AP World History Unit 1
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Hunting and Gathering
Means of obtaining subsistence by humans before the mastery of sedentary agriculture; normally typical of tribal social organization

Neolithic
The New Stone Age between 8000 and 5000 B.C.E.; period in which adaptation of sedentary agriculture occurred; domestication of plants and animals accomplished

Nomads
Cattle- and sheep-herding societies normally found on the fringes of civilized societies; commonly referred to as "barbarian" by civilized societies

Culture
Combination of ideas, objects, and patterns of behavior that result from human social interaction

Neolithic/Agricultural/Agrarian revolution
Occurred between 8000 and 5000 B.C.E.; transition from hunting and gathering to sedentary agriculture

Pastoralism
A nomadic agricultural lifestyle based on herding domesticated animals; tended to produce independent people capable of challenging sedentary agricultural societies

Mesopotamia
Literally "between the rivers"; the civilization that arose in the alluvial plain of the Tigris-Euphrates river valleys
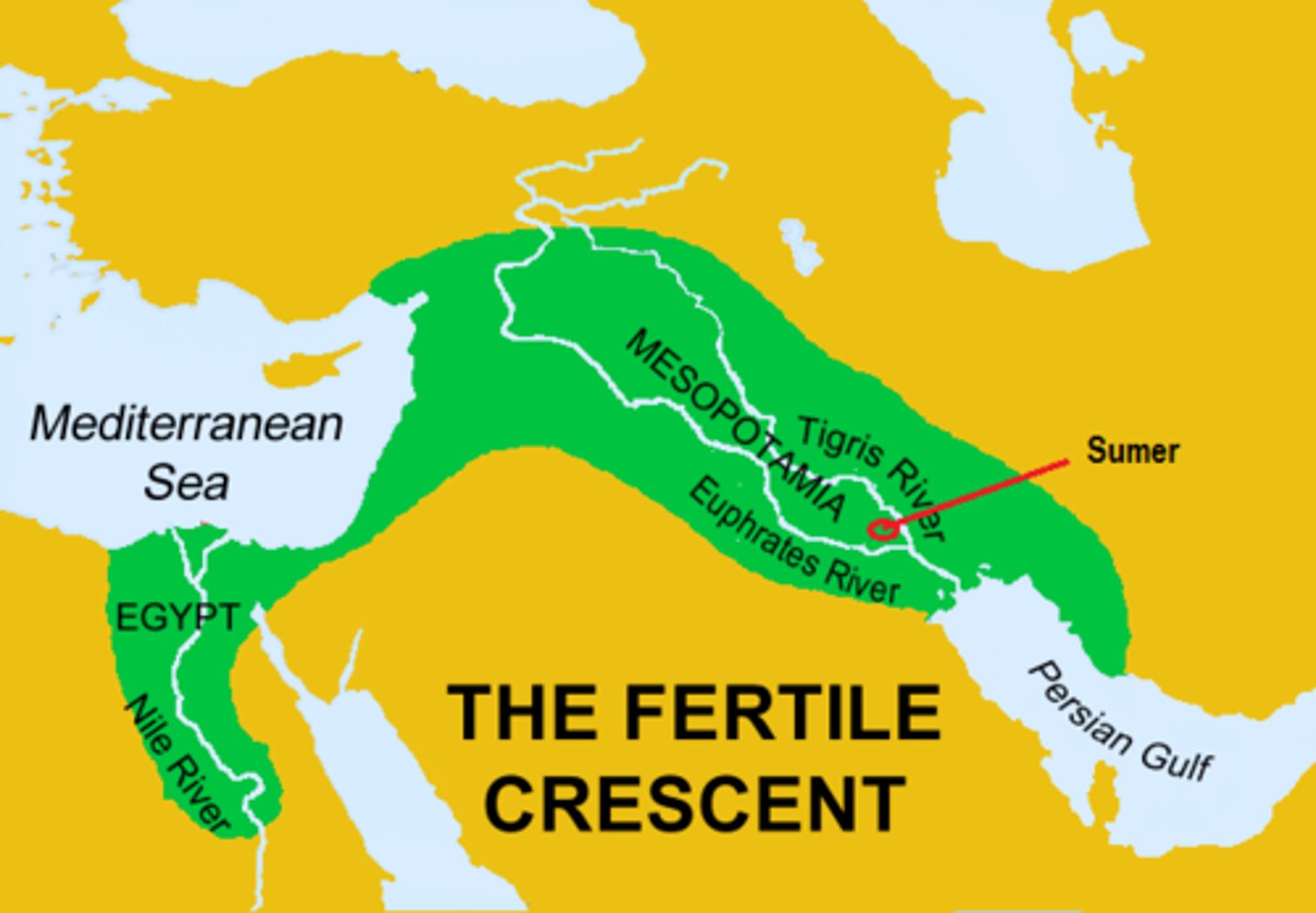
Sumerians
People who migrated into Mesopotamia circa 4000 B.C.E.; created the first civilization within the region; organized area into city-states

