1.3 Classification and Structure of Prokaryotic Cells
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
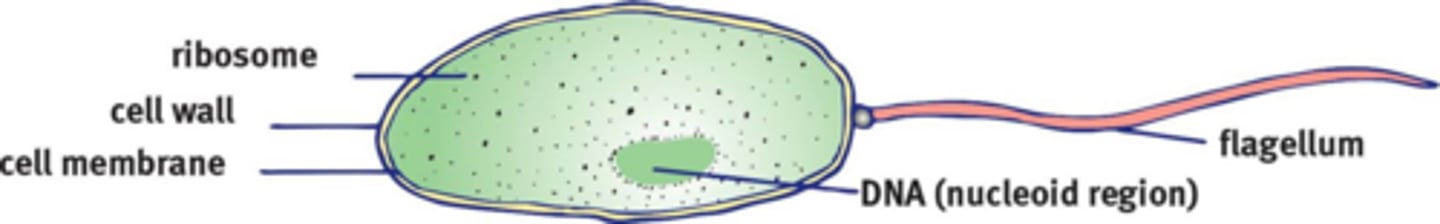
Nucleoid Region
Houses the circular DNA.
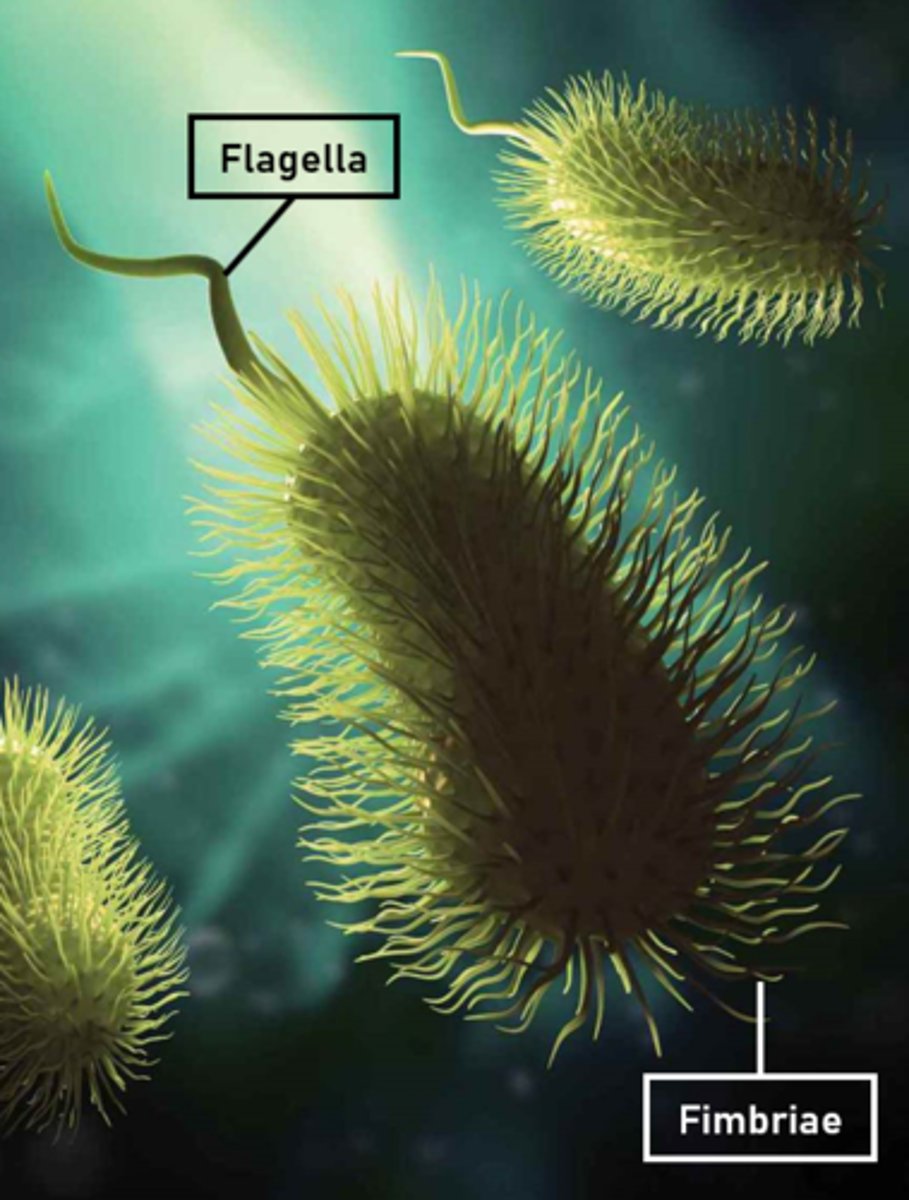
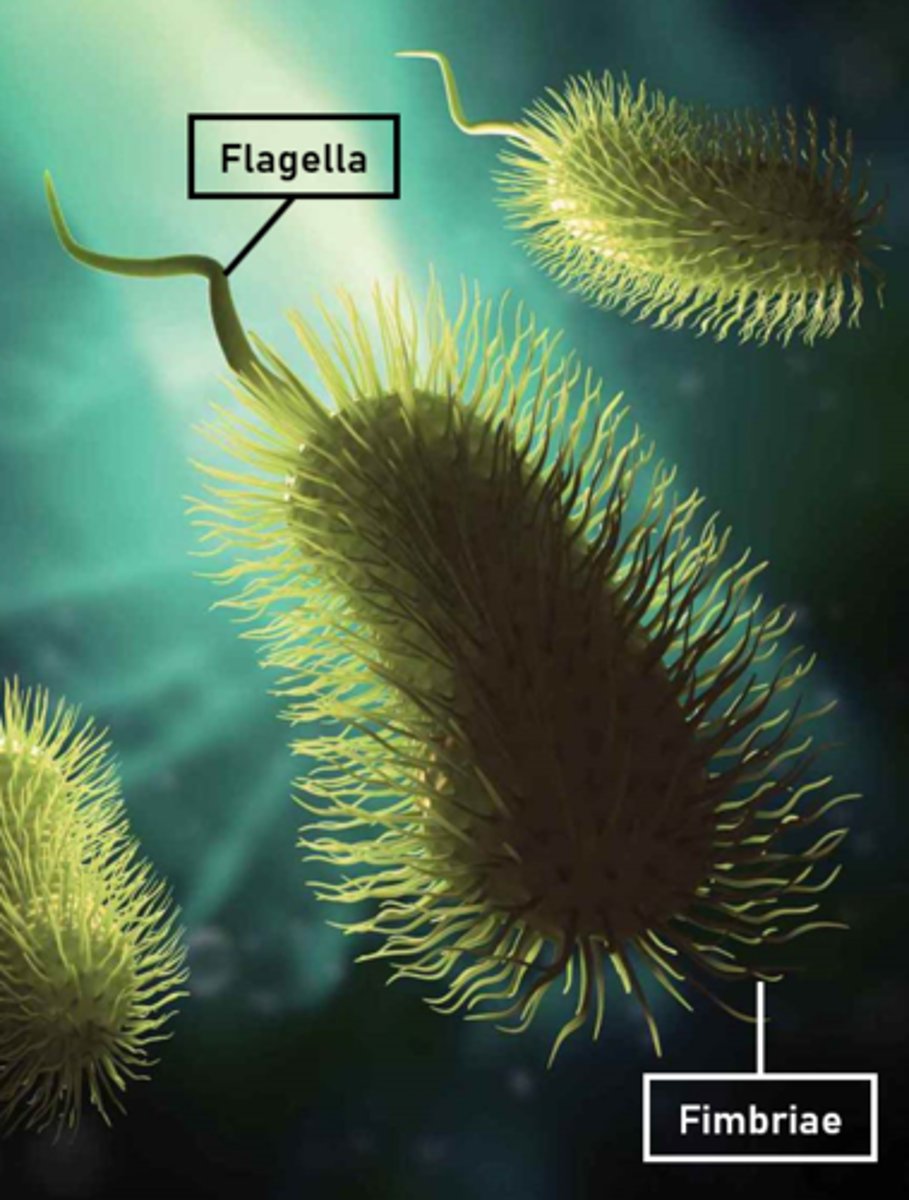
Fimbriae
Similar to cilia.
Bacteria in the Human Gut
Produce vitamin K and biotin which prevents the growth of harmful bacteria.
Chlamydia Trachomatis
Live inside the cells of the reproductive tract and cause a common STI.
Clostridium Tetani
Live outside of cells and produce toxins that cause tetanus.
