Spine (C/T/L), Sacrum & Coccyx
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
131 Terms
Where does the spinal CANAL begin and end?
begins at the base of the skull and extends into the sacrum
The spinal canal contains the spinal cord and is filled with what?
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
The spinal CORD begins w/ the _______ _________ of the brain
medulla oblongata
What is the point where the spinal CORD tapers off called?
conus medullaris
What are the different ways the location of the conus medullaris can be described as?
- inferior border of L1
- between L1 & L2
- superior border of L2
What are each vertebrae separated by?
intervertebral disk
What are the sections of the vertebral column?
cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacrum, coccyx
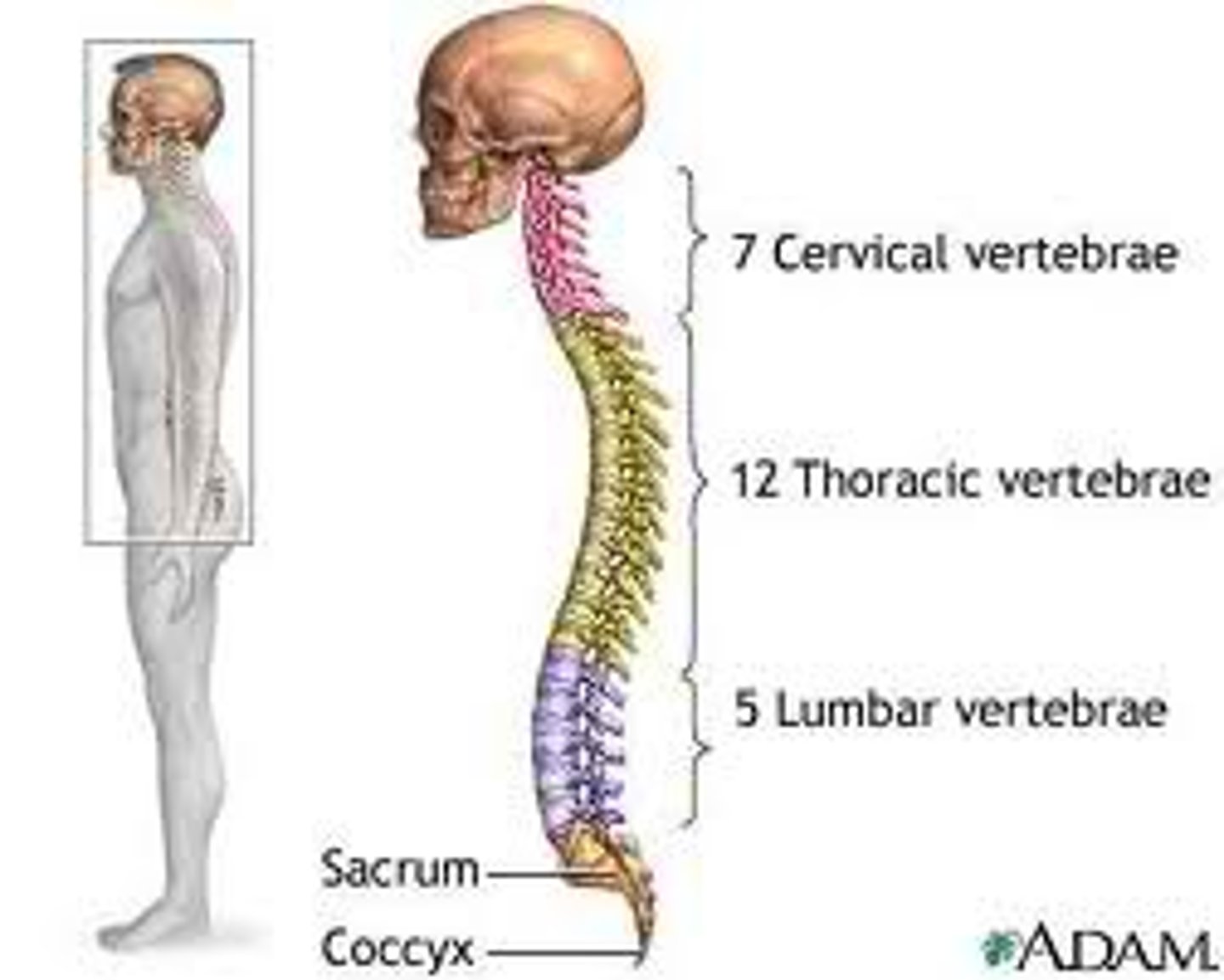
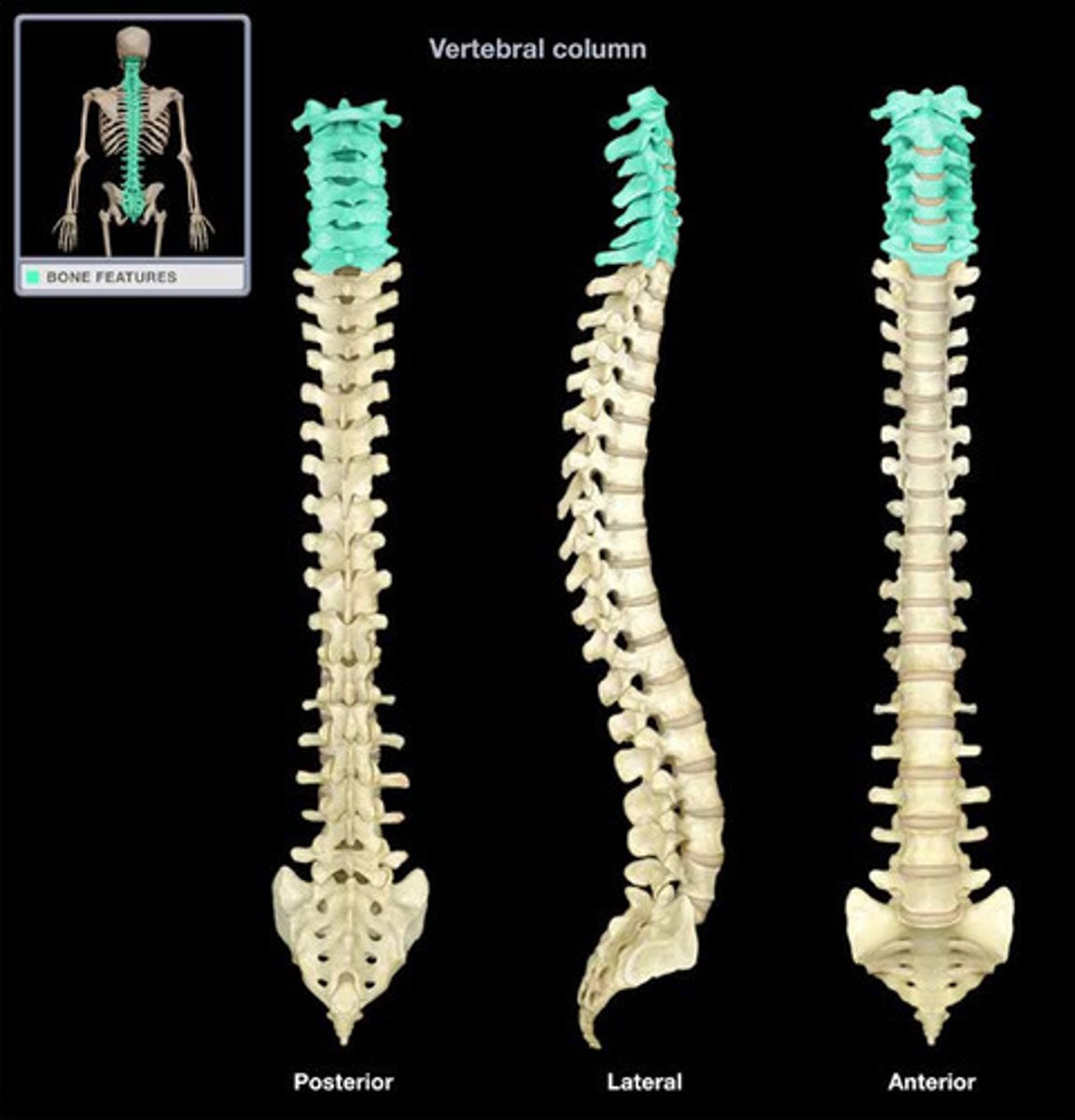
How many vertebrae make up the cervical spine?
7
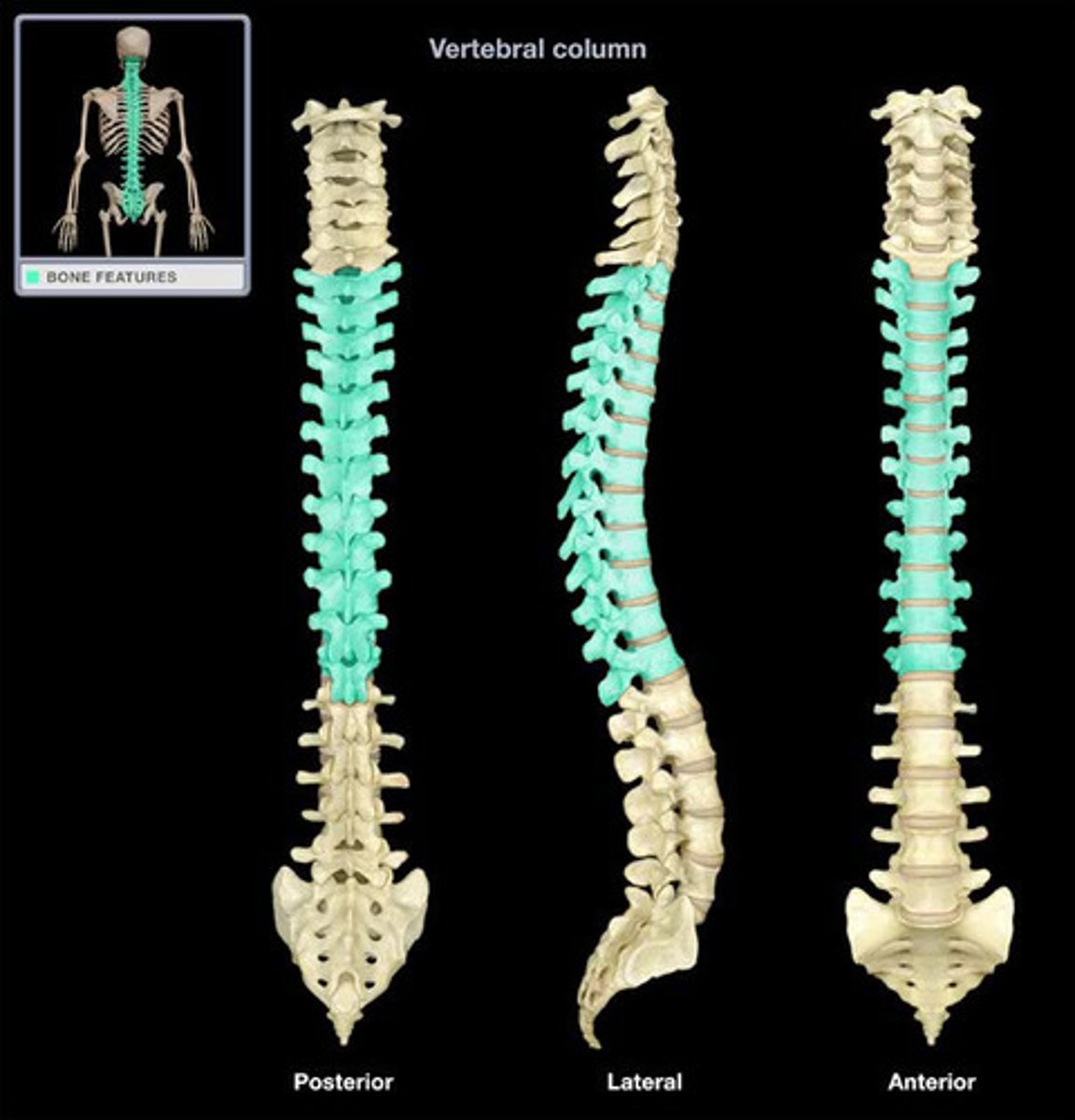
How many vertebrae make up the thoracic spine?
12
How many vertebrae make up the lumbar spine?
5
How many vertebrae make up the sacral spine?
5 fused to form 1
How many vertebrae make up the coccyx spine?