Cuneiform
A form of writing developed by the Sumerians using a wedge-shaped stylus and clay tablets

City-state
A form of political organization typical of Mesopotamian civilization; consisted of agricultural hinterlands ruled by an urban-based king
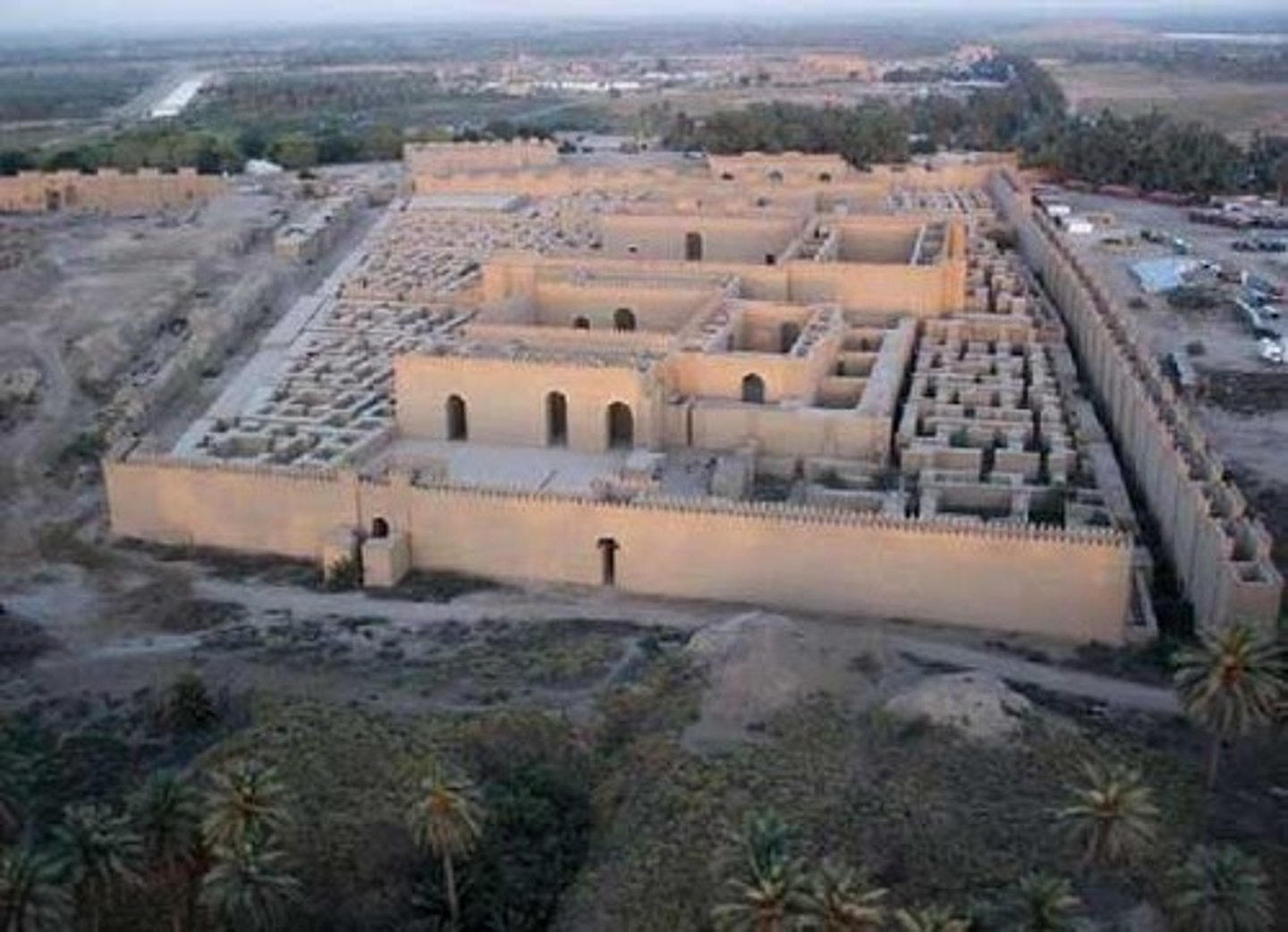

Ziggurats
Massive towers usually associated with Mesopotamian temple connections

Babylonian Empire
Unified all of Mesopotamia circa 1800 B.C.E.; collapsed due to foreign invasion circa 1600 B.C.E.