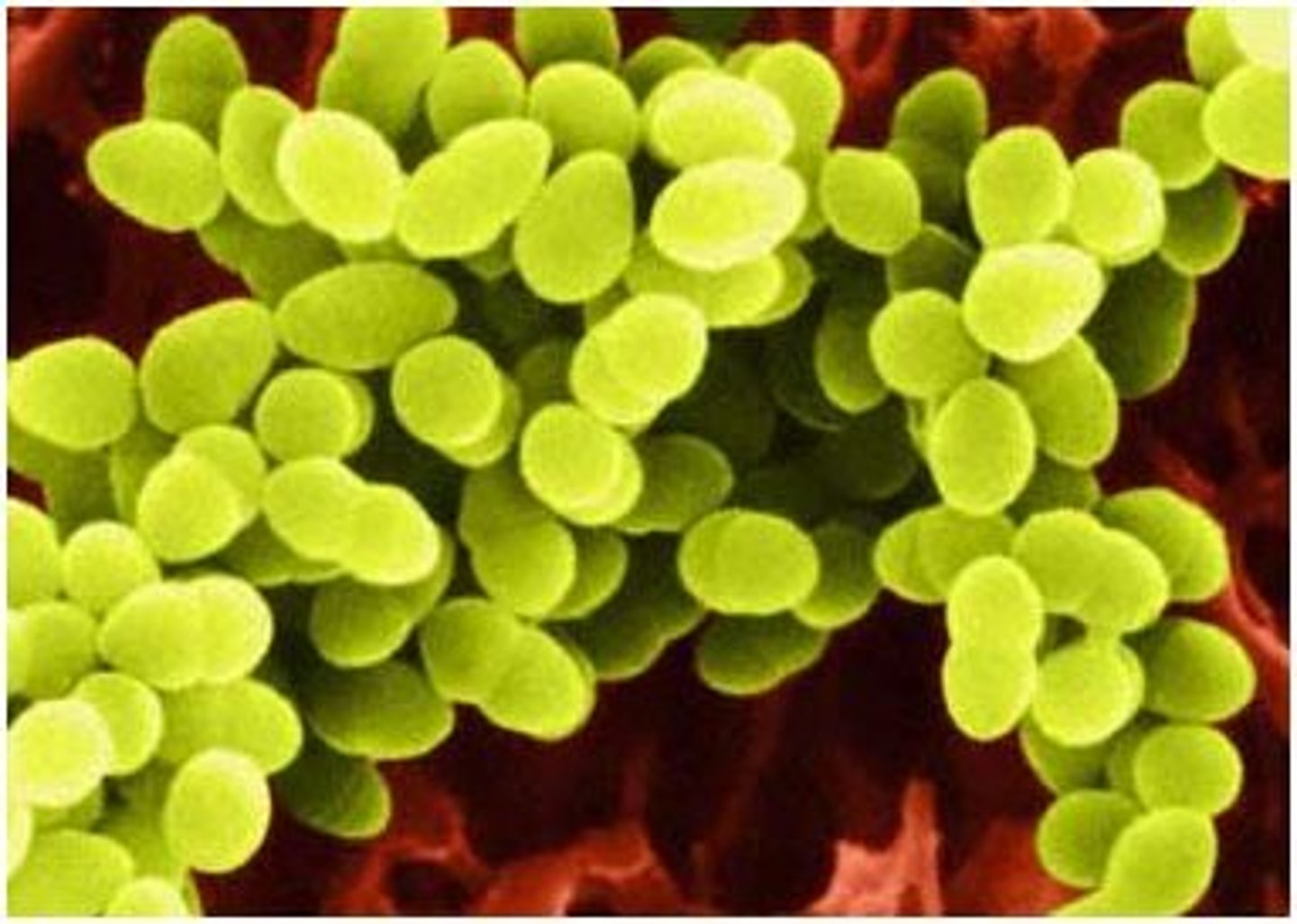