3 to 5 fused to form 1
What does convex mean?
rounded outward or elevated surface
What does concave mean?
a rounded inward or depressed surface like a cave
What are concave curvatures described as?
lordotic
What are convex curvatures described as?
kyphotic
Which regions of the spine have CONCAVE curvatures and are described as LORDOTIC?
cervical and lumbar
Which regions of the spine have CONVEX curvatures and are described as KYPHOTIC?
thoracic and sacral
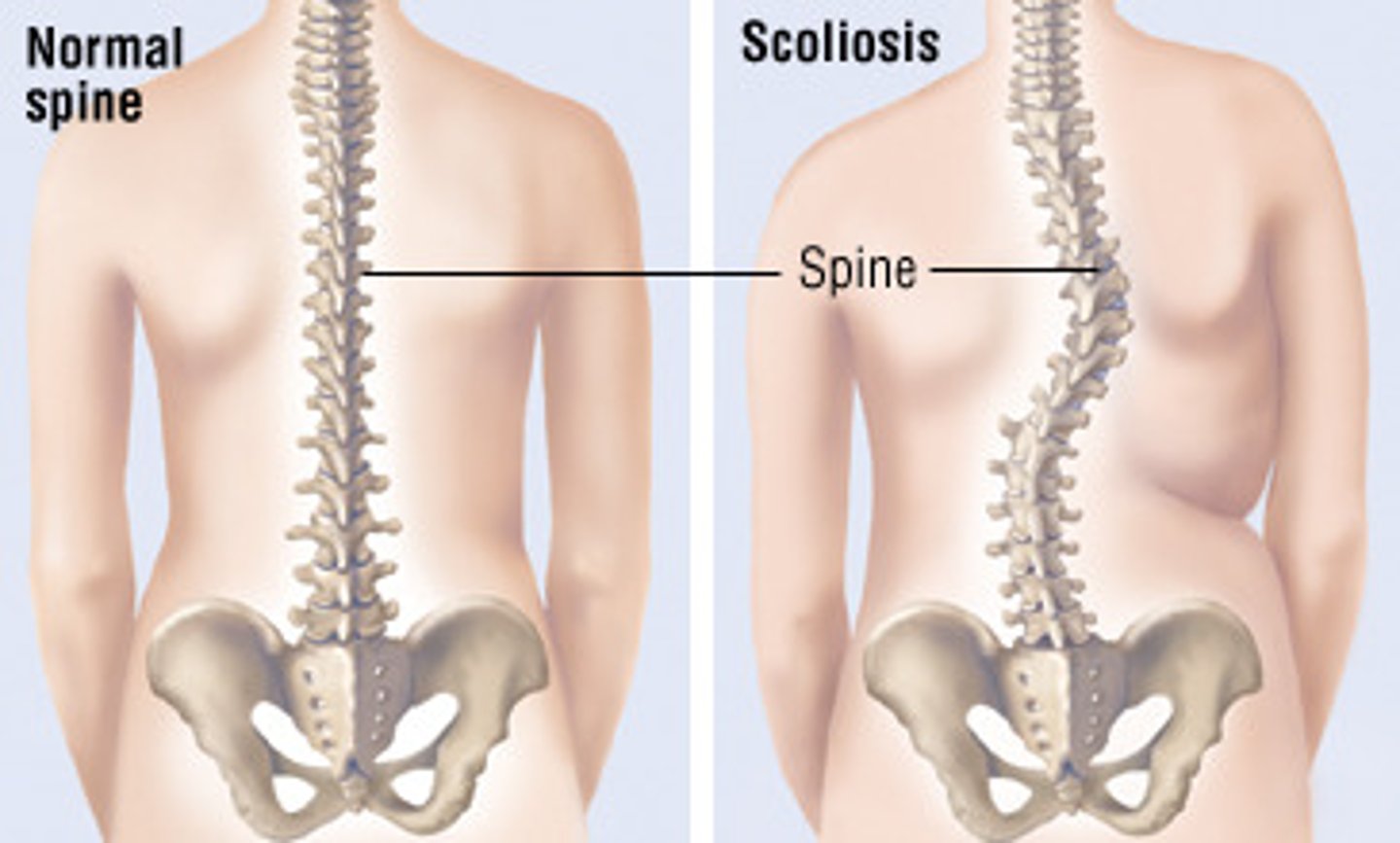
What is scoliosis?
abnormal lateral curvature of the spine
What are the two main parts a typical vertebra is composed of?
1. body
2. vertebral arch
The body and the vertebral arch enclose a space called the _________ _______
vertebral foramen
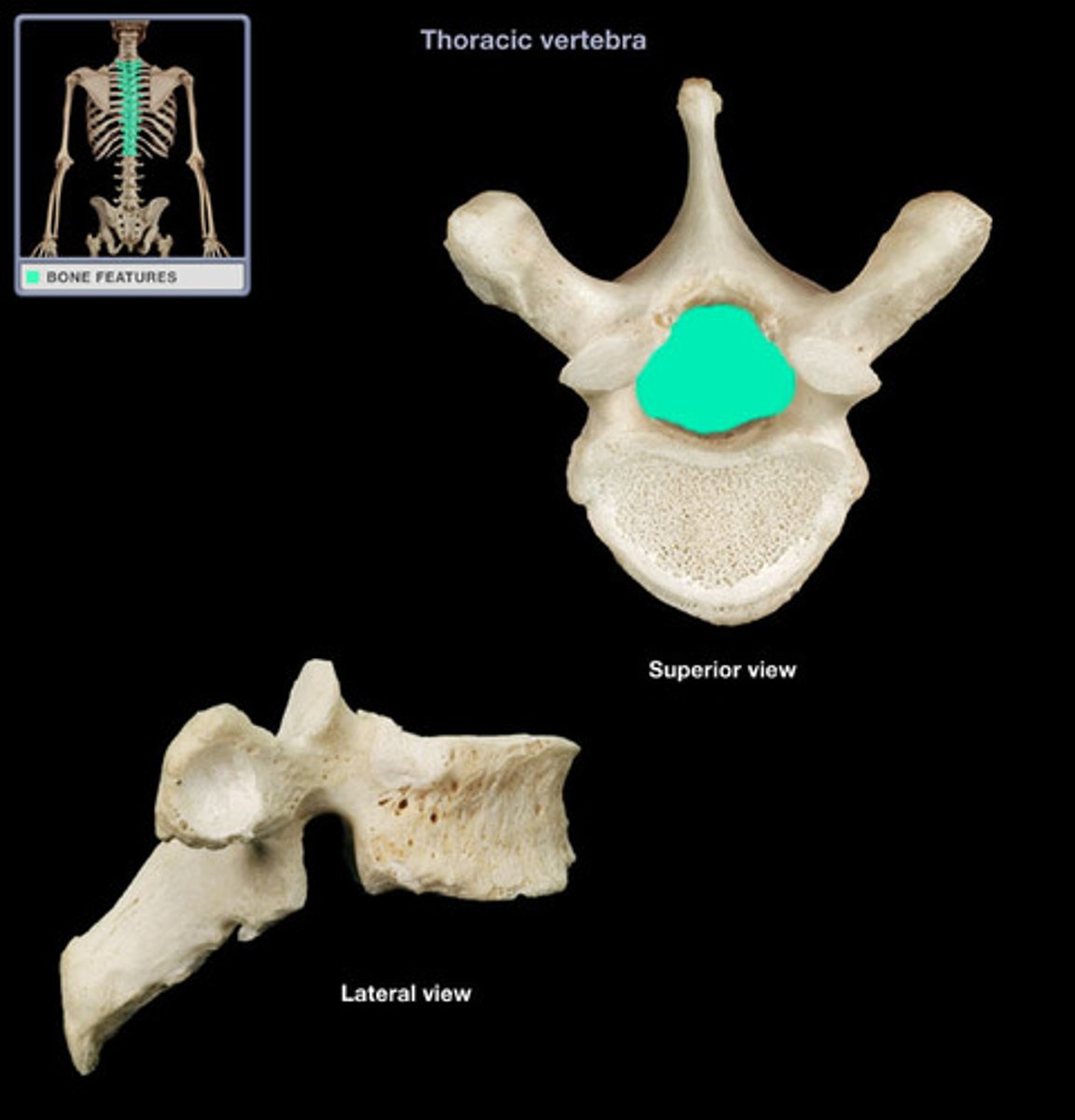
True/False: you can see the vertebral and transverse foramen on an x-ray
FALSE
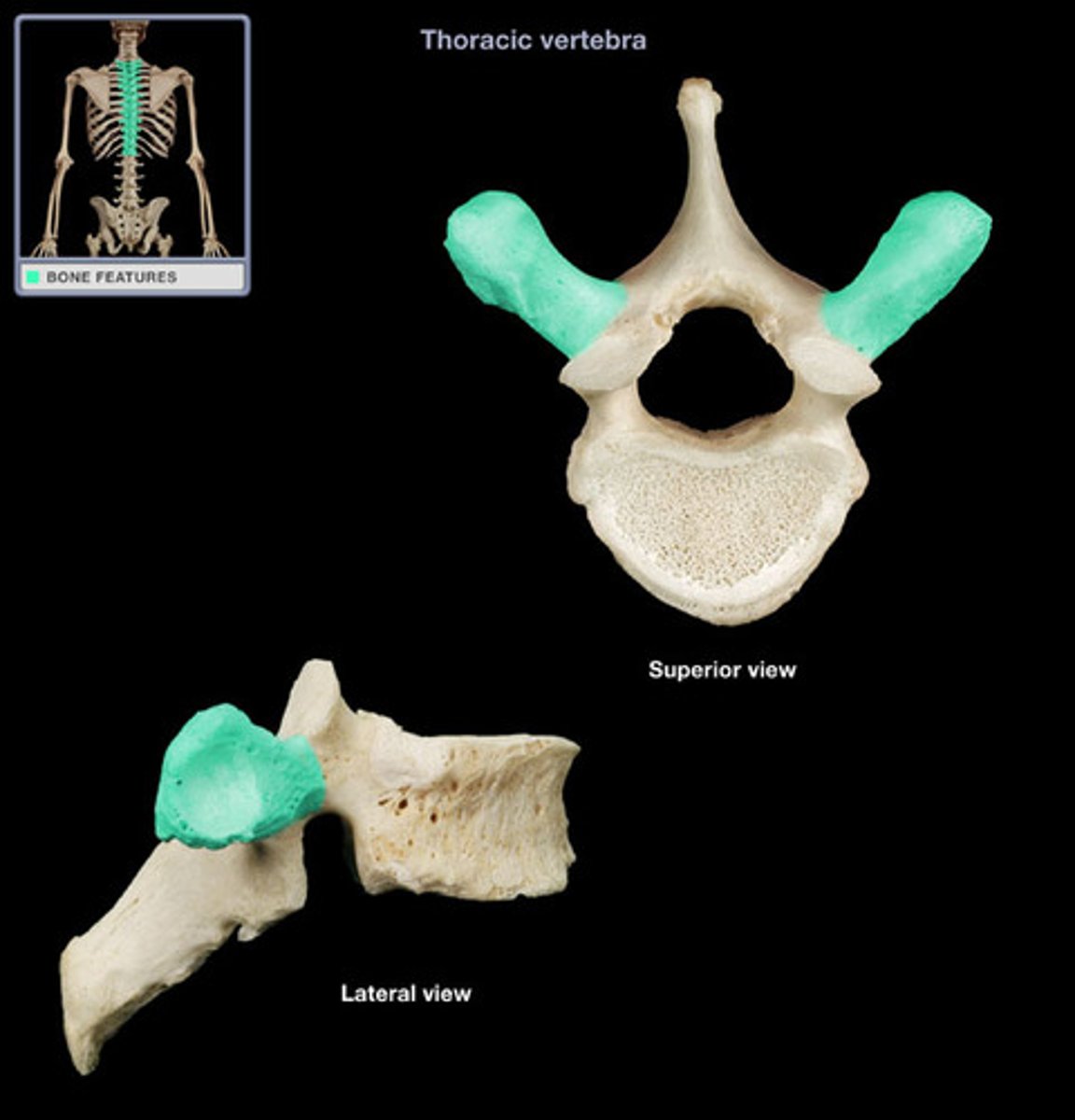
Where the pedicle and the lamina meet forms the __________ _______
transverse process
What joint do the superior and inferior articulating processes form?
