GCSE Edexcel B Geography Paper 1
1/134
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
135 Terms
Aftershock
A less powerful earthquake which follows a more powerful earthquake
Aid
Short or long term help given in emergency e.g. food and water or medical training
Atmosphere
The layer of Earth's gases above the Earth's surface
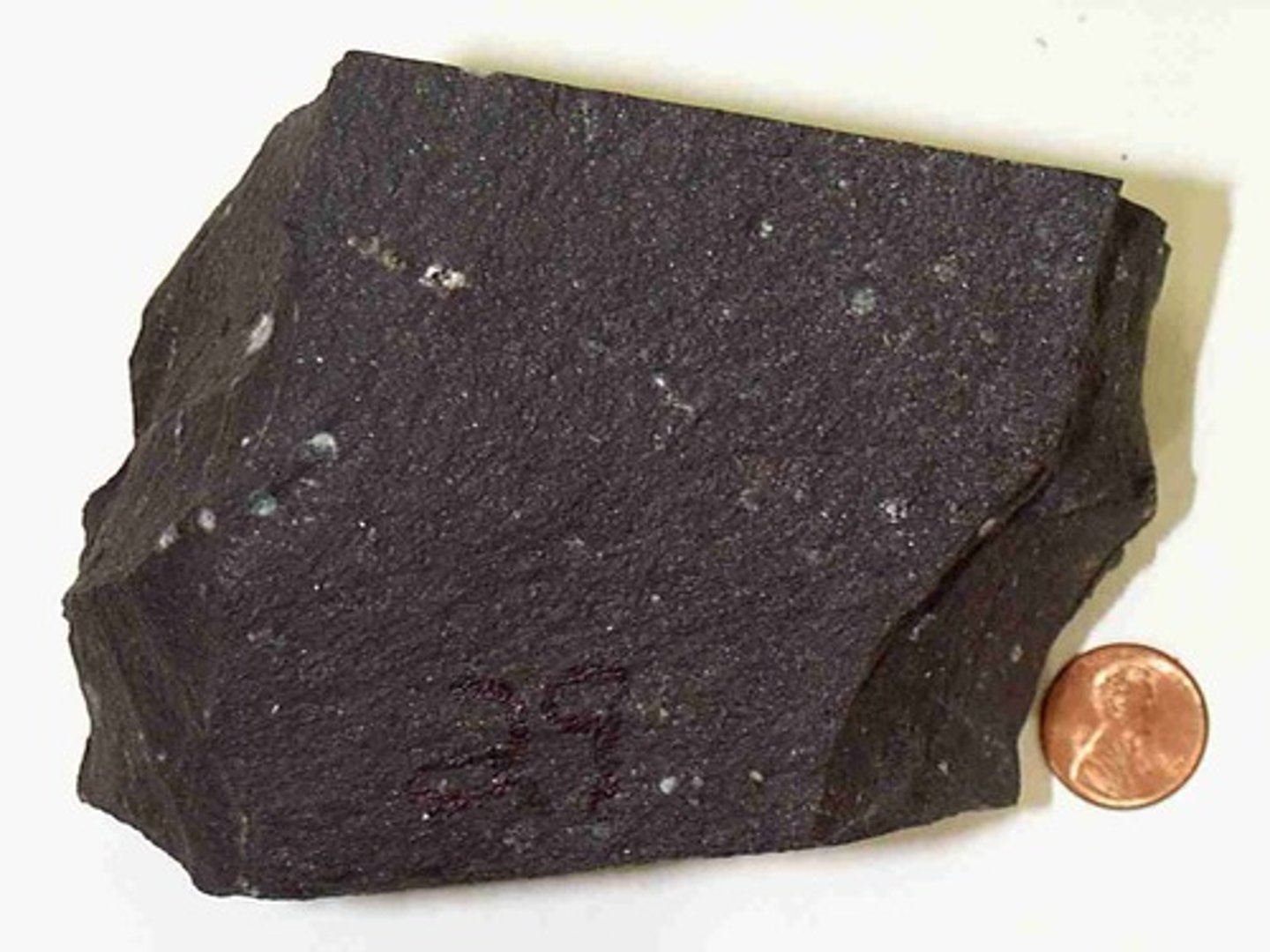
Basalt
Dark coloured volcanic rock, when molten spreads rapidly.

