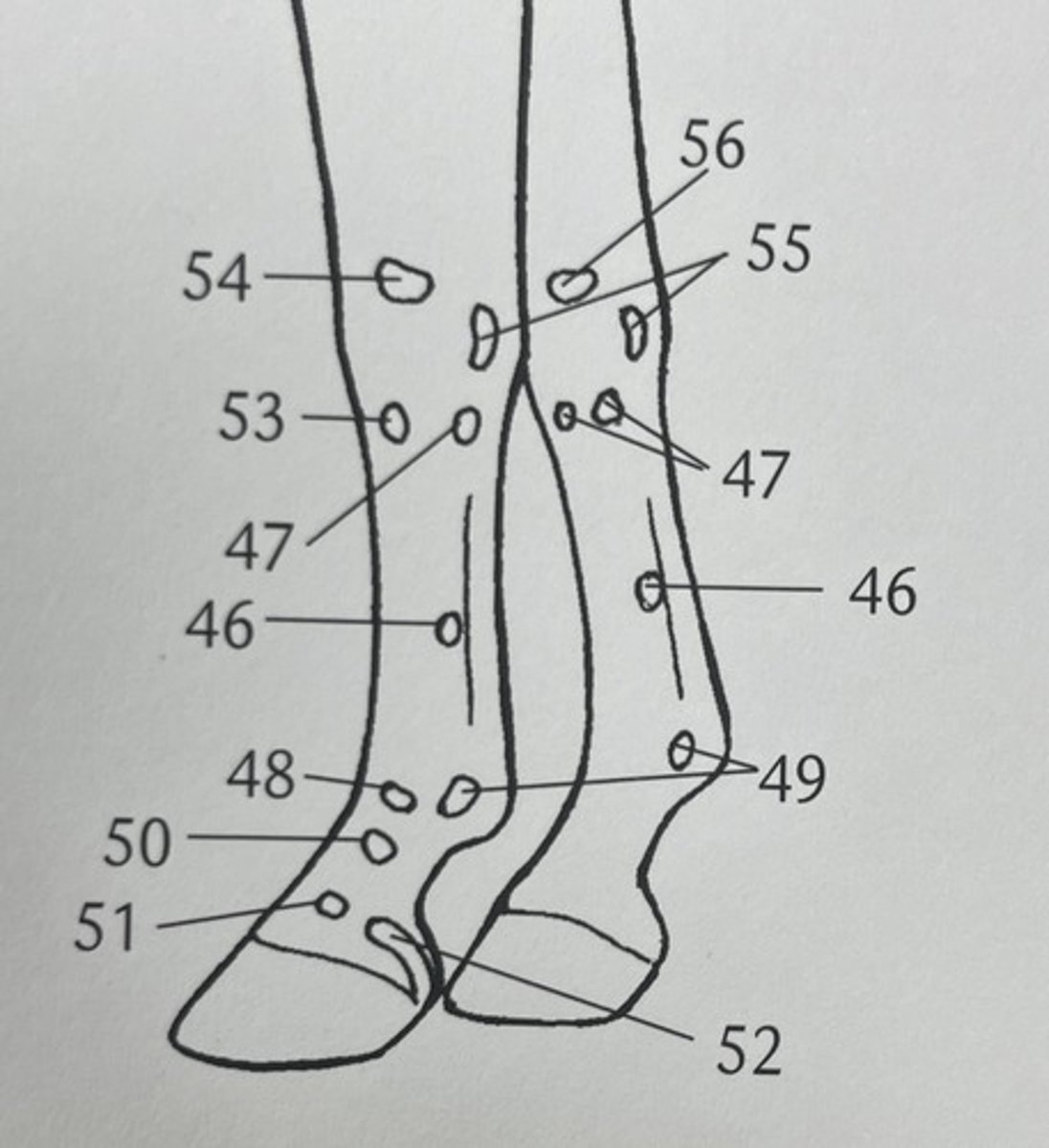
which palpable bone structure is 55 ?
