108.5
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
what is the purpose of the microscopic examination of urine?
to detect and identify insoluble materials present in the urine
List the seven chemical parameters commonly used as markers in macroscopic screening.
Color,Clarity, Blood, Protein, Nitrite, Leukocyte esterase, glucose
List the three CLSI recommendations for urine macroscopic screening
Requested by the physician, Laboratory- specified patient population, Any abnormal physical or chemical result
What is an important step in specimen preparation to ensure an adequate urine sediment?
Fresh urine or 2-4 hours in the refrigerator, thoroughly mix specimen before putting it on the slide.
Why is 10-12 ml indicated for a urine volume to perform an accurate urine microscopic?
Reagent strips are easily immersed in this volume and capped centrifuge tubes are often calibrated to this volume.
Why is the centrifugation speed or centrifugal force (RCF) important in standardization
Produces an optimum amount of sediment with the least chance of damaging the elements,
what is the recommended RCF and time of centrifugation?
5 mins. at 400 RCF
Why is RCF a more accurate way to determine optimum speed of centrifuge?
RCF corrects for variations in the diameter of centrifuge heads, revolutions per minute does not.
What is the desired ratio of urine volume to sediment?
12:1
Why should the amount of supernatant poured off be controlled?
So, you don't lose any sediment at the bottom of the test tube
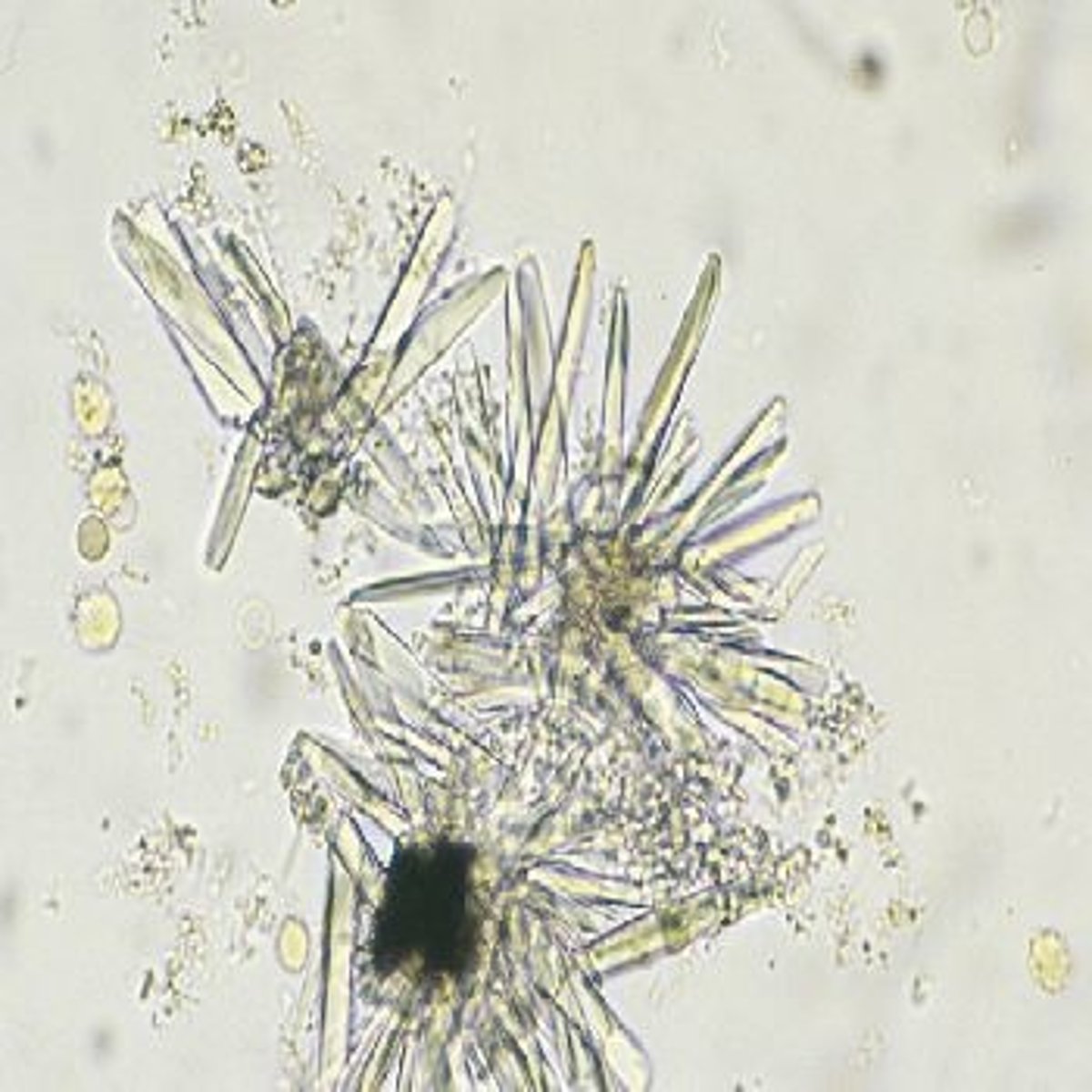
Sulfonamide crystal
dehydration, shapes include neeldes, rhombic, whetstones, sheaves of wheat, and rosettes with colors ranging from colorless to yellow brown, infection treatment
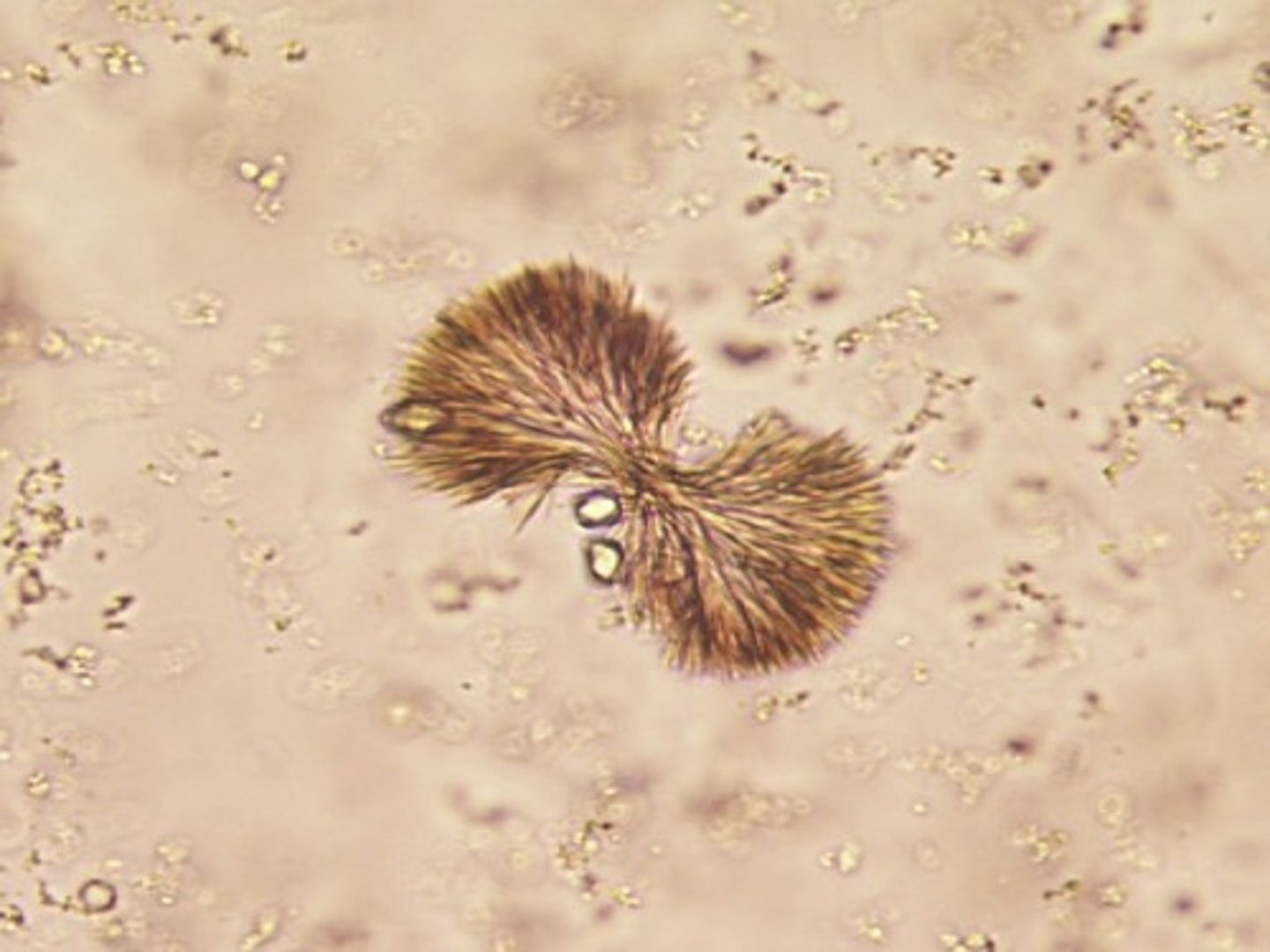
Amorphous urates
acidic urine, pink precipitate
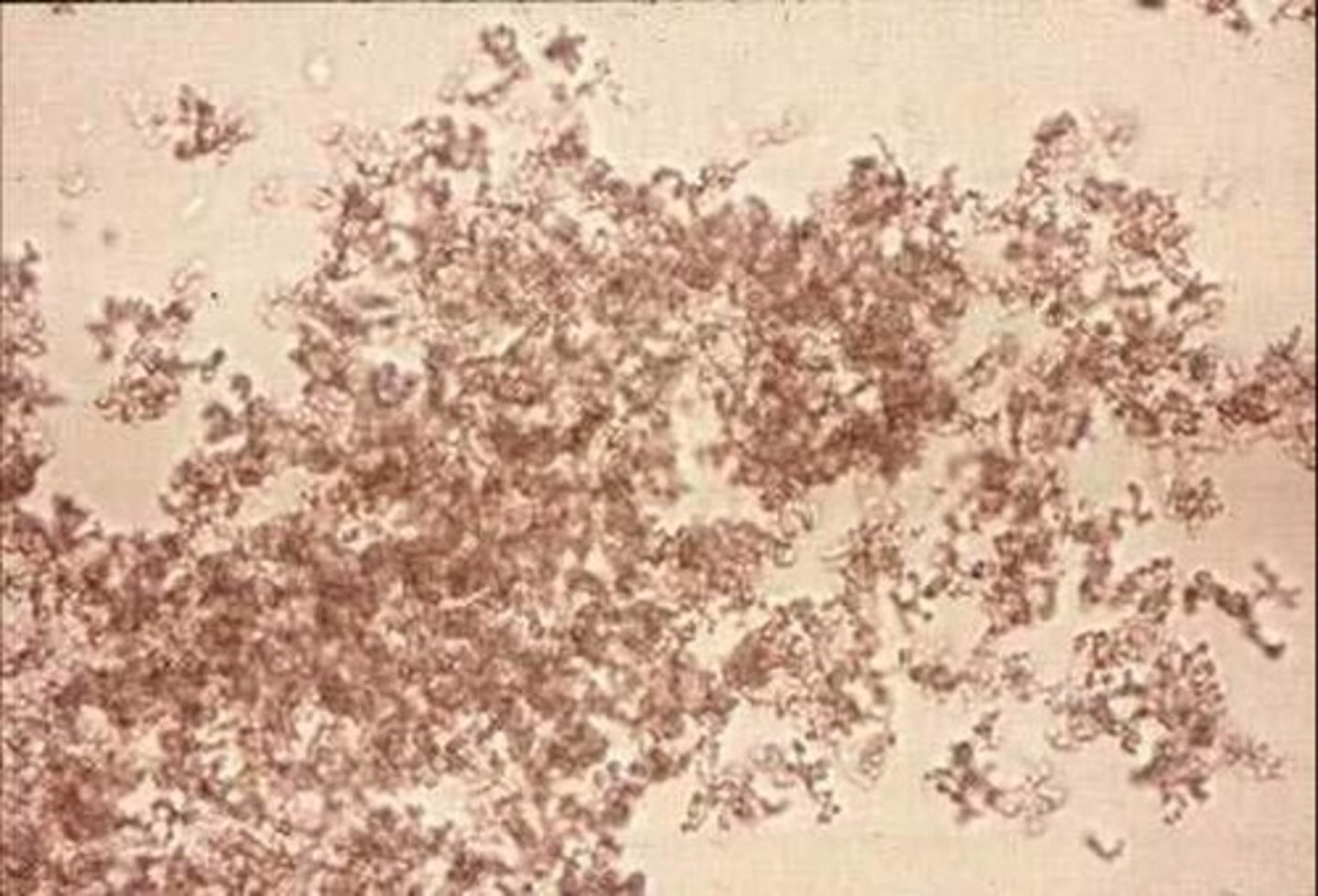
uric acid
acidic urine, rhombode, rosettes