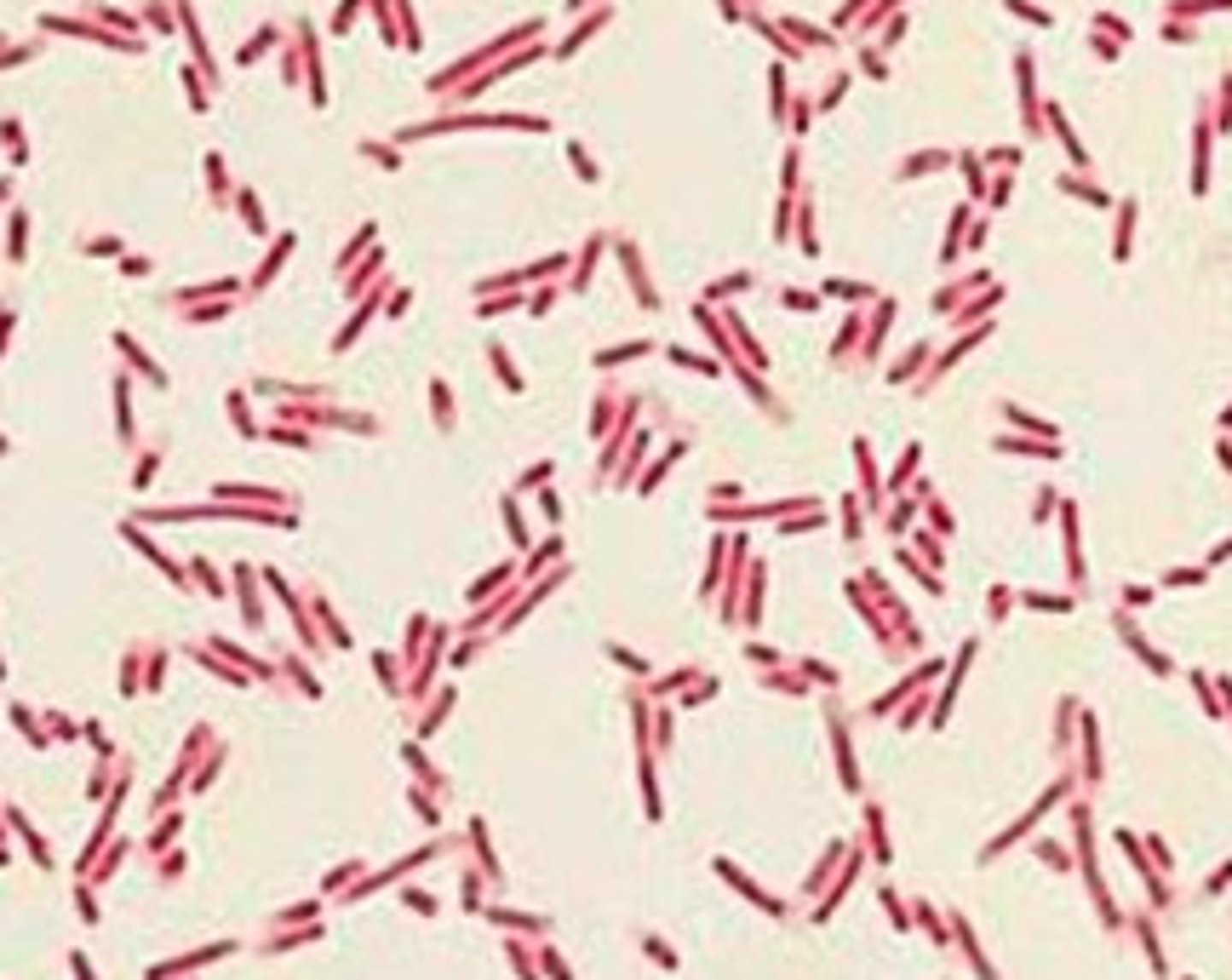
Cocci
Spherical bacteria.