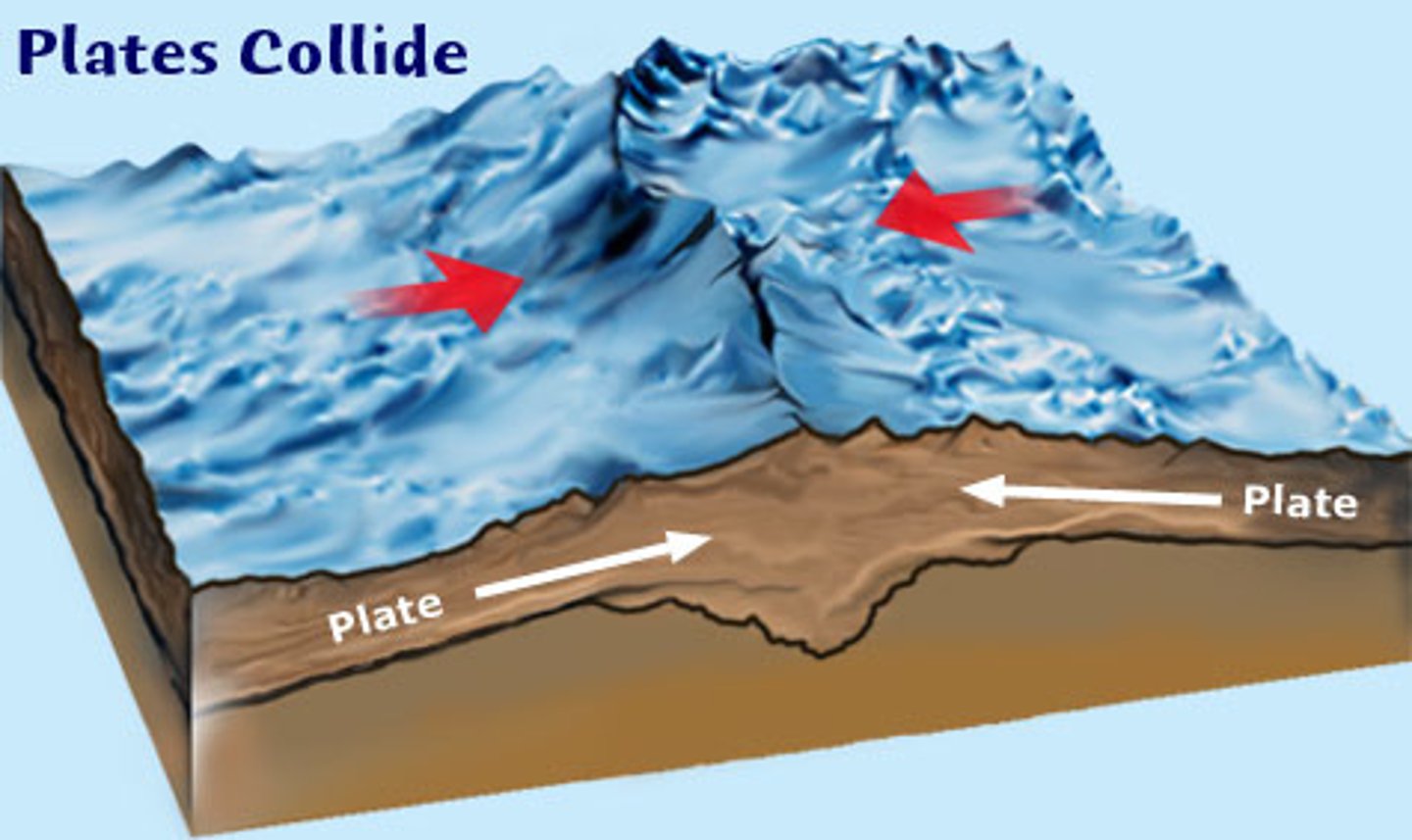
Collision Zones
Where two tectonic plates collide e.g Himalayas