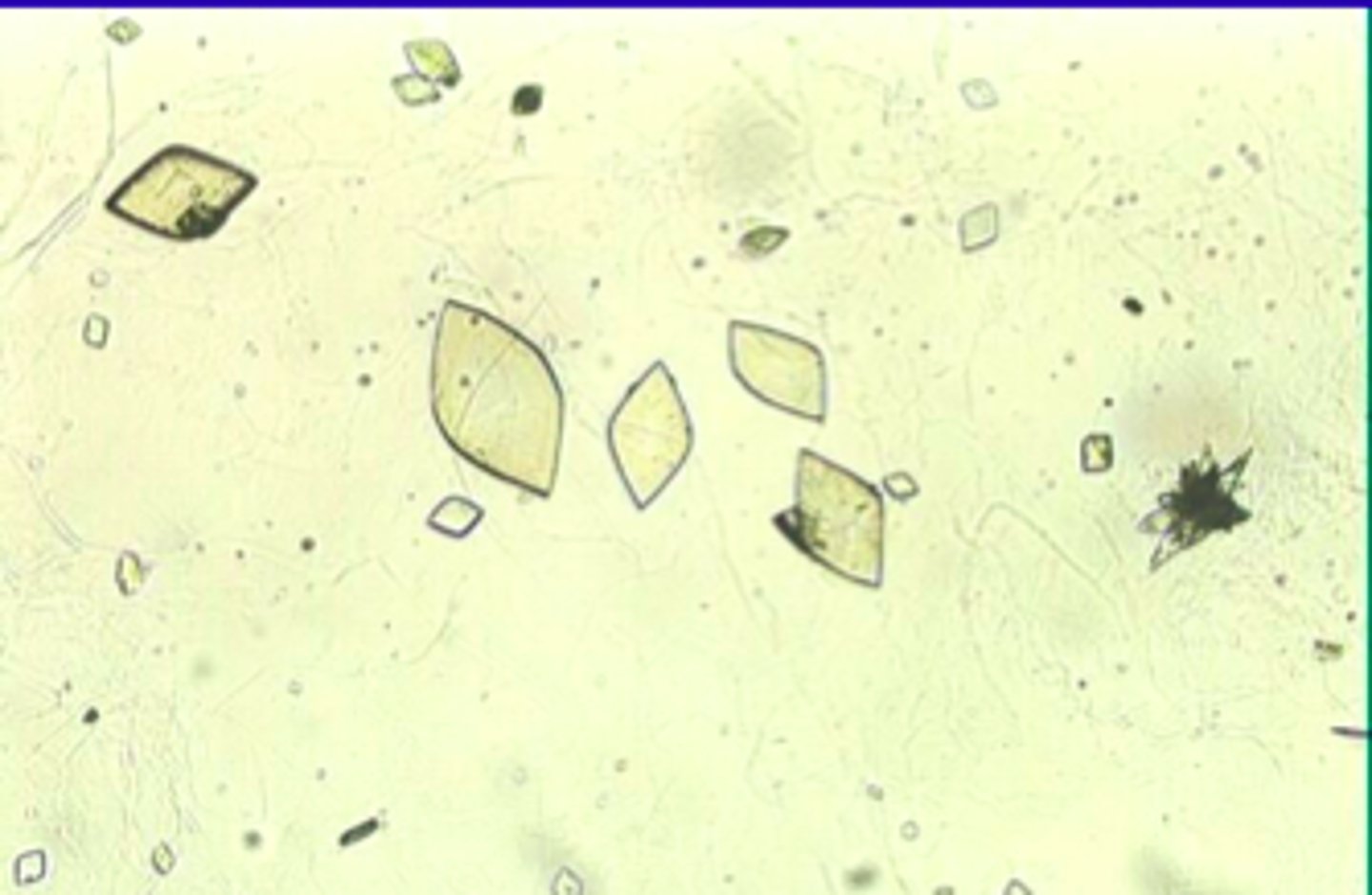
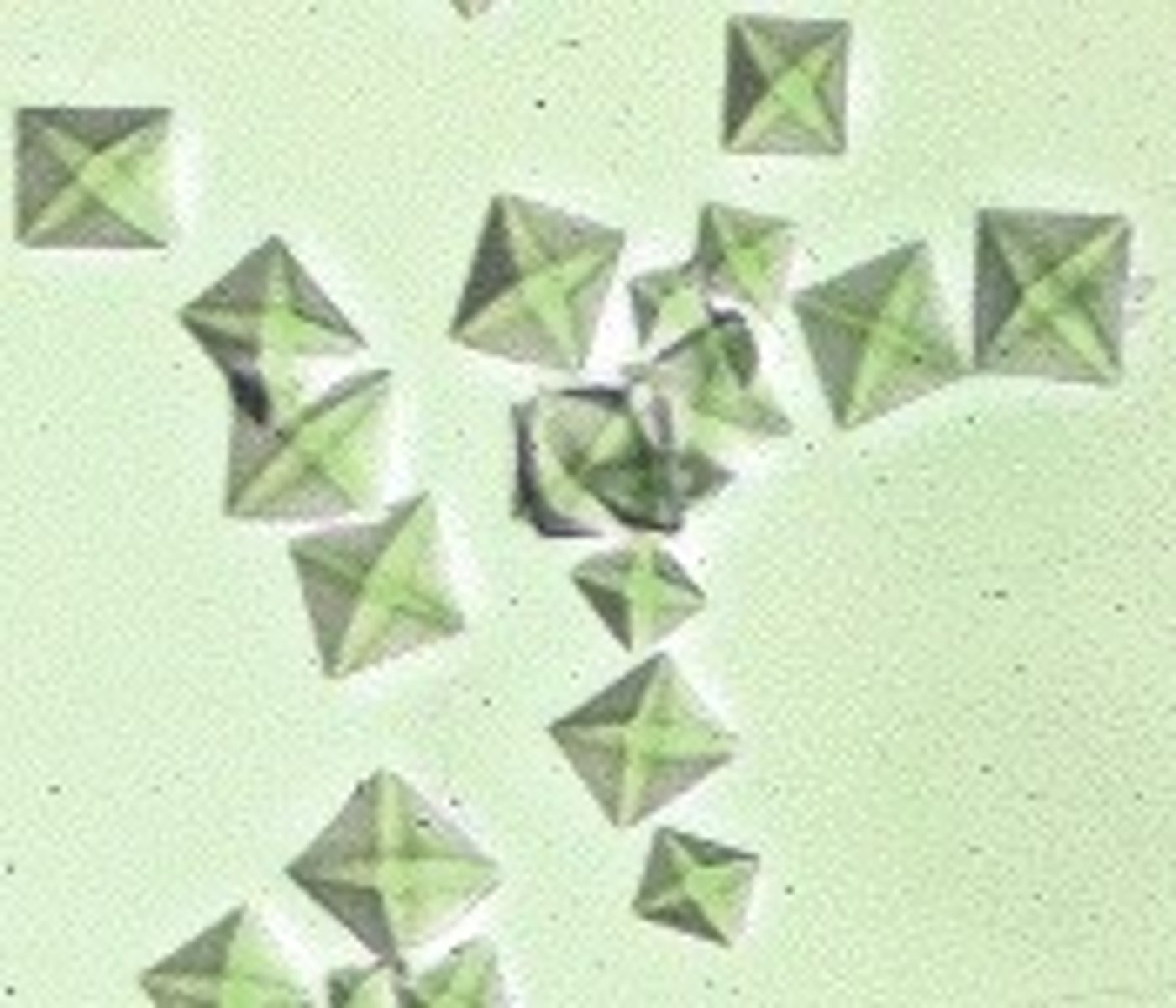
calcium monohydrate
acidic urine, ovoid calcium oxalate
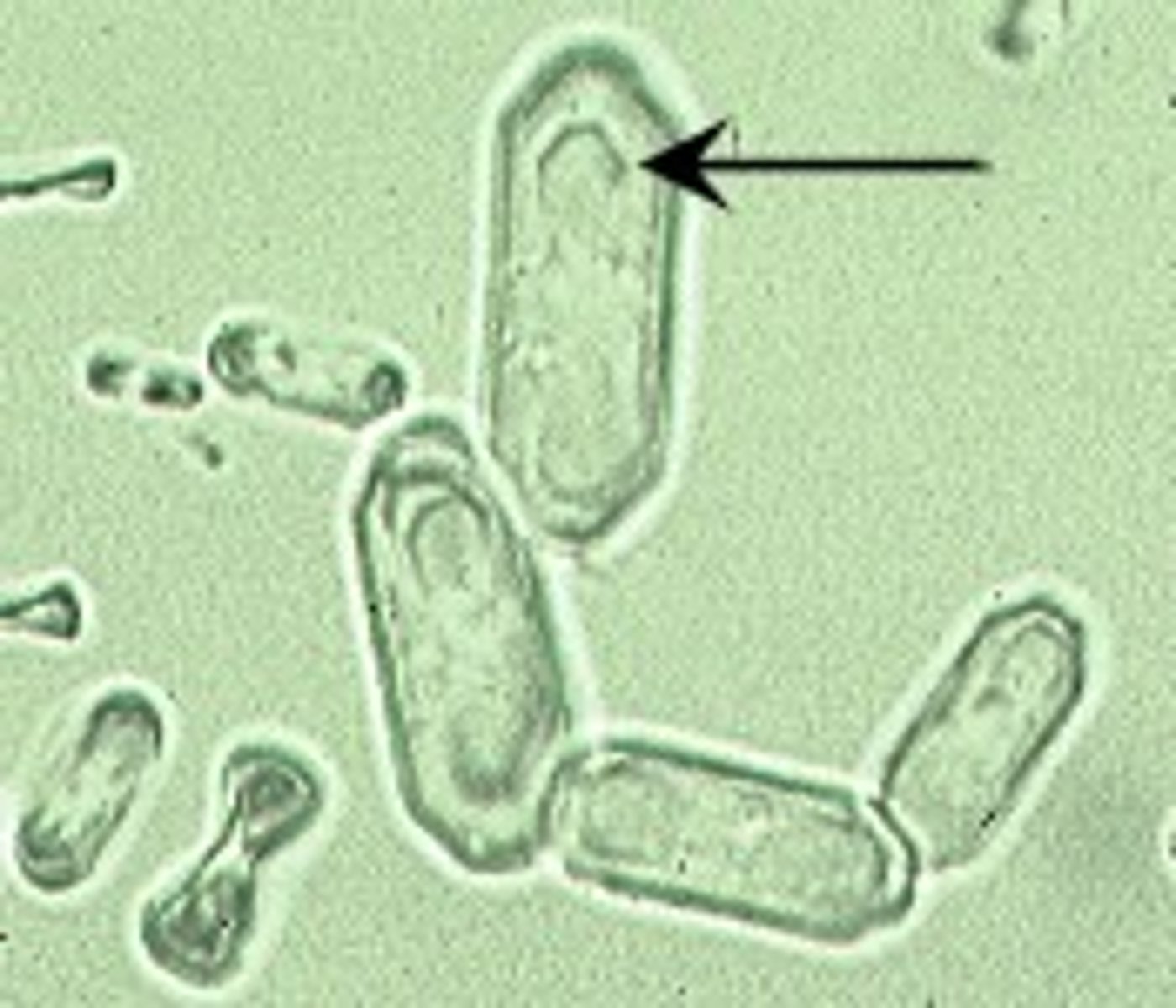
calcium oxalate
acidic urine, envelopes

sodium urates
acidic urine, thin needles
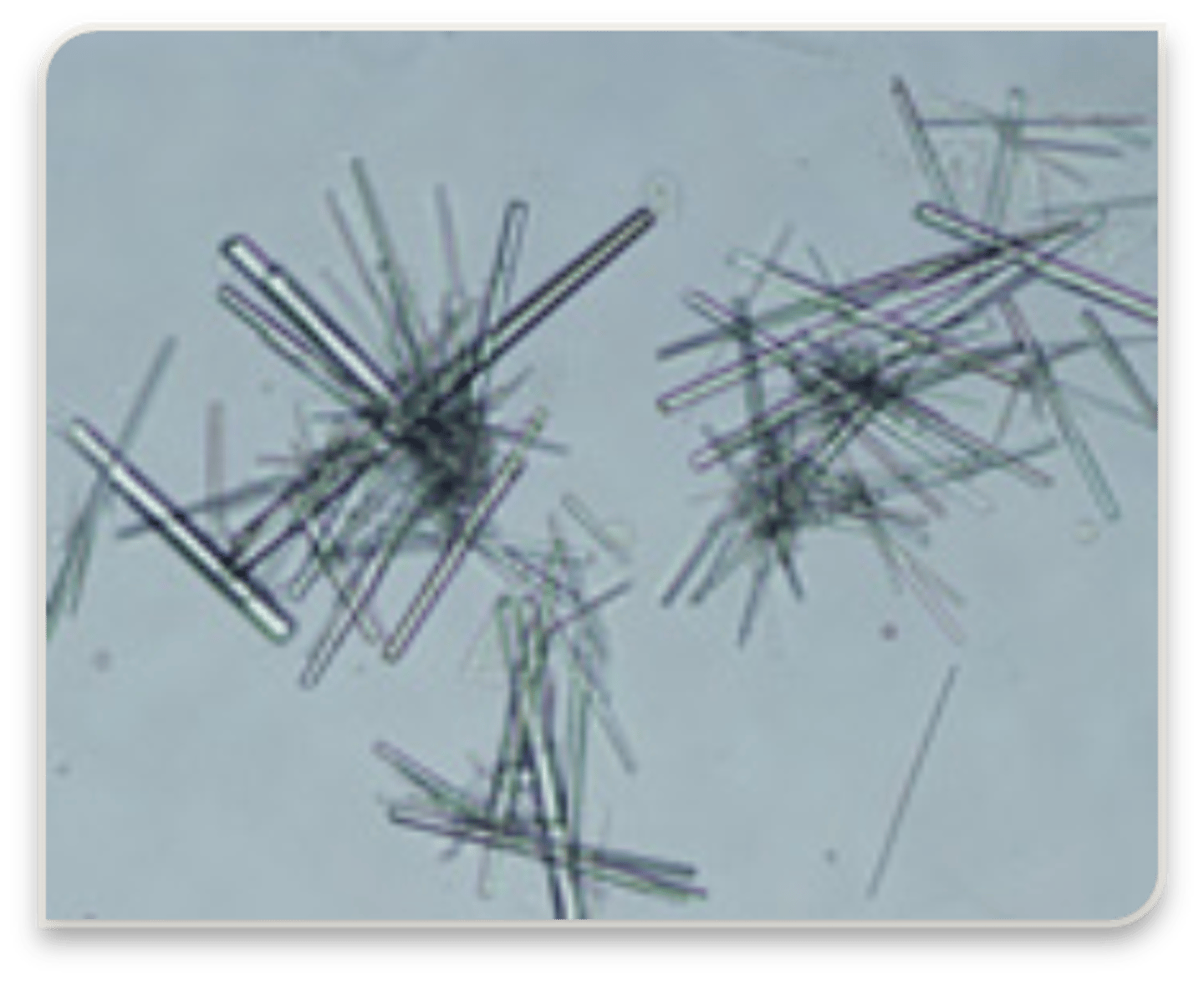

amorphous phosphates
alkaline urine, white precipate
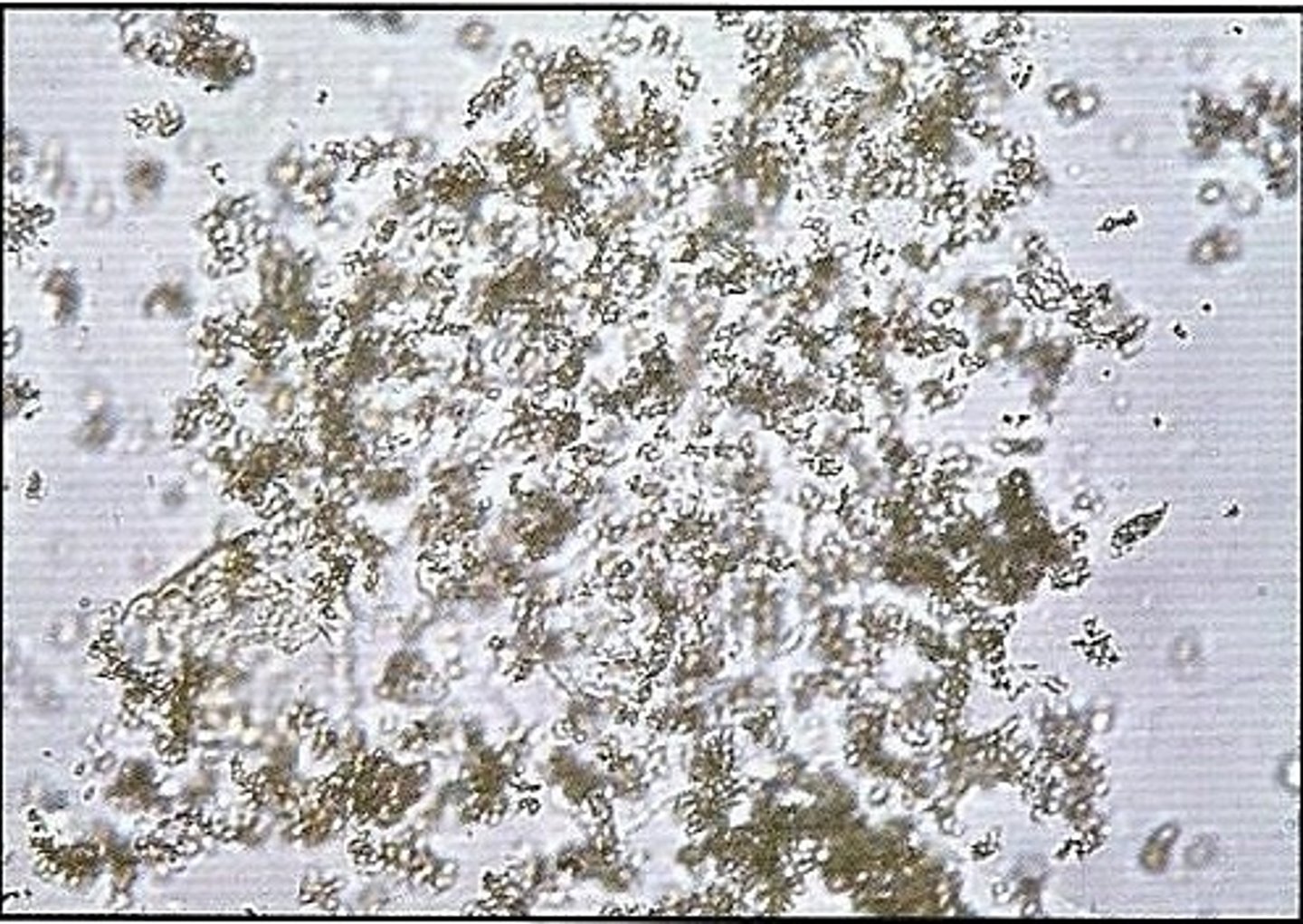
triple phosphate
alkaline urine, "coffin lids", colorless
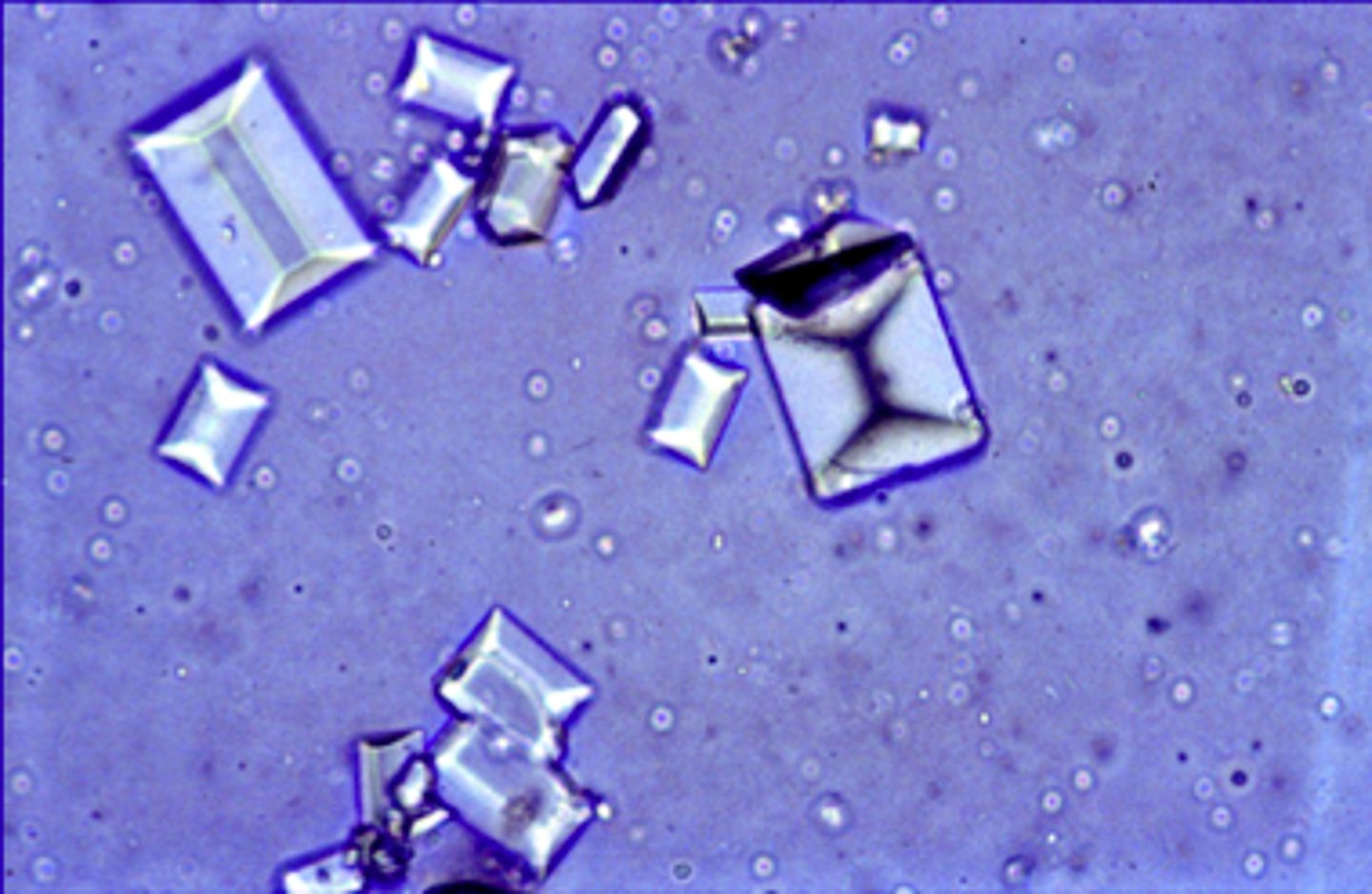
ammonium biurate
alkaline urine, thorny apple phosphate, yellow brown
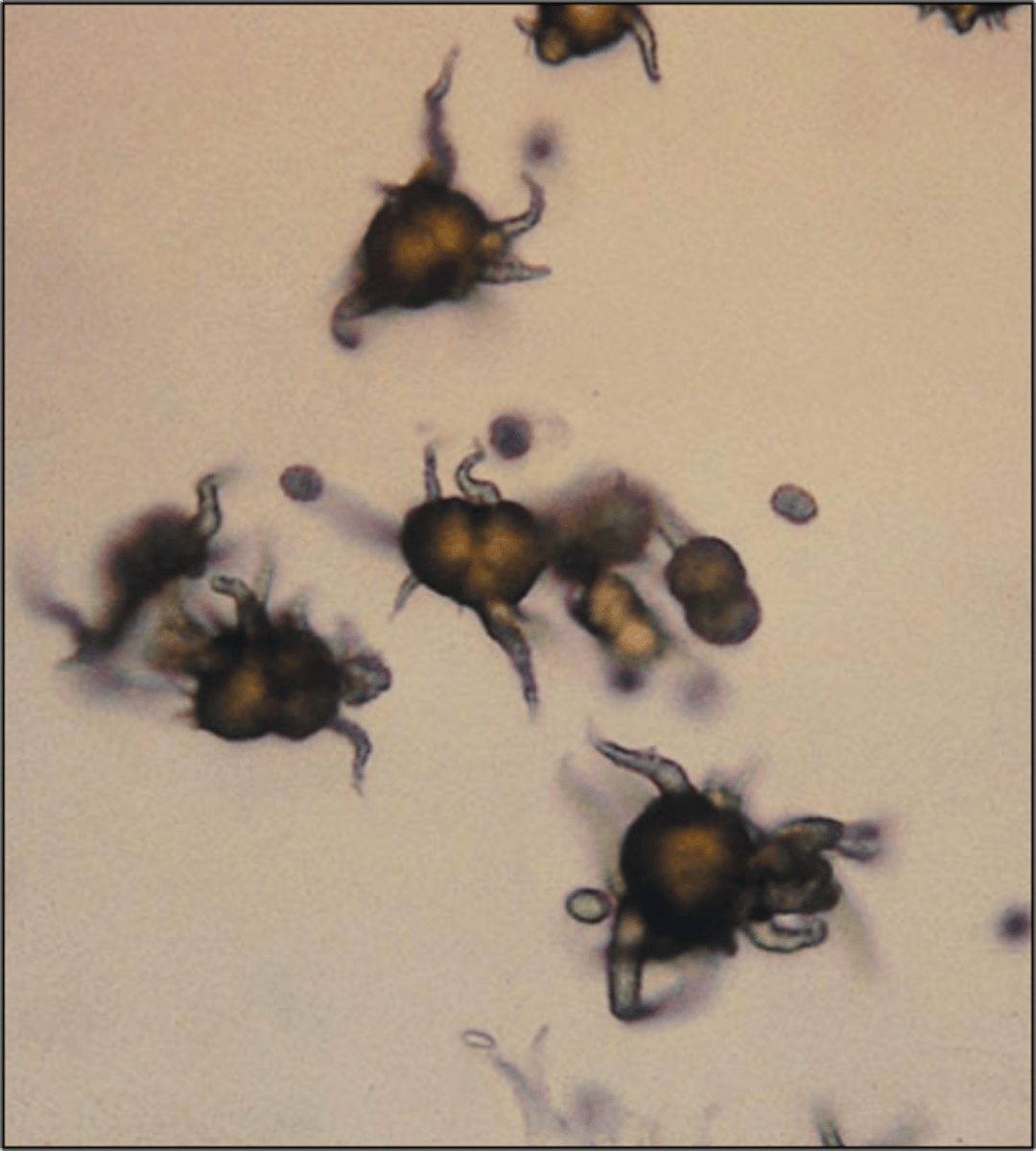
calcium phosphate
alkaline urine, thin prisms, flat rectangles, colorless
calcium carbonate
alkaline urine, dumbbell shape, small, colorless
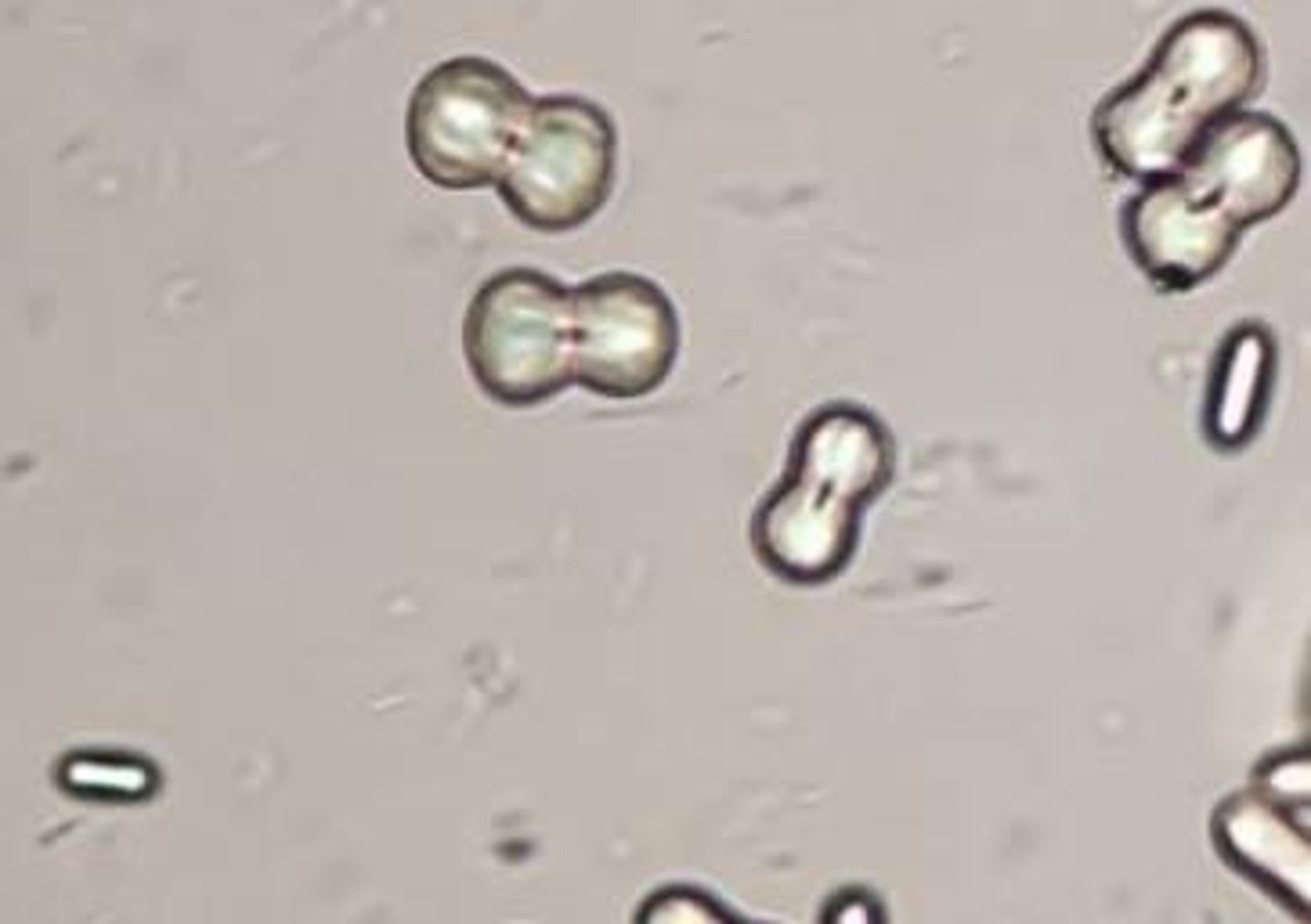
Cystine crystal
abnormal, hexagonal plates, thin and thick plated, colorless, inherited cystinuria
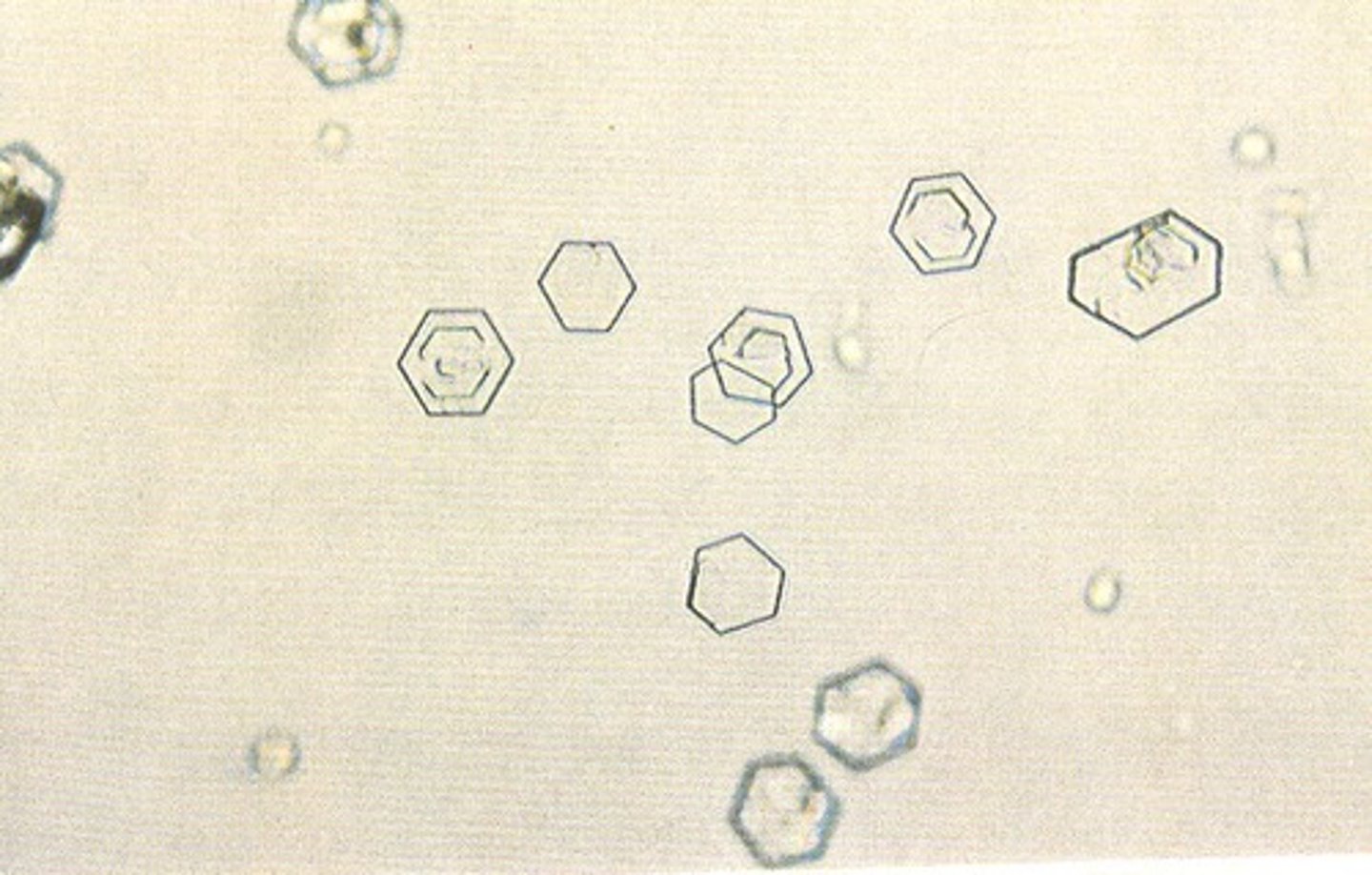
Cholesterol crystal
