Comprehensive Bio201 Lab: Rat Dissection, Anatomical Terms, and Body Cavities
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Directional Terms
Terms used to describe locations in the body.
Sagittal Plane
A vertical plane that divides the body into right and left parts.
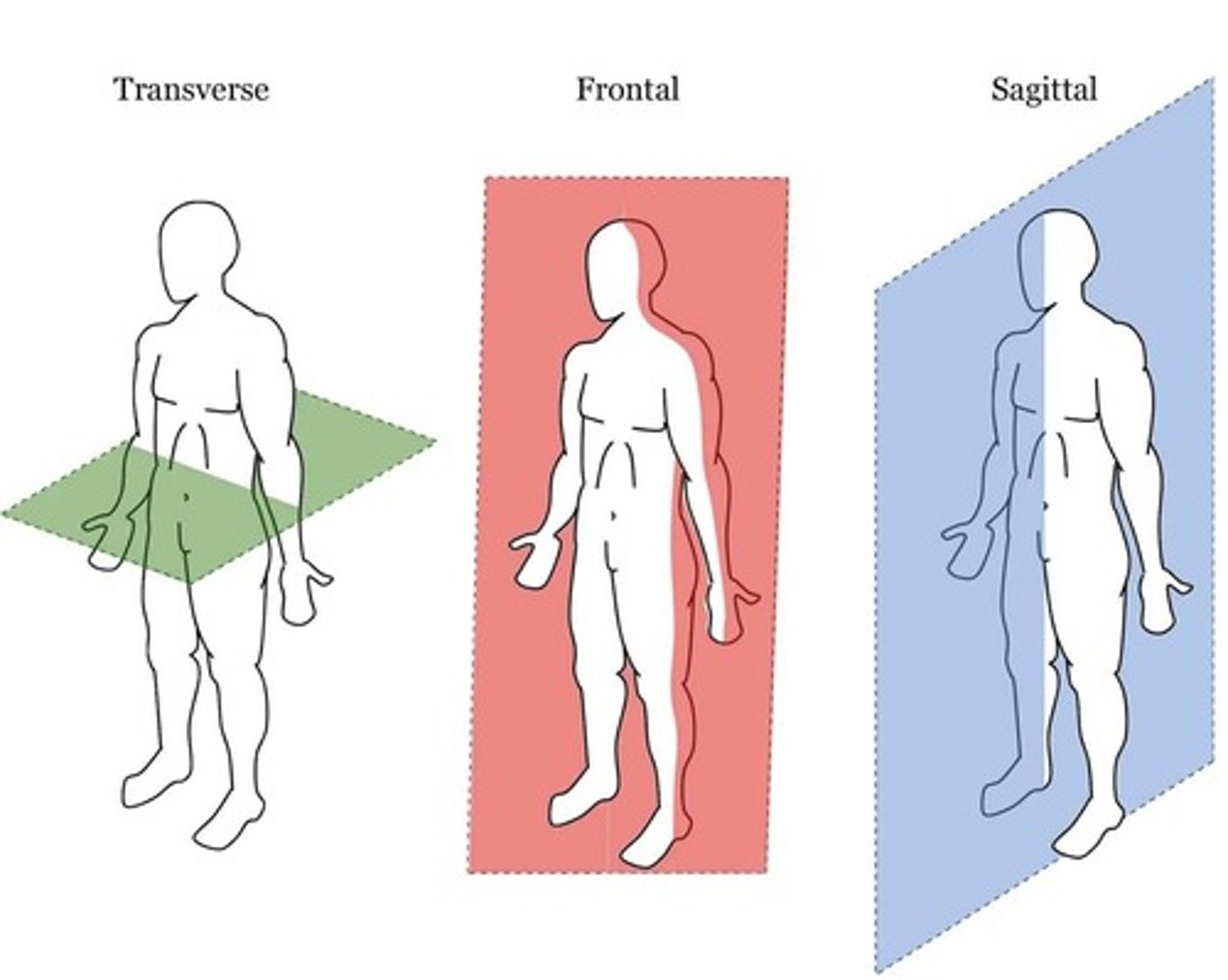
Frontal Plane
A vertical plane that divides the body into anterior and posterior parts.
Transverse Plane
A horizontal plane that divides the body into superior and inferior parts.