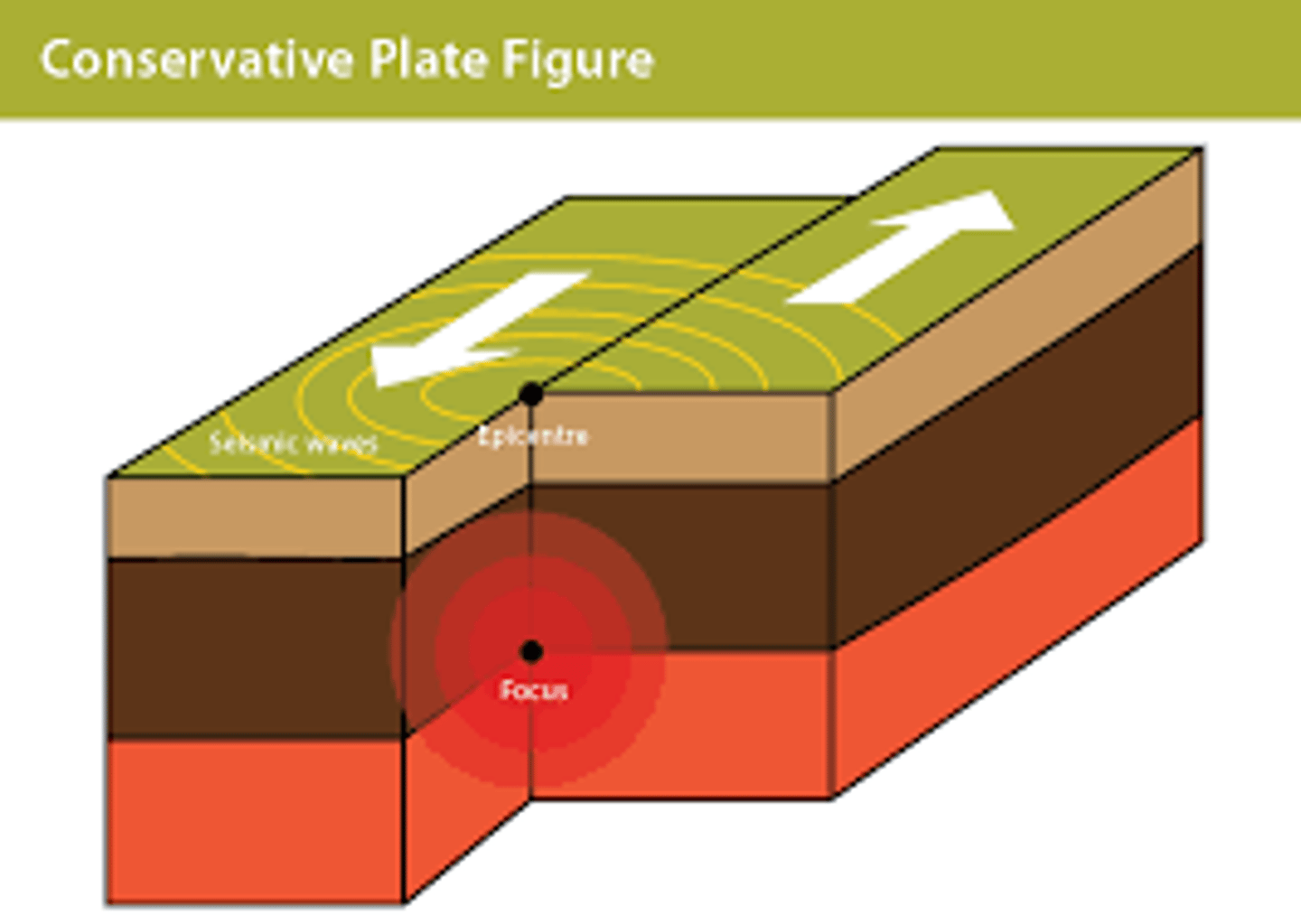
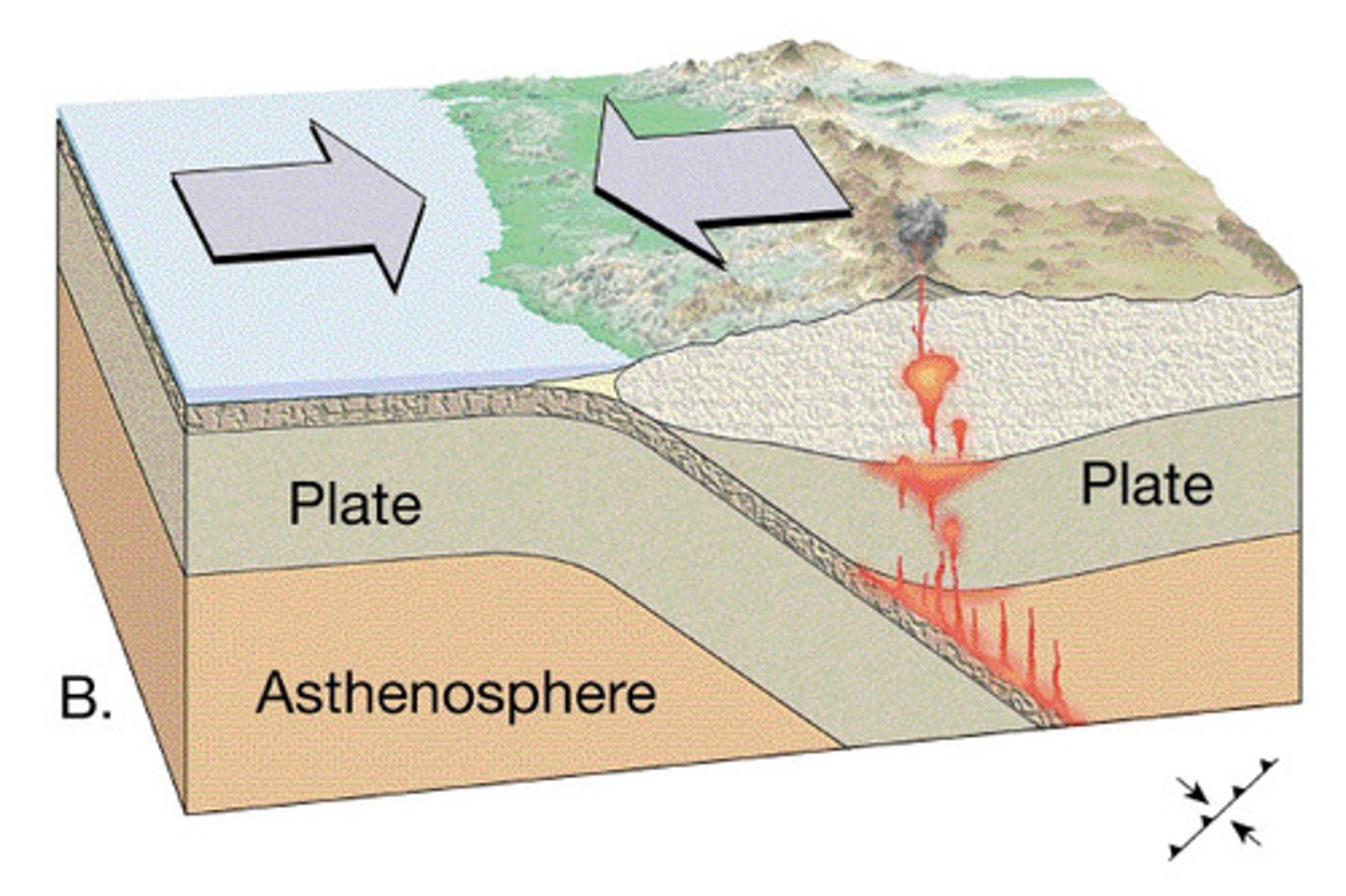
Conservative Plate Boundary
Where two plates