LIDS VL2 (Martin, VL2)
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What is the goal of Load Reduction Instruction (LRI)?
LRI reduces cognitive load by starting with explicit instruction and later shifting to discovery learning, helping students move from novice to expert learners.
Why is LRI necessary?
Because working memory is very limited (15–20 seconds, small capacity), while long-term memory has vast capacity. LRI supports the transfer of information into long-term memory and prevents overload.
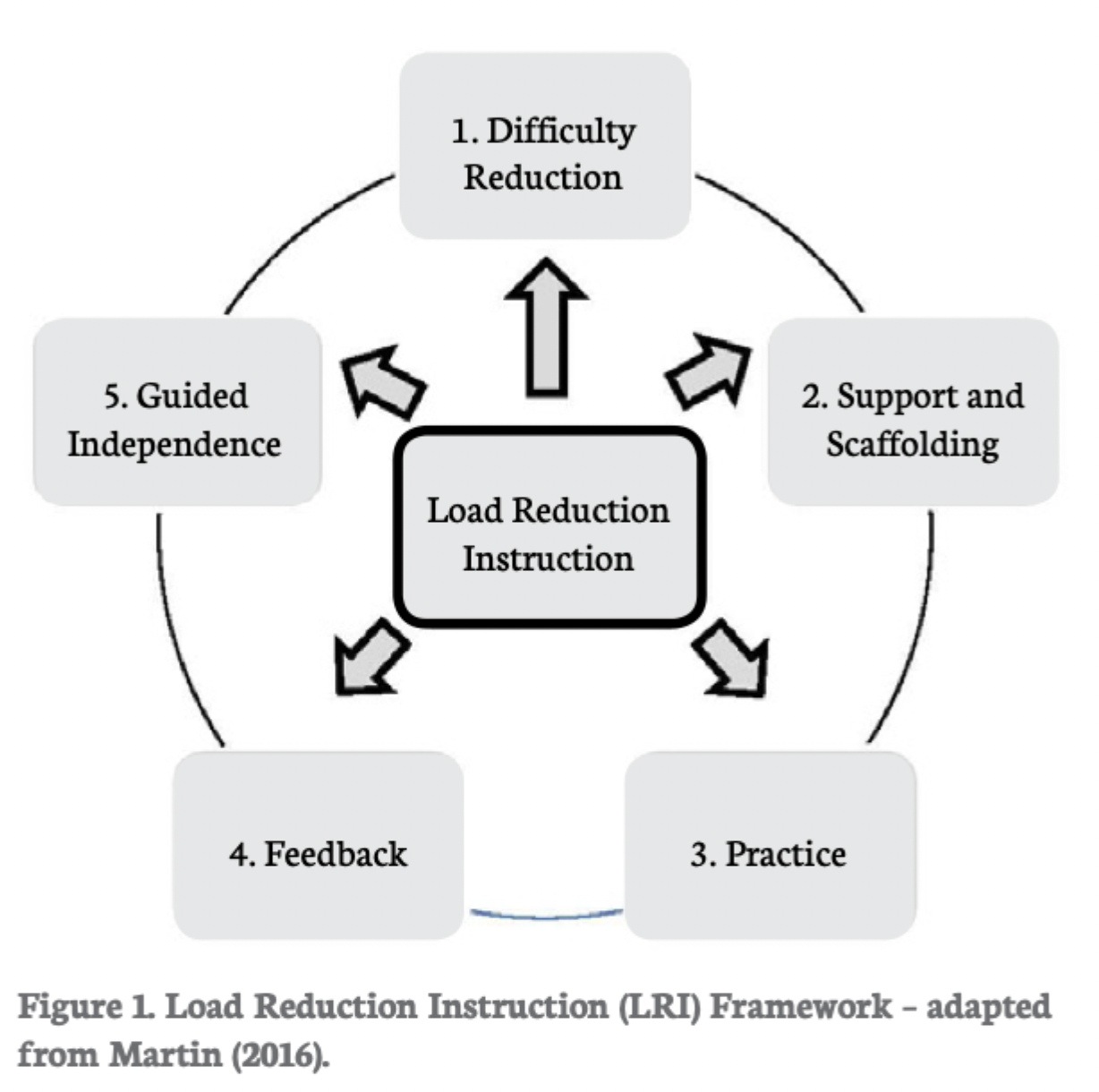
What are the five core principles of LRI?
Difficulty reduction at the start of learning
Instructional support and scaffolding
Structured practice
Instructional feedback
Independent practice and guided discovery
What strategies belong to difficulty reduction in LRI?
Pre-training or revision, teacher modelling, breaking work into small chunks, and regular early learning checks.
What does instructional support and scaffolding in LRI involve?
Focusing attention on central information, logical sequencing, integrating key information, signalling important points, using templates and worked examples, prompts, and personalized tasks.
What forms of practice are used in LRI?
Deliberate practice (repetition until mastery), mental practice (mental rehearsal of examples), and guided practice with prompts.
What does instructional feedback look like in LRI?
Concrete feedback on correctness, showcasing strong examples of work, and feedforward that gives advice for future improvement.
When does the phase of independent practice and discovery learning begin in LRI?
Once skills and knowledge are automated, students practice independently and then engage in guided discovery and real-world problem solving.
Is LRI teacher-centered or student-centered?
While the early phase is more teacher-led, LRI is student-centered because instruction is tailored to the cognitive needs of learners.