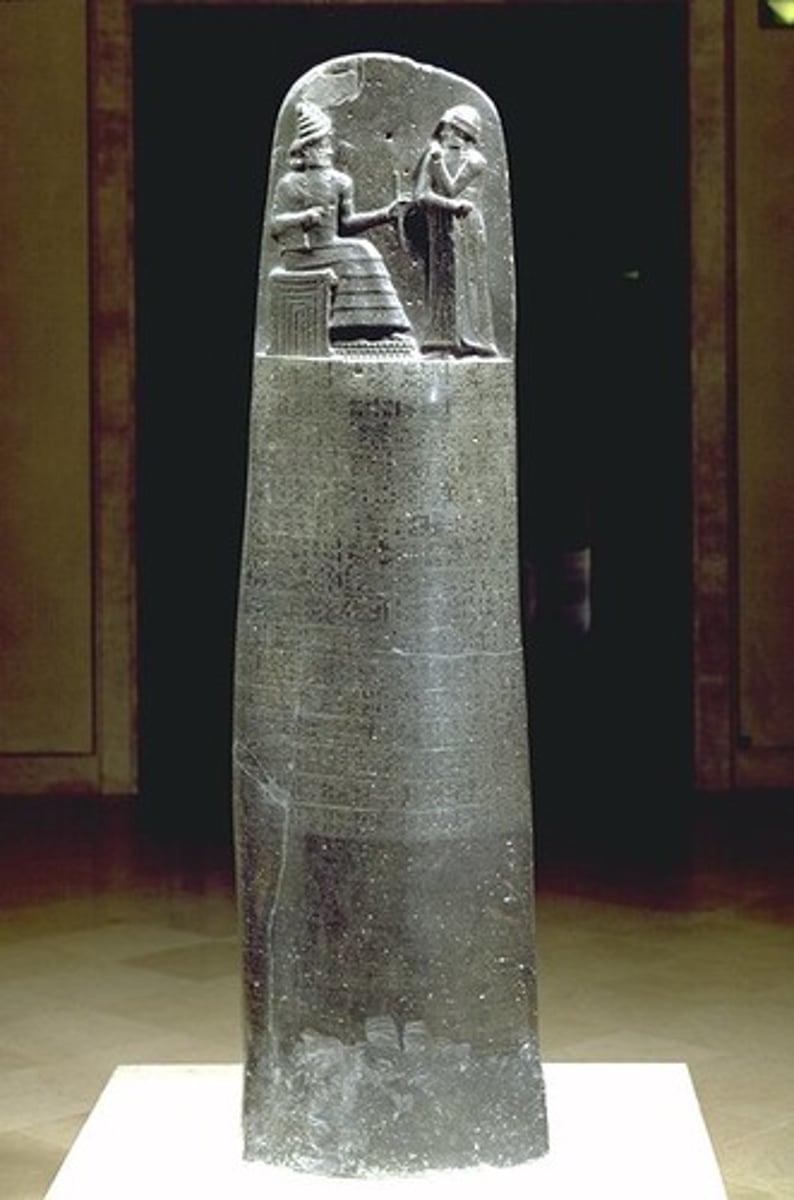
Hammurabi
The most important Babylonian ruler; responsible for codification of the law

Pharaoh
The term used to denote the kings of ancient Egypt; considered a god as well as a political and military leader. The term, "great house" refers to the palace of the pharaohs