slide along each other
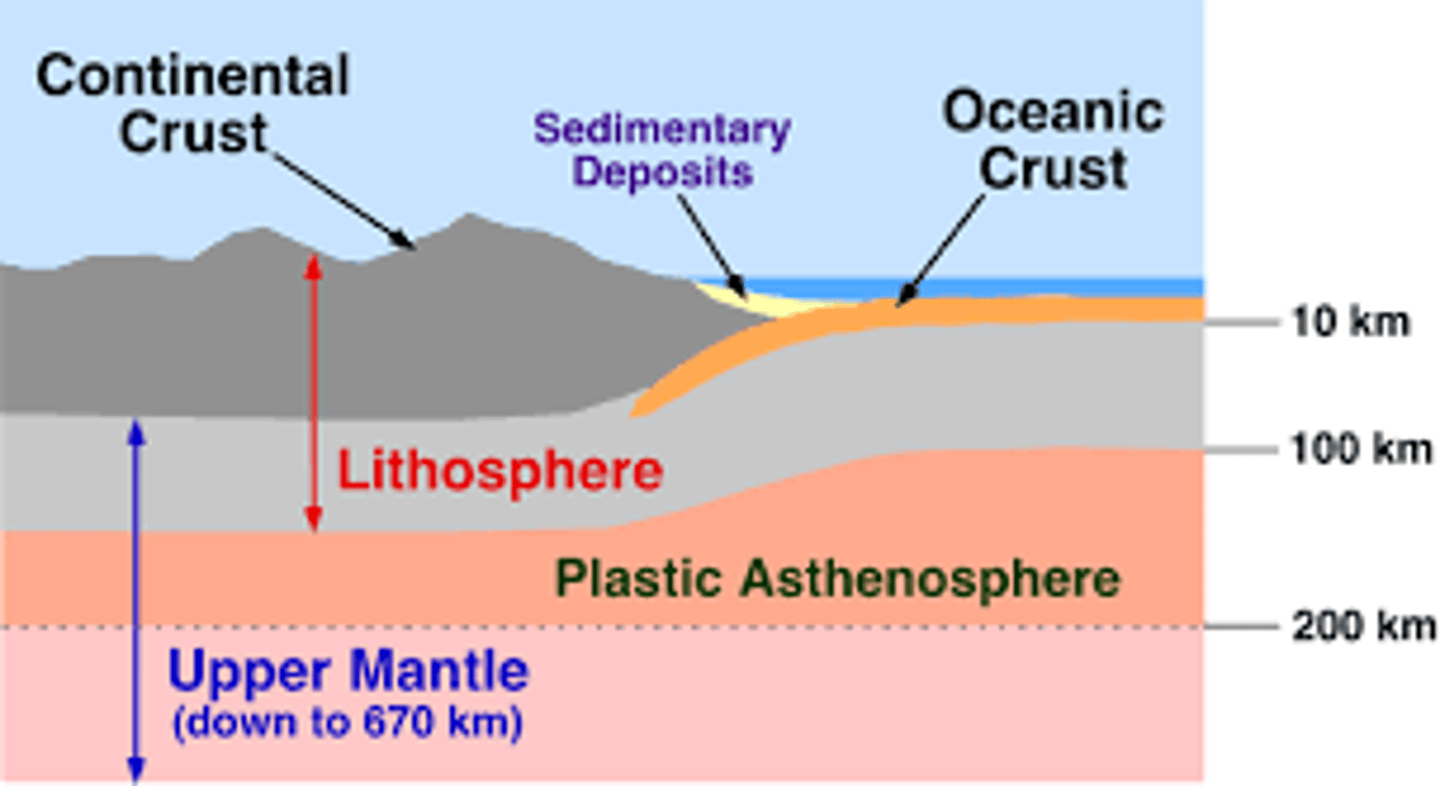
Continental Crust
The part of the Earth's crust that makes