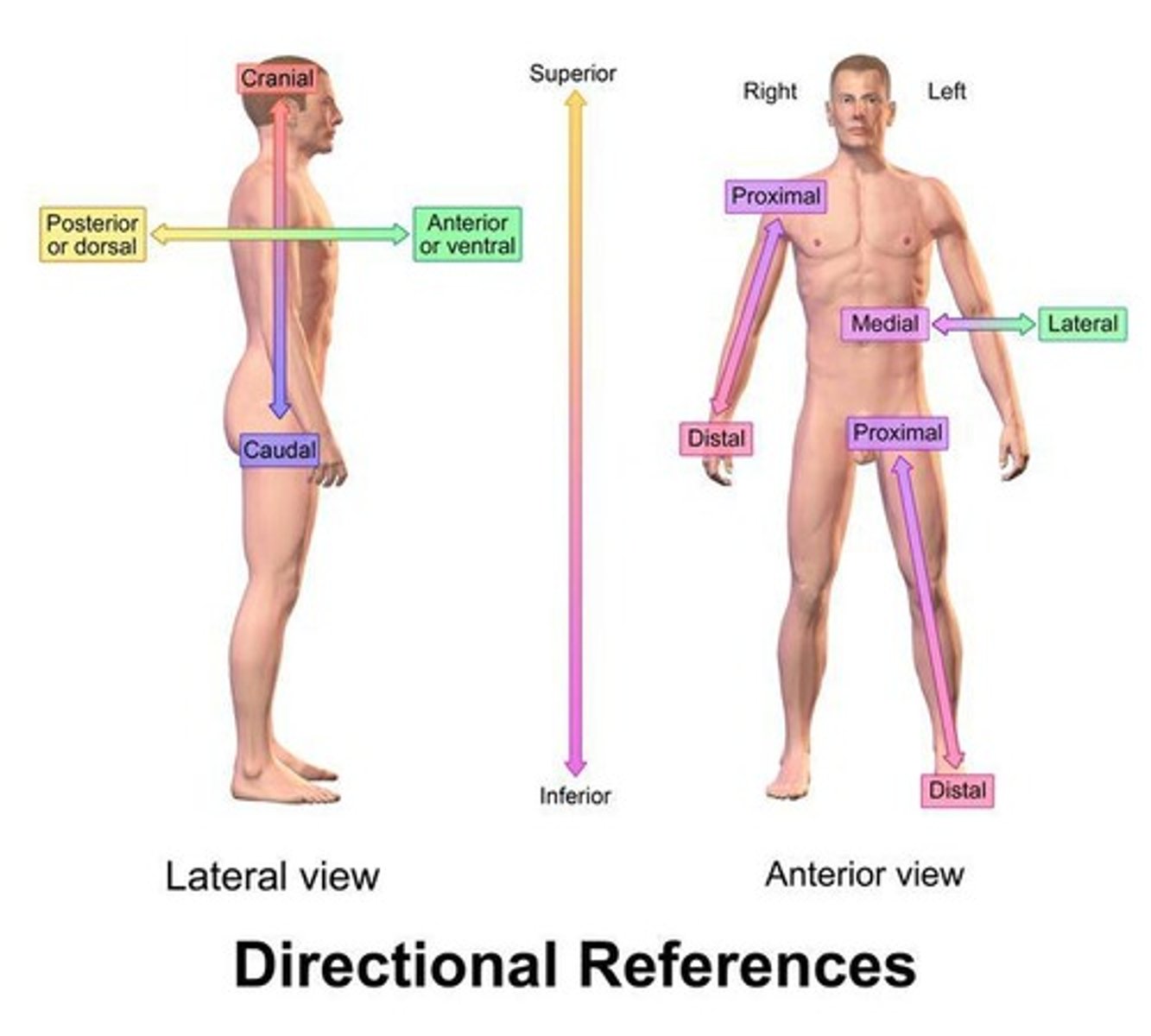
Anterior
Refers to the front of the body.
Posterior
Refers to the back of the body.
Dorsal Surface
The back surface of the body.
Inferior
Refers to a position lower than another part.
Superior
Refers to a position higher than another part.
Palmar Surface
The front surface of the hand.
Plantar Surface
The bottom surface of the foot.
Proximal
Refers to a position closer to the point of attachment.
Distal
Refers to a position further from the point of attachment.
Lateral
Refers to a position away from the midline of the body.
Medial
Refers to a position closer to the midline of the body.
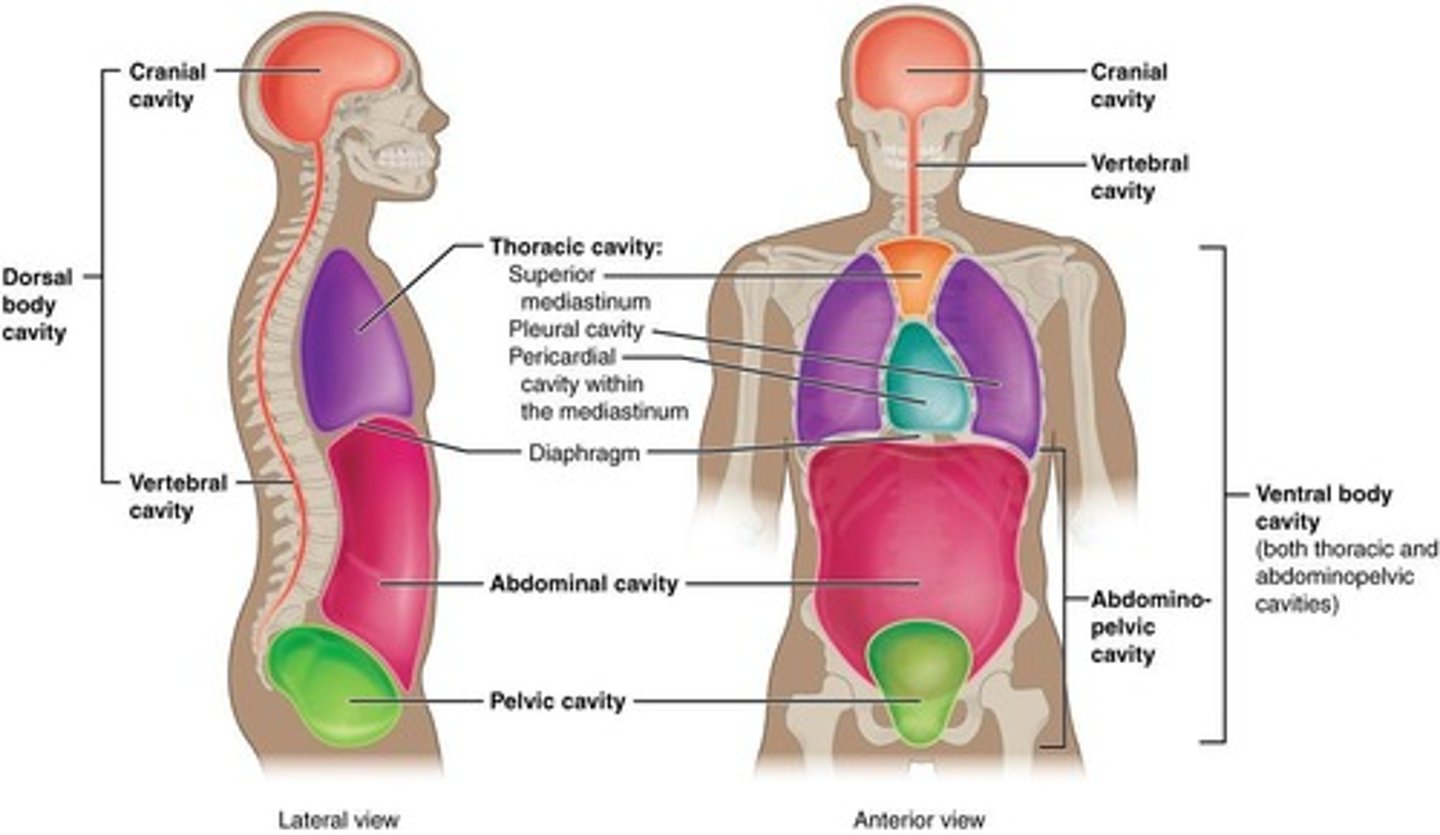
Major Cavities of the Human Body
Includes cranial cavity, spinal cavity, thoracic cavity, abdominal cavity, pelvic cavity, and abdominopelvic cavity.
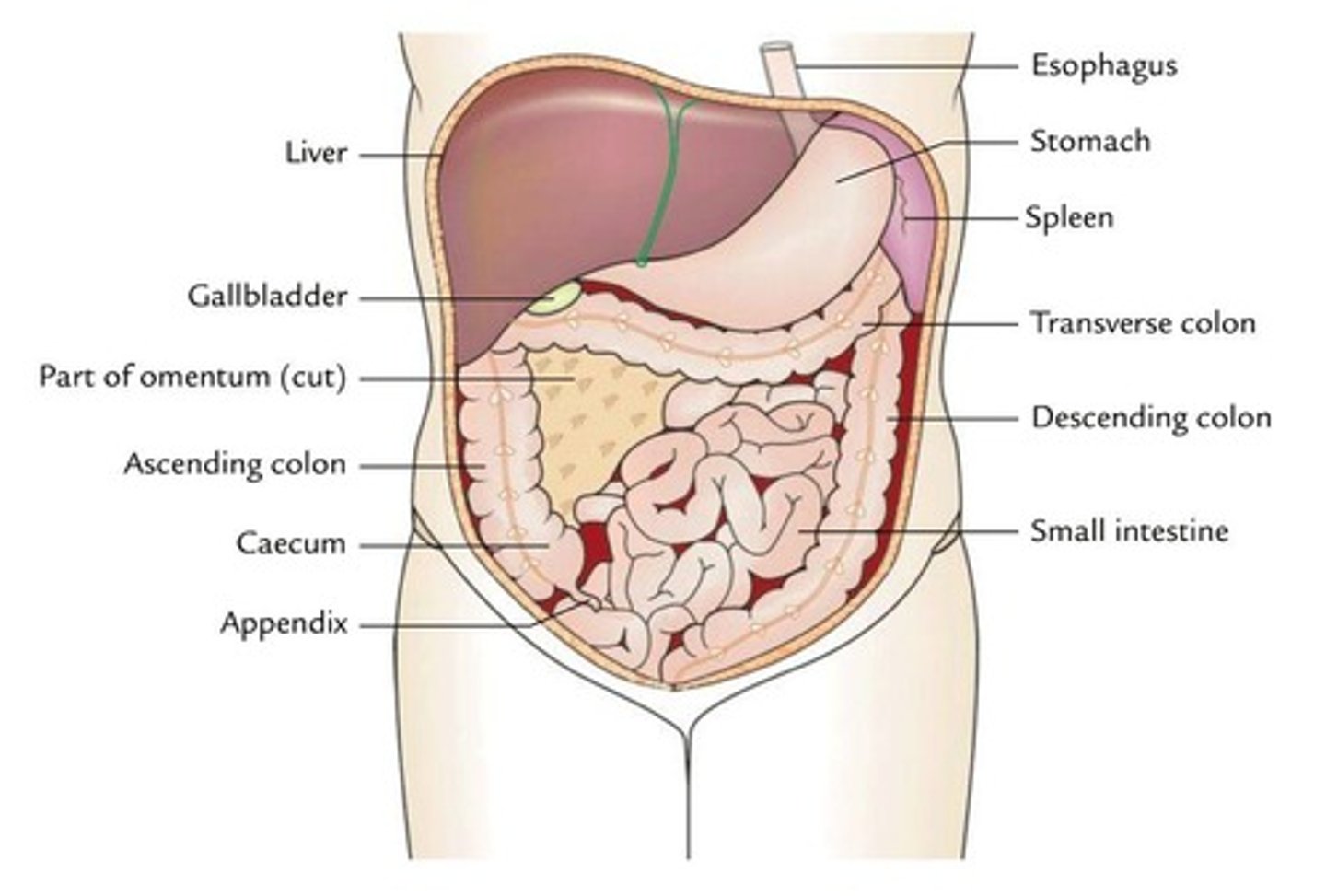
Abdominal Cavity
The space inferior to the diaphragm, superior to the hip bones, and enclosed by the peritoneum.
Pericardium
The membrane that surrounds the heart.
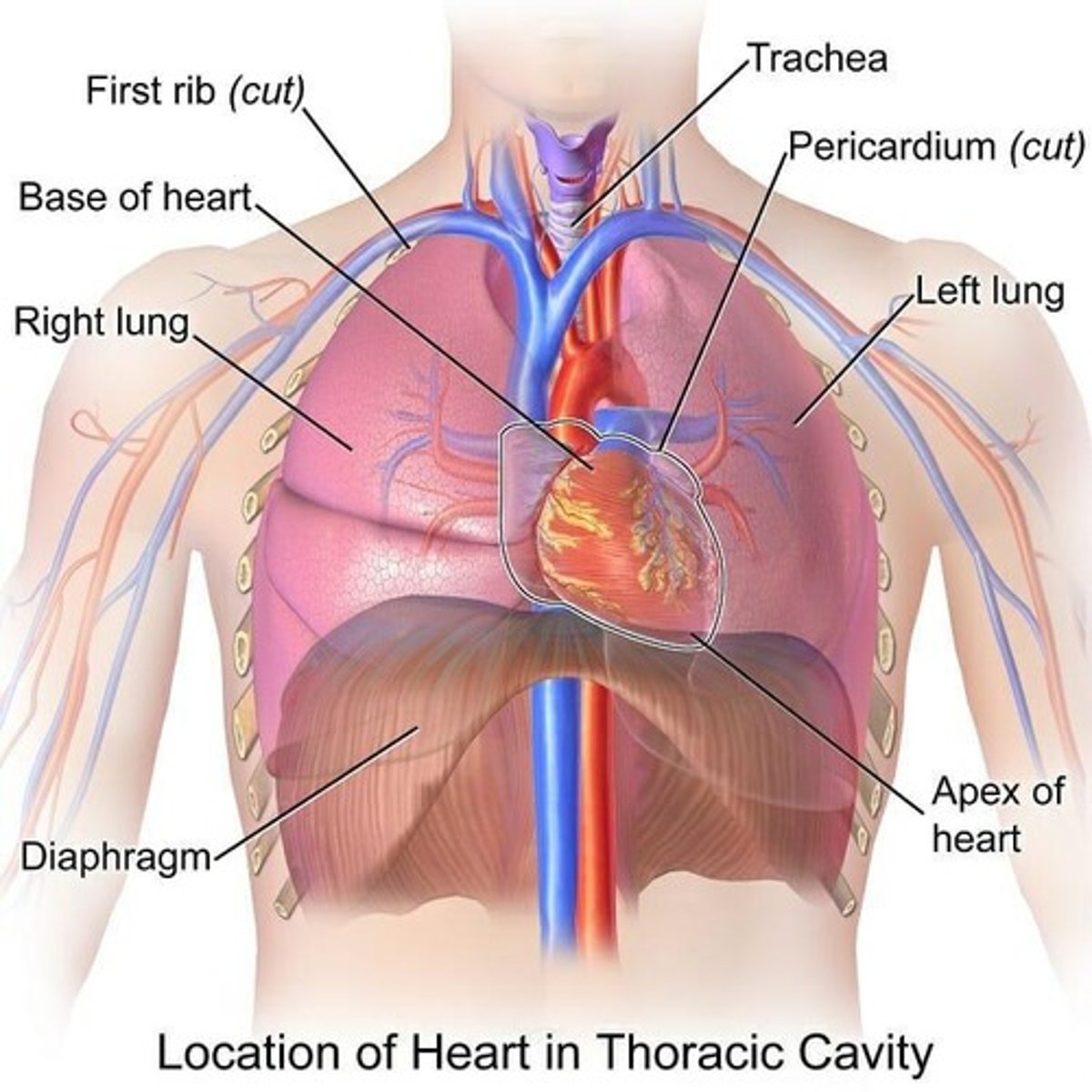
Membrane surrounding the lungs
Pleura.
Diaphragm
A muscle that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity.
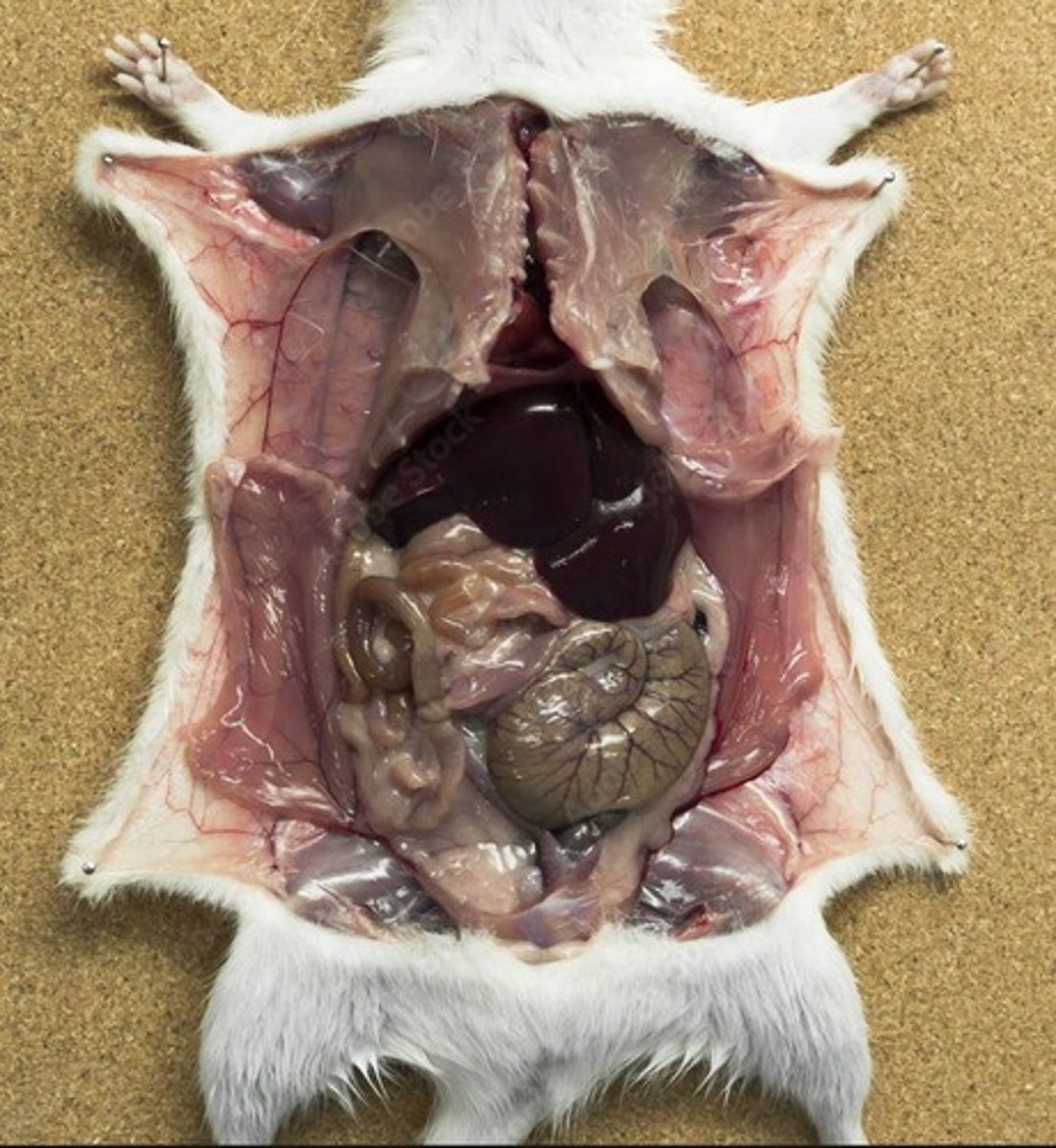
Spleen
An organ involved in filtering blood and immune response.
Liver
An organ that processes nutrients and detoxifies substances.
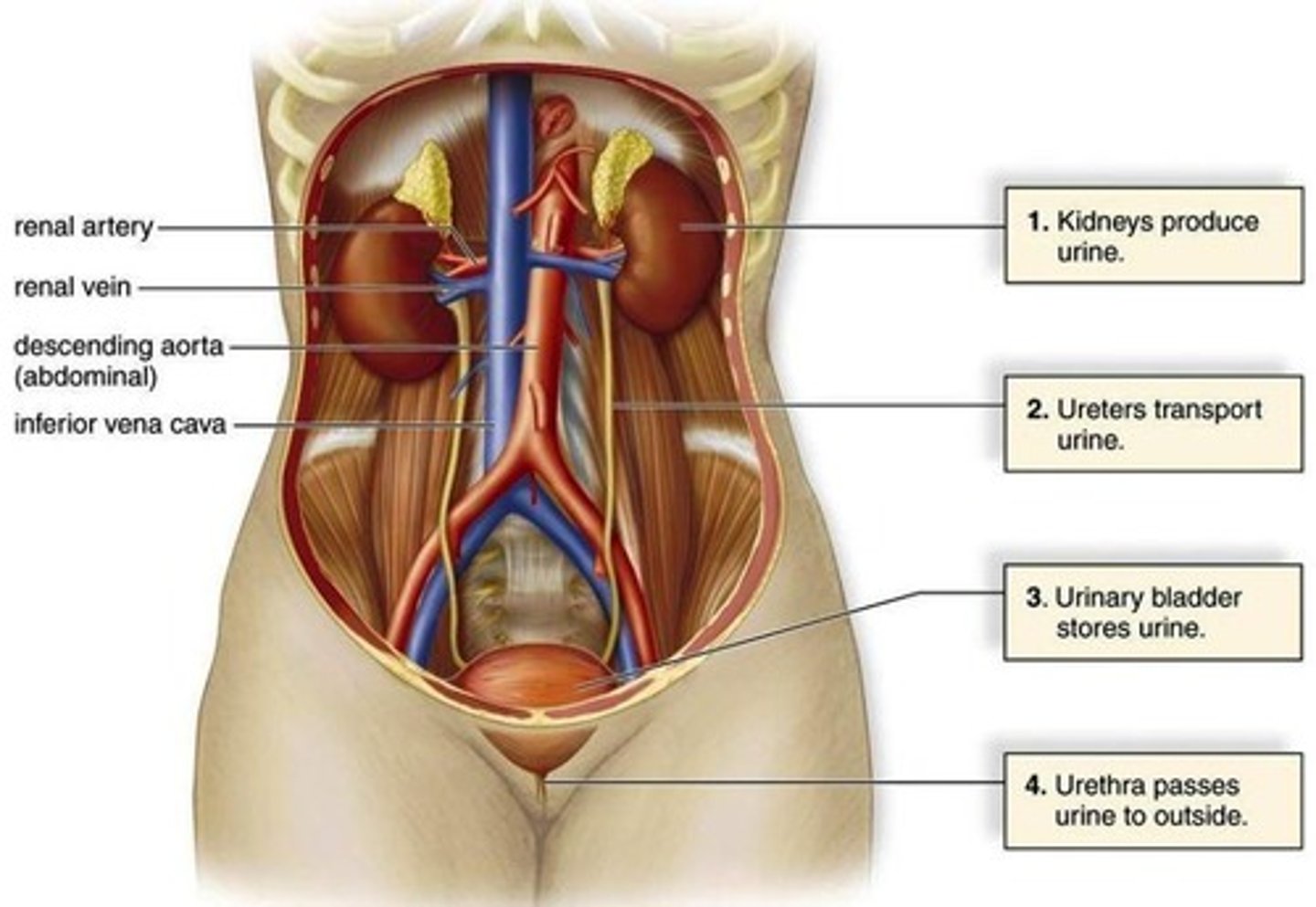
Ureters
Tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
Large intestine
The part of the digestive system that absorbs water and forms feces.
Pancreas
An organ that produces digestive enzymes and hormones like insulin.
Kidneys
Organs that filter blood to produce urine.
Small intestine
The part of the digestive system where most digestion and absorption occurs.
Stomach
An organ that breaks down food using acids and enzymes.
Lungs
Organs responsible for gas exchange in the respiratory system.
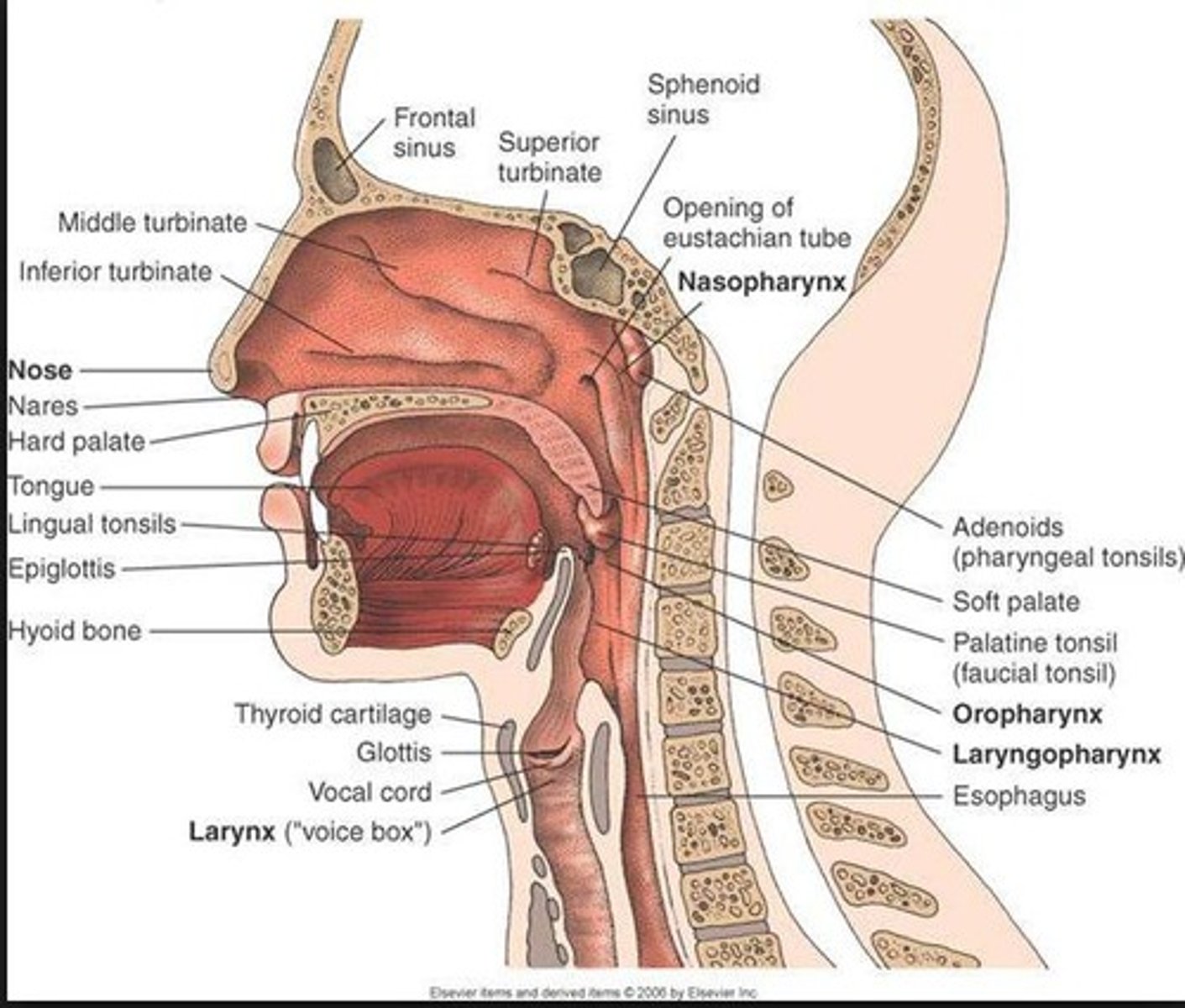
Esophagus
The tube that carries food from the mouth to the stomach.
Mesentery
Tissue that attaches the small intestine to the abdominal wall.
Trachea
The windpipe that connects the throat to the lungs.
Aorta
The main artery that carries blood from the heart to the body.
Cecum
The beginning of the large intestine.
Adrenal glands
Glands that produce hormones like adrenaline.
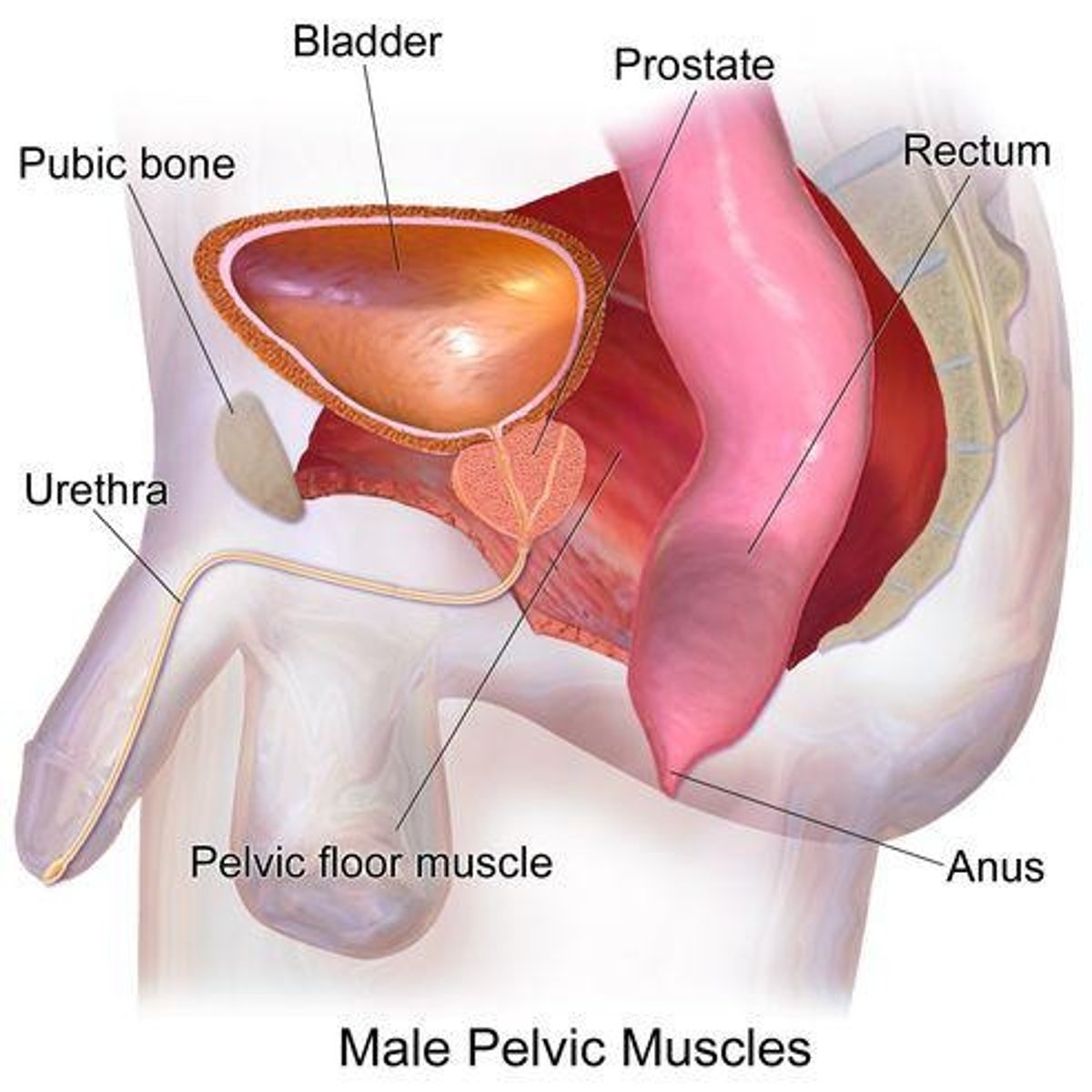
Bladder
An organ that stores urine before it is excreted.