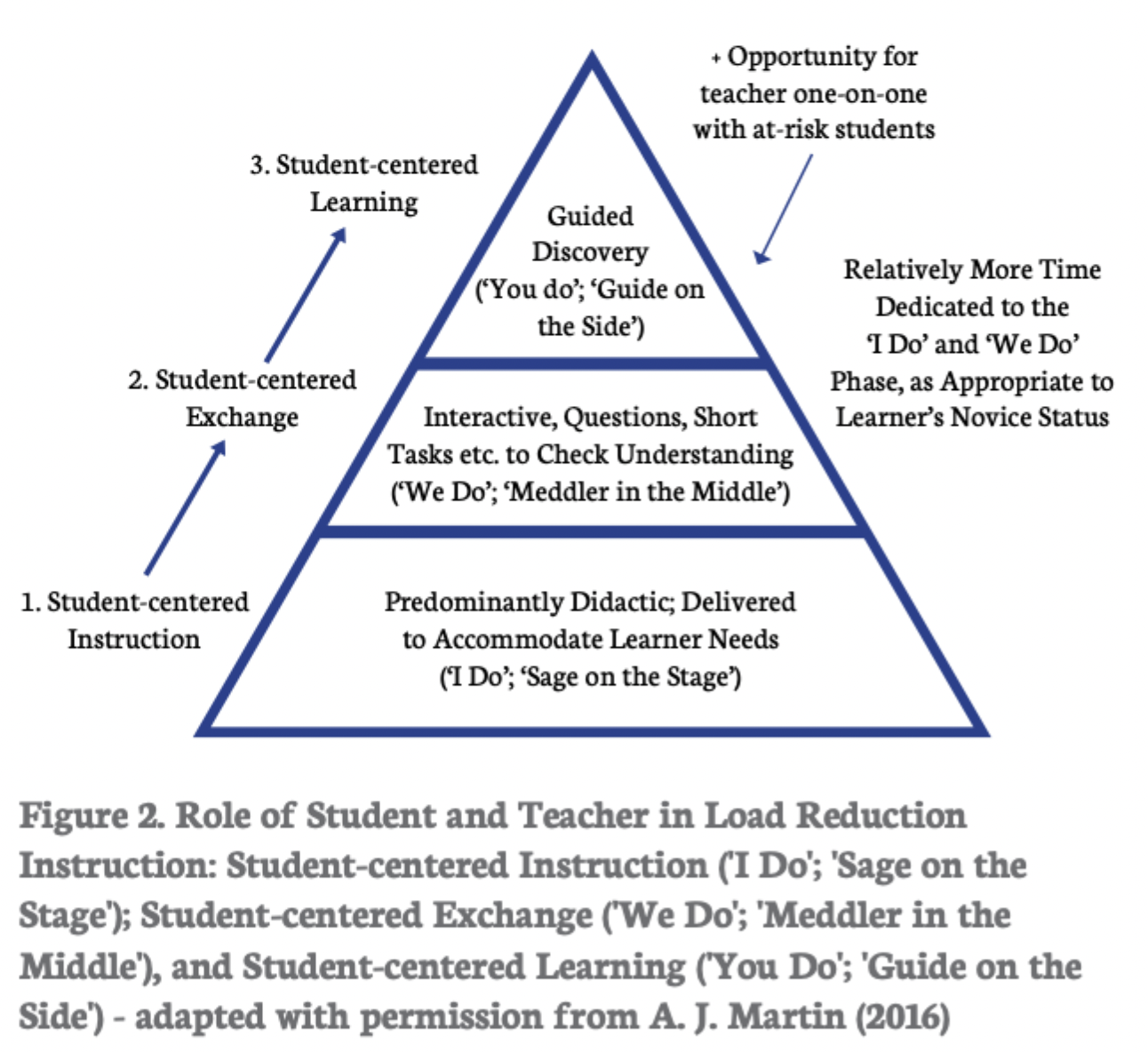
What are the phases of teacher and student roles in LRI?
“I Do” (Sage on the Stage): Teacher-centered instruction
“We Do” (Meddler in the Middle): Shared interaction, questioning, feedback
“You Do” (Guide on the Side): Independent learning, discovery, autonomy
What theoretical foundations support LRI?
Piaget (1951): Cognitive structures, schemas
Vygotsky (1978): Zone of Proximal Development, scaffolding
Bandura (1965): Modeling (attention, retention, reproduction, motivation)
Wood, Bruner & Ross (1976): Scaffolding in problem solving
Cognitive Load Theory (Sweller 2012; Mayer & Moreno 2010)
What is the central benefit of LRI for students?
Optimized learning and achievement through reduced working memory load in early phases and enhanced independence and discovery in later phases.
