Human nutrition
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
What is a balanced diet?
A diet that contains all the nutrients in the right proportions relative to lifestyle
What are the nutrients that should be included in a balanced diet?
Carbohydrates
Protein
Lipids
Vitamins
Minerals
Dietary fibre
Water
Sources, functions & deficiency symptoms of carbohydrates
Sources → Bread, rice, pasta, potatoes
Functions → To provide energy
Deficiency symptoms → Lack of energy, low blood sugar levels (hypoglycemia)
Sources, functions & deficiency symptoms of protein
Sources → Meat, fish, eggs, pulses
Functions → Growth & repair, production of enzymes, hormones & anitbodies, some are used structurally for hair & nails
Deficiency symptoms → Stunted growth, kwashiorkor
Sources, functions & deficiency symptoms of lipids
Sources → Butter, oils, dairy products
Functions → Energy source, insulation, protection of organs
Deficiency symptoms → Lack of energy
Sources, functions & deficiency symptoms of vitamin A
Sources → Carrots, green vegetables
Functions → Needed for vision, helps cell growth & healthy skin
Deficiency symptoms → Night blindness
Sources, functions & deficiency symptoms of vitamin C
Sources → Citrus fruit
Functions → Keeps healthy skin, teeth & gums, helps absorb iron
Deficiency symptoms → Scurvy
Sources, functions & deficiency symptoms of vitamin D
Sources → Sunlight, dairy products, oily fish
Functions → Helps to absorb calcium
Deficiency symptoms → Rickets
Sources, functions & deficiency symptoms of calcium
Sources → Dairy products
Functions → Strengthens teeth & bones, prevents blood clotting
Deficiency symptoms → Rickets
Sources, functions & deficiency symptoms of iron
Sources → Red meat, spinach
Functions → Needed for haemoglobin
Deficiency symptoms → Anaemia
Sources, functions & deficiency symptoms of dietary fibre
Sources → Wholegrains, vegetables
Functions → Helps food move along the digestive system by efficient peristalsis
Deficiency symptoms → Bowel cancer, constipation
Sources, functions & deficiency symptoms of water
Sources → Water, fruits
Functions → Needed for cell reactions to take place, temperature control, transport
Deficiency symptoms → Dehydration, headaches
How do energy requirements vary with age?
Young children & teenagers need more energy because they are rapidly growing & developing
Adults & elderly need less energy as they have stopped developing & they often have lower activity levels
How do energy requirements vary with activity levels?
People who have high activity levels need more energy to replenish the energy they used during their activity
People who have low activity levels do not require as much energy
How do energy requirements vary with pregnancy?
Pregnant women need more energy for the growth & maintenance of the foetus
The also need more energy for the extra weight they are carrying
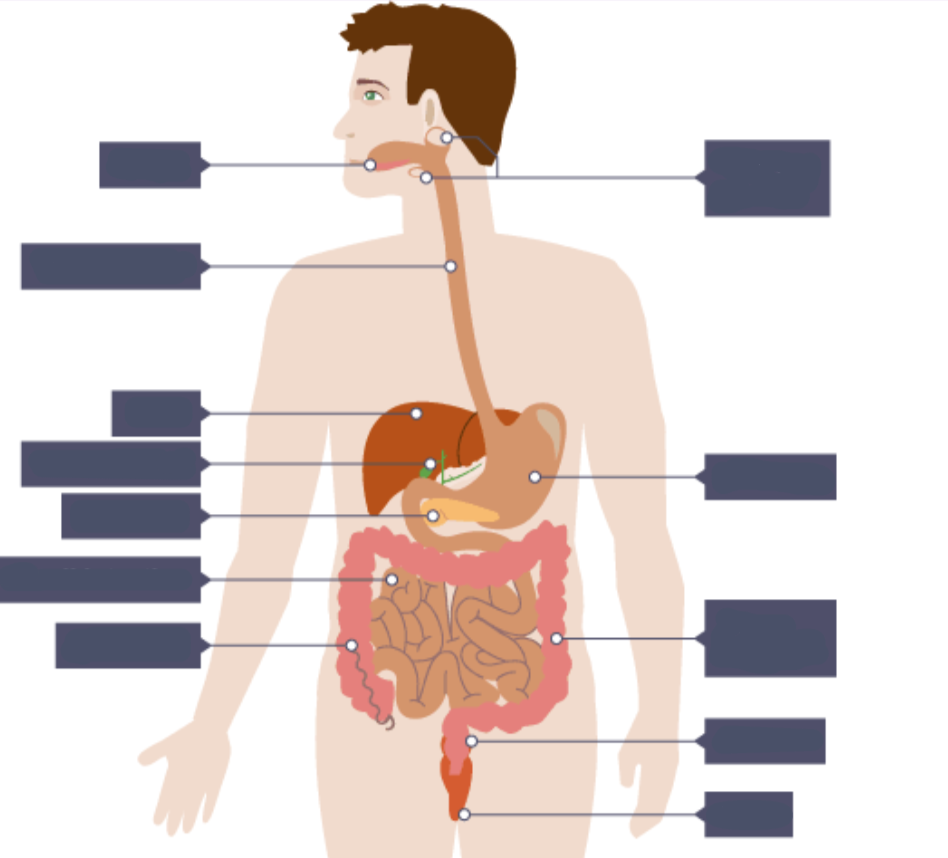
Label this diagram of the digestive system
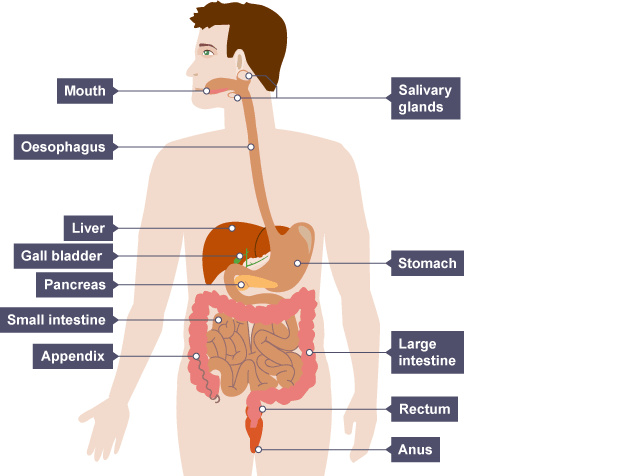
Mouth
Chews up food to make it easier to swallow
This also increase the surface area, making it easier for digestive enzymes to act on it
Tongue
Helps chewed food form a ball called a bolus
Salivary gland
Releases saliva which moistens & lubricates food, making it easier to swallow
Saliva contains amylase which helps break down carbohydrates
Oesophagus
Connects the mouth to the stomach
Boluses move down it by the wave-like contractions created by circular muscles & longitudinal muscles that make a squeezing action