zygapophyseal joint
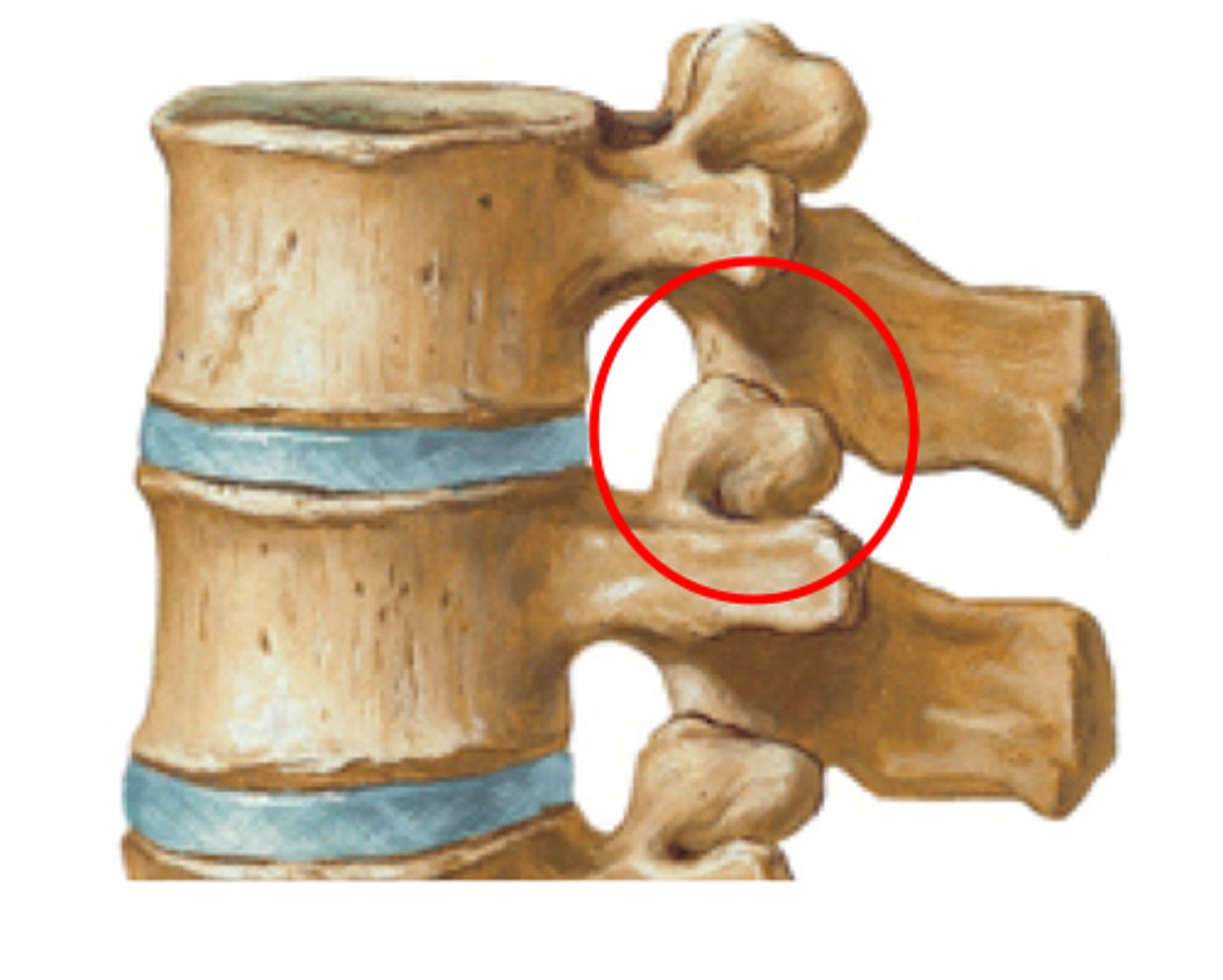
What are the other names for the zygapophyseal joint?
apophyseal, atlantoaxial
True/False: you can see the intervertebral foramen on an x-ray
TRUE
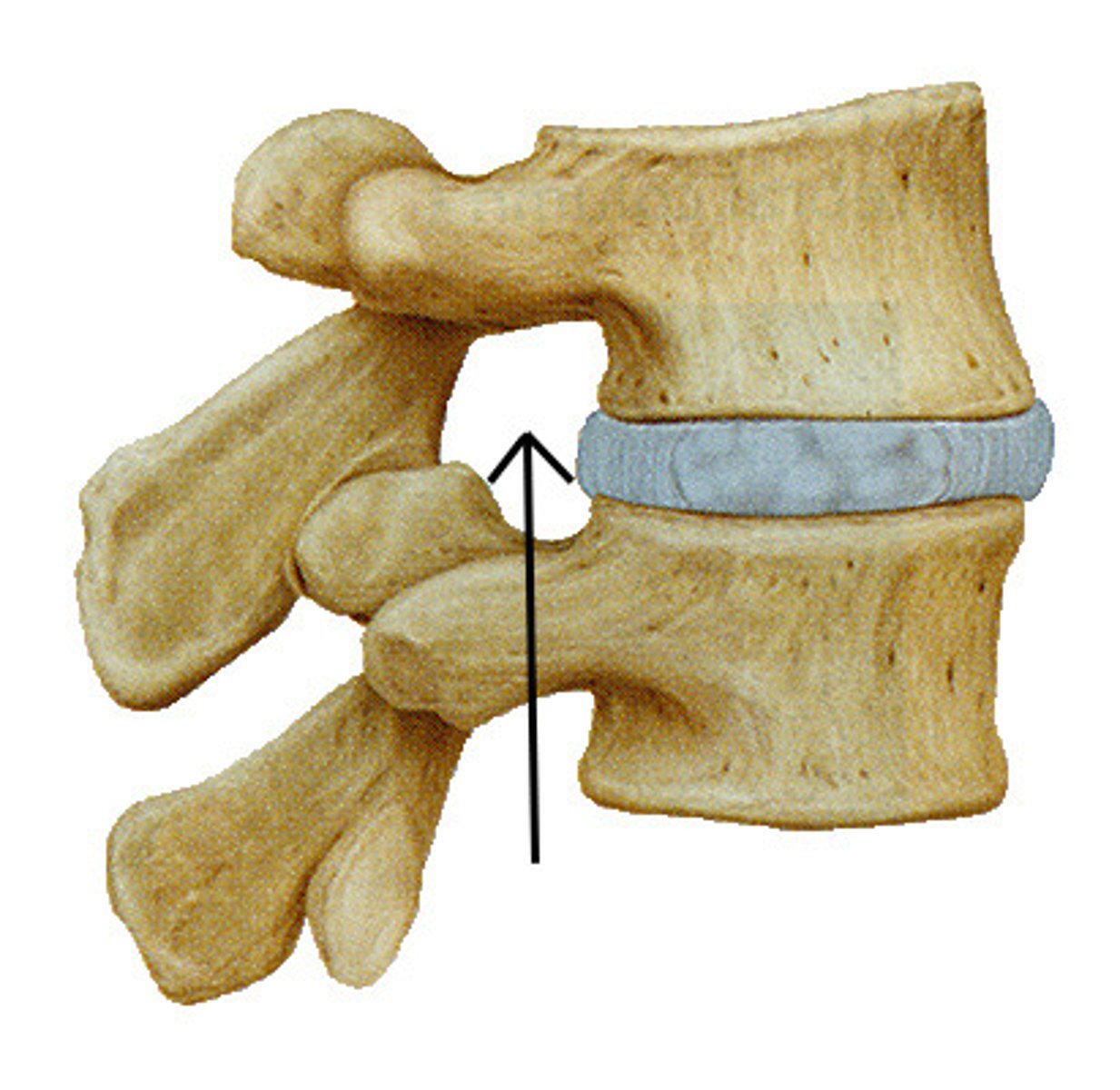
When vertebrae are stacked, the superior and inferior vertebral notches line up to form a single opening called the ______________ ________
intervertebral foramen
The intervertebral foramen allows for passage of what?
important spinal nerves, blood vessels
What is it called when the nucleus pulposus protrudes through the annulus fibrosus layer?
- herniated nucleus pulposus (HNP)
- commonly known as herniated disk
What are the unique characteristics of the cervical spine?
- transverse foramina
- bifid spinous process
- overlapping vertical bodies
What is the most important feature of the axis?
dens or odontoid process
True/False: the odontoid process goes up through C1 and is held in place by the transverse atlantal ligament
true
Which of the foramina run vertically?
transverse and vertebral foramen
On the cervical vertebrae the spinous processes are short and have double pointed _____ tips
bifid
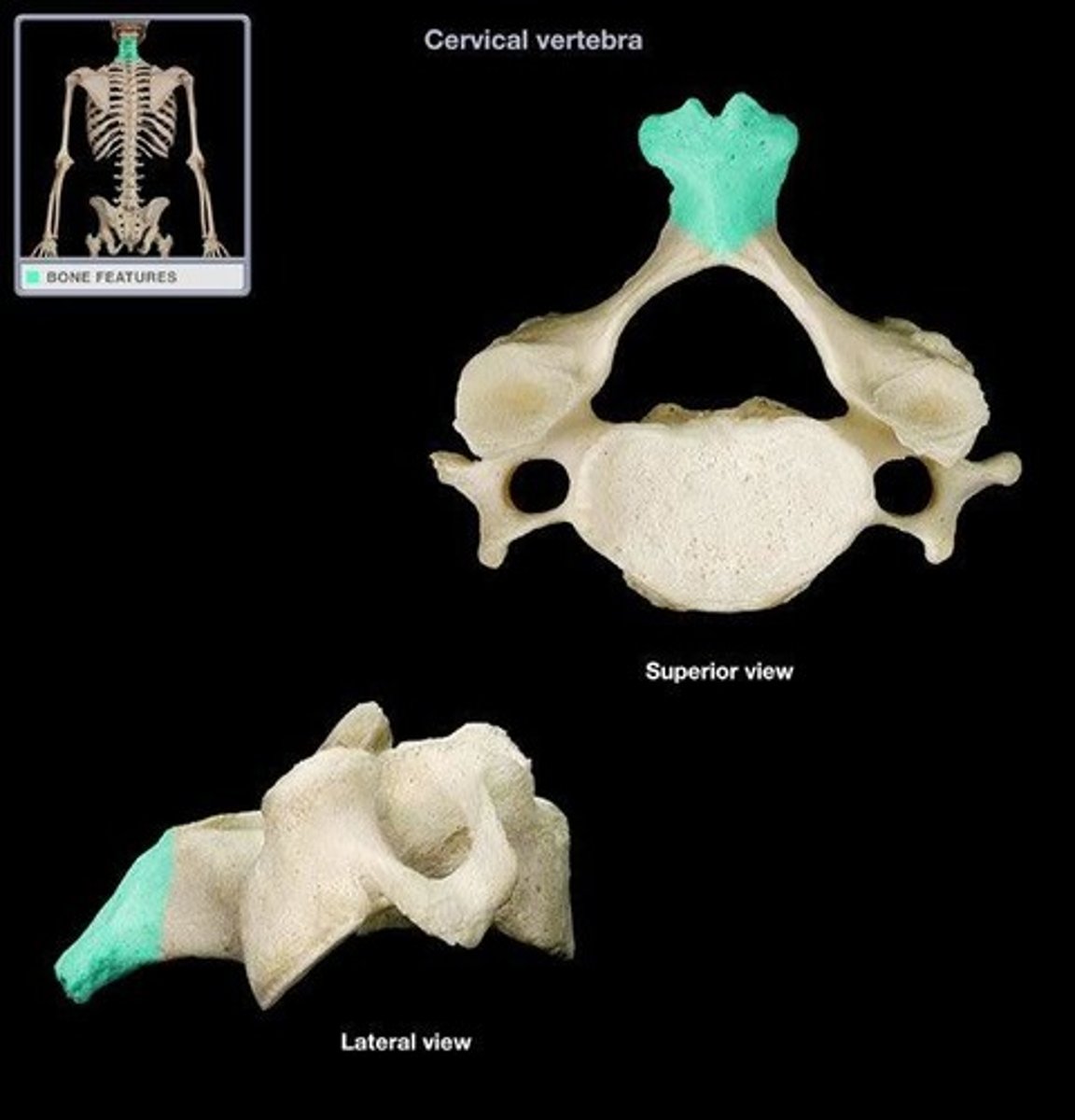
The CERVICAL zygapophyseal joints are ONLY demonstrated on what view(s)?
- true Lateral
- joint between C1 - C2 only seen on true AP
The CERVICAL intervertebral foramina are ONLY demonstrated on what view?
obliques (w/ 15 degree cephalic tube angle)
Do the bodies of the thoracic vertebrae increase or decrease in size from T1 - T12?
increase
What is the unique characteristic of the thoracic spine?
facets for rib articulation
The THORACIC zygapophyseal joints are ONLY demonstrated on what view?
70 degree oblique
The THORACIC intervertebral foramina are ONLY demonstrated on what view?
true lateral
True/False: the lumbar spine increases in size from L1 to L5
true
Because the lumbar spine carries most of the body weight, there are more ________ to this area
injuries
The LUMBAR intervertebral foramina are ONLY demonstrated on what view?
true lateral
The Lumbar zygapophyseal joints are ONLY demonstrated on what view?