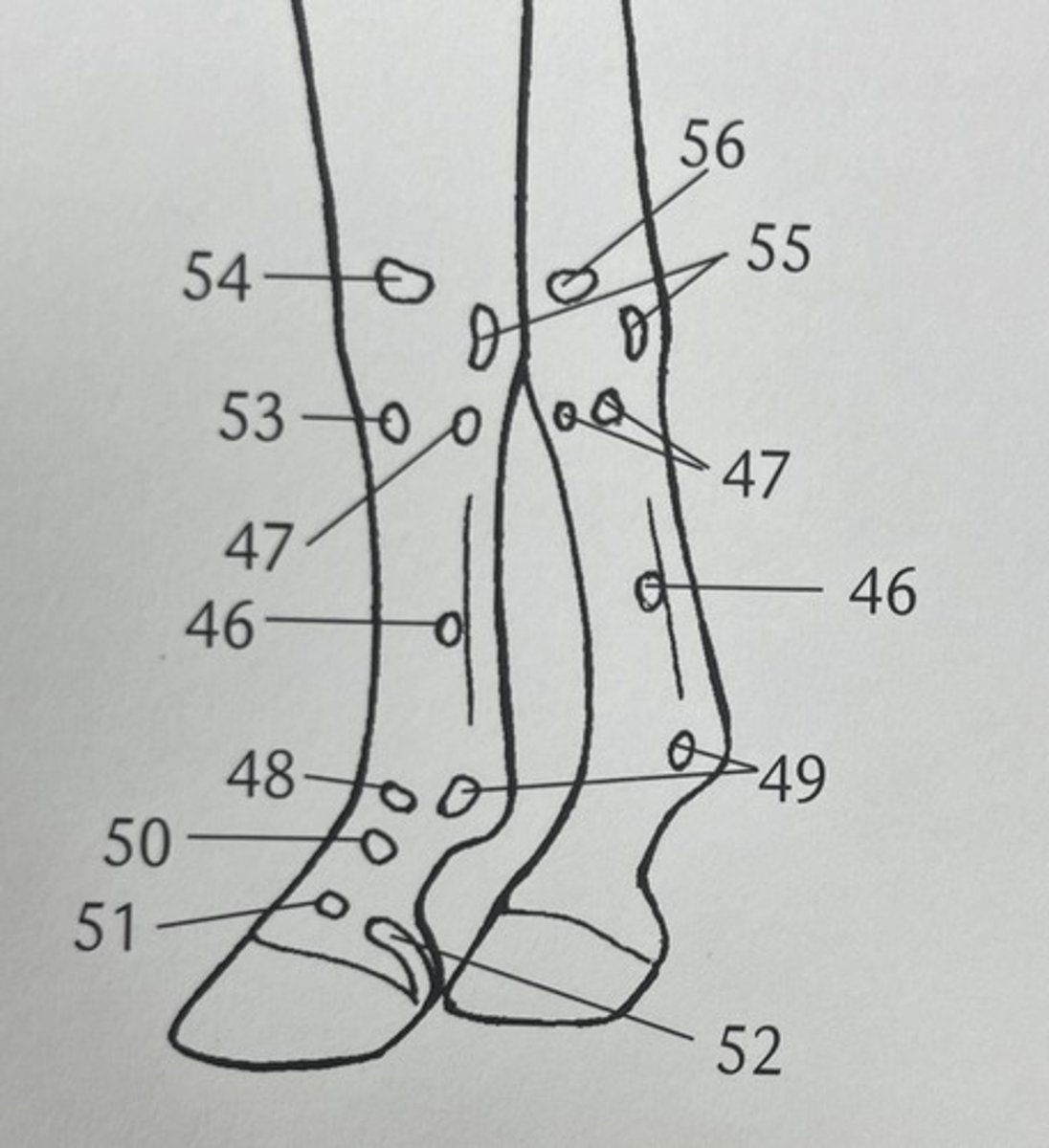
proximal extremity of metatarsals and rudimentary metatarsals
which palpable bone structure is 45 ?
distal extremity of MC II/IV (terminal buttons)
what palpable bone structure is 46 ?
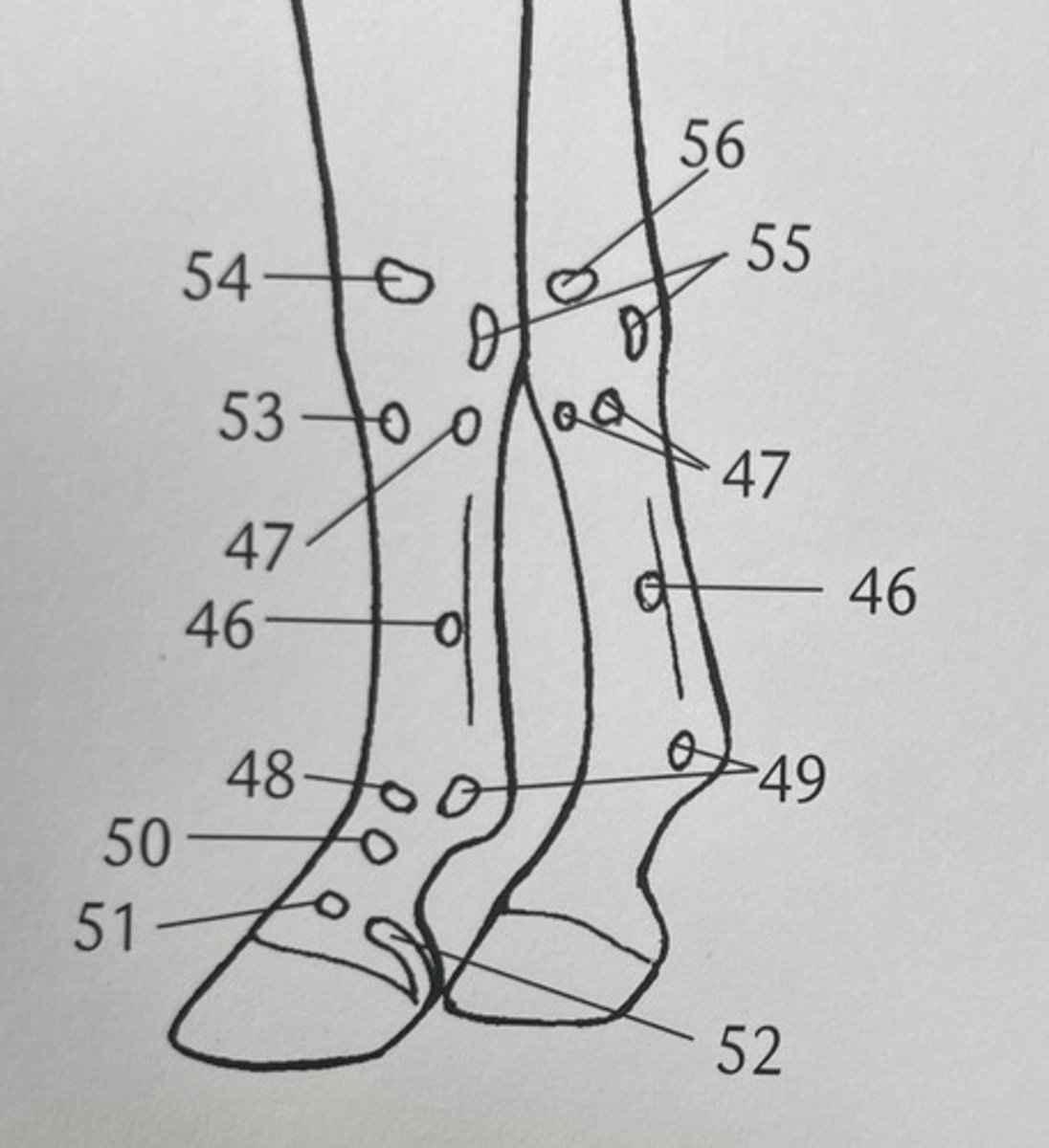
distal extremity of rudimentary metatarsals
which palpable bone structure is 46 ?