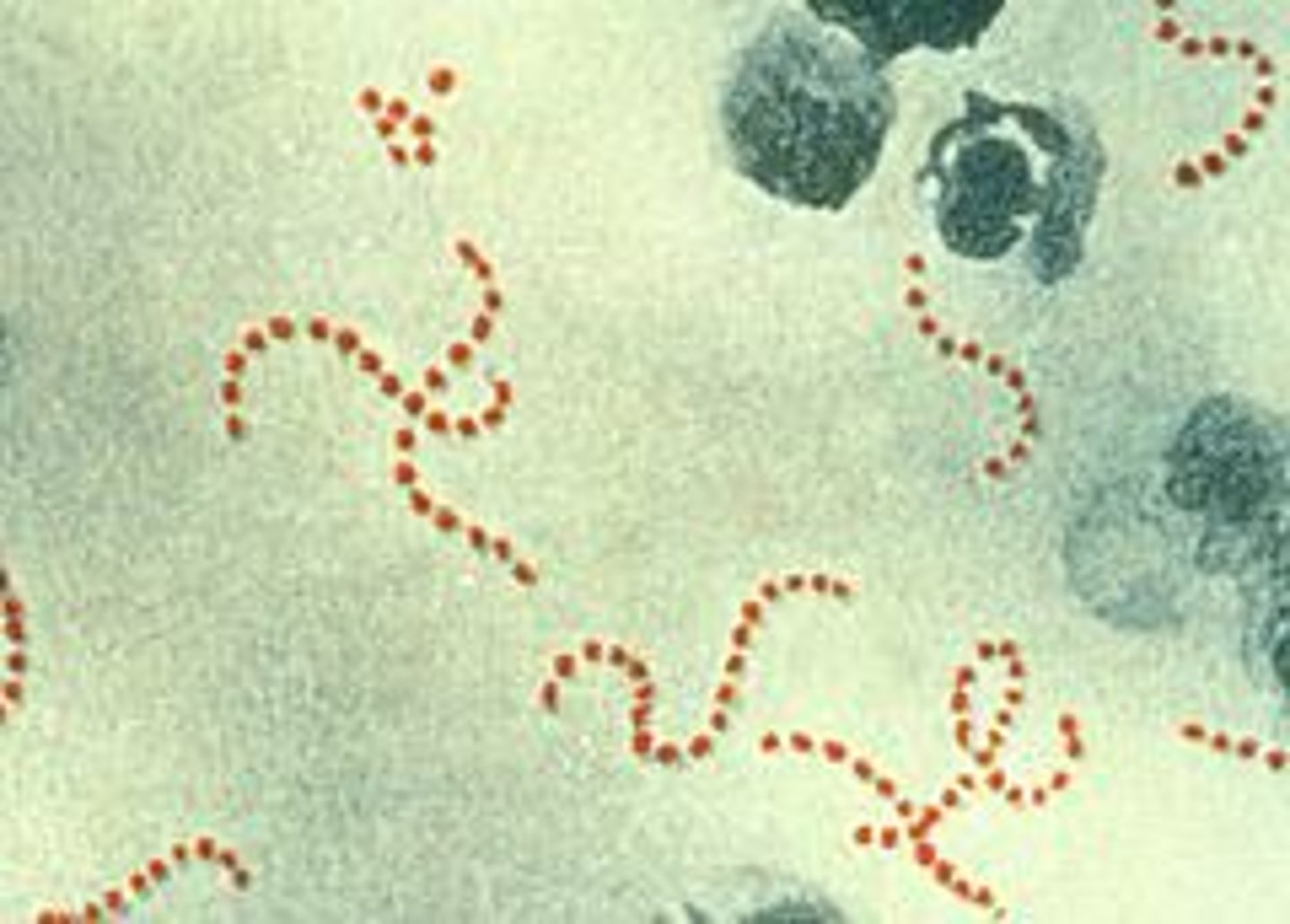
Streptococcus Pyogenes
Common pathogenic spherical bacteria.
Bacilli
Rod-shaped bacteria.