45 degree obliques (will see "scotty dog")
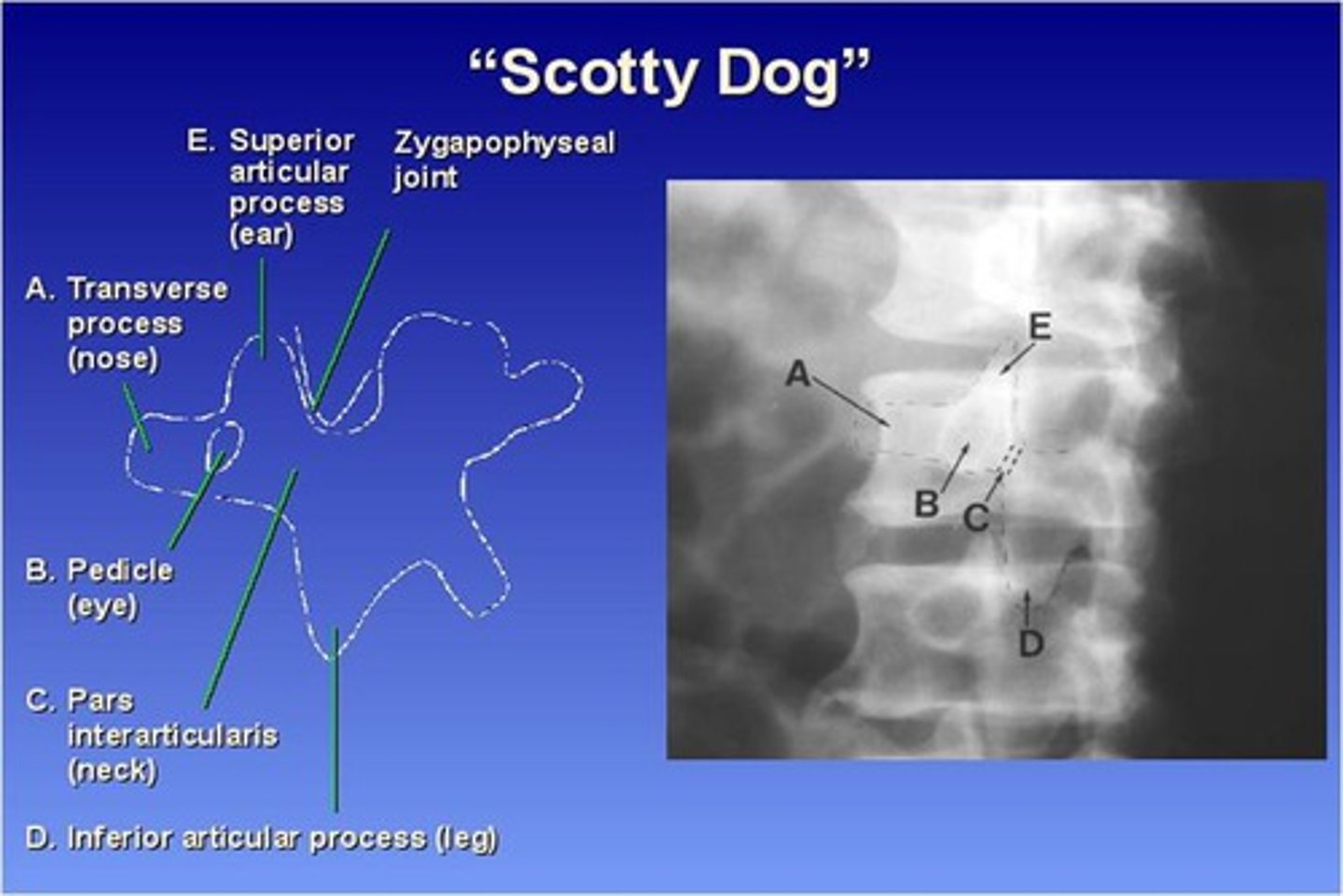
What part of the lumbar spine makes up the "nose" of the "scotty dog"?
transverse process
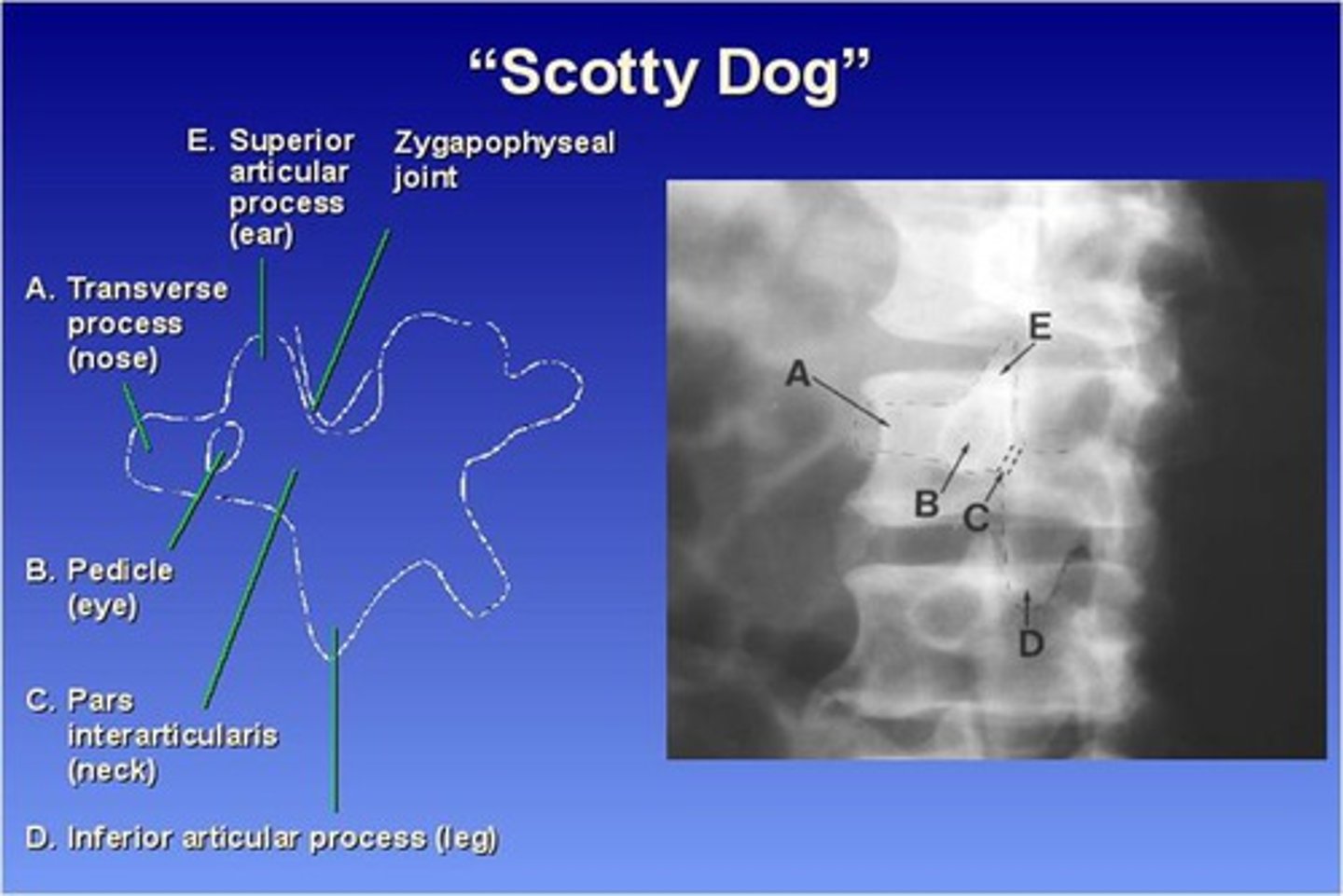
What part of the lumbar spine makes up the "eye" of the "scotty dog"?
pedicle
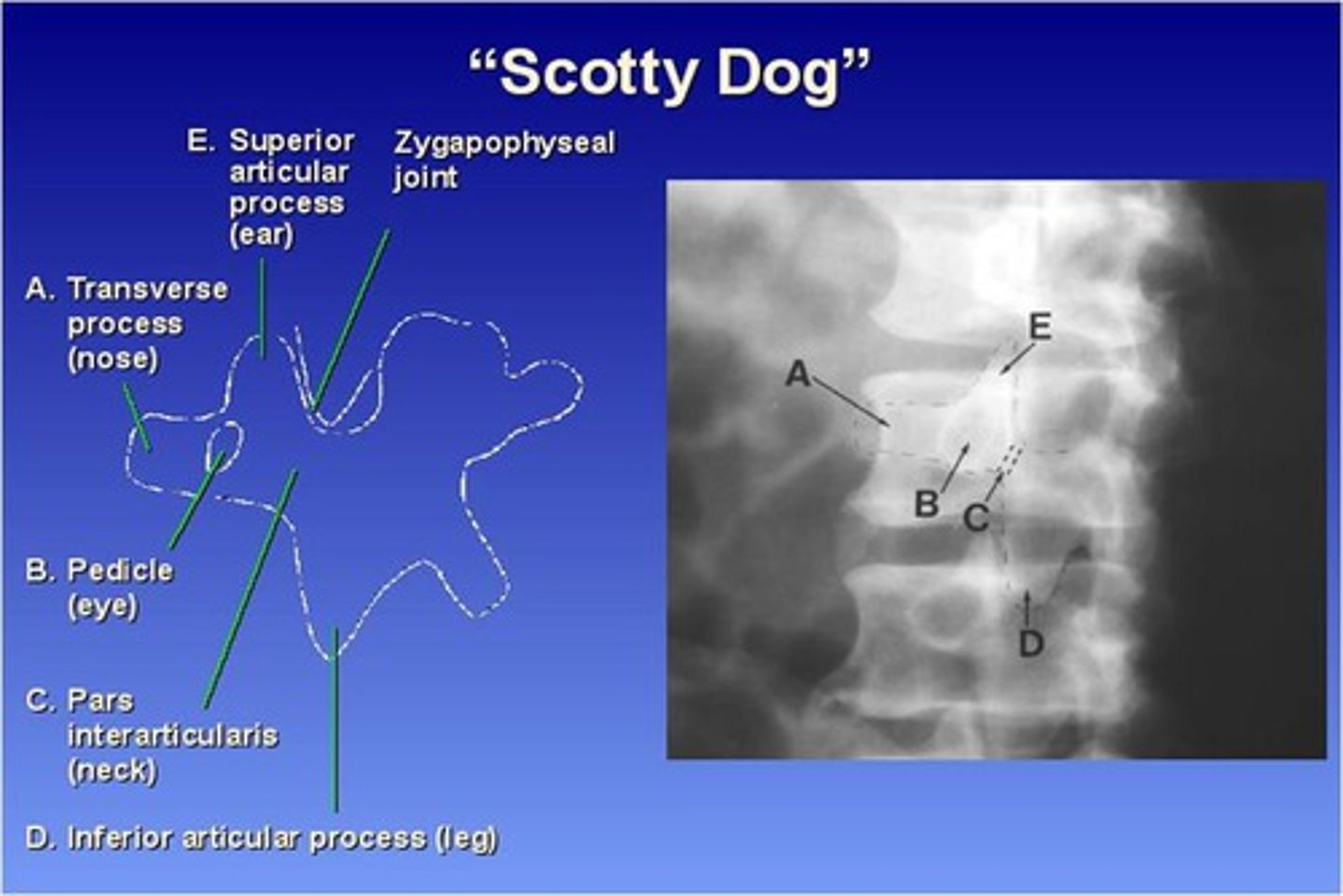
What part of the lumbar spine makes up the "neck" of the "scotty dog"?
pars interarticularis
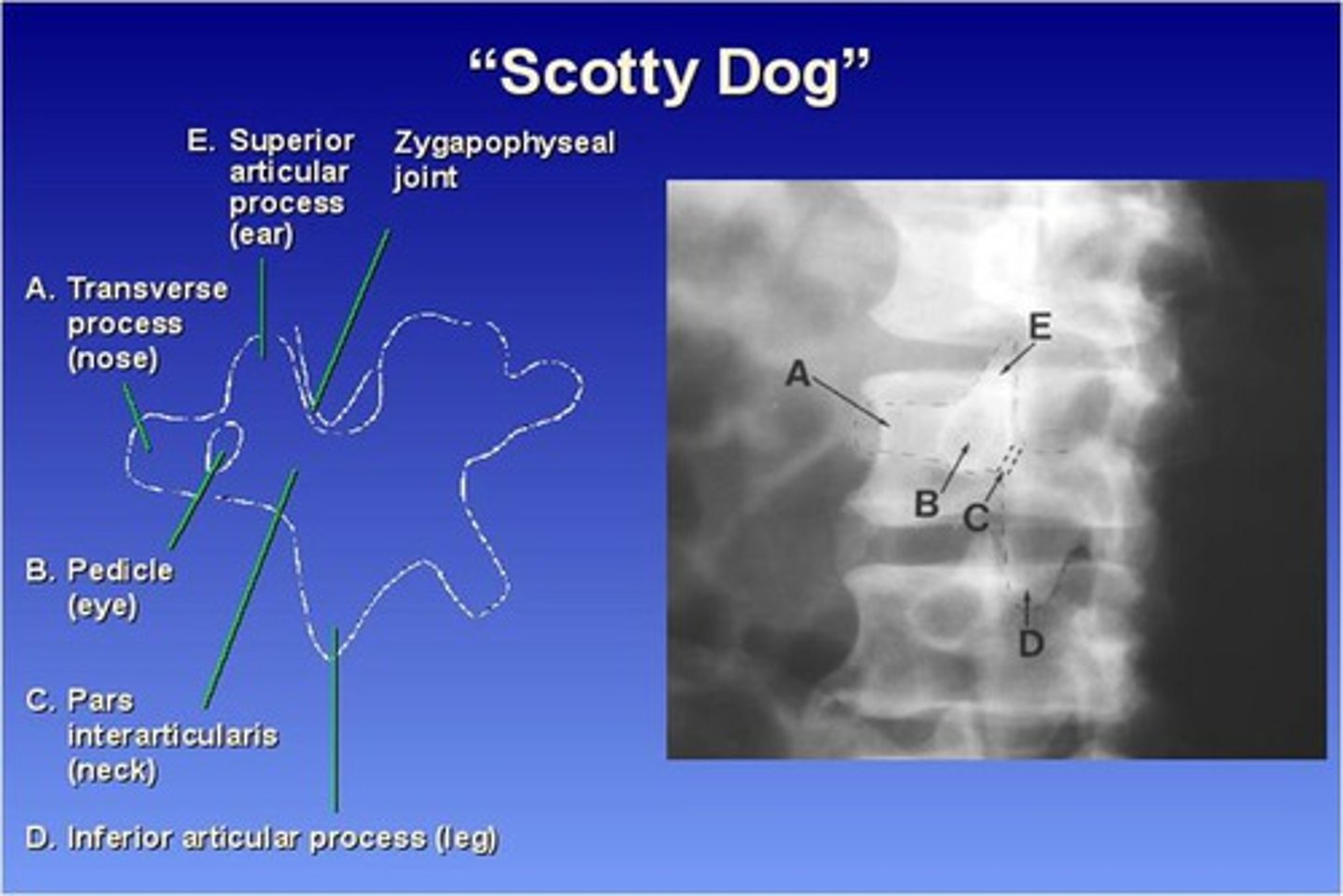
What is the pars interarticularis?