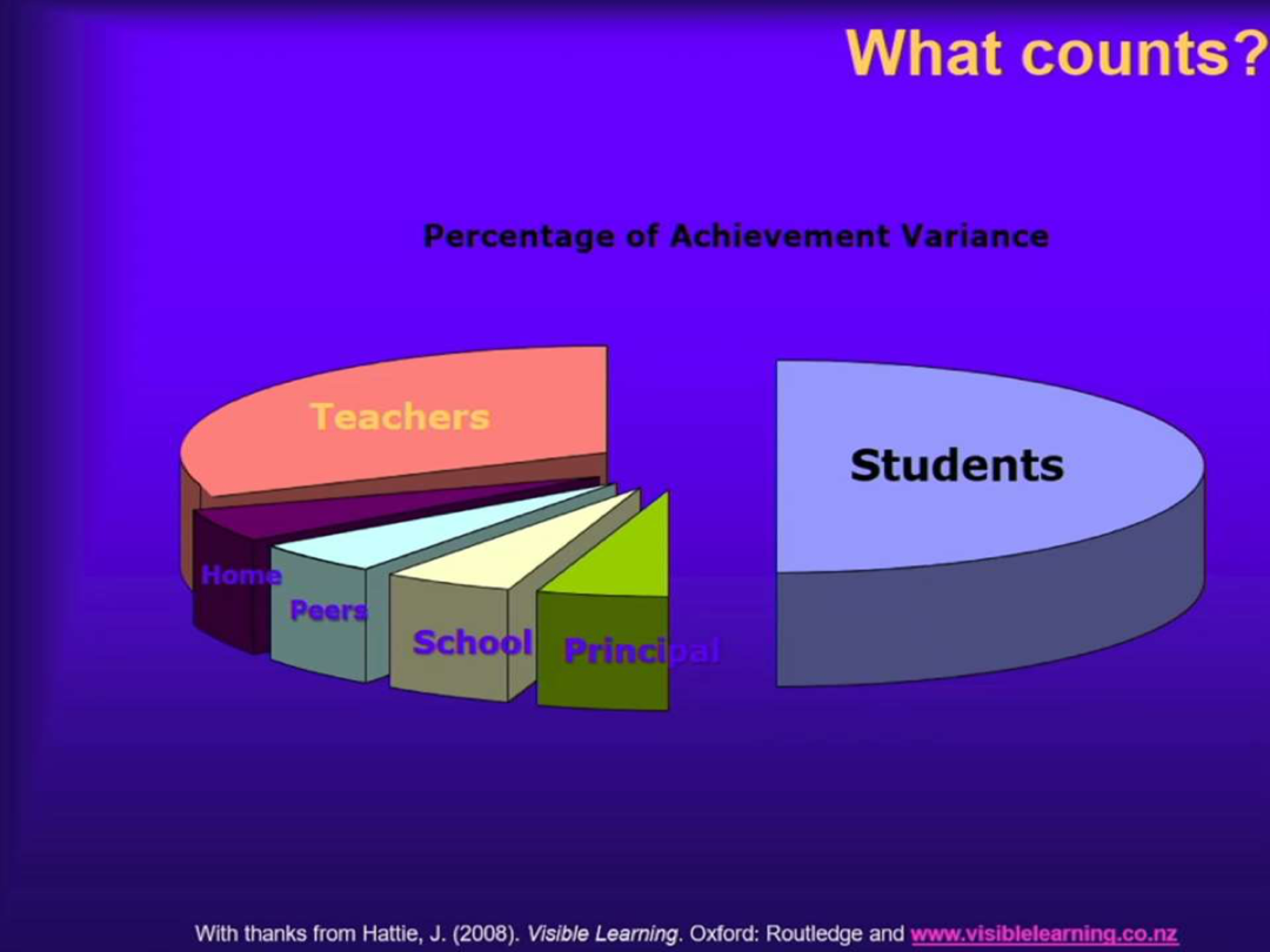
What explains the variance in terms of achievement in school?
The largest share is explained by students, followed by teachers. Smaller shares come from school/leadership, peers, and home.
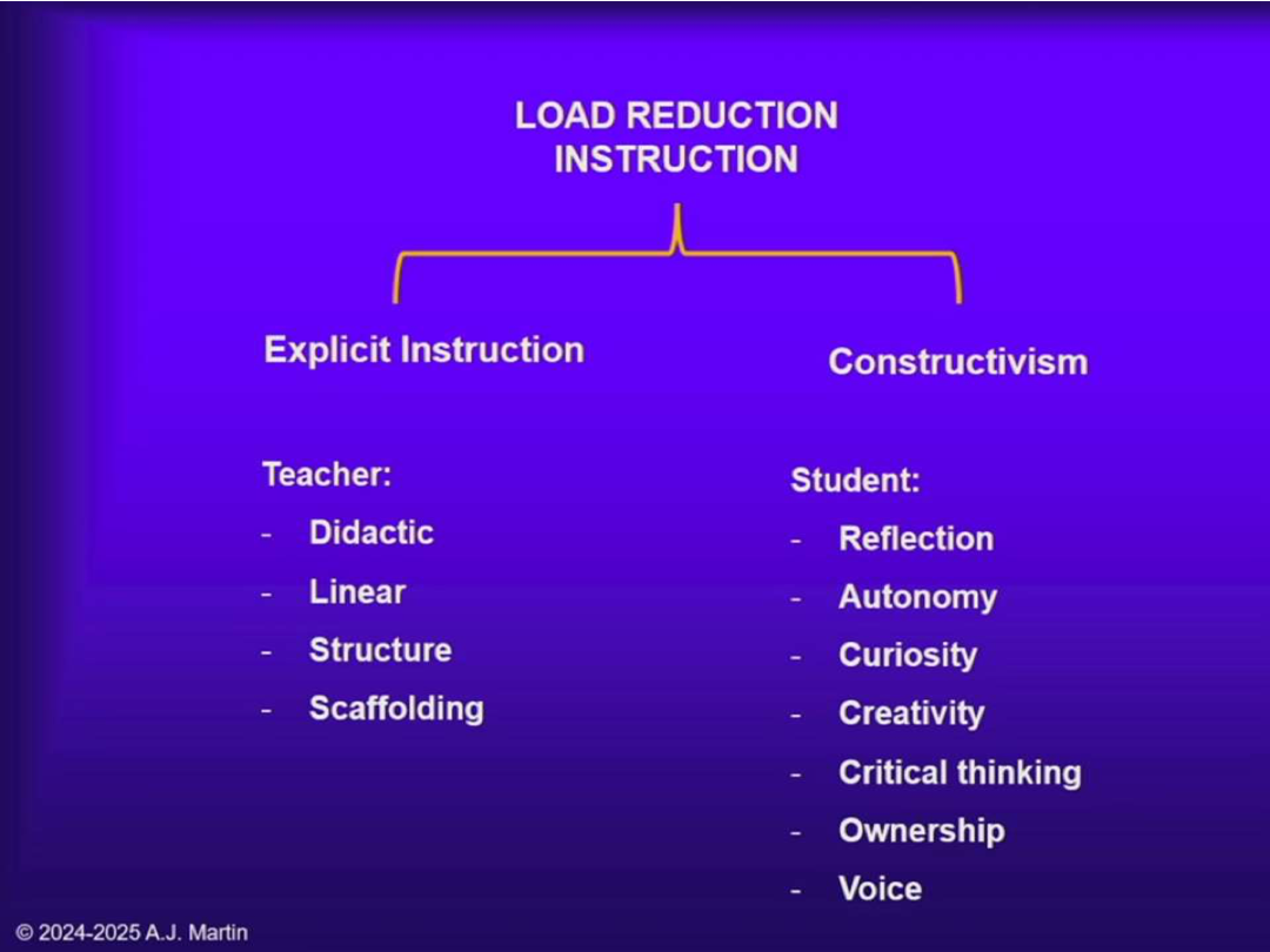
What have been the two dominant instruction branches over the past decades? Which one is better?
Explicit instruction and constructivism. The best approach is to combine them as LRI (Load Reduction Instruction): start with explicit/structured guidance, then move to discovery/self-directed learning.