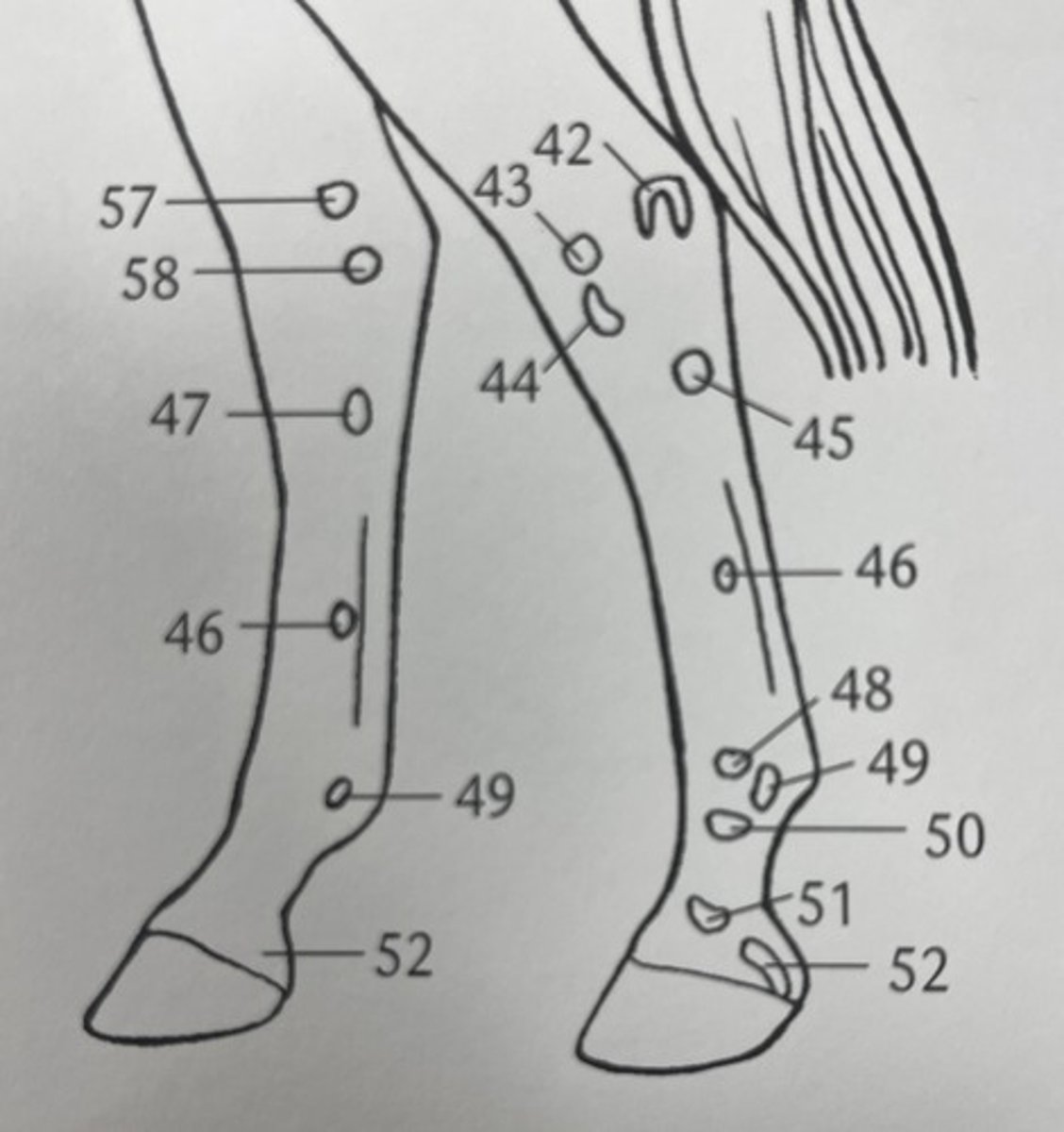
calcaneum tuberculosis
what is palpable bone structure 42 ?