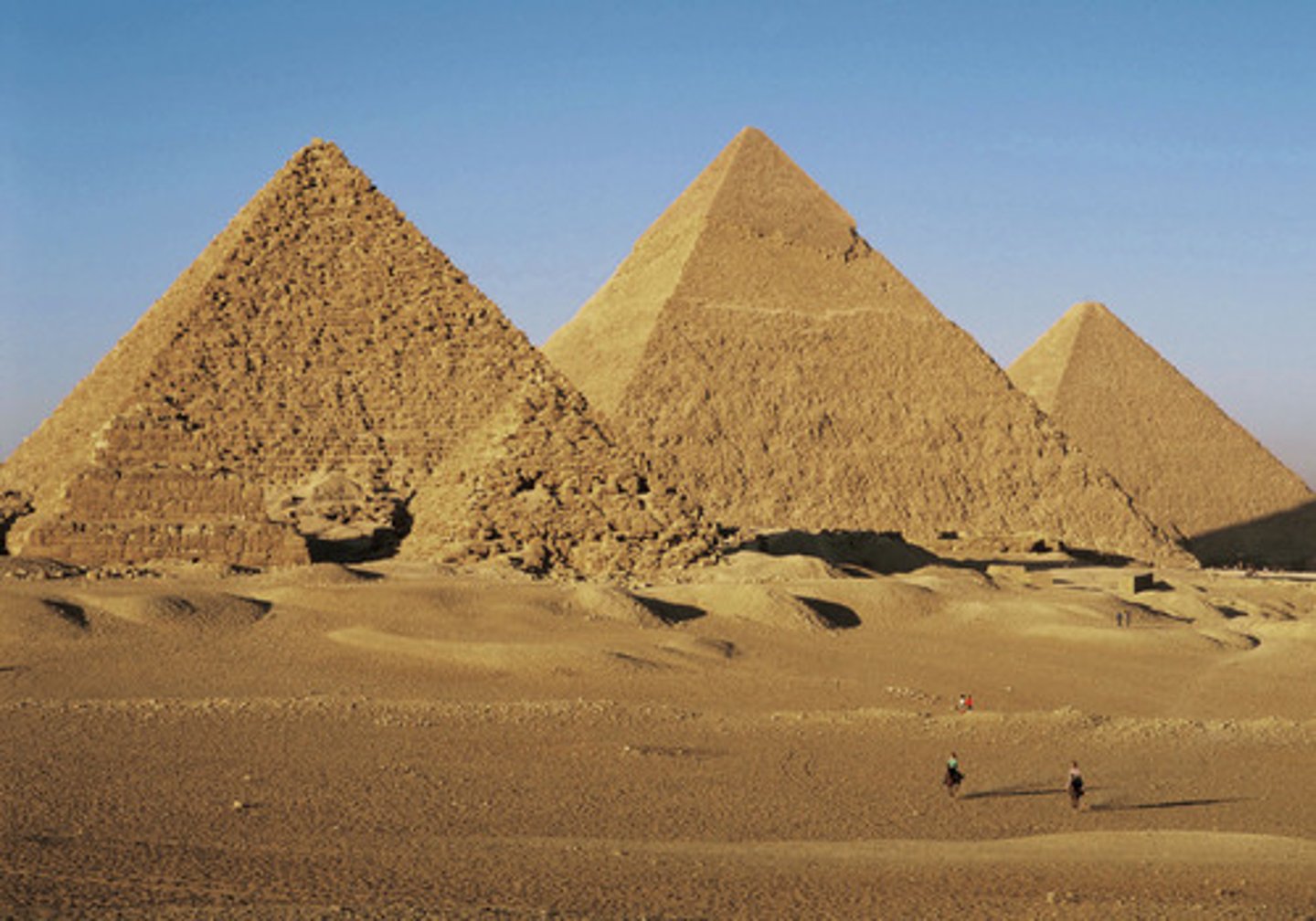
Pyramids
Monumental architecture typical of Old Kingdom Egypt; used as burial sites for pharaohs

Hieroglyphs
Form of writing developed in ancient Egypt; more pictorial than Mesopotamian cuneiform

Monotheism
The exclusive worship of one god; introduced by Jews into Middle Eastern civilization