up land (30-50km thick)
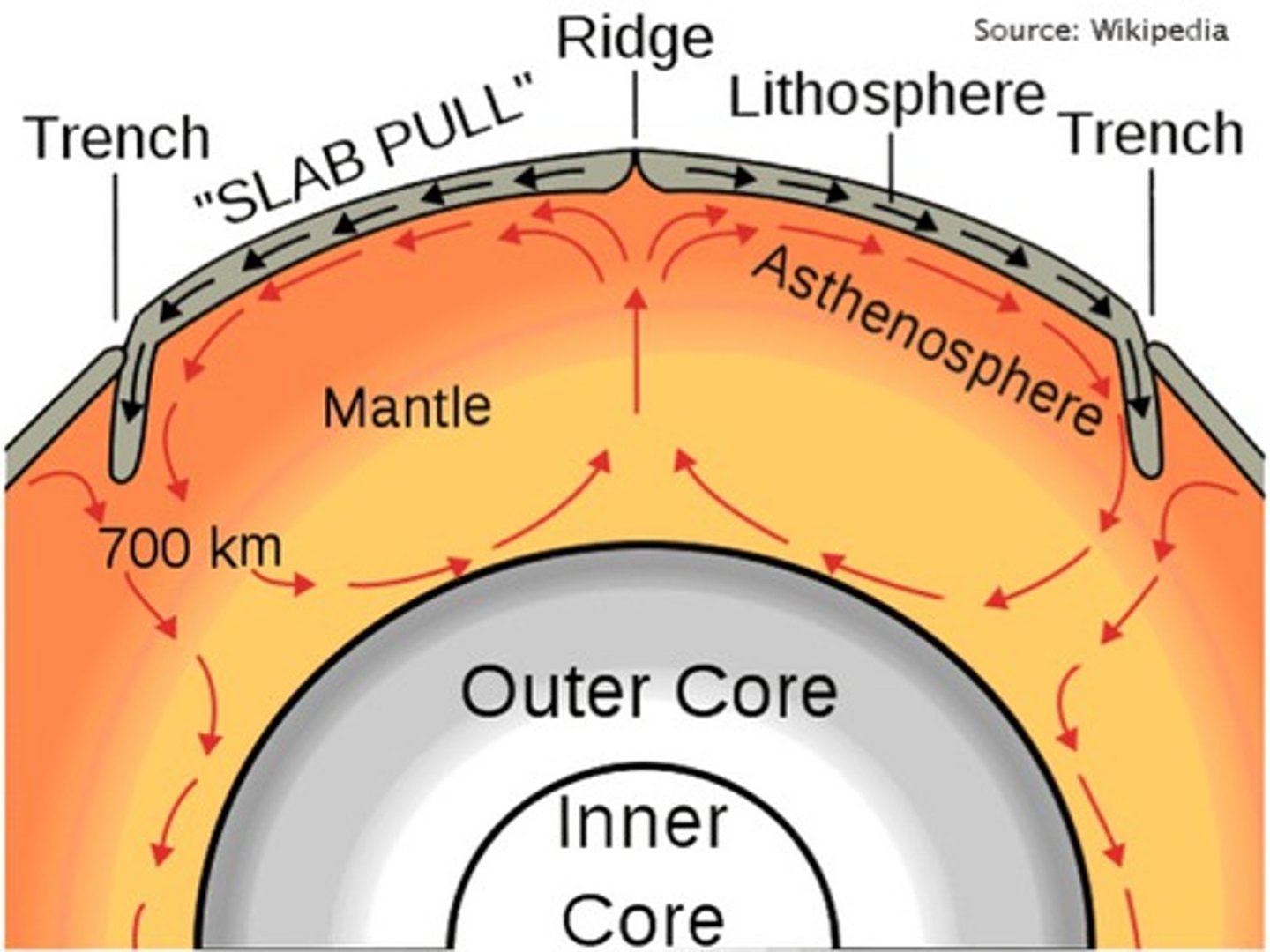
Convection Currents
Currents which transfer heat