portion of each lamina between the superior and inferior articular processes
What part of the lumbar spine makes up the "leg" of the "scotty dog"?
inferior articular process
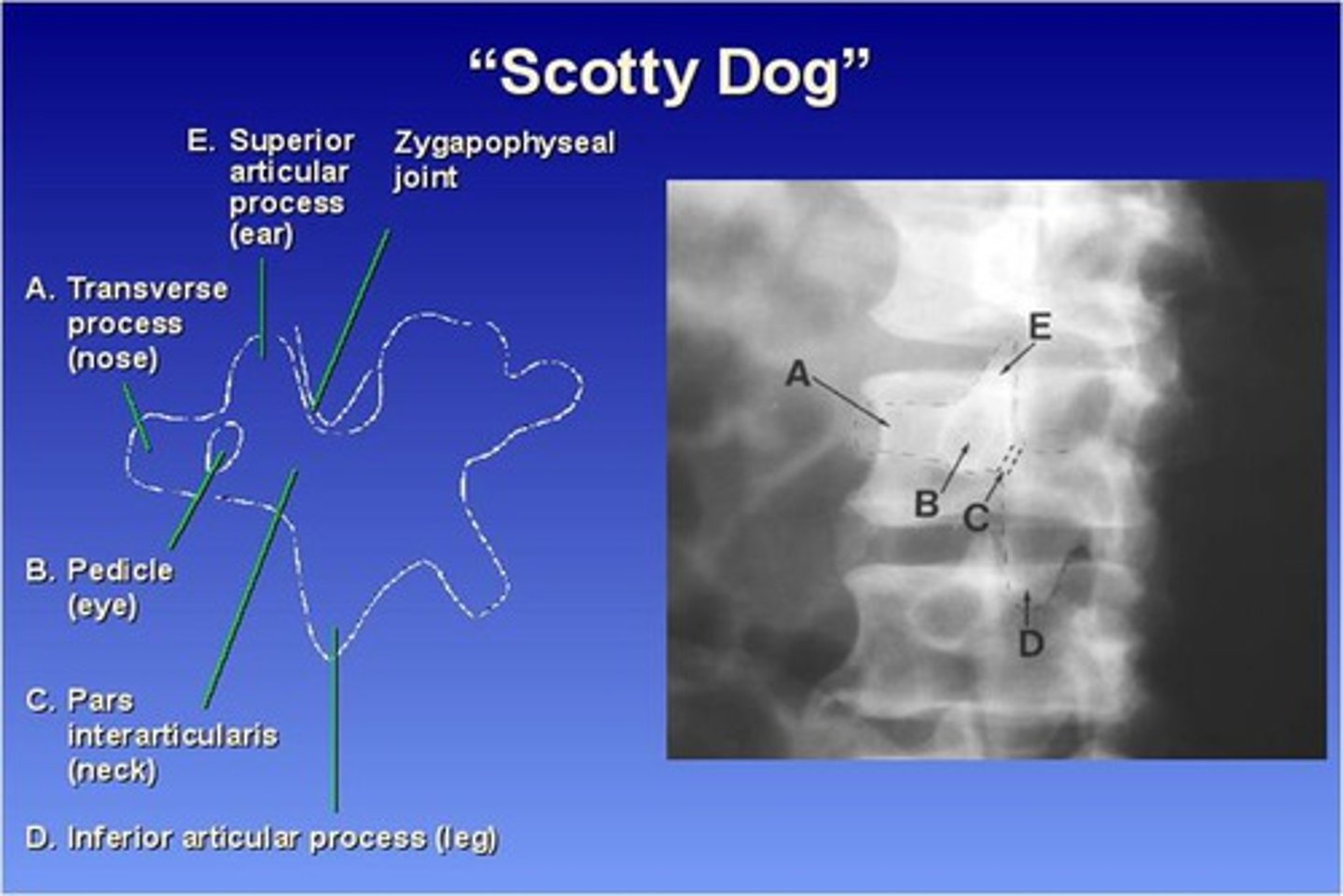
What part of the lumbar spine makes up the "ear" of the "scotty dog"?
superior articular process
What is spondylolisthesis?
anterior sliding of one vertebrae over another
What is spondylolysis?
fracture of pars interarticularis due to lack of development
True/False: in males, the sacral bone is usually longer, narrower, and more evenly curved than in females
true
What is the superior portion of the sacrum called?
base
What is the inferior portion of the sacrum called?
apex
What is the sacral promontory?
prominent ridge on superior anterior margin of base
What is the sacral canal?
continuation of vertebral canal
The pelvic sacral foramen provide passage for what?
nerves and blood vessels
What is the auricular surface?
where the ilium articulates with the sacrum
How is the median sacral crest formed?
by fused spinous processes of the sacral vertebrae
The coccyx is commonly referred to as the ________
tailbone
True/False: the coccyx diminishes in size from base (superior) to apex (inferior)
true
Does the coccyx tend to curve more anteriorly in males or females?
males
Go through the STAMPSBC list for the Lateral C-spine
S - shielding around waist
T - 25 mAs @ 75 kVp
A - no angle
M - marker along curve of neck
P - left side against board, chin elevated slightly
S - 72
B - suspend breathing after expiration
C - 10 x 12 lengthwise
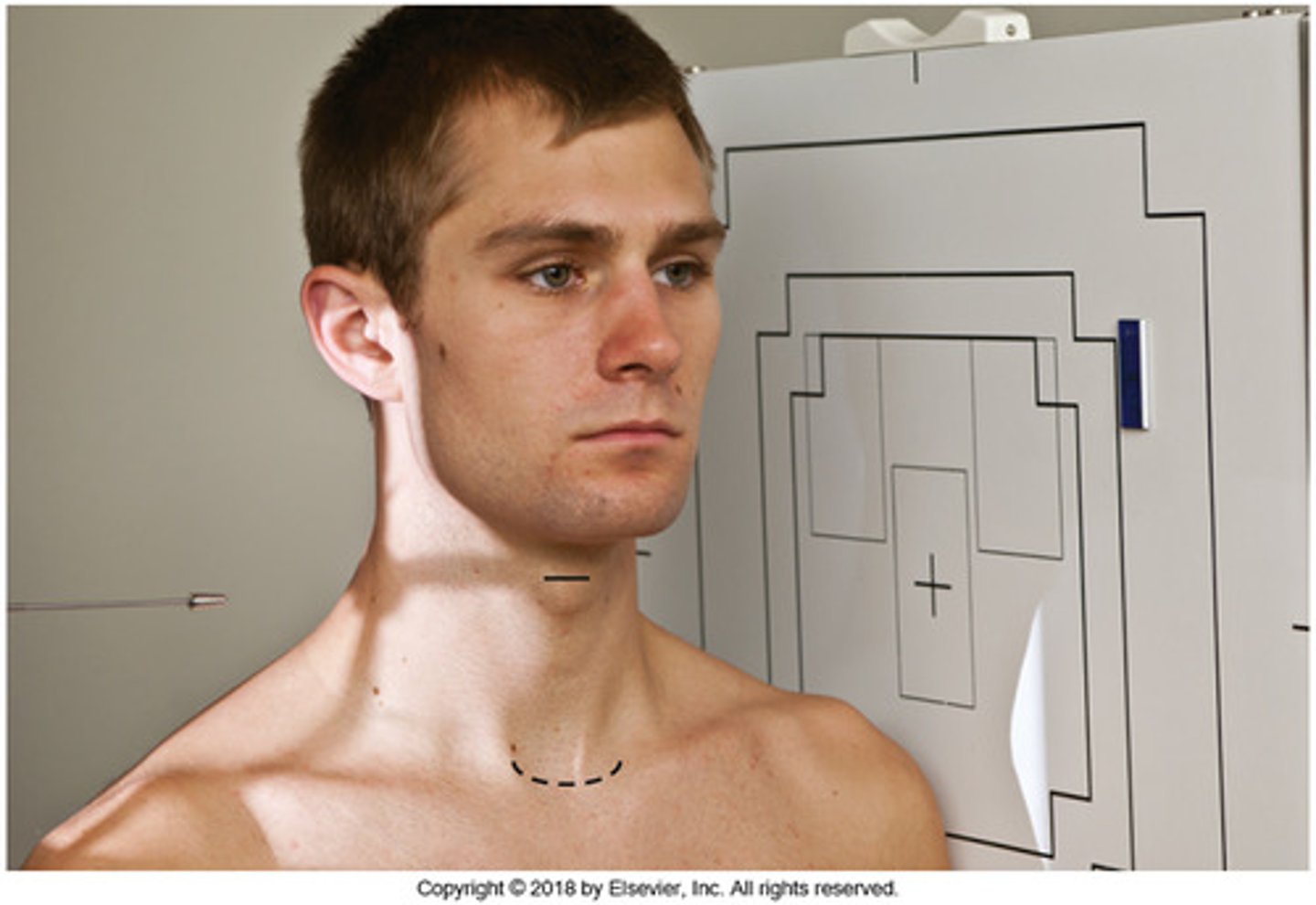
Where do you center for the Lateral C-spine?
C4 - C5
Go through the STAMPSBC list for the Oblique C-spine
S - shielding around waist
T - 25 mAs @ 75 kVp
A - 15 degrees cephalic
M - marker along curve of neck
P - PT rotated 45 degrees from AP, chin elevated slightly
S - 72
B - suspend breathing
C - 10 x 12 lengthwise
Where do you center for the Oblique C-spine?
C4 - C5
If you are doing an AO Oblique C-spine, what MUST you change?
15 degree cephalad angle to caudad
PO Oblique C-spines show the intervertebral foramen farthest or closest to the bucky?
farthest from bucky
AO Oblique C-spines show the intervertebral foramen farthest or closest to the bucky?
closest to the bucky
Go through the STAMPSBC list for the AP Axial C-spine
S - shielding around waist
T - 18 mAs @ 75 kVp
A - 15 degree cephalad
M - marker along curve of neck
P - back against board, chin elevated slightly
S - 40
B - suspend breathing
C - 10 x 12 lengthwise, can collimate to 8 x 10
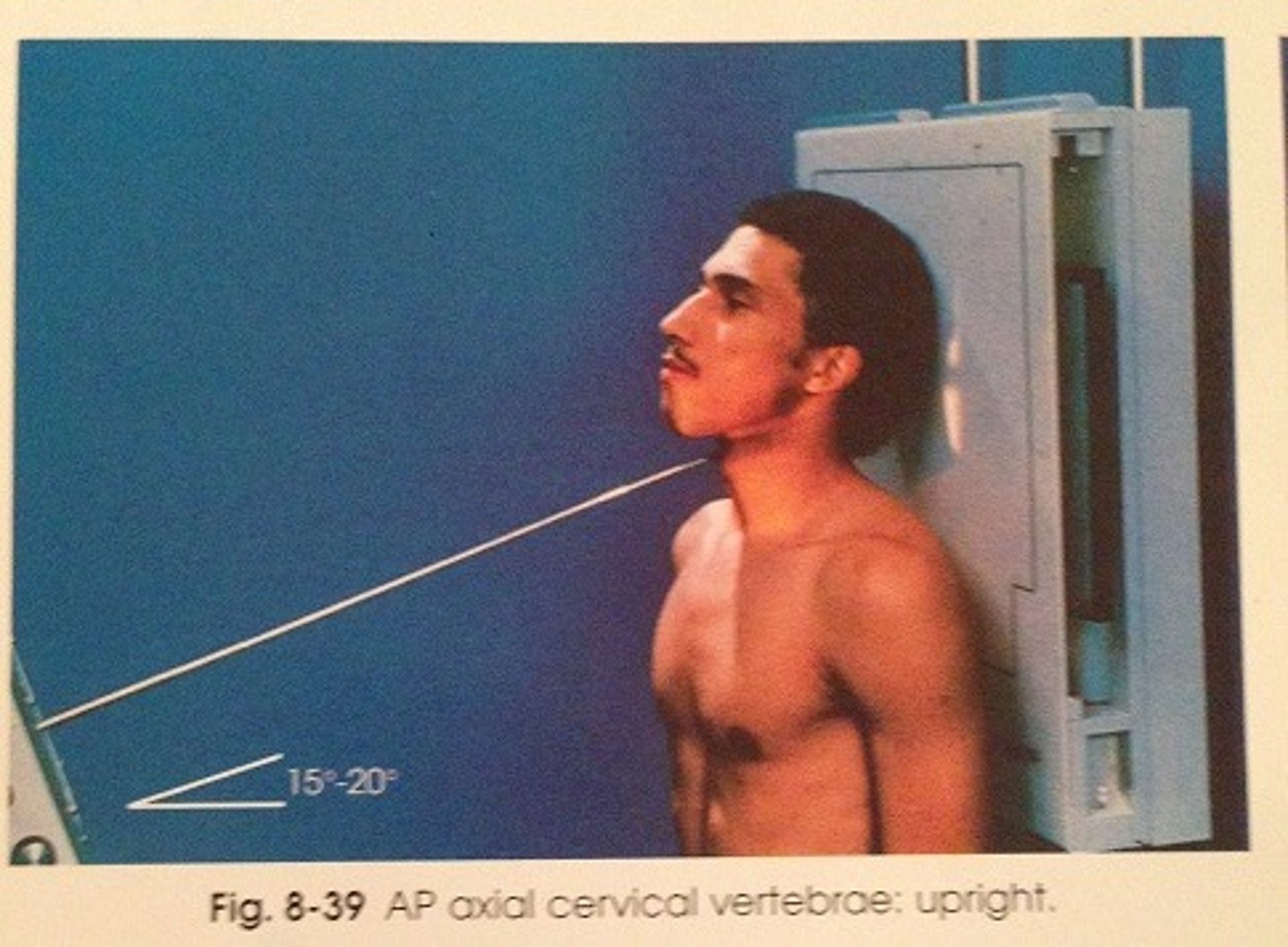
Where do you center for the AP Axial C-spine?