abnormal, rectangular plates with notched corners, nephrotic syndrome
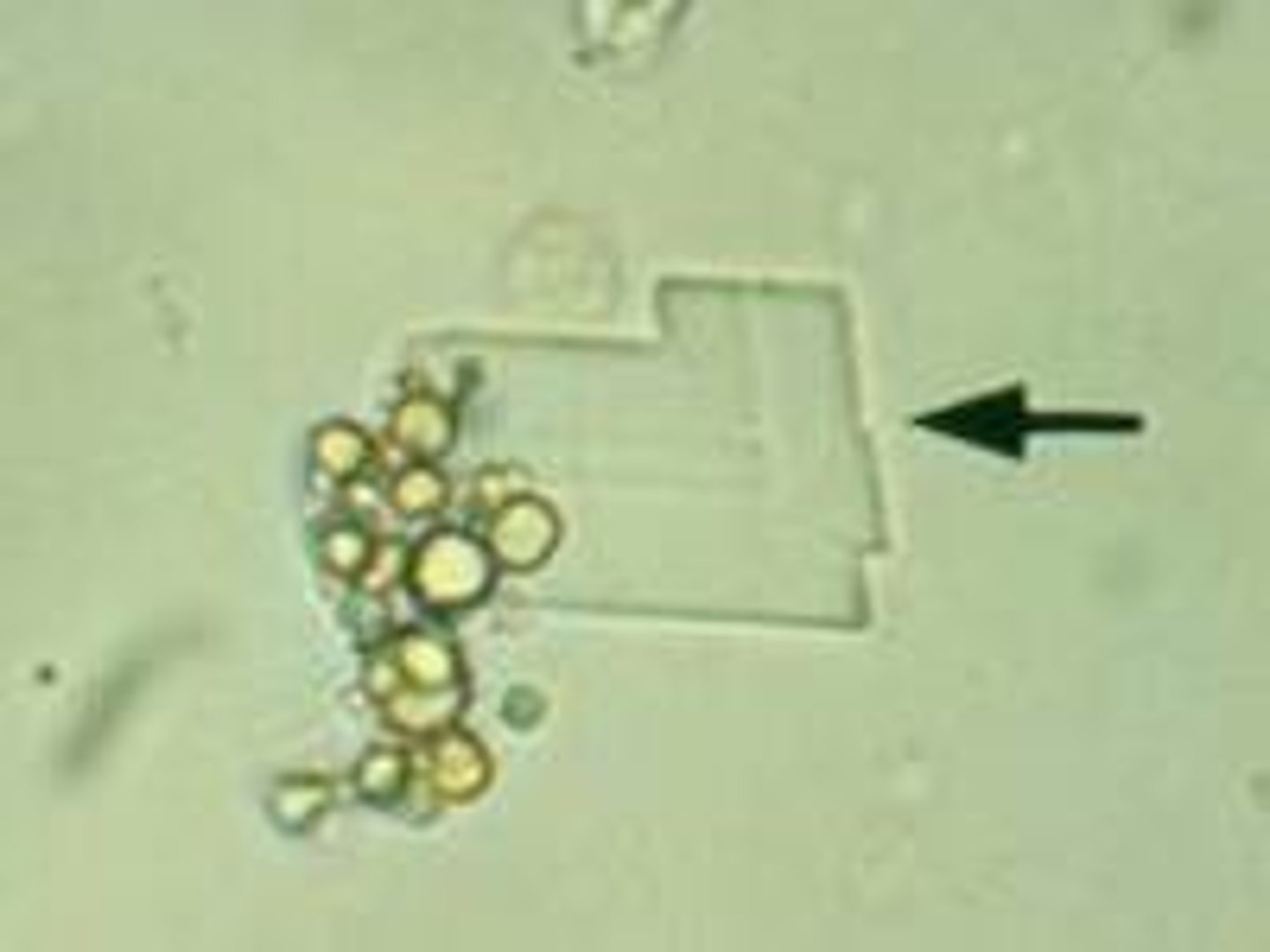
Tyrosine crystal
abnormal, fine, colorless to yellow needles in clumps or rosettes, positive bilirubin and seen with leucine crystals, liver disease
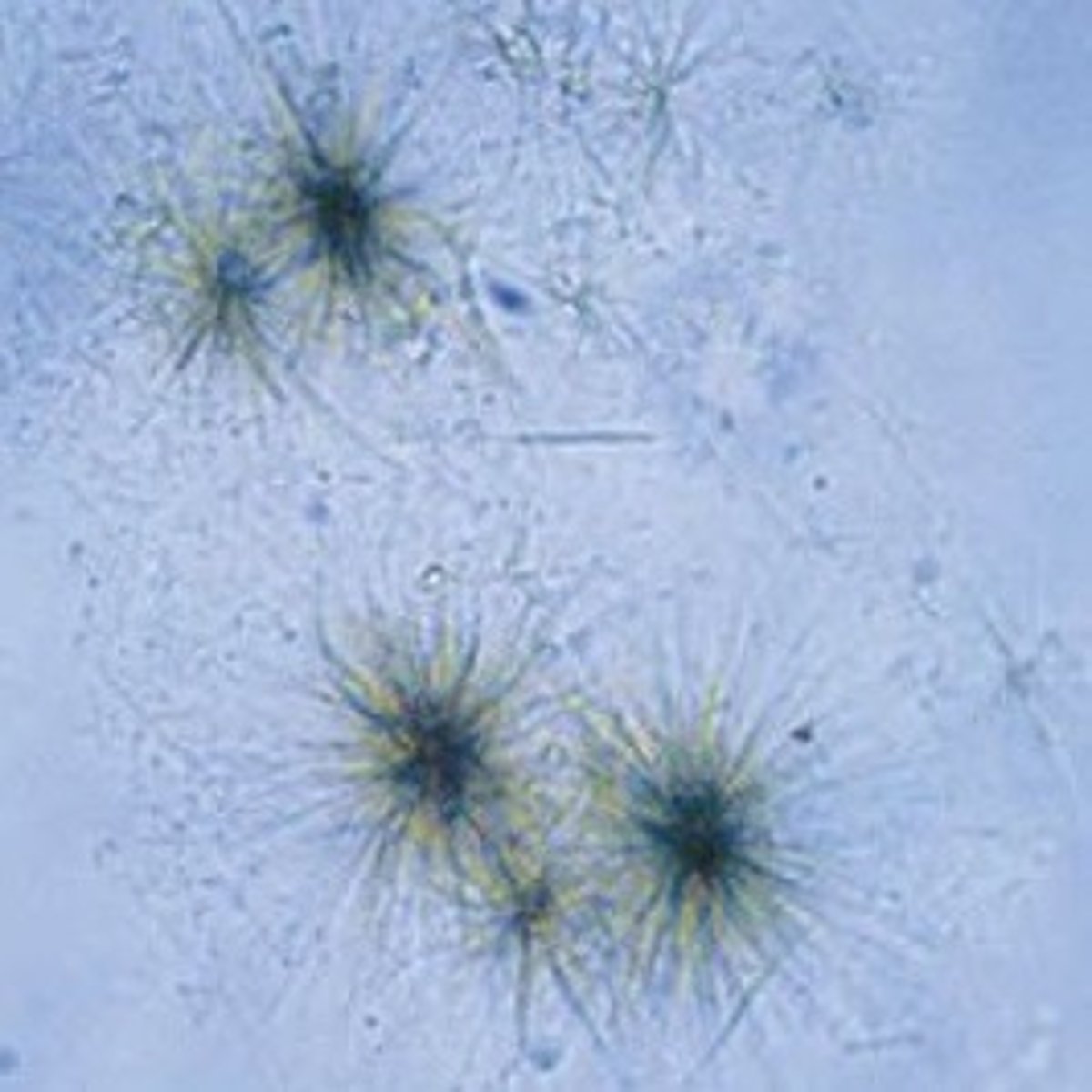
Leucine crystal
abnormal, yellow-brown spheres with concentric circles and radial striations, sen with tyrosine crystals, liver disease
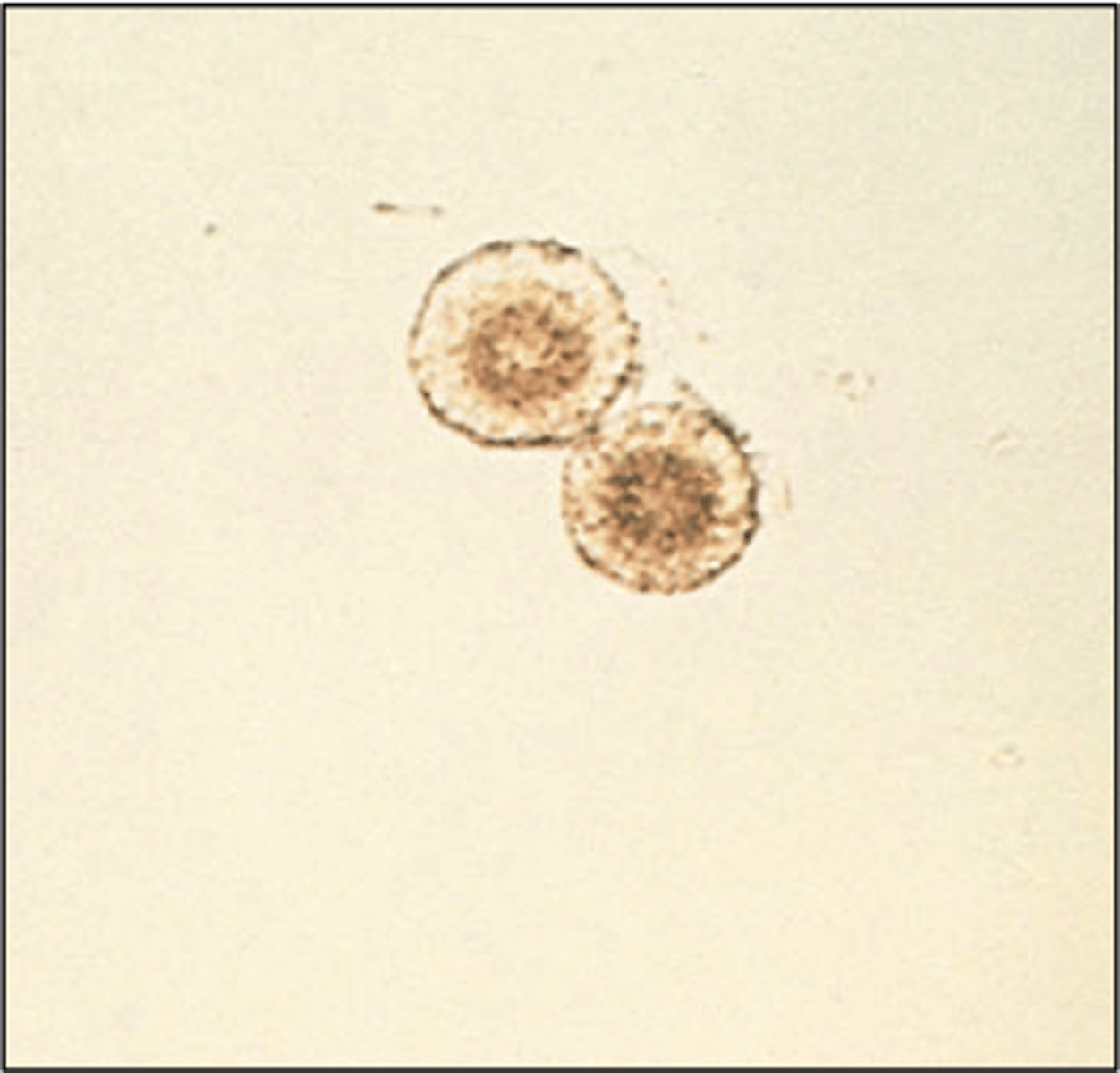
Bilirubin crystals
abnormal, bright yellow clumps-clumped needles/granules, liver disease
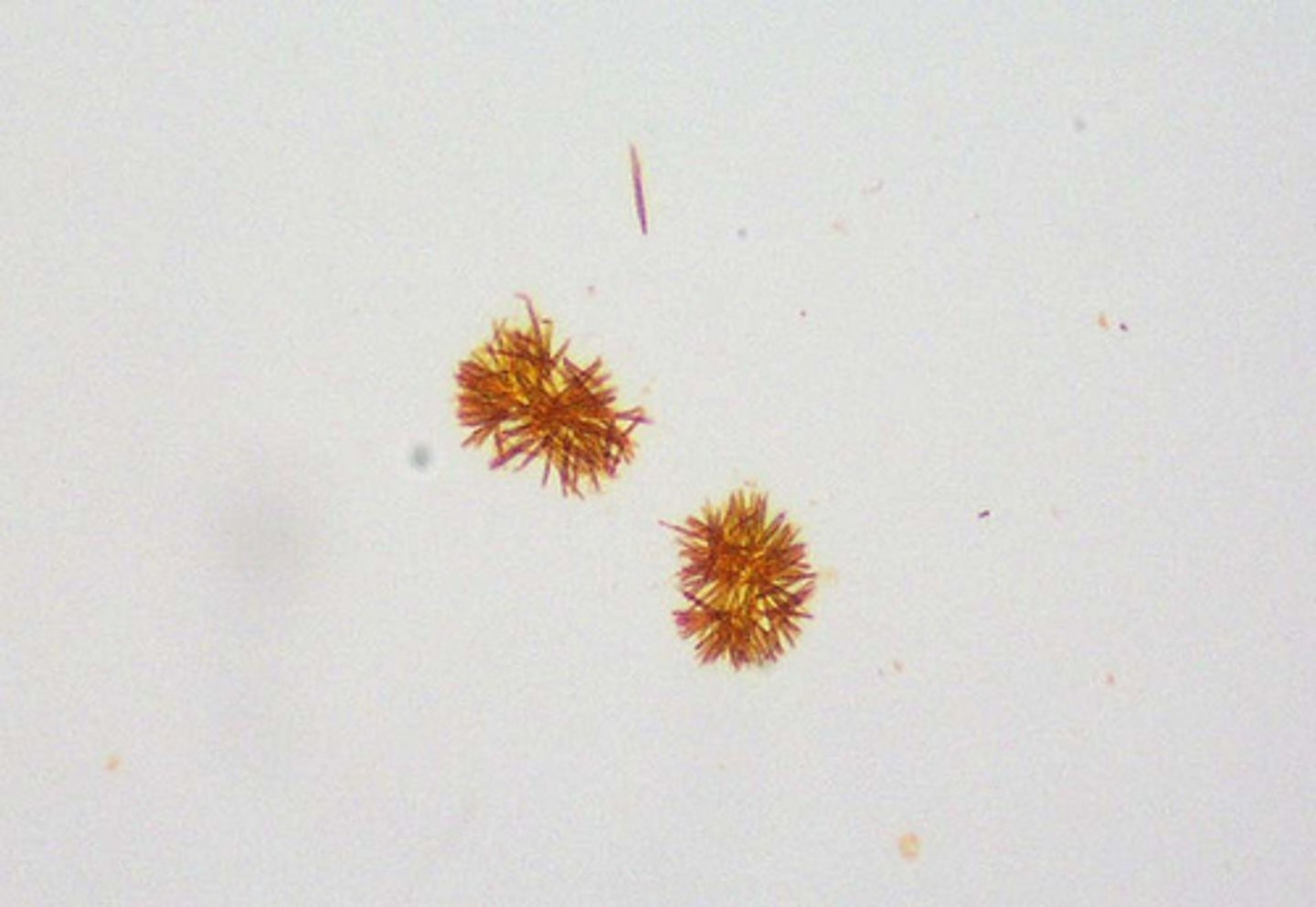
Ampicillin
abnormal, bundles following refrigeration, infection treatment
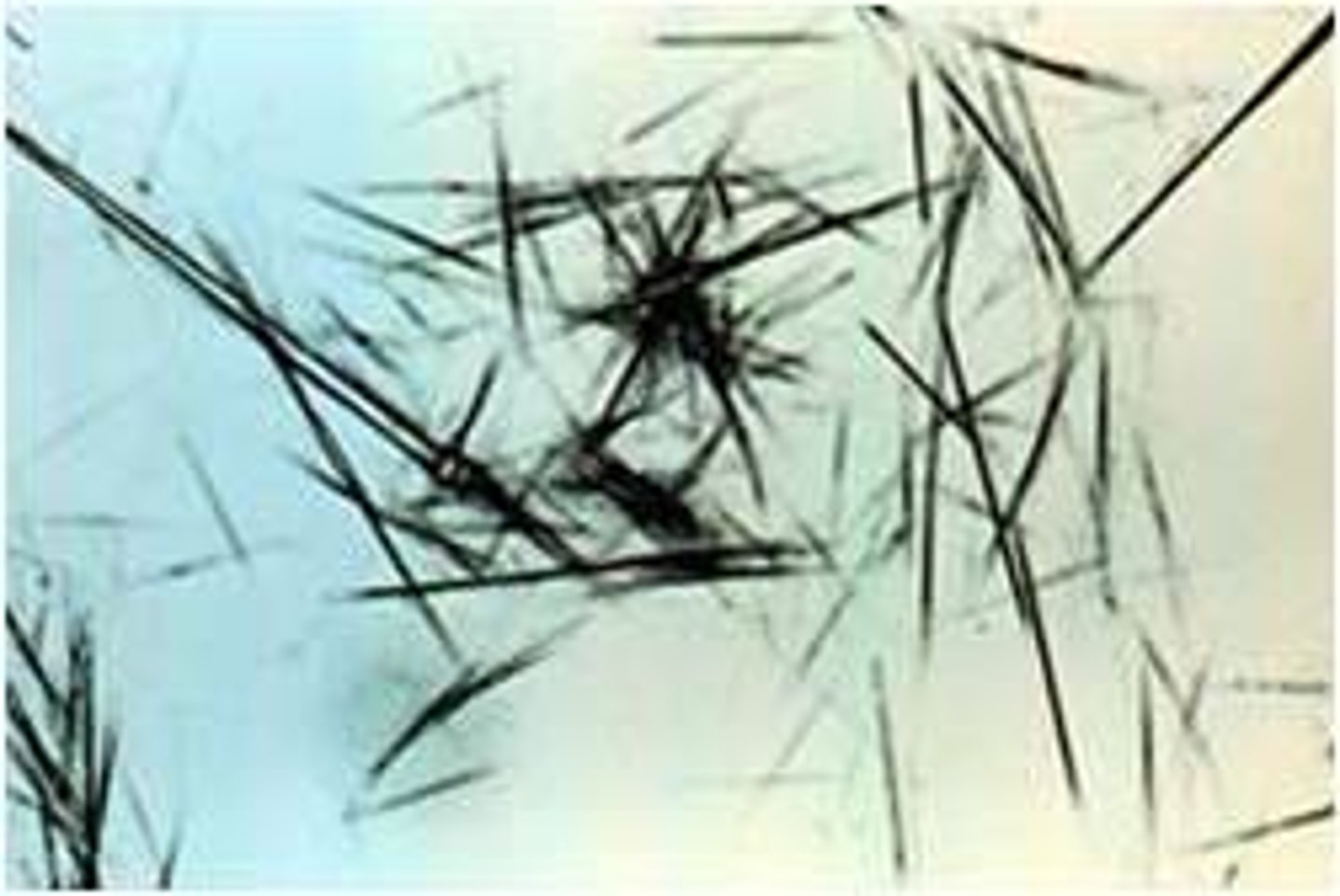

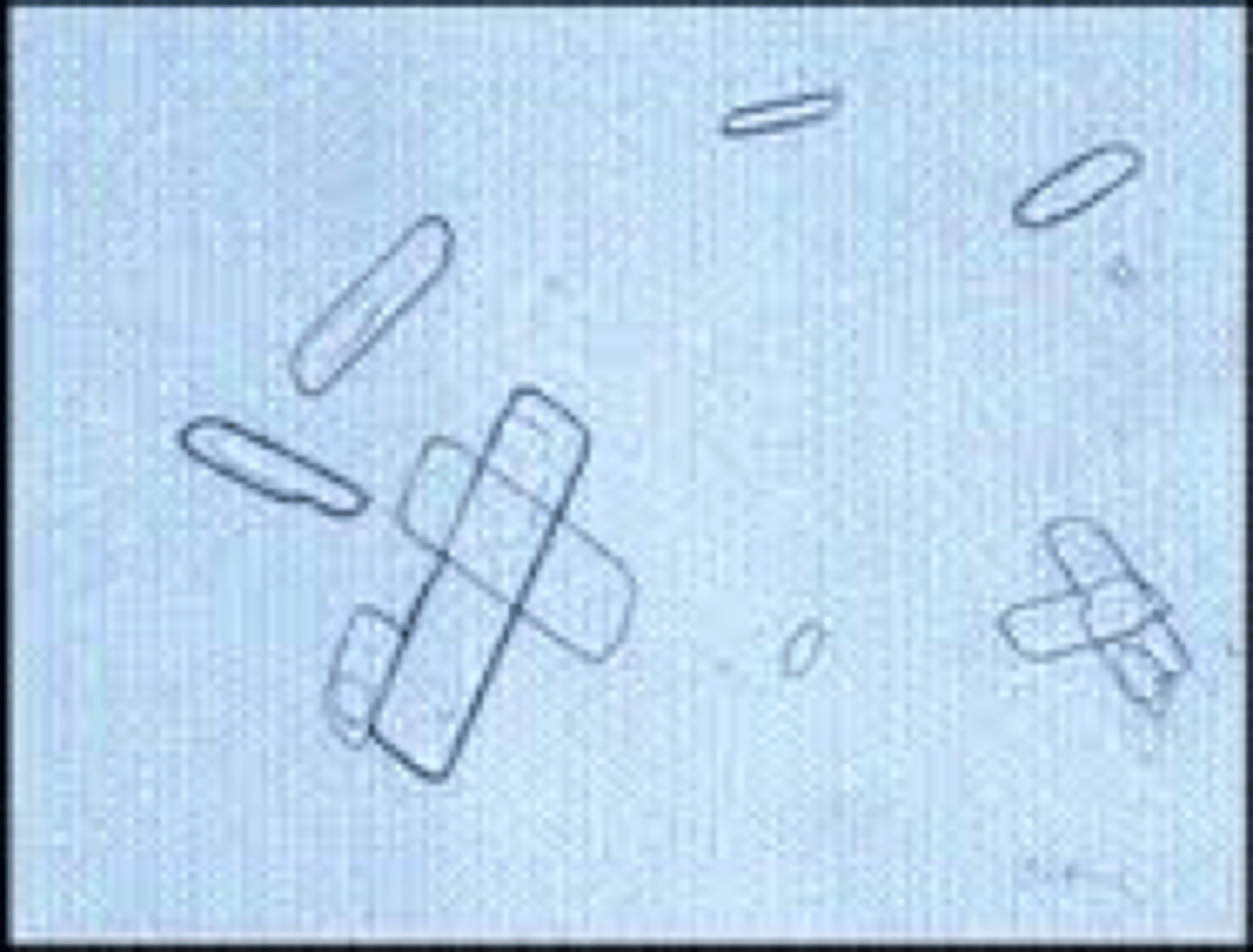
radiographic
abnormal, flat plates, high specific gravity/refractometer, radiographic procedure
Give the physical, chemical and exceptions of RBC
physical: turbidity, red, chemical: + blood, + protein, exceptions: number, hemolysis