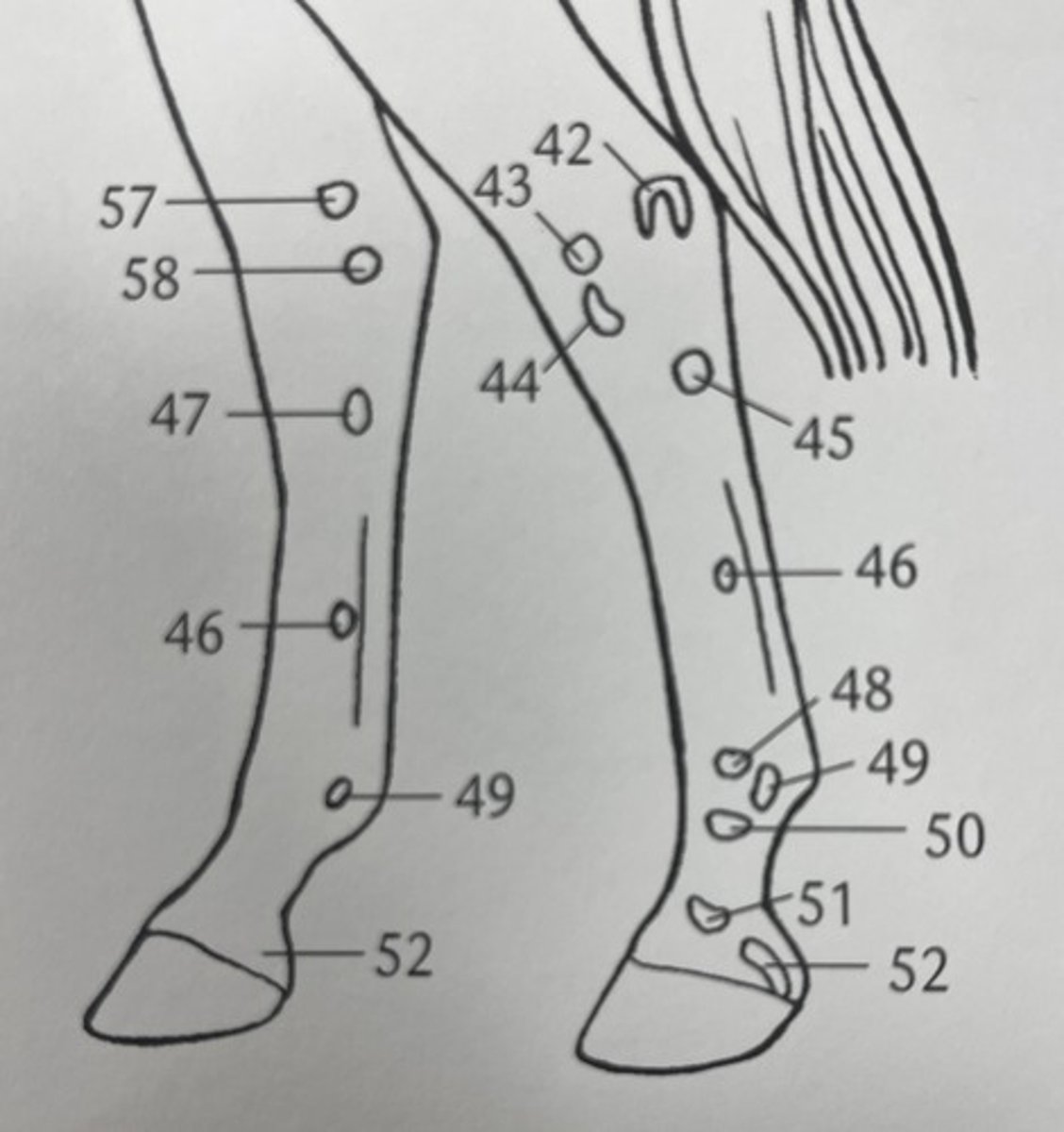
gastrocnemius muscle
what is this ?

proximal sesamoid bones
what is 49 ?
sesamoid level - palmar/plantar digital artery
where do we take the digital pulse ?
pastern joint
what joint for P1 - P2
coffin joint
what joint for P2 - P3
fetlock joint
what joint for MIII - P1
long pastern bone
phalange 1 is also known as ?
short pastern bone
phalange 2 is also known as ?
coffin bone
phalange 3 is also known as ?
just above caudal part of coffin bone
where is the navicular bone located ?
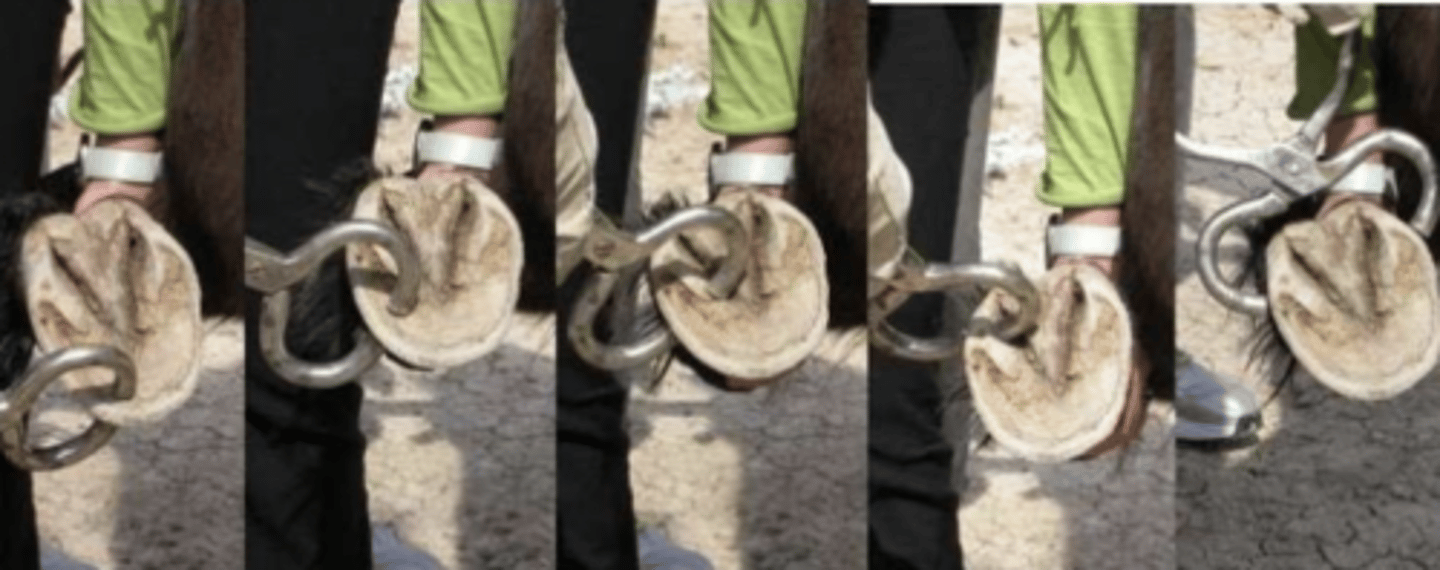
taking the digital pulse
what is happening here ?