Phoenicians
Seafaring civilization located on the shores of the eastern Mediterranean; established colonies throughout the Mediterranean; extensive trade, communication networks, early alphabetical script
Harappa and Mohenjo Daro
Major urban complexes of Harappan civilization; laid out on planned grid pattern
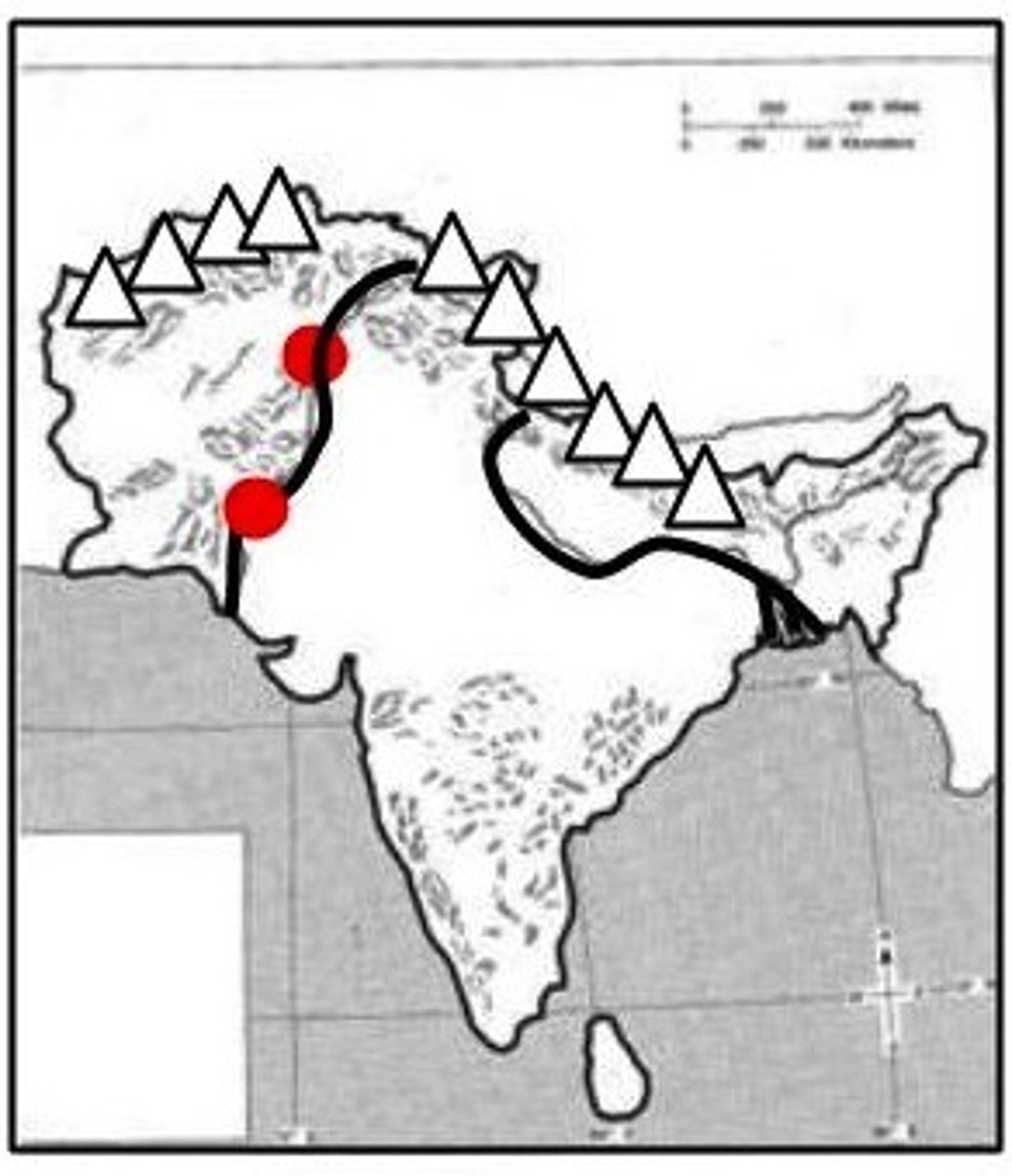
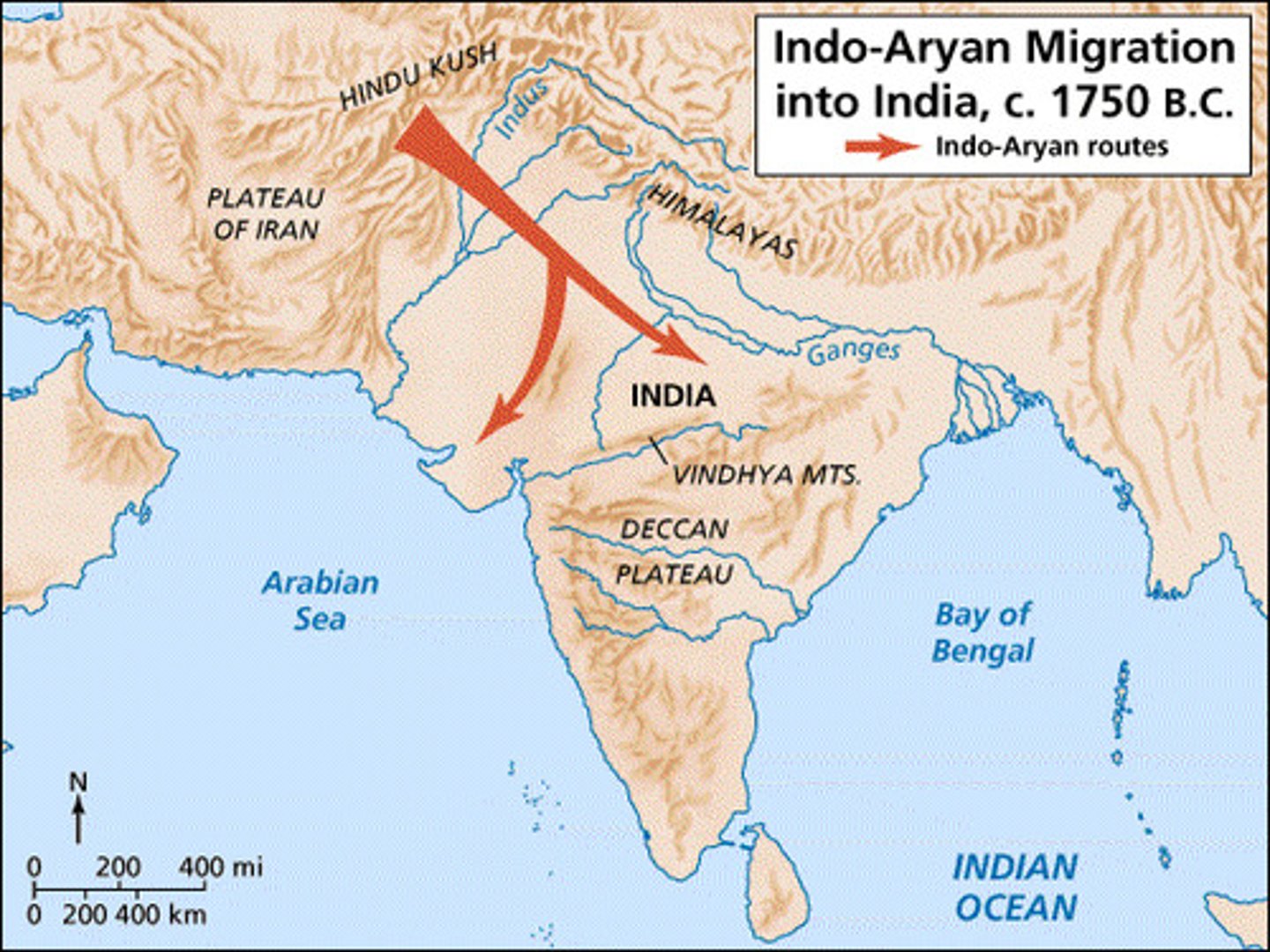
Aryans
Indo-European nomadic, warlike, pastorialists who replaced Harappan civilization
Huanghe (Yellow) River Basin
Site of the development of sedentary agriculture in China
Shang
1st Chinese dynasty