C4 - C5
Go through the STAMPSBC list for the AP Open Mouth C-spine
S - shielding around waist
T - 40 mAs @ 75 kVp
A - no angle
M - marker along skin line of neck
P - back against board, bottom of front teeth line up w/ base of skull
S - 40
B - suspended breathing
C - 10 x 12 lengthwise, can collimate to 7 x 7
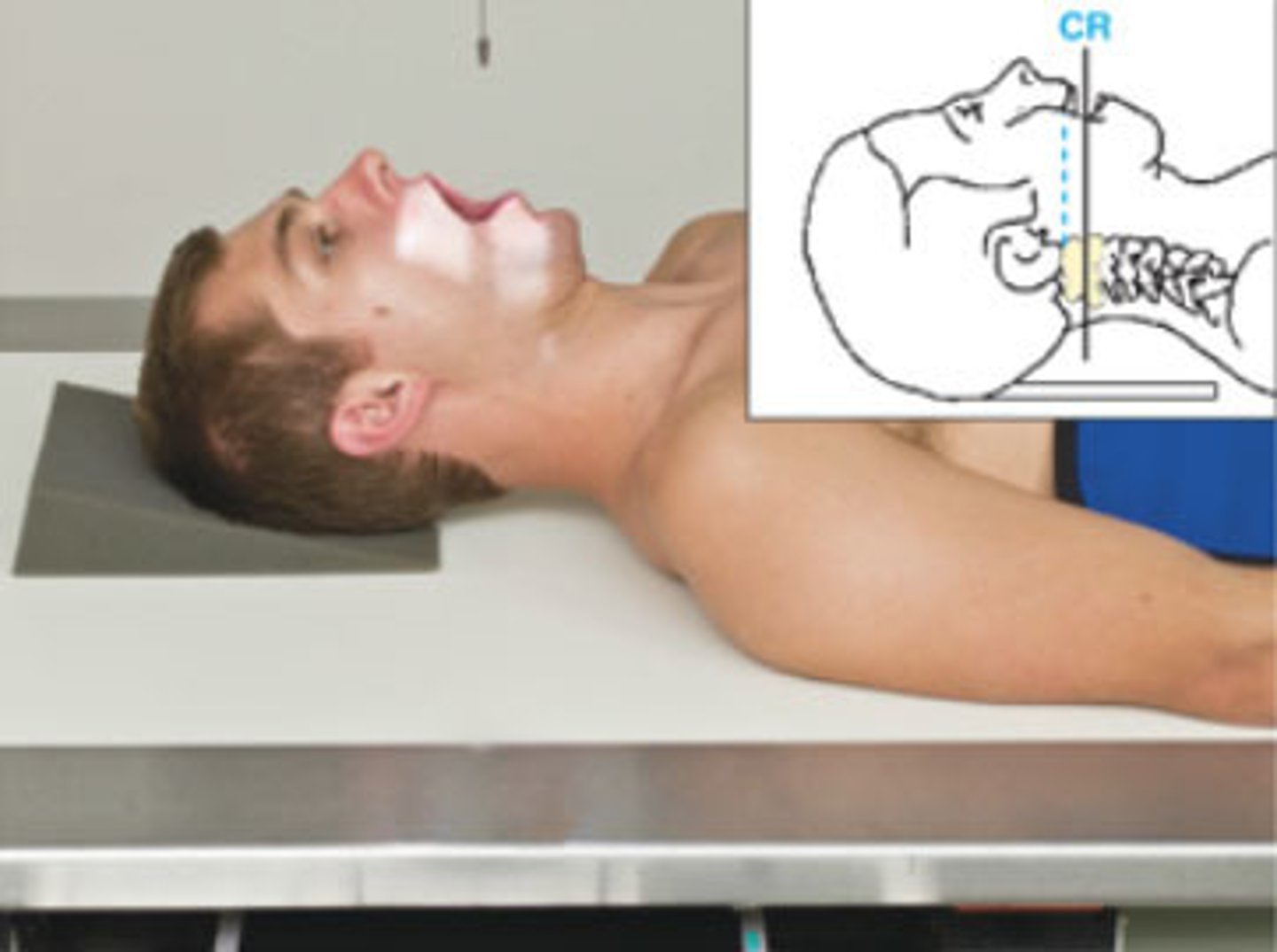
Where do you center for the AP Open Mouth C-spine?
center of mouth
What does the AP Open Mouth C-spine demonstrate?
C1 - C2 articulation
Go through the STAMPSBC list for the Swimmers C-spine
S - shielding around waist
T - 120 mAs @ 80 kVp
A - no angle
M - marker along curve of neck
P - left side against board, left arm above head
S - 72
B - suspend breathing after expiration
C - 14 x 17 lengthwise, can collimate side to side
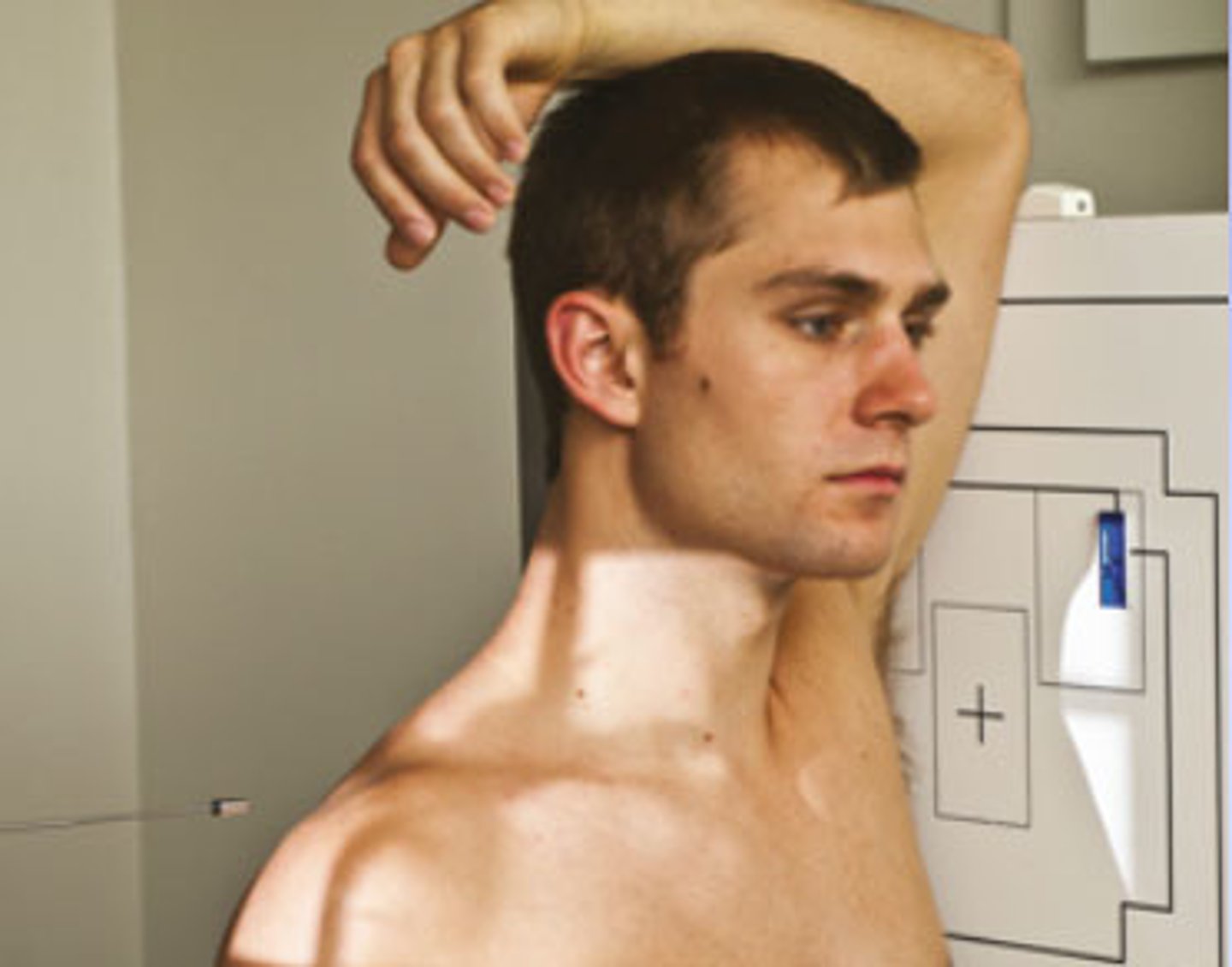
Where do you center for the Swimmers C-spine?
1 inch above jugular notch
If the PT cannot separate humeral heads enough on the Swimmers C-spine what do you use?
3 - 5 degree caudad angle
Why is a Swimmers C-spine view done?
because C7 wasn't seen on normal Lateral
Why are flexion and extension C-spine views done?