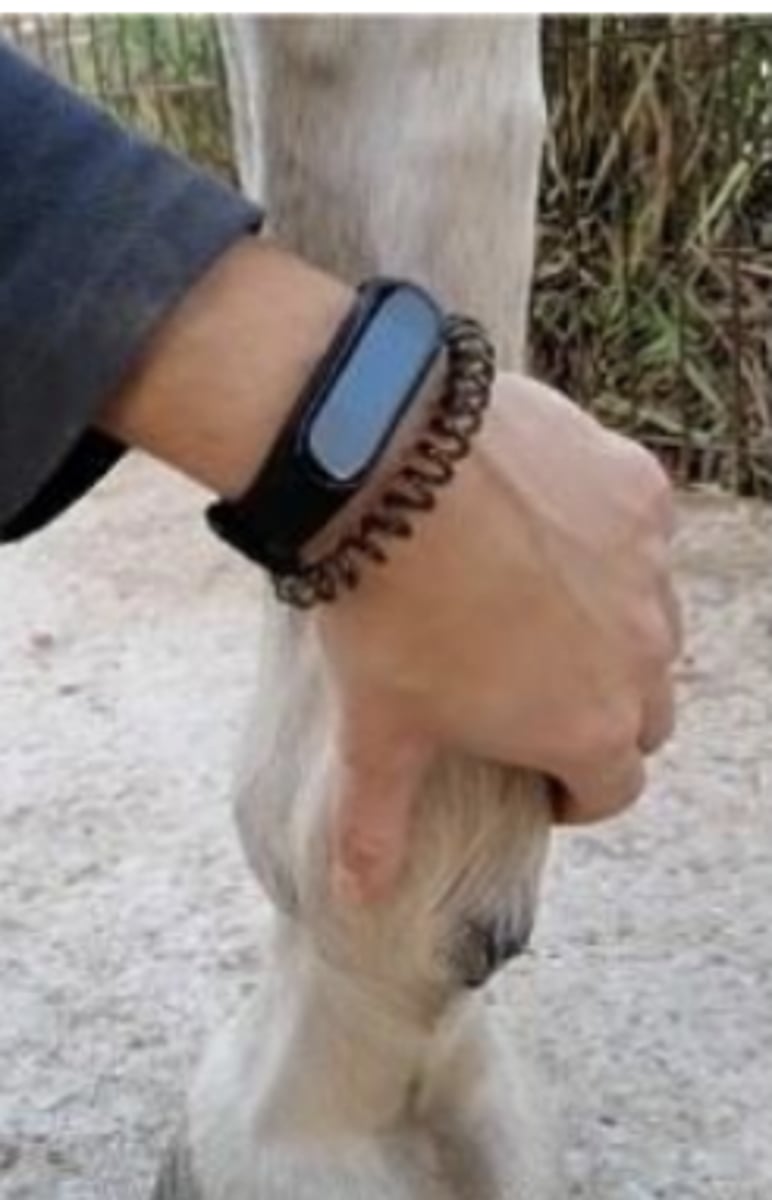

flex each joint, applying pressure to check for pain response
what happens during the passive flexion test ?
superficial digital flexor tendon
deep digital flexor tendon
suspensory ligament of the fetlock
the most important package of a horse's limb is composed of what structures ?
deep digital flexor tendon
what is 4 ?
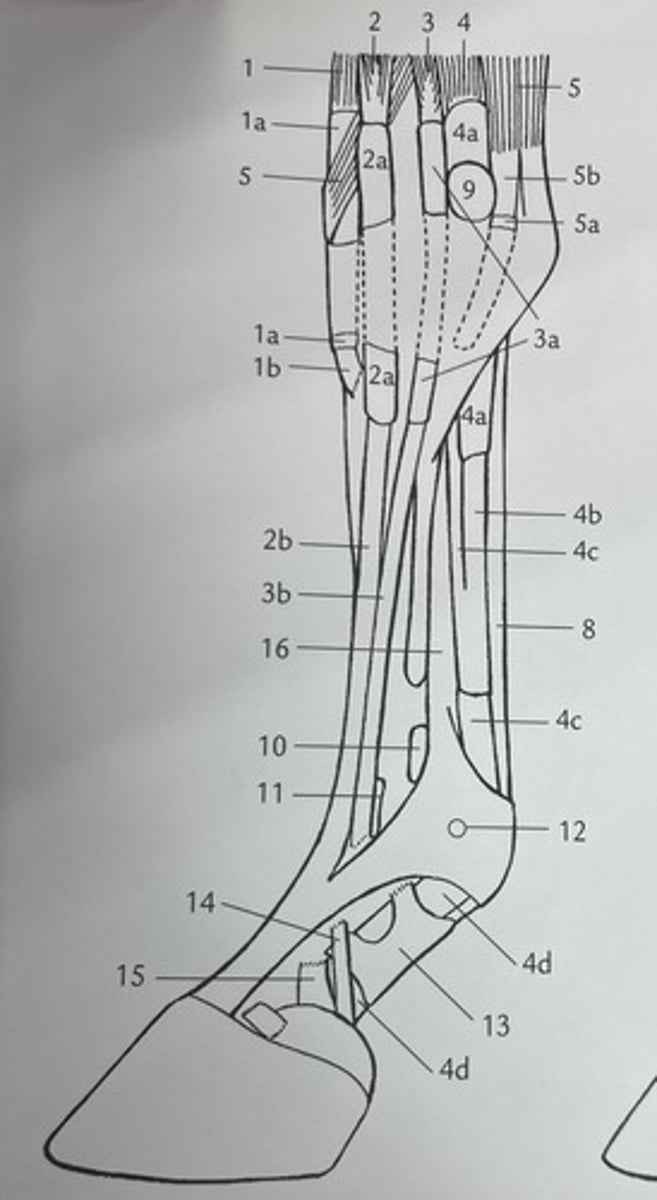
suspensory ligament of the fetlock
what structure is coloured in purple ?