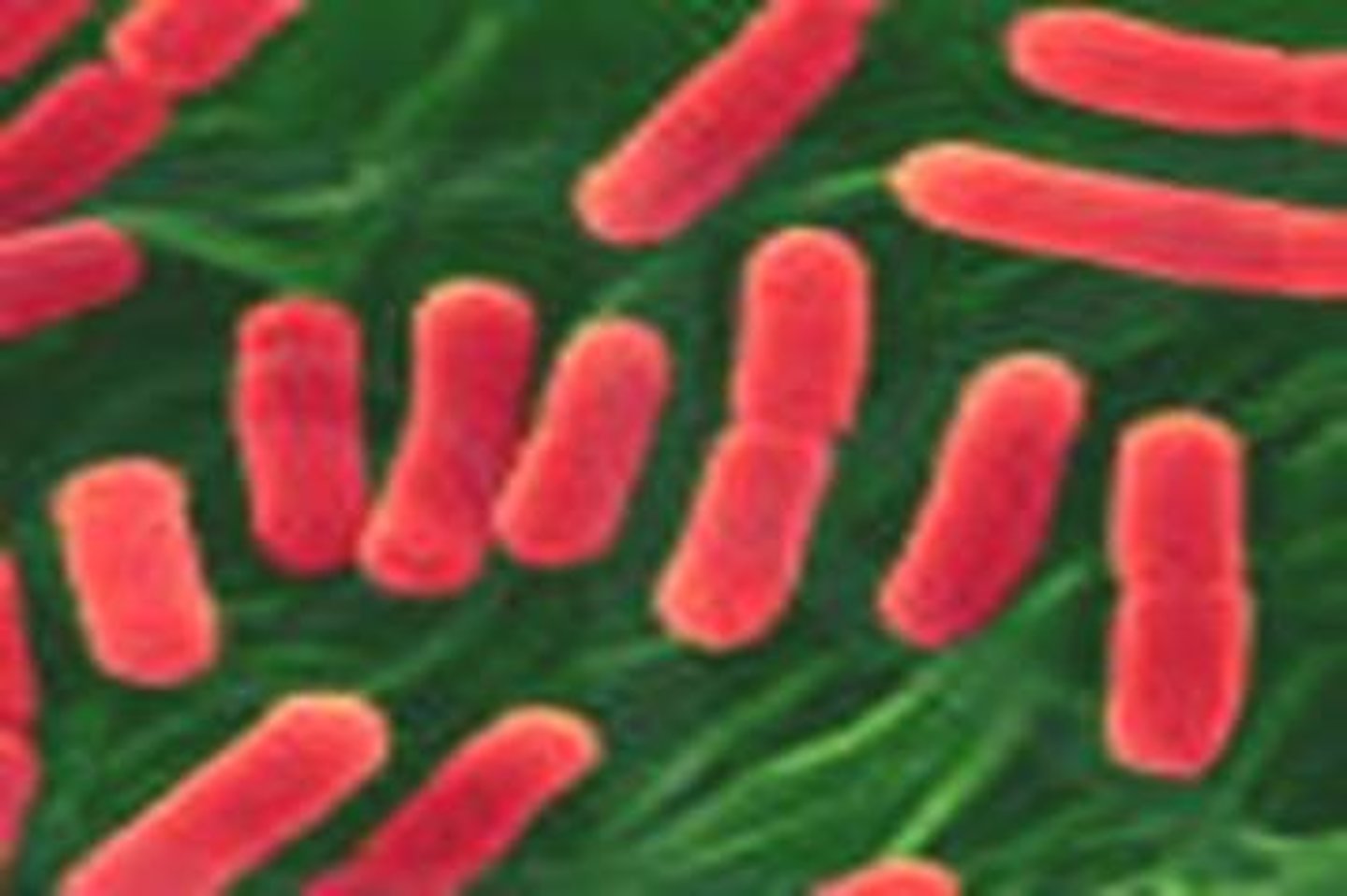
Escherichia Coli
Common pathogenic rod-shaped bacteria.
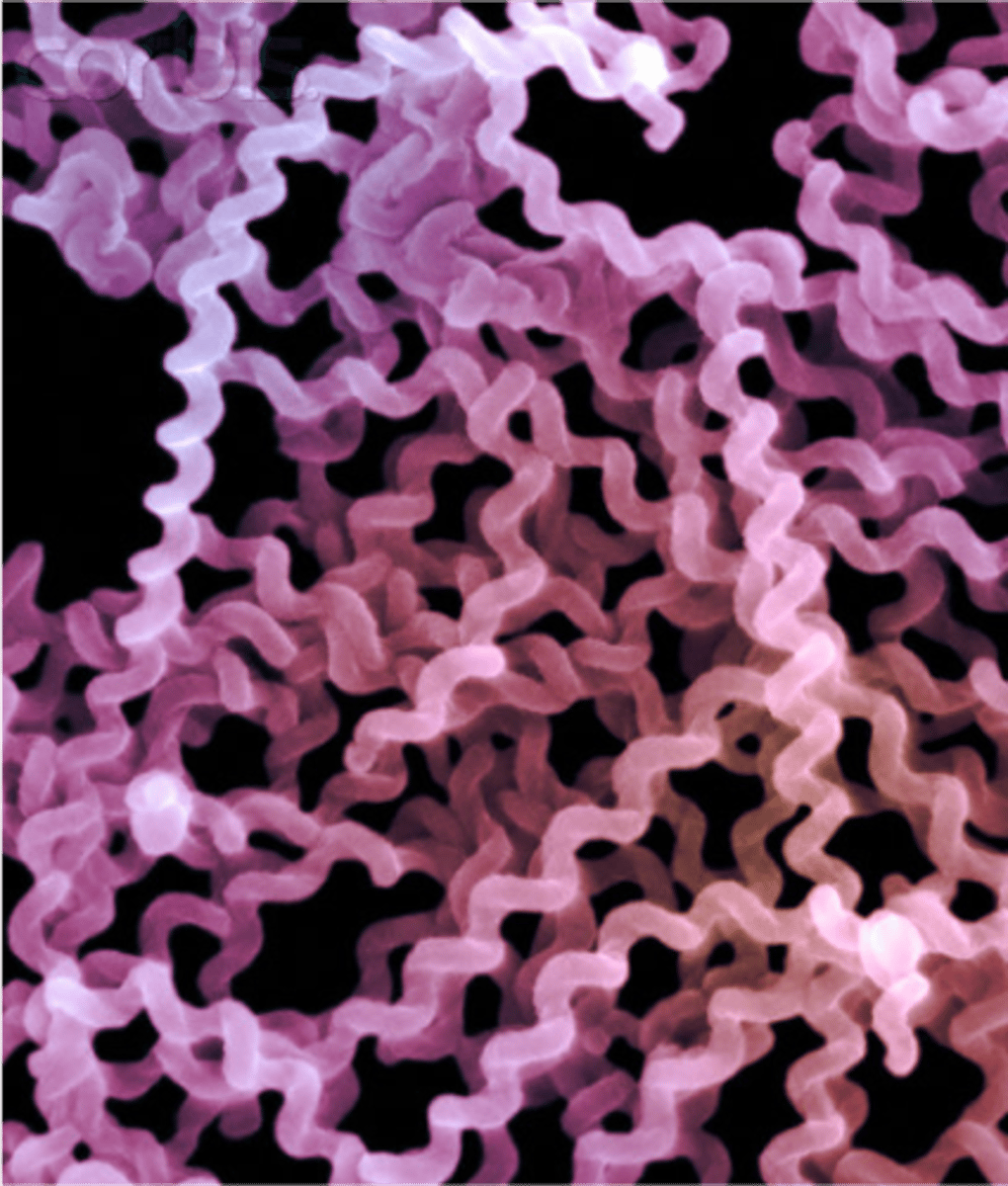
Spirilli
Spiral-shaped bacteria.
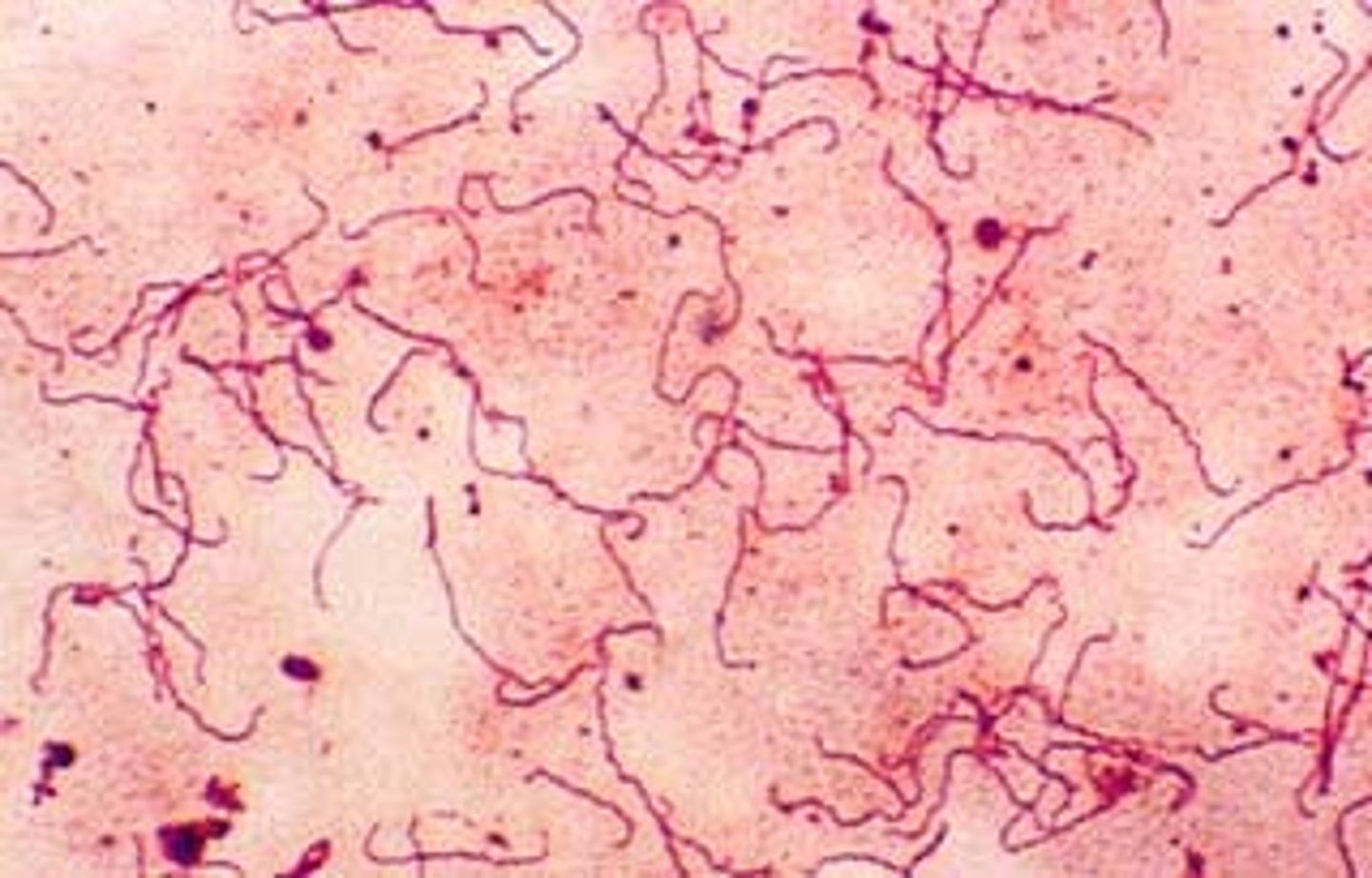
Treponema Pallidum
Common pathogenic spiral-shaped bacteria which causes syphilis.
Obligate Aerobes
Bacteria that use oxygen for metabolism.
Anaerobes
Bacteria that don't use oxygen for metabolism.
Obligate Anaerobes
Bacteria that cannot survive in an oxygen environment.
Facultative Anaerobes
Bacteria that can use oxygen for metabolism but usually toggle back and forth.
Aerotolerant Anaerobes
Bacteria that do not use oxygen, but can survive in an oxygen-present environment.
Bacterial Envelope
The cell wall and cell membrane together.
Gram Stain
Crystal violet and then safranin.
Gram-Positive Stain