from one part of a gas or liquid to another
Convergent Plate Boundary
When two tectonic plates collide (see collision zone)
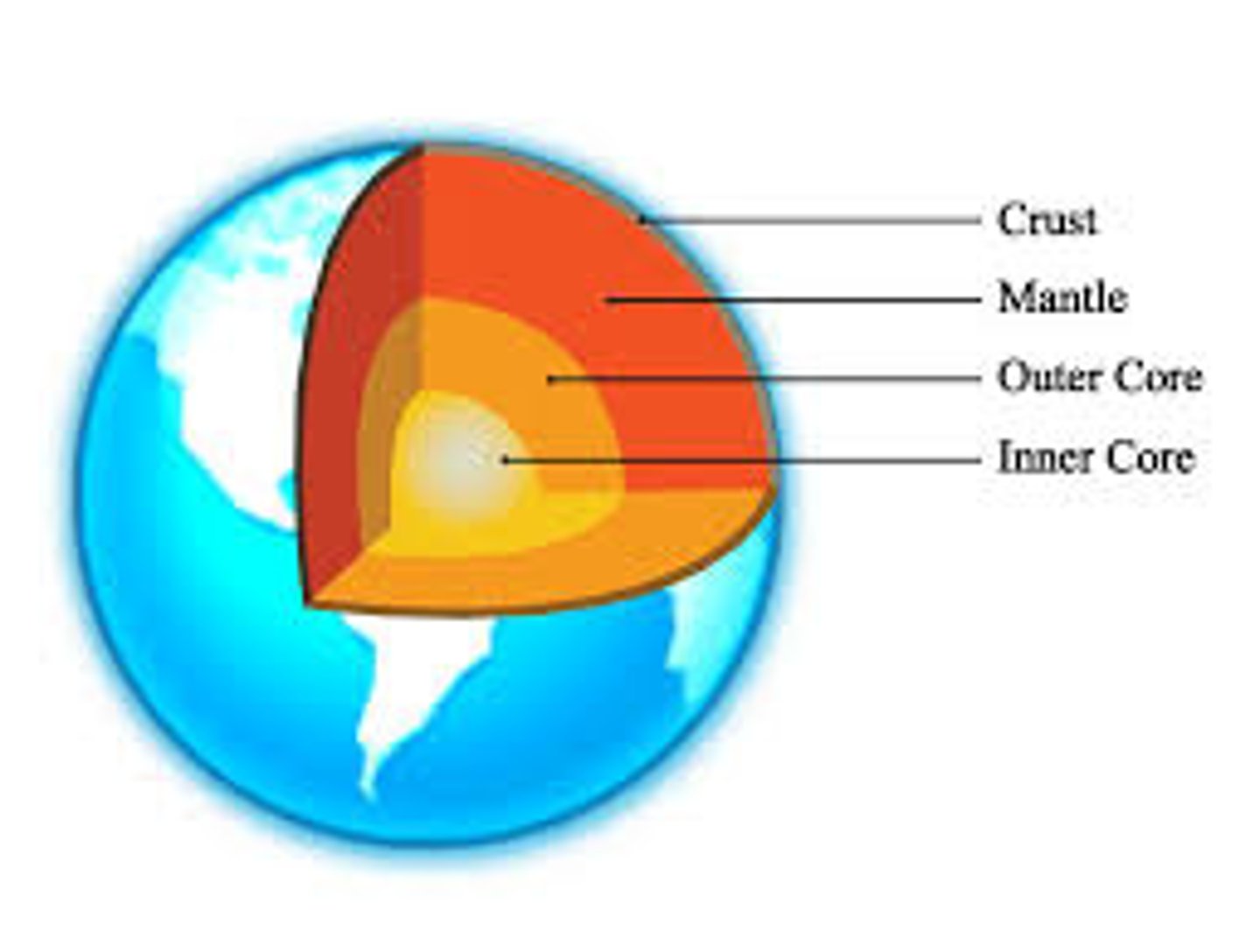
Core
Centre of the Earth, made up of a solid inner and molten outer core