superficial digital flexor tendon
what is 8 ?
soft & hard ground
straight line & in circles
at walk, trot & canter
how is the horse evaluated in a dynamic exam ?
Flex each joint → pressure
Distal joints: 30 sec
Proximal joints: 45 sec
Immediately trot on hard ground
how to perform active flexing test ?
intramuscular
intravenous
oral
what are the 3 ways to administer medication to horses ?
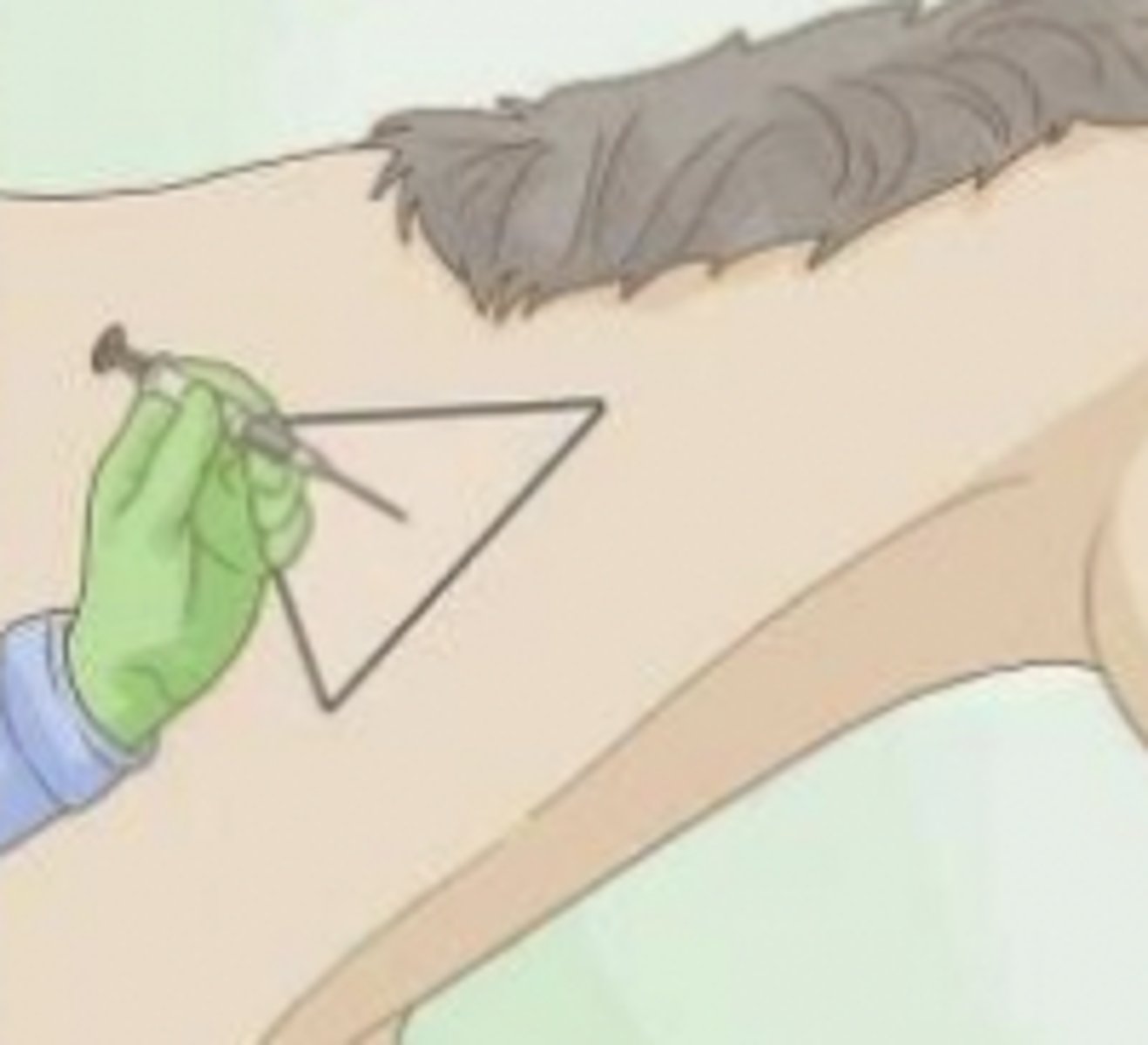
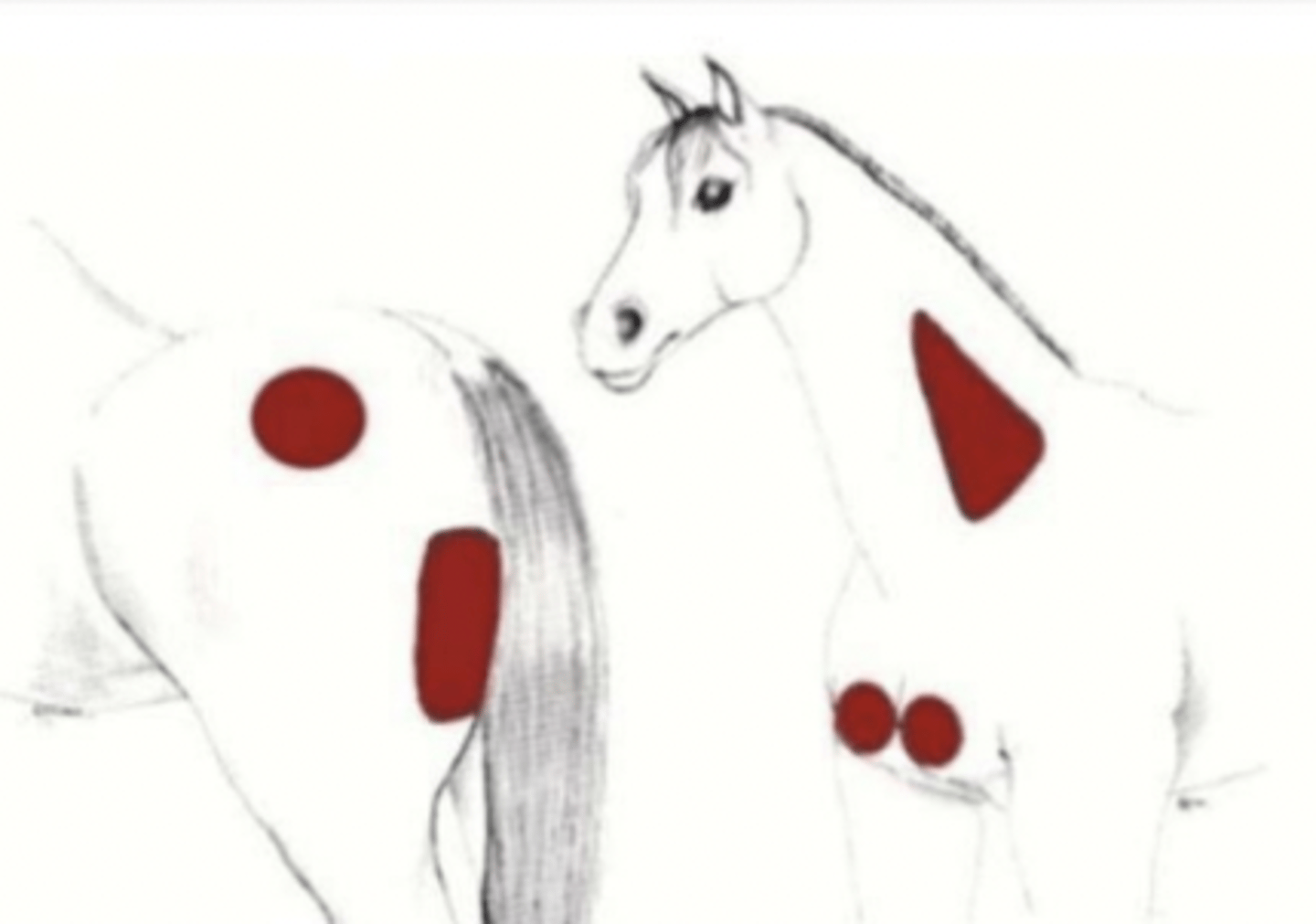
neck (triangle)
pectoral muscles