whiplash injury or post operation to test mobility
Go through the STAMPSBC list for the PA Judd C-spine
S - shielding around waist
T - 40 mAs @ 75 kVp
A - no angle
M - correct marker on correct side
P - PA w/ chin on crosshairs of board
S - 40
B - suspended breathing
C - 10 x 12 lengthwise, can collimate to 7 x 7
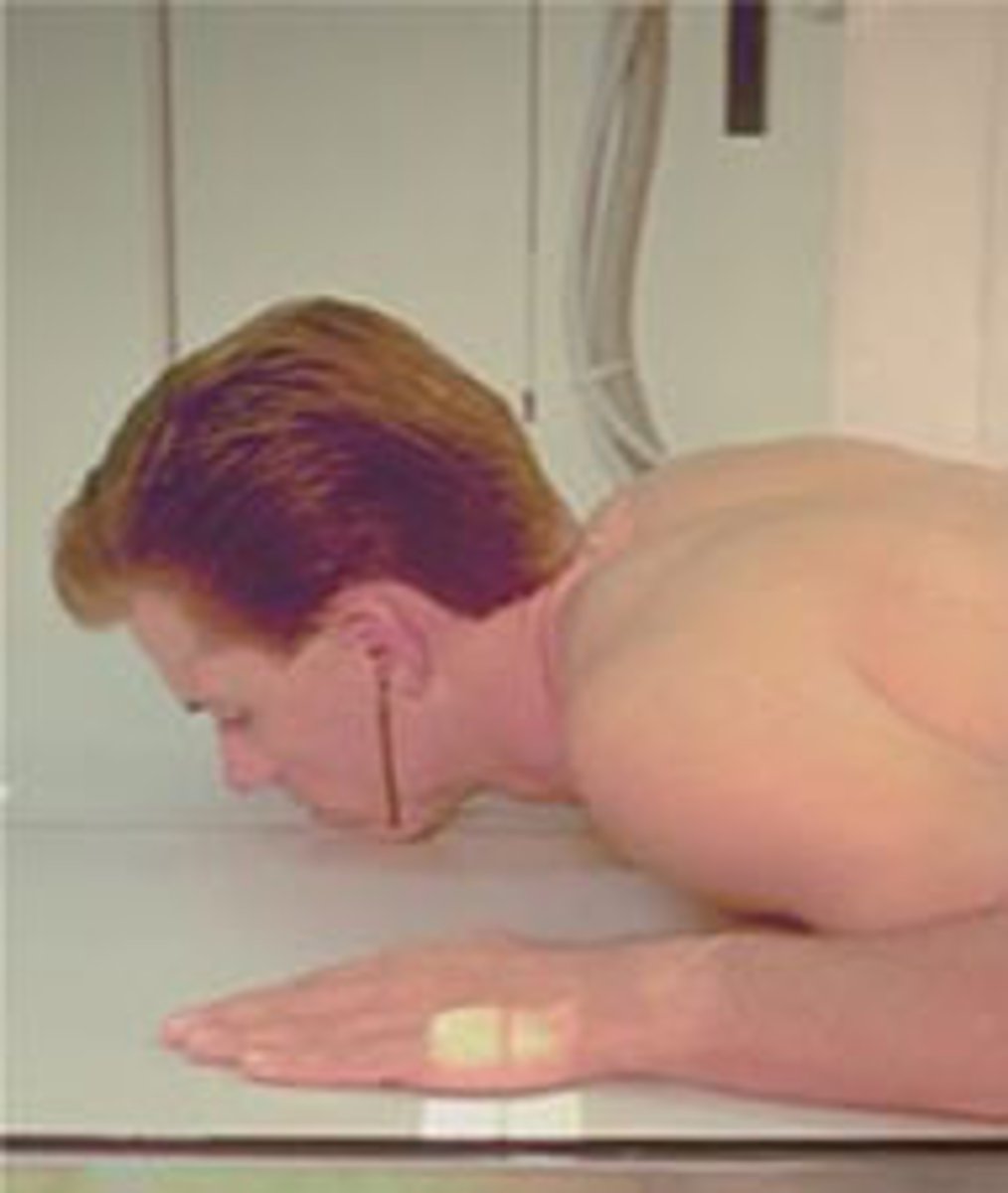

Go through the STAMPSBC list for the AP Fuchs C-spine
S - shielding around waist
T - 40 mAs @ 75 kVp
A - no angle
M - correct marker on correct side
P - laying on back, chin elevated so MML is parallel to beam
S - 40
B - suspended breathing
C - 10 x 12 lengthwise, can collimate to 7 x 7
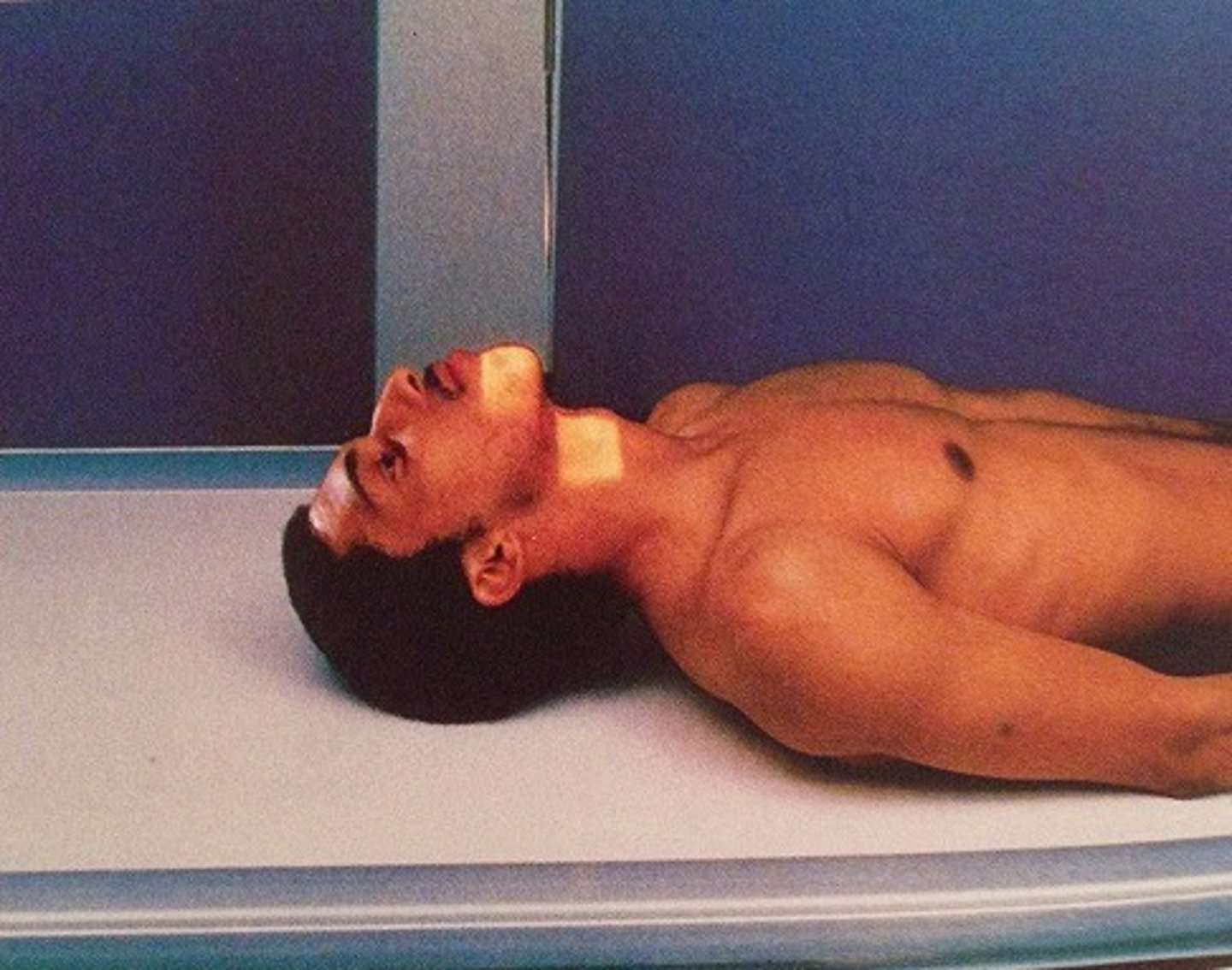
Go through the STAMPSBC list for the AP T-spine
S - shielding over lap
T - 12 mAs @ 75 kVp
A - no angle
M - marker on cassette in collimated light field
P - on back w/ knees bent, pillow ONLY under head
S - 40
B - suspend after expiration
C - 14 x 17 lengthwise, can collimate side to side
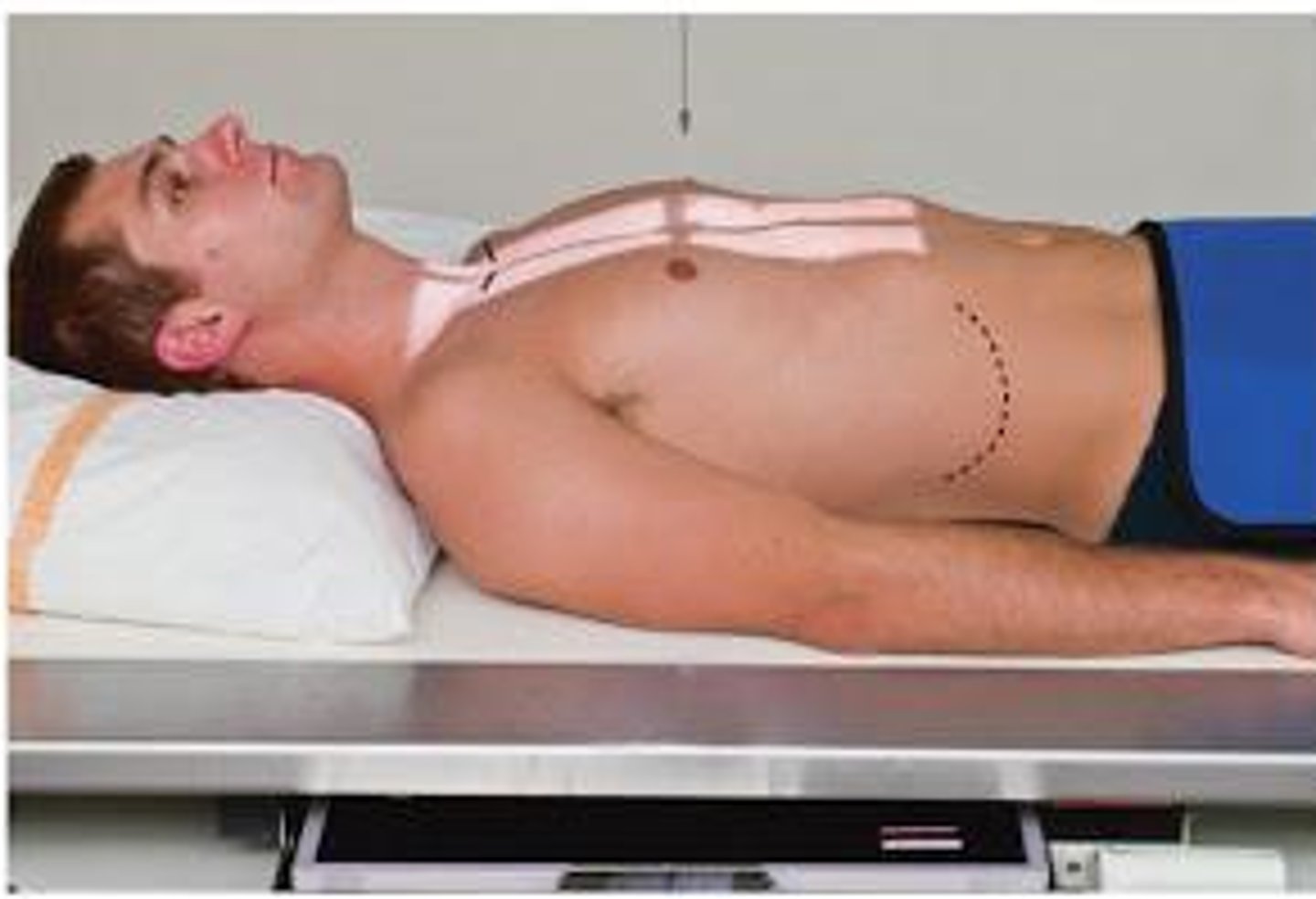
Where do you center for AP T-spine?
T7
Where do you center for Lateral T-spine?
T7 and one inch back from midcoronal plane
Go through the STAMPSBC list for the Lateral T-spine
S - shielding over hip
T - 40 mAs @ 80 kVp
A - no angle
M - on cassette in collimate light field, in front of PT,
P - on left side, small sponge under soft spot of side
S - 40
B - orthostatic breathing
C - 14 x 17 lengthwise, can collimate in side to side
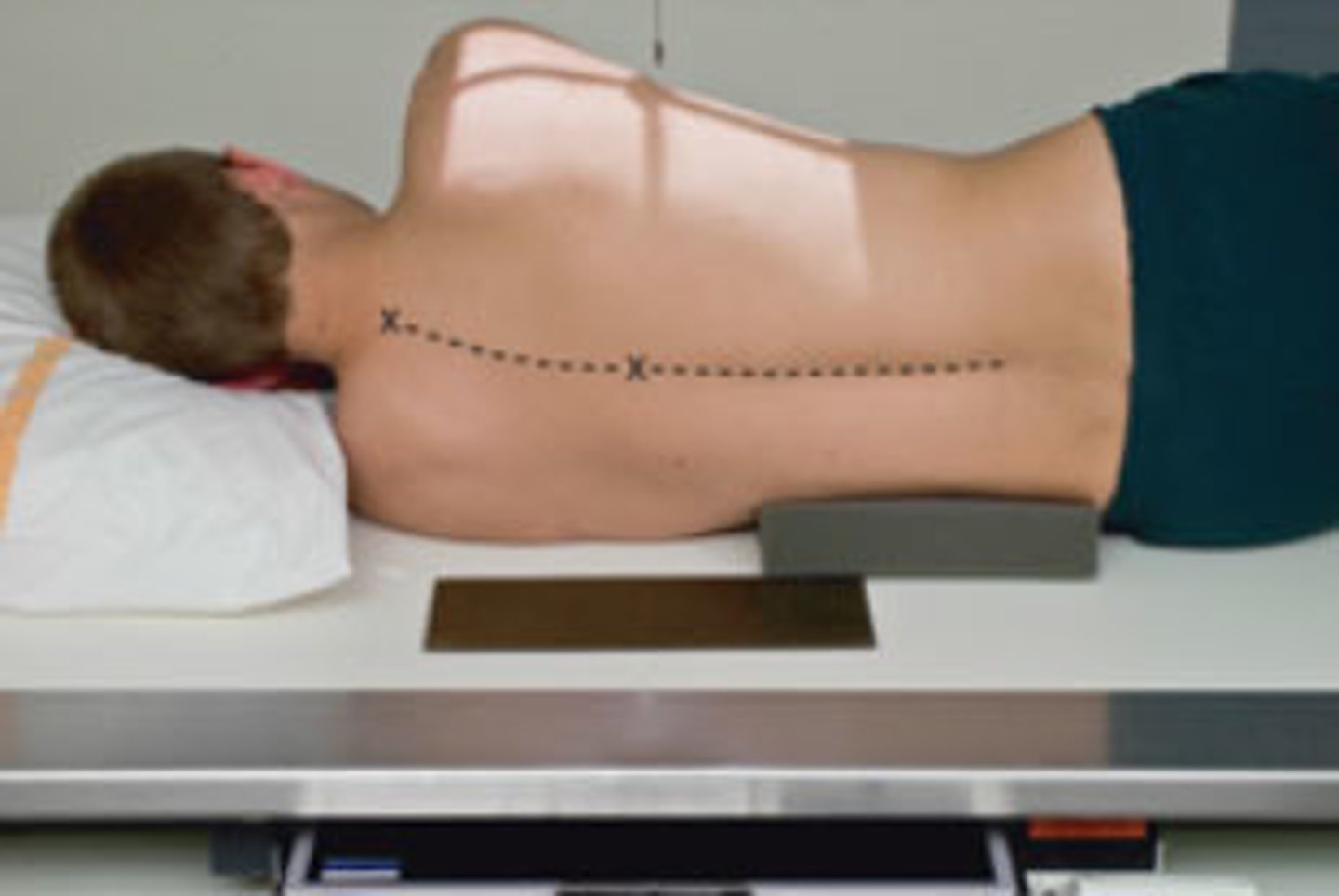
What should you use to absorb scatter on a Lateral T-spine?
lead strip outside of skin line
What does the lateral T-spine demonstrate?
intervertebral foramina
What does the Oblique T-spine demonstrate?
zygapophyseal joints
The PO Oblique T-spine demonstrates which zygapophyseal joint?
upside joint
The AO Oblique T-spine demonstrates which zygapophyseal joint?
downside joint
If the PT is in a Lateral T-spine position and you have to move them to an Oblique T-spine position, how many degrees do you oblique them?