Absorbs the crystal violet and produces a deep purple appearance.
Gram-Negative Stain
Does not absorb the crystal violet, but instead absorbs the safranin counterstain, producing a pink-red appearance.
Gram-Positive Bacteria
Thick peptidoglycan cell wall. 20-80nm
Lipoteichoic Acid
Another component of gram-positive cell walls, it is the substance that triggers the immune system.
Gram-Negative Bacteria
Thin peptidoglycan cell wall. 7-8nm
Lipopolysaccharides
Component of the gram-negative cell wall that triggers the immune system and inflammation more than lipoteichoic acid.
Periplasmic Space
Separate the cell membrane and cell wall in gram-negative bacteria.
Chemotaxis
The ability for cells to move toward or away from environmental chemicals such as food or host immune cells.
Flagella
Bacteria use these for chemotaxis.
Basal Body, Filament, Hook
Three components of flagella.
Filament
Hollow component of flagella composed of flagellin.
Basal Body
Complex structure that connects the flagella to the cytoplasmic membrane and it acts as the motor.
Hook
Connects the filament to the basal body so that as the basal body rotates, it exerts torque on the filament.
Prokaryotic DNA
Form a single circular chromosome containing the genetic material that is necessary for survival.
Plasmid
Contain the bacterial DNA that is not necessary for immediate survival but may encode for things that allow for antibiotic resistance.
Prokaryotic Ribosomes
30S and 50S
Prokaryotic ETC
Done in the cell membrane for the generation of ATP.
Aminoglycosides, Macrolides, Tetracyclines
Antibiotic classes that specifically target the prokaryotic ribosome.