Big Geography
A term that draws attention to the global nature of world history.

Paleolithic
The period that ended about 3,000 years after the end of the last Ice Age, it lasted until about 10,000 years ago. (Old Stone Age) The period of the Stone Age associated with the evolution of humans. It predates the Neolithic period.

Path of migration for humans during Paleolithic era
From Africa to Eurasia, Australia, and the Americas
Eglitarian
Believing in the equality of all peoples
Pastoralists were often the developers and disseminators of of ____ and ___ that transformed warfare in agrarian civilizations
new weapons
modes of transportation
_____ developed in this period continued to have strong influences in later periods
New religious beliefs
Mediterranean Sea
Sea connecting Mesopotamia, Anatolia, and N. Africa
Polytheism
Belief in more than one god
Nile River
Principal water source of water flowing through North Africa (site of sophisticated cultural development); flooded regularly and enriched the soil in the process
history
the study of past events and changes in the development, transmission and transformation of cultural practices
stone age
the earliest known period of human culture, marked by the creation and use of stone tools and other nonmetallic substances
foragers
Food collectors who gather, fish, or hunt
city-state
A sovereign state comprising a city and its immediate surrounding area
Babylon
an ancient city of Mesopotamia known for its wealth, luxury, and vice.
Hammurabi
Babylonian king who codified the laws of Sumer and Mesopotamia (died 1750 BCE)
scribe
a person who copies or writes out documents; often a record keeper
cuneiform
A form of writing developed by the Sumerians (Mesopotamia) using a wedge shaped stylus and clay tablets.
bronze
A metal that is a mixture of copper and tin
paleolithic
stone age period when human used stone tools and survived by hunting and foraging
Homo sapiens
human species derived from apes with more brain capacity for intelligence
venus figurines
paleolithic female figurines that emphasize physical attributes associated with fecundity
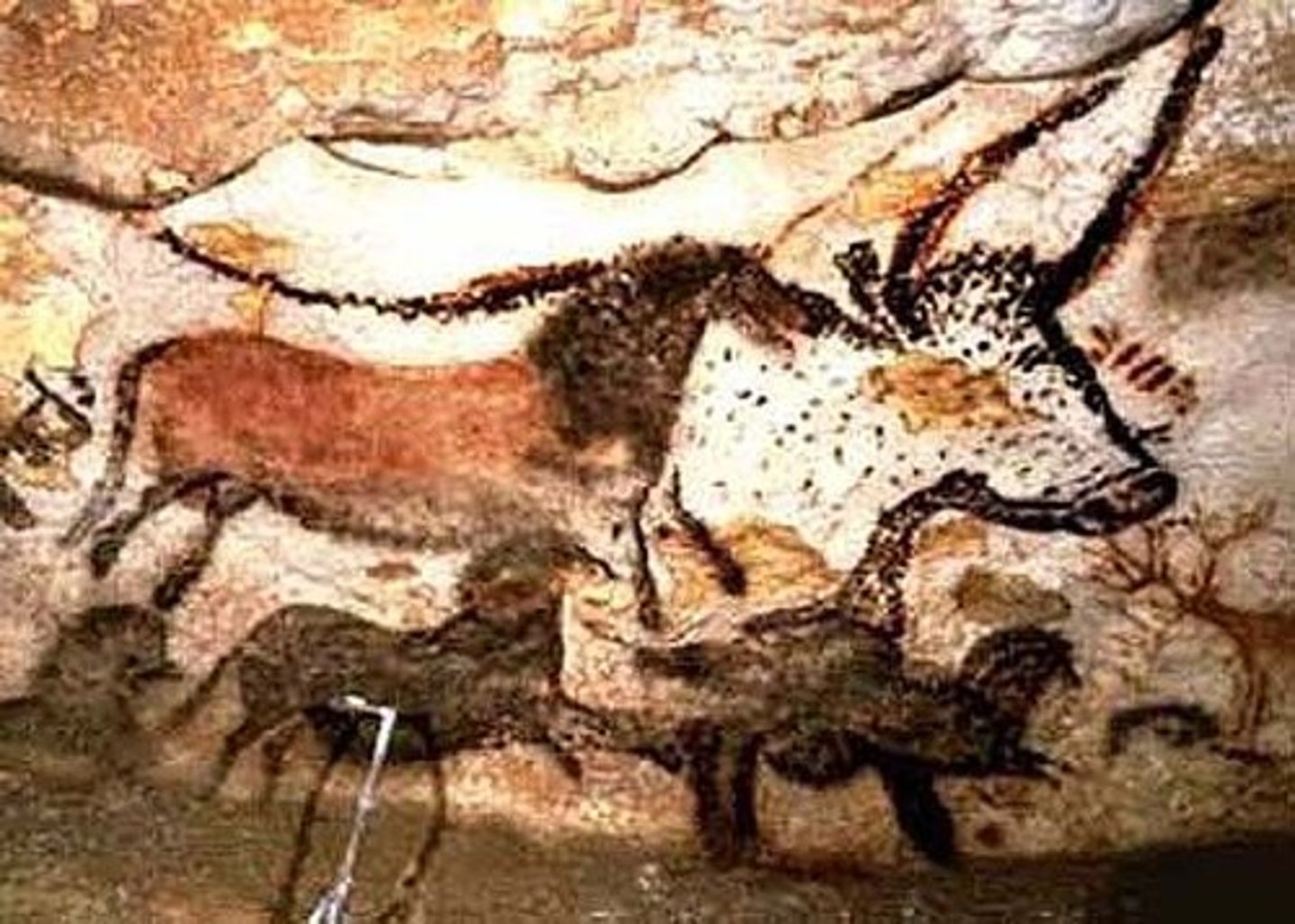
cave paintings
paleolithic cave paintings that emphasize hunting--Lascaux France is most famous
pastoralism
the process of domestication, raising, and herding of animals
specialization of labor
people in civilizations could be assigned different jobs and statuses in society due to having a surplus of food
patriarchy
the idea that males have a right to rule and reign over states and families
civilization
large scale communities that had certain characteristics in common such as: recordkeeping, complex institutions (government, economy, organized religion), cities, specialization of labor, long-distance trade, technology
Euphrates and Tigris
two principle Mesopotamian rivers
Sumer
earliest Mesopotamian city state
Babylon
second oldest Mesopotamian city state, succeeds Sumer, most important king was Hammurabi
Hammurabi's Code
first law code in the world, of Babylonia, dealt with legal contracts and responsibility for wrong doing
bronze metallurgy
alloy of copper, tin, and zinc, this metal began to be produced from about 2800 BCE improved military equipment, agricultural knives, and plows
iron metallurgy
a changeable metal, less hard than bronze, but more flexible, developed around 1500 BCE by the Hittites
wheel
round object used to move heavy weights and to create vehicles first in Sumer
cuneiform
a very early form of writing, from Sumer in Mesopotamia, done by pressing a cone-shaped stylus into soft clay
Epic of Gilgamesh