How does school change over time? What demand follows from this, and which branches of psychology provide input?
School demands increase in complexity over time. This requires reducing cognitive load. Relevant input comes from cognitive psychology and instructional psychology.
What are the types of cognitive load? Examples?
Intrinsic load: inherent to the task/content (e.g., learning many new concepts). Extraneous load: caused by poor instruction, communication, or presentation (e.g., unclear slides).

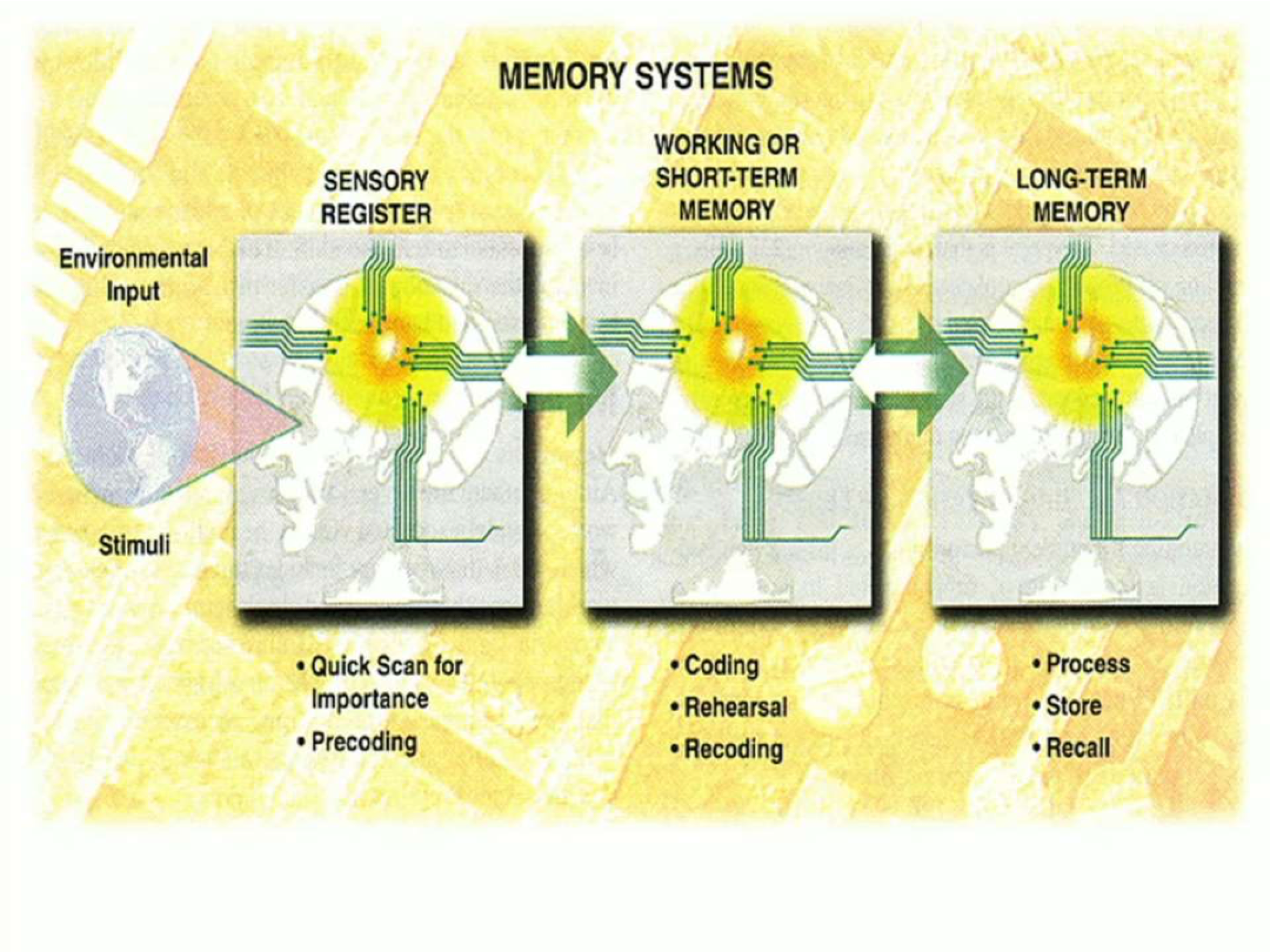
What are the roles of the memory systems?