20 degrees from lateral
If the PT is in an AP T-spine position and you have to move them to an Oblique T-spine position, how many degrees do you oblique them?
70 degrees from AP
Where do you center for Oblique T-spine?
T7
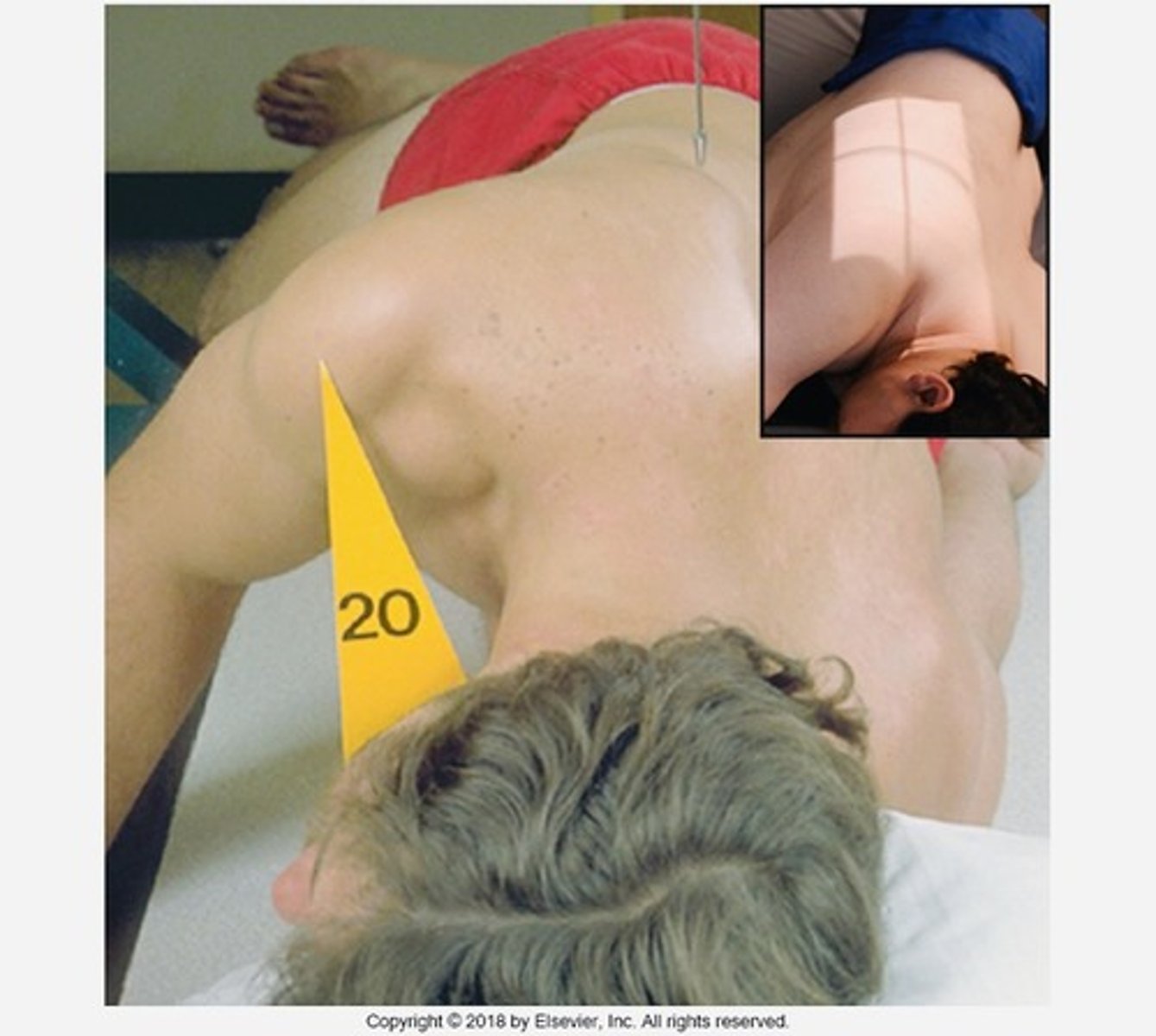
Go through the STAMPSBC list for the AP lumbar spine
S - no shielding
T - 30 mAs @ 75 kVp
A - no angle
M - marker on cassette in light field
P - supine with knees bent
S - 40
B - expiration
C - 14 x 17 lengthwise, can collimate to 10 x 17
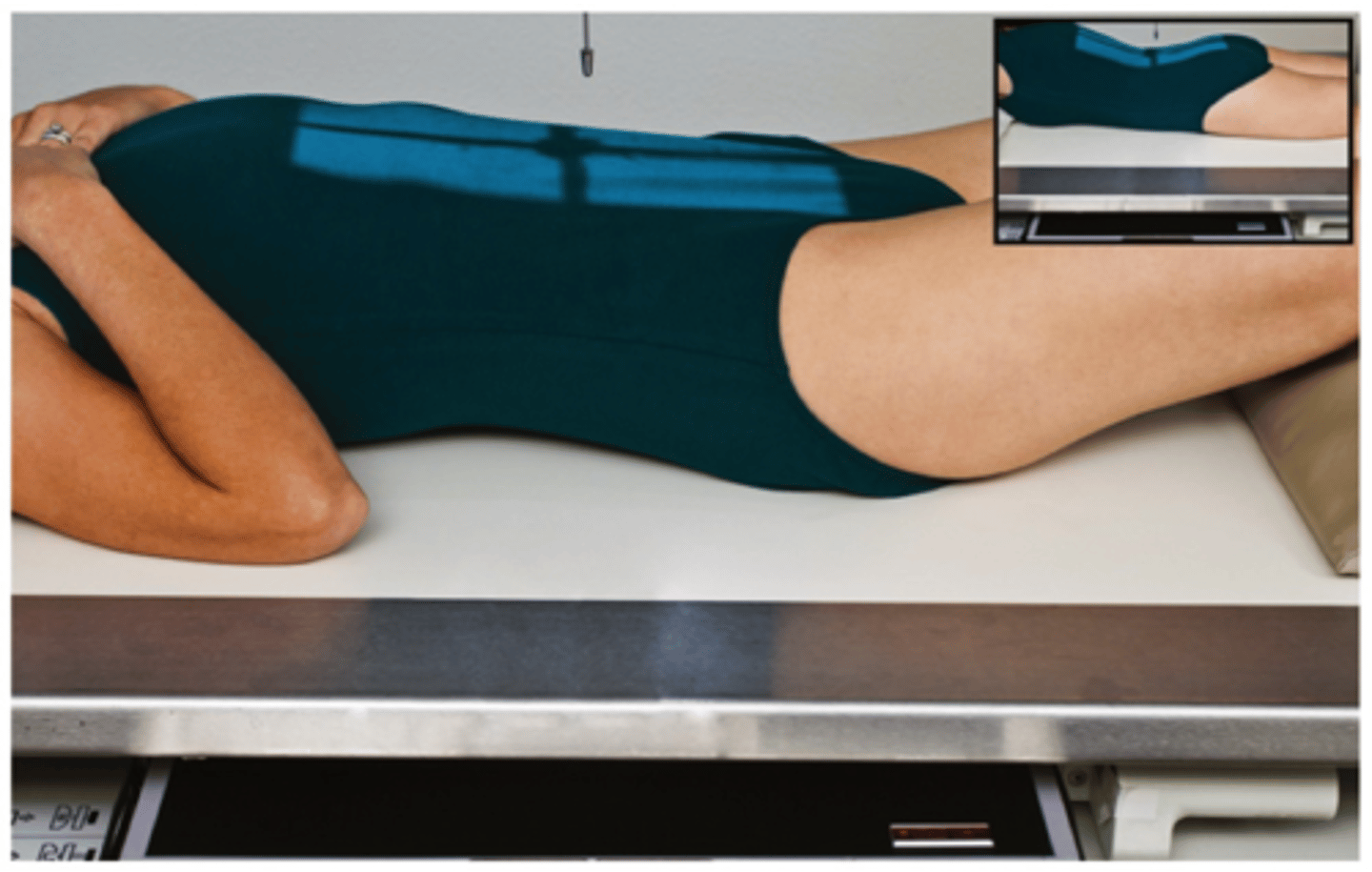
Where do you center for AP L-spine?
at the crest
Go through the STAMPSBC list for the Oblique lumbar spine
S - no shielding
T - 40 mAs @ 80 kVp
A - no angle
M - marker on cassette in light field
P - supine w/ 45 degree rotation
S - 40
B - expiration
C - 14 x 17 lengthwise
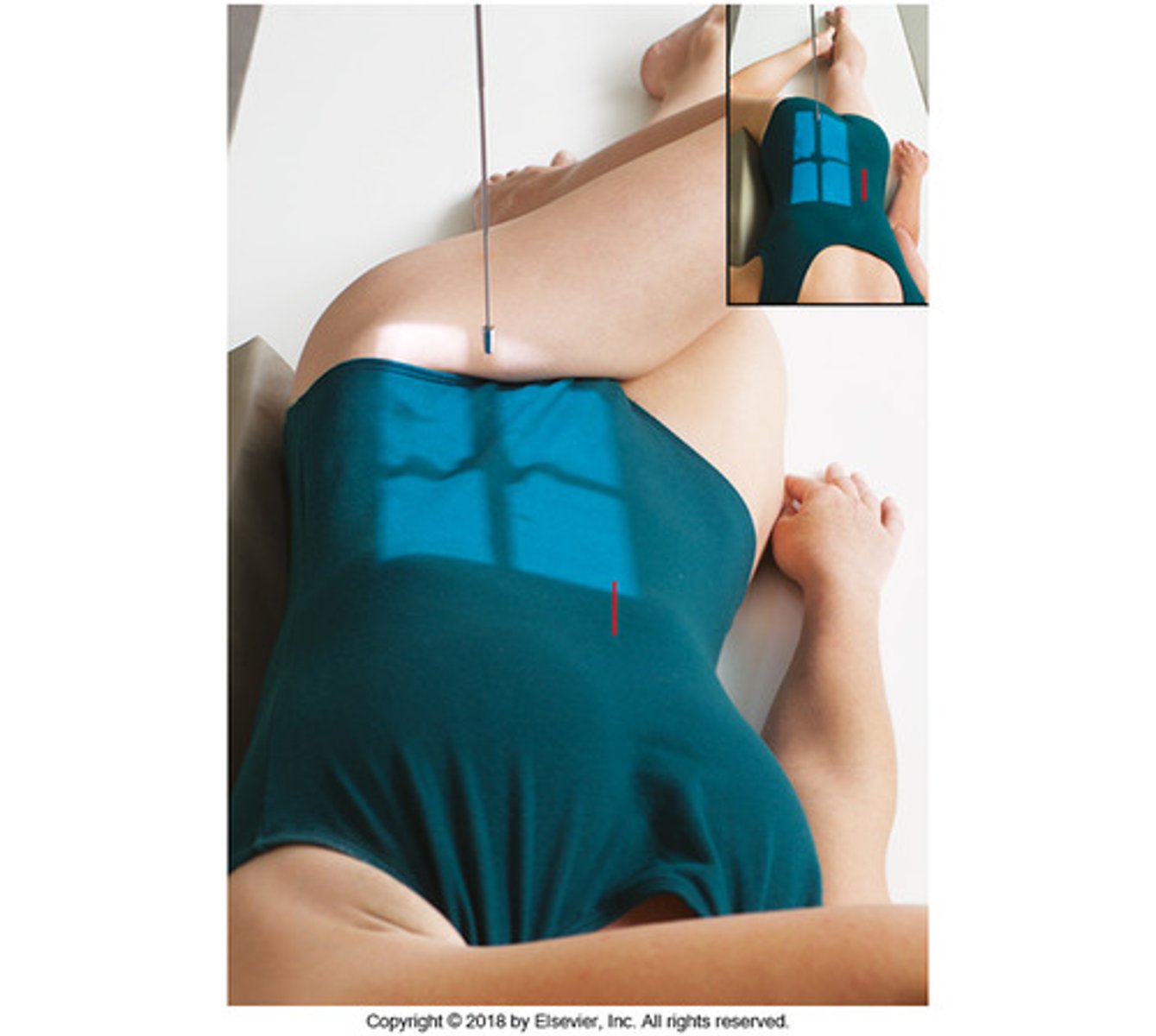
Where do you center for Oblique L-spine?
at the crest & 2" in from upside ASIS
PO Oblique L-spine demonstrate which zygapophyseal joint?
downside
AO Oblique L-spine demonstrates which zygapophyseal joint?
upside