Stomach
Releases gastric juice which contains hydrochloric acid & pepsin
Pepsin breaks down protein & hydrochloric acid kills bacteria & provides the optimum pH (pH 2) for pepsin
Muscular movements in the stomach wall help to churn food into chyme
Liver
Produces bile
Excess glucose is removed from the blood & stored as glycogen
Excess amino acids cannot be stored so are broken down to form urea which is then passed to the kidney
Gall bladder
Bile is stored here & passed into the small intestine through the bile duct
Bile
Alkaline to neutralise the hydrochloric acid from the stomach when it enters the small intestine
Emulsifies large drops of fat into smaller droplets which increases the surface area, therefore allowing lipase enzymes to break it down faster
Pancreas
Secretes carbohydrase, protease & lipase enzymes into the small intestine
Small intestine (duodenum)
First part of the small intestine
Completes the breaking down of food using carbohydrase, protease & lipase enzymes
Small intestine (illeum)
Second part of the small intestine
Lined with villi which helps absorb digested food back into the blood
Large intestine
Absorbs water & some vitamins from indigestible food to produce faeces
Rectum
Where faeces is compacted & stored
Anus
Where faeces is egested out of the body
How is food moved through the gut by peristalsis?
Muscular tissue all throughout the alimentary canal squeezes balls of food (boluses) through the gut
These waves of circular muscle contraction that squeeze the food down is called peristalsis
Without peristalsis bits of food would clog up the gut
Carbohydrase enzymes break down ____
Starch is broken down into ____ by ____ enzymes
Maltose is broken down into ____ by ____ enzymes
1 = Carbohydrates
2 = Maltose
3 = Amylase
4 = Glucose
5 = Maltase
Protease enzymes break down ____
____ enzymes are found in the stomach & break down protein into peptides
Trpepsin also break down protein into peptides but are found in the ____
____ enzymes break down peptides into amino acids
1 = Protein
2 = Pepsin
3 = Small intestine
4 = Peptidase
Lipids are broken down by ____ enzymes into ____ & ____
1 = Lipase
2 = 3 fatty acids
3 = glycerol
How has the small intestine adapted for absorption?
- Very long which gives enough time for food to be broken down & absorbed
- Covered in millions of villi which provides a large surface area for absorption
How have villi adapted for absorption?
- Covered in microvilli which increases the surface area
- Surrounded by capillaries which provides a steep concentration gradient
- Has a single layer of permeable cells (epithelial cells) which decreases the diffusion distance
- Epithelial cells contain lots of mitochondria to provide energy for active transport
Ingestion is…
The intake of food into the body via the mouth
Digestion is…
The breaking down of large soluble food into smaller soluble molecules
Absorption is…
When small soluble food molecules are taken back into the blood through the wall of the intestine
Assimilation is…
The manufacturing of new substances in cells using the products of digestion
Egestion is…
The removal of undigested food via the anus
What is the difference between egestion & excretion?
Egestion is the removal of undigested food as faeces via the anus whereas excretion is the removal of metabolic waste products
(e.g. CO2 via the lungs, urine via the kidney, sweat via the skin)