Sensory register: scanning, pre-coding. Working memory: encoding, rehearsal, recoding. Long-term memory: storing, integrating, retrieving knowledge.
What does “dump and reload” mean?
Analogy to RAM: working memory clears space (“dump”) and loads new information (“reload”) to prevent overload.

Why is it easy to overload working memory? What happens then? Pedagogical implications?
Working memory is tiny and short-lived (seconds, 4±1 items). Overload → info lost, misunderstood, not transferred to long-term memory. Teaching must apply LRI principles.
How vast is the capacity of working memory? Analogies?
Very limited: ~4±1 units for a few seconds. Analogies: RAM in a computer or small desk space – must stay uncluttered, long-term memory is the storage.

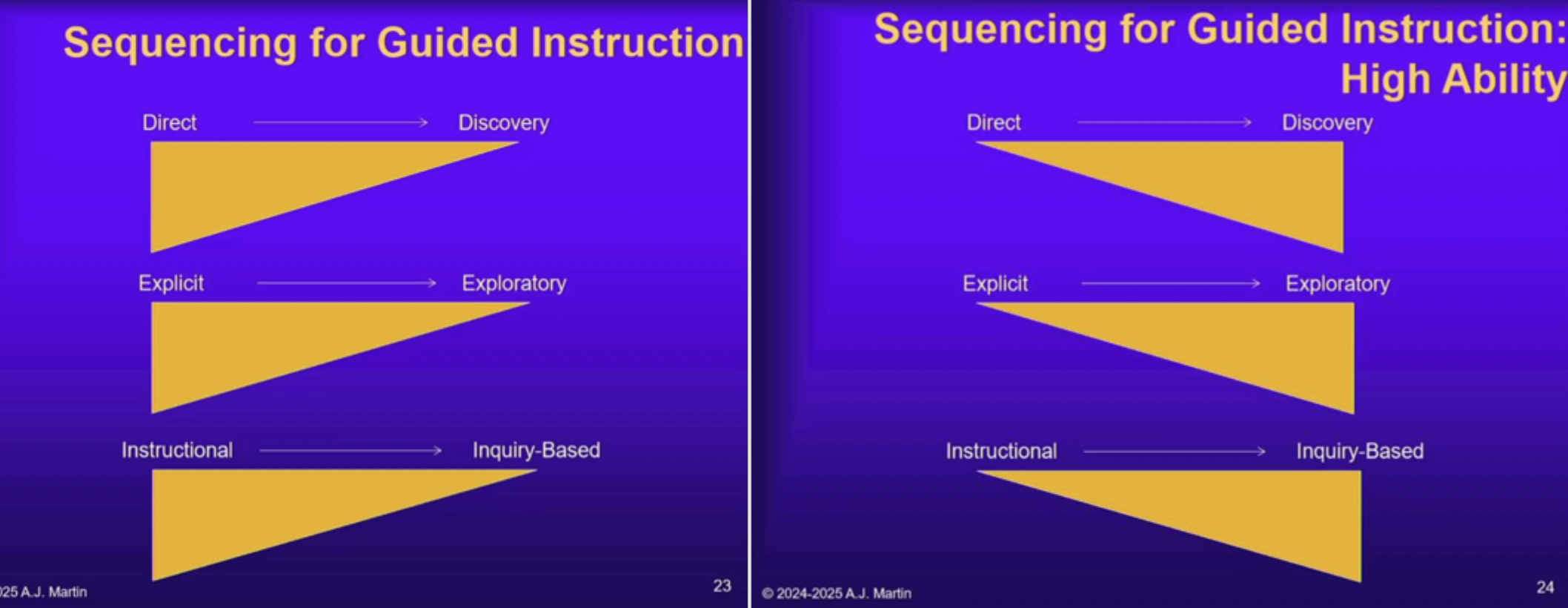
How does LRI differ for bright/high-ability students?
They transition faster from structured guidance to exploratory/inquiry learning, but it’s still necessary.
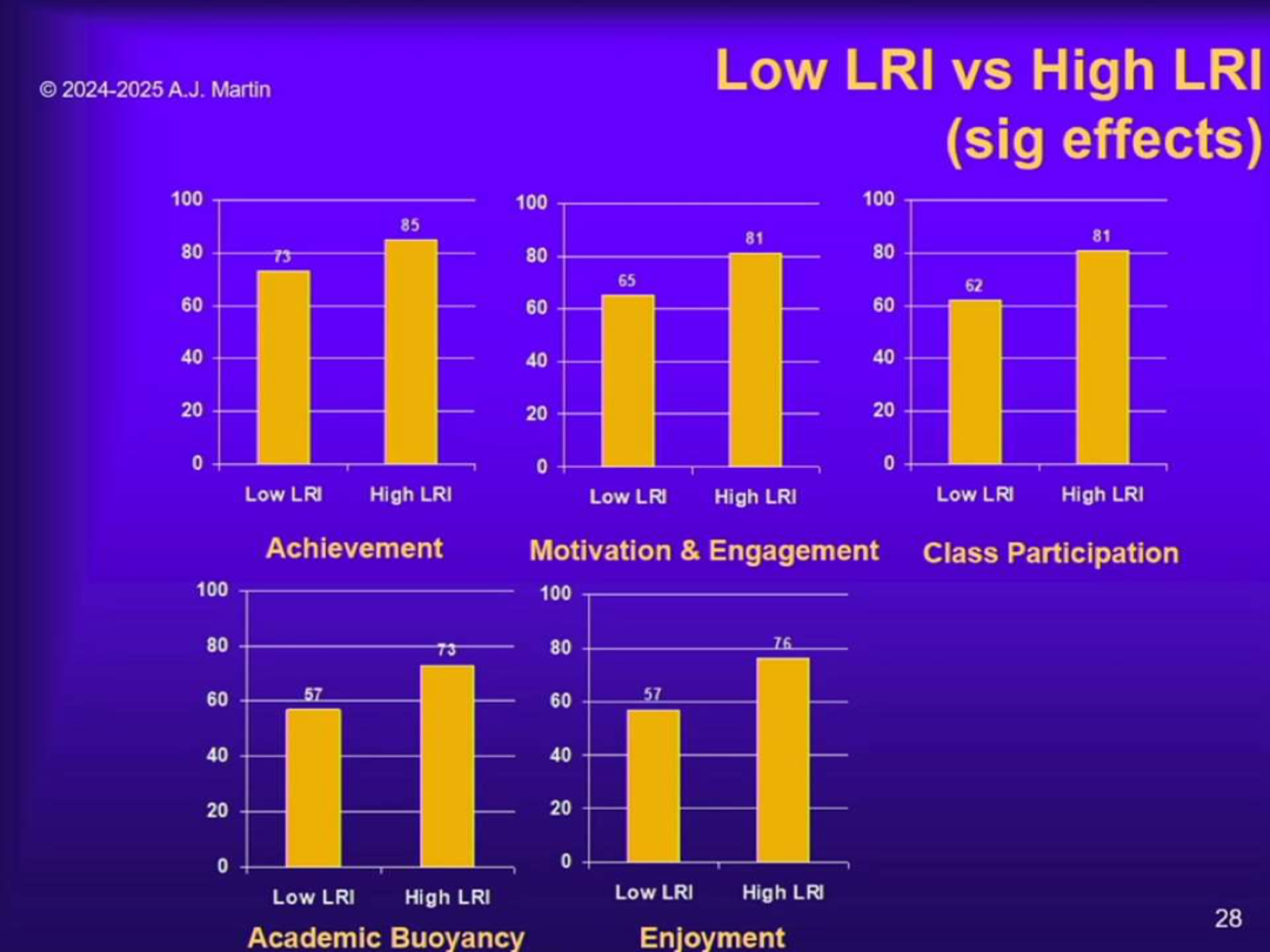
What were the results of Martin & Evans (2018, Study 1)?
High LRI classes showed higher achievement, motivation, engagement, academic buoyancy, and enjoyment compared to low LRI classes.
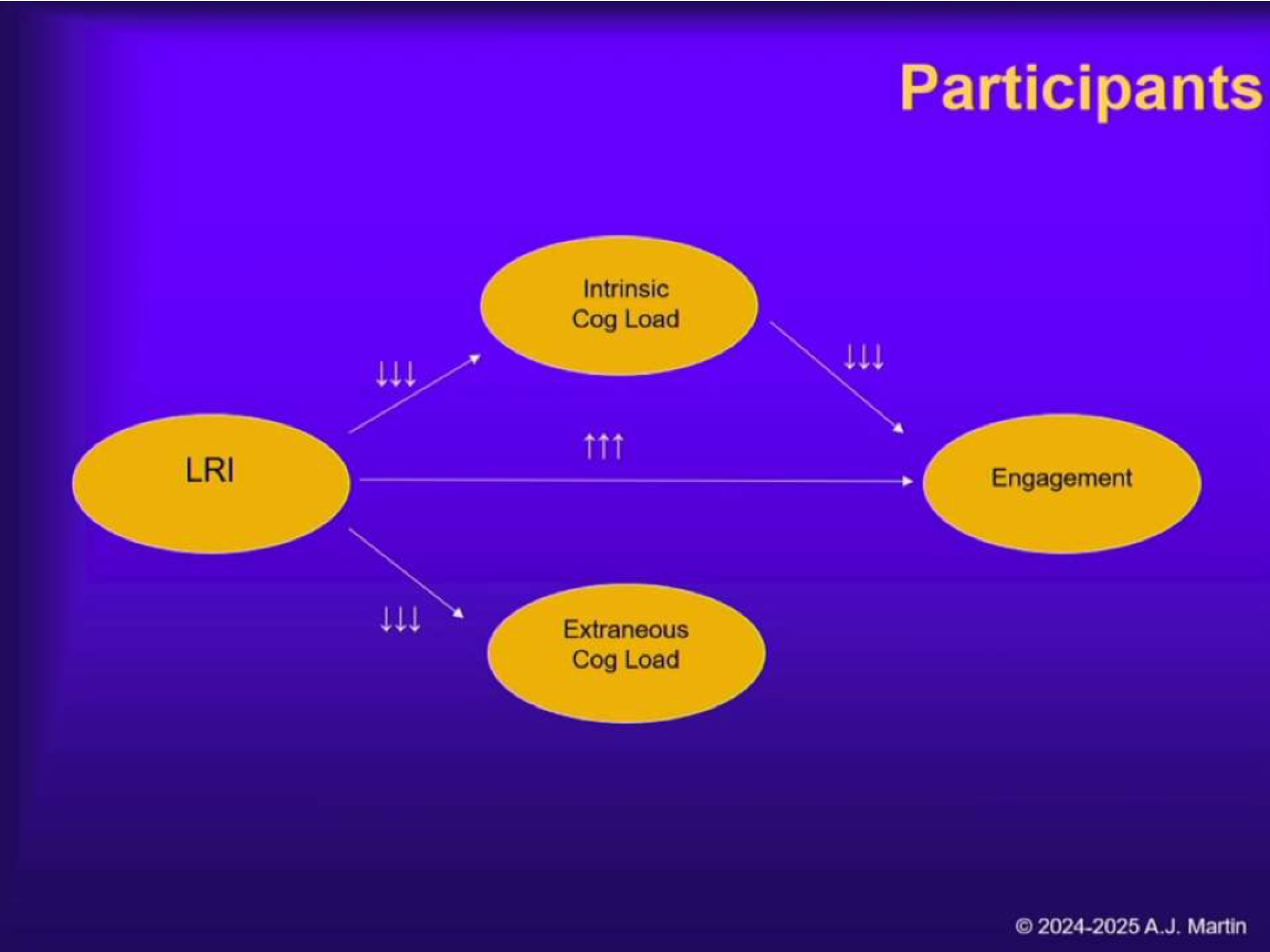
What were the results of Sun et al. (2024, Study 2)?
LRI reduces extraneous load, manages intrinsic load, and increases engagement. Direct path to achievement = not significant; indirect path via engagement = positive.
What were the results of Martin et al. (2021, Study 3)?
In science classrooms, LRI increased engagement and performance, with effects on achievement mostly mediated by engagement.
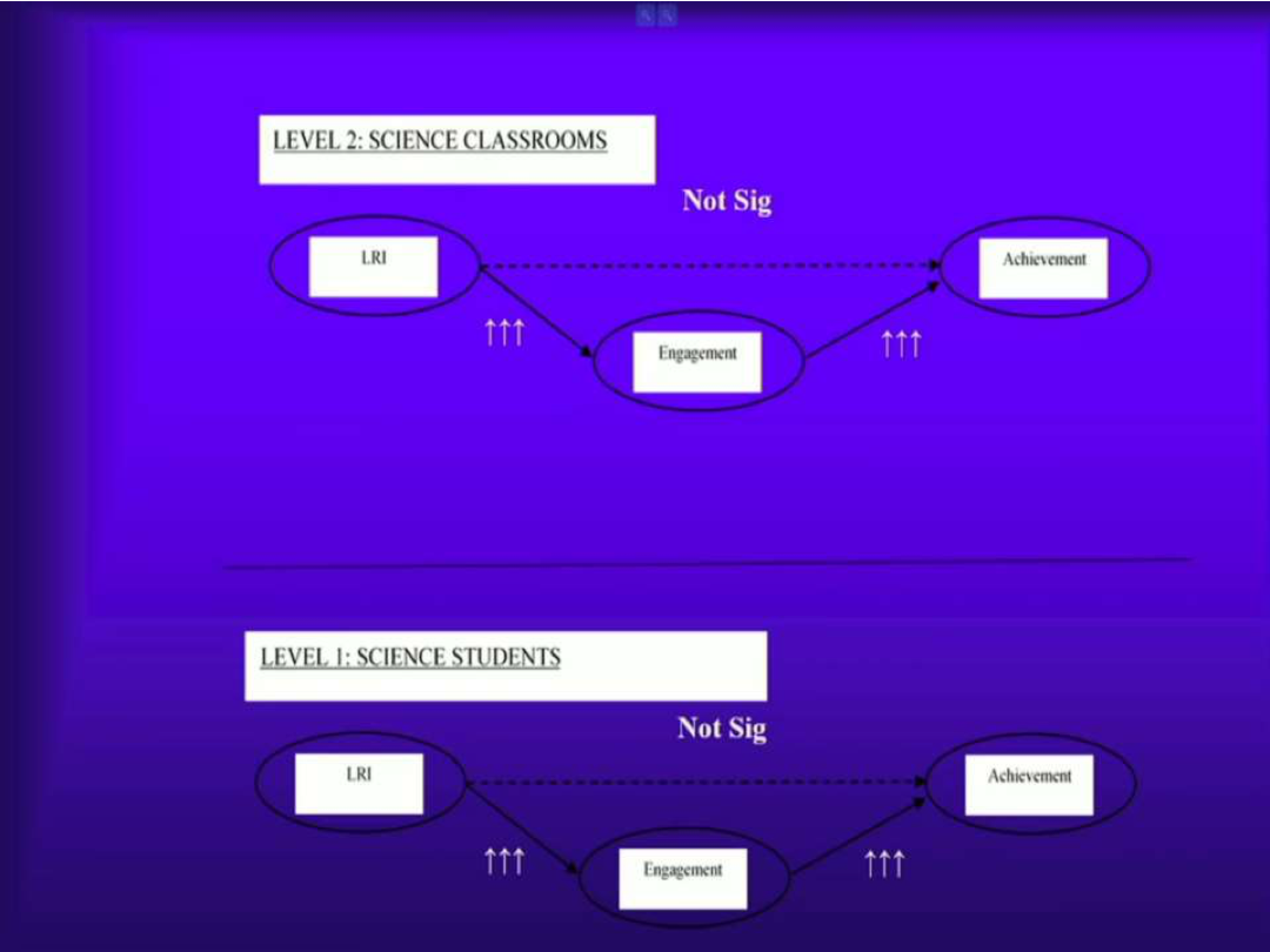
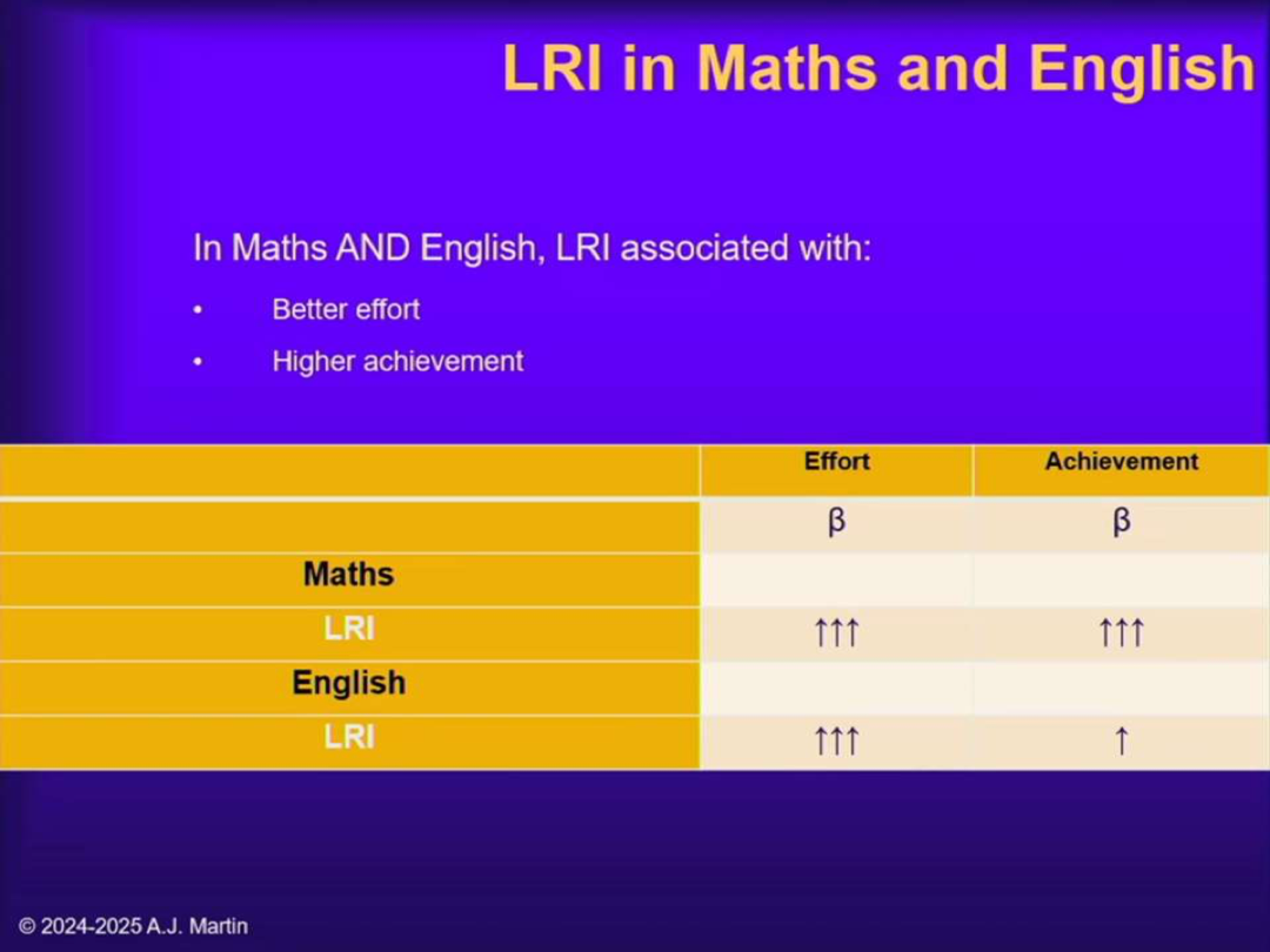
What were the results of Martin et al. (2023, Study 4)?
In both Maths and English, LRI led to more effort and higher achievement.
Does LRI reduce intrinsic or extrinsic cognitive load?
Both: extrinsic is reduced clearly (better explanations); intrinsic is managed (by sequencing and initial simplification).
What is chunking?
Breaking tasks/content into small, manageable parts. Completing each part counts as a success.

What is the Personal Best Index?
A self-referenced progress measure: students compare current performance to their own previous best, not to peers.