Prostate
A gland that produces fluid that nourishes and transports sperm.
Thymus
An organ involved in the immune system, particularly in T-cell maturation.
Brain
The organ that serves as the control center of the nervous system.
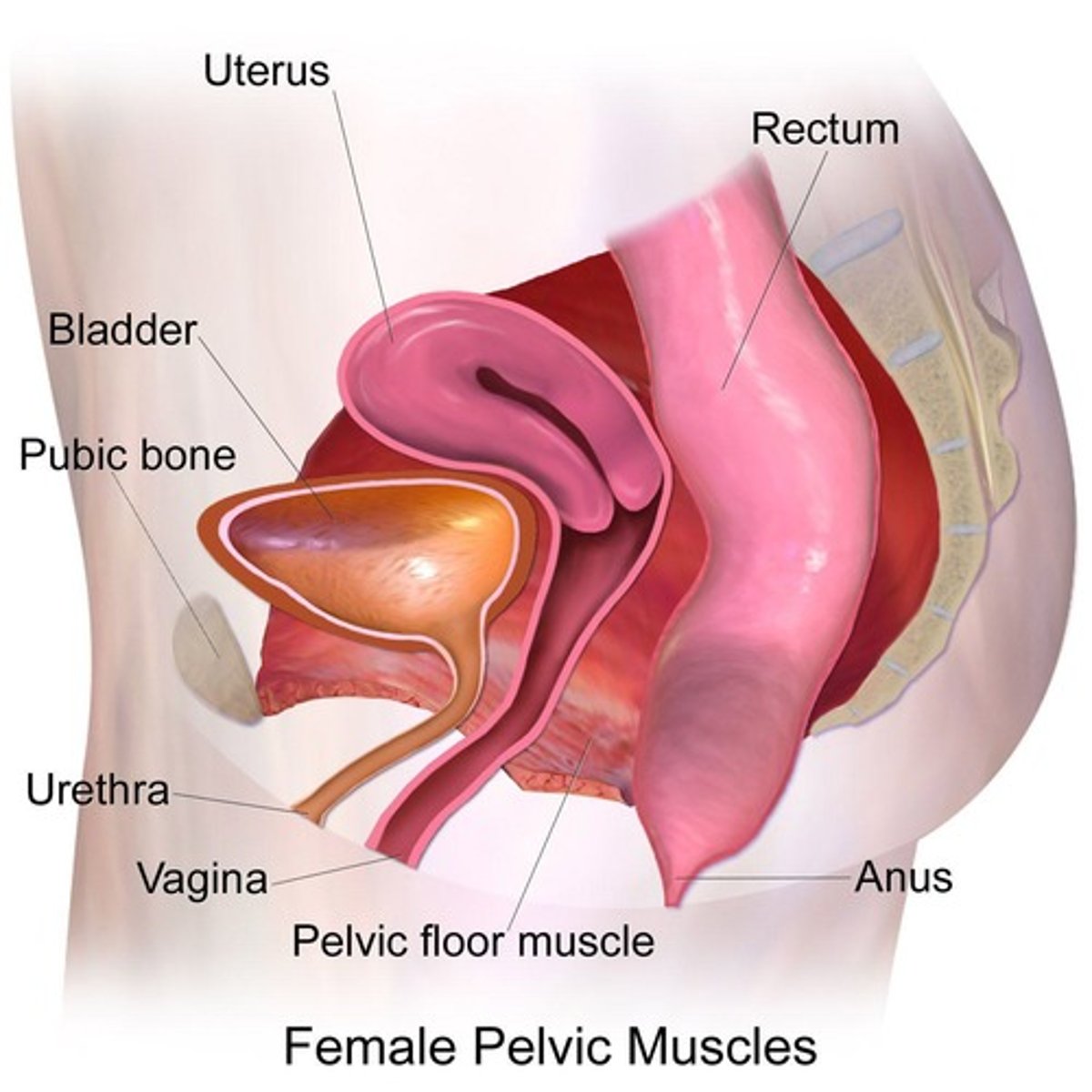
Vagina
The canal that leads from the external genitals to the uterus.