epic Mesopotamian poem that highlights the stresses of civilization
Egypt
a founding civilization along the Nile in Northeastern Africa
Hieroglyphics
Egyptian writing (pictographs & symbols representing sounds+ideas)
Harrappa & Mohenjo Daro
Two early, very large, and complex Indus Valley city states. Little is known about these but their size and complexities imply central planning.
Indus River
River in Northern India on which the first Indian civilizations were built; flooded twice a year in a predictable manner
Vedas
A belief system based on the caste system brought into India by peoples probably from the Caucasus between about 5000 and 4000 BCE
Varna
Caste system of India: Brahmin, Khsatriya, Vaishya, Shudra--people could not move out of the caste they were born into
China
earliest civilization in Asia
Huang He and Yangzi He
two rivers in China that supported early civilization
Shang Dynasty
The dominant people in the earliest Chinese dynasty for which we have written records (ca. 1750-1027 B.C.E.). Ancestor worship, divination by means of oracle bones, and the use of bronze vessels for ritual purposes were major elements of this culture.
Hinduism
Term for a wide variety of beliefs and ritual practices that have developed in the Indian subcontinent since antiquity. It has roots in ancient Vedic, Buddhist, and south Indian religious concepts and practices.
Zoroastrianism
Founded by Zoroaster; taught that humans had the freedom to choose between right and wrong, and that goodness would triumph in the end. Marked by dualism between God = Good and the Evil. Influenced Christianity. Was one of the first monotheistic religions.
Judaism
Monotheistic (belief in one god), founded by Abraham, code of law found in the Torah (first 5 books of the Bible), led to the development of two other Abrahamic religions: Christianity and Islam.
Confucianism
The system of ethics, education, and statesmanship taught by Confucius and his disciples, stressing love for humanity, ancestor worship, reverence for parents, and harmony in thought and conduct.
Mandate of Heaven
A political theory of ancient China in which the emperor is given the power to rule by a divine sources. This tie could be severed by ineffectual rule
Oracle bones
bones on which the ruling class in China wrote questions and had them divined by the priestly class
Mesoamerica
cultural area in the Americas extending from central America to present-day Peru
Olmec
the first major civilization in Mexico
Maya
Mesoamerican civilization in and near the Yucatan Peninsula--had the first and only pre-Columbian writing system in the Americans
Chavin
Mesoamerican civilization in present-day Peru that had highly developed art and architectural practices
Carthage
City located in present-day Tunisia, founded by Phoenicians ca. 800 B.C.E. It became a major commercial center and naval power in the western Mediterranean until defeated by Rome in the third century B.C.E. (p. 107)
irrigation systems
replacement or supplementation of rainfall with water from another source in order to grow crops
Indus River Valley Civilization
an ancient civilization thriving along the Indus River in what is now Pakistan and western India. This civilization is also sometimes referred to as the Harappan or Harappa-Mohenjodaro Civilization of the Indus Valley, in reference to the excavated cities of Harappa and Mohenjodaro
Persian Wars
a series of conflicts between the Greek world and the Persian Empire that started about 500 BC and lasted until 448 BC.
Alexander the Great
United Ancient Greece; Hellenistic Age, conquered a large empire.
Socrates and Plato
Greek philosopher and his student