Give the physical, chemical and exceptions of WBC
physical: turbidity, chemical: + protein, +nitrite, +LE, exceptions: number, lysis
Give the physical, chemical and exceptions of epithelial cells
physical: turbidity, chemical: none, exceptions: number
Give the physical, chemical and exceptions of casts
physical: none chemical: + protein, exceptions: number
Give the physical, chemical and exceptions of bacteria
physical: turbidity chemical: pH, +nitrite, +leukocytes, exceptions: number and type
Give the physical, chemical and exceptions of crystals
physical: turbidity, color, chemical: pH, +bilirubin, exceptions: number and type
what does a kova slide stain?
nucleus
what is the 0.5% of toluidone blue stain used for?
wbc differenation and renal cells
what is acetic acid used for?
will lyse RBC
what will lipids stains do?
triglycerides and neutral fats stain orange - red; cholesterol does not stain but polarizes
what is a gram stain used for?
differentiates gram negative bacteria and gram positive; can ID bacterial casts; fixed smear
what is hansel stains used for?
preferred for urinary eosinophils
what is prussian blue used for?
hemosiderin granules(iron); stains blue
what does CytoDiagnostics urine testing monitor?
renal disease/malignancies; permanent stain
Bright-field microscopy
used for routine urinalysis
Phase-contrast microscopy
enhances visualizations of elements with low refractive indices, such as hyaline casts, mixed cellular casts
Polarizing microscopy
aids in identification of cholesterol in oval fat bodies, fatty casts, and crystals
dark-field microscopy
Aids in identification of Treponema pallidum
fluorescence microscopy
Allows visualization of naturally fluorescent microorganisms or those stained by a fluorescent dye including labeled antigens and antibodies
Interference- contrast microscopy
Produces a three-dimensional microscopy image and layer-by-layer imaging of a specimen