semitendinous/semimembranous muscles
which areas to do an intramuscular injection ?
jugular vein
which is the most common area for intravenous injection ?
Needle alone (no syringe) at 30° angle → check blood:
Vein = dark, no pressure
Artery = bright red, spurting (WRONG!)
Connect syringe after confirmation.
what steps must we take to complete intravenous injection ?
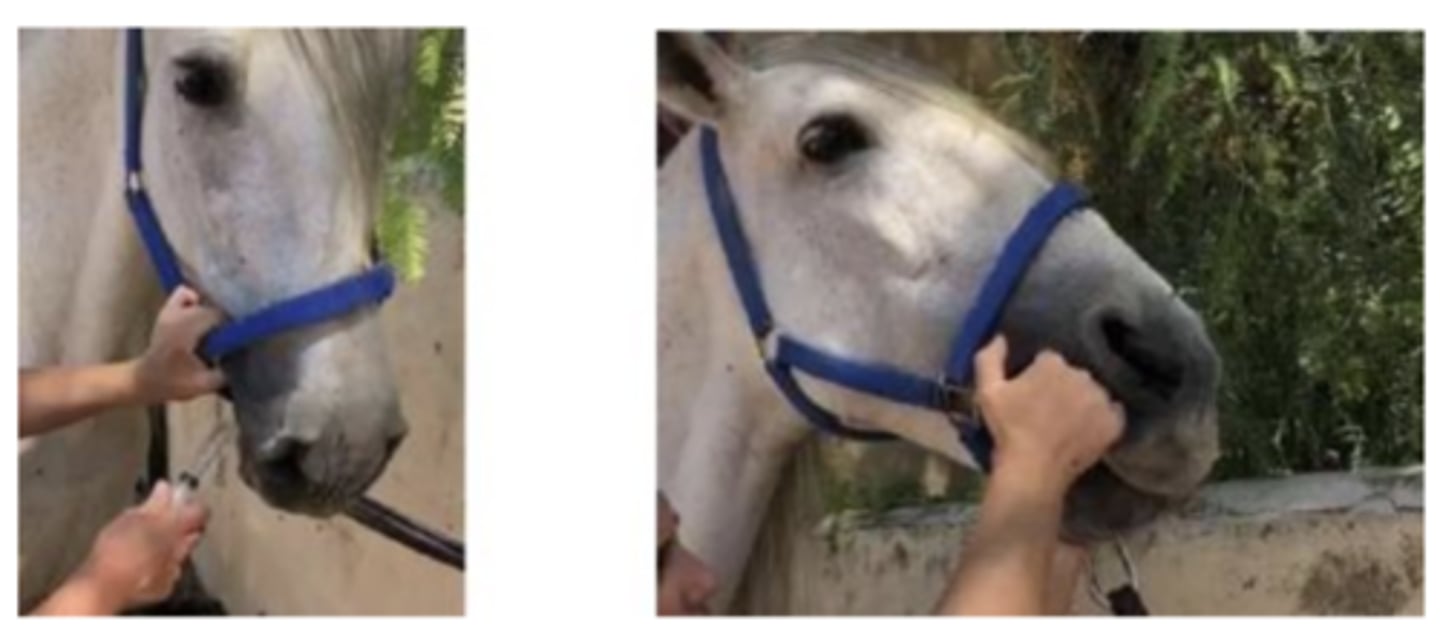
through diastema, head slightly elevated
how do we administer medication orally ?
the triangle where we can administer intramuscular injections
what is this image showing ?
the different areas for intramuscular injections
what is this diagram showing ?

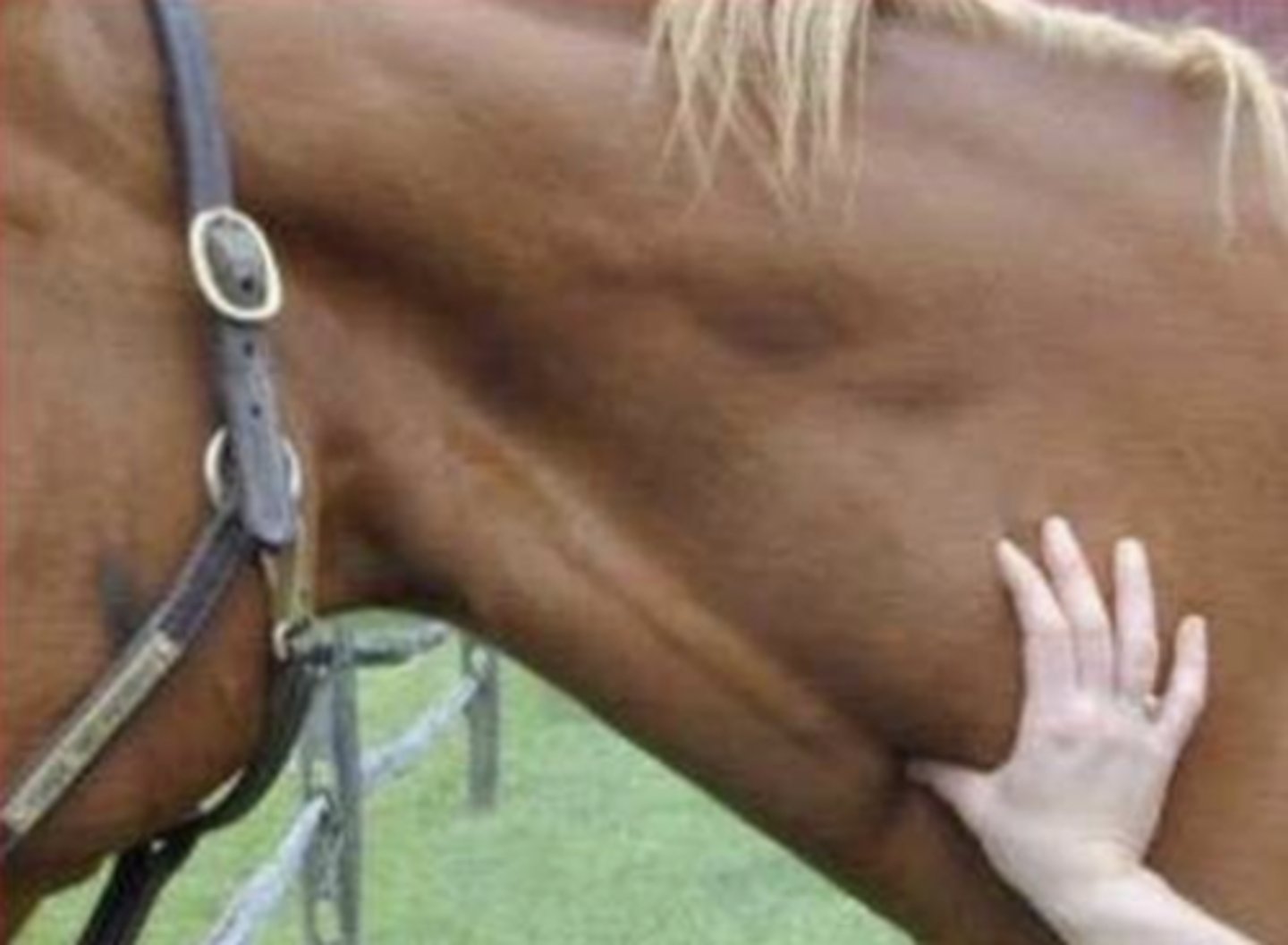
applying pressure to fill jugular vein
what is this image showing ?

administering oral medication
what is this image showing ?