Which cell can be used to focus on the correct plane in a urine specimen?
epitheal cells due to size and typically present in urine
Which urine elements are reported by lower power field? And high power field?
Lpf: casts, Hpf: RBC, WBC
What are some advantages to using stain on urine sediment?
Stains the nucleus and makes it stand out, more characteristics stand out
What does birefringent property refer to in an object?
Refracts light in different dimensions; polarization microscope
List two urine elements that have birefringent properties.
crystals and fats
What is the significance of red cells in urine?
Rbc casts = urinary stasis = higher in urinary tract glomerular nephritis
Which elements may be confused with rbcs microscopically?
Yeast; look for budding yeast and look for blood on your dipstick to be present
Name and describe a clinically significant form of squamous epithelial cells. Describe the appearance of cell.
Clue cells but called from a vaginal it is bacteria that is sticking to the cytoplasm of the squamous cell
Renal tubular cells: Columnar
larger;proximal convoluted tubule
Renal tubular cells: Round, oval
smaller; distal convoluted tubule
Renal tubular cells: Cuboidal
collecting duct, never round
Renal tubular cells: 3 or more cells
renal fragment
How is the WBC and RTE cells differentiated?
Eccentric nucleus
Name three substance RTE may absorb and show up in RTE appearance.
Absorb: bilirubin, hemoglobin, lipids
At which pH do abnormal crystals precipitate?
acidic urine
Why would iatrogenic compounds precipitated in urine considered significant?
We have introduced them(iatrogenic); X-ray contrast media or medications; indicates some kidney damage because our kidneys should filter it out unless there is stasis then it will show up in the urine.
What is the significance of white cells in urine?
infection; pyelonephritis if you see wbc casts because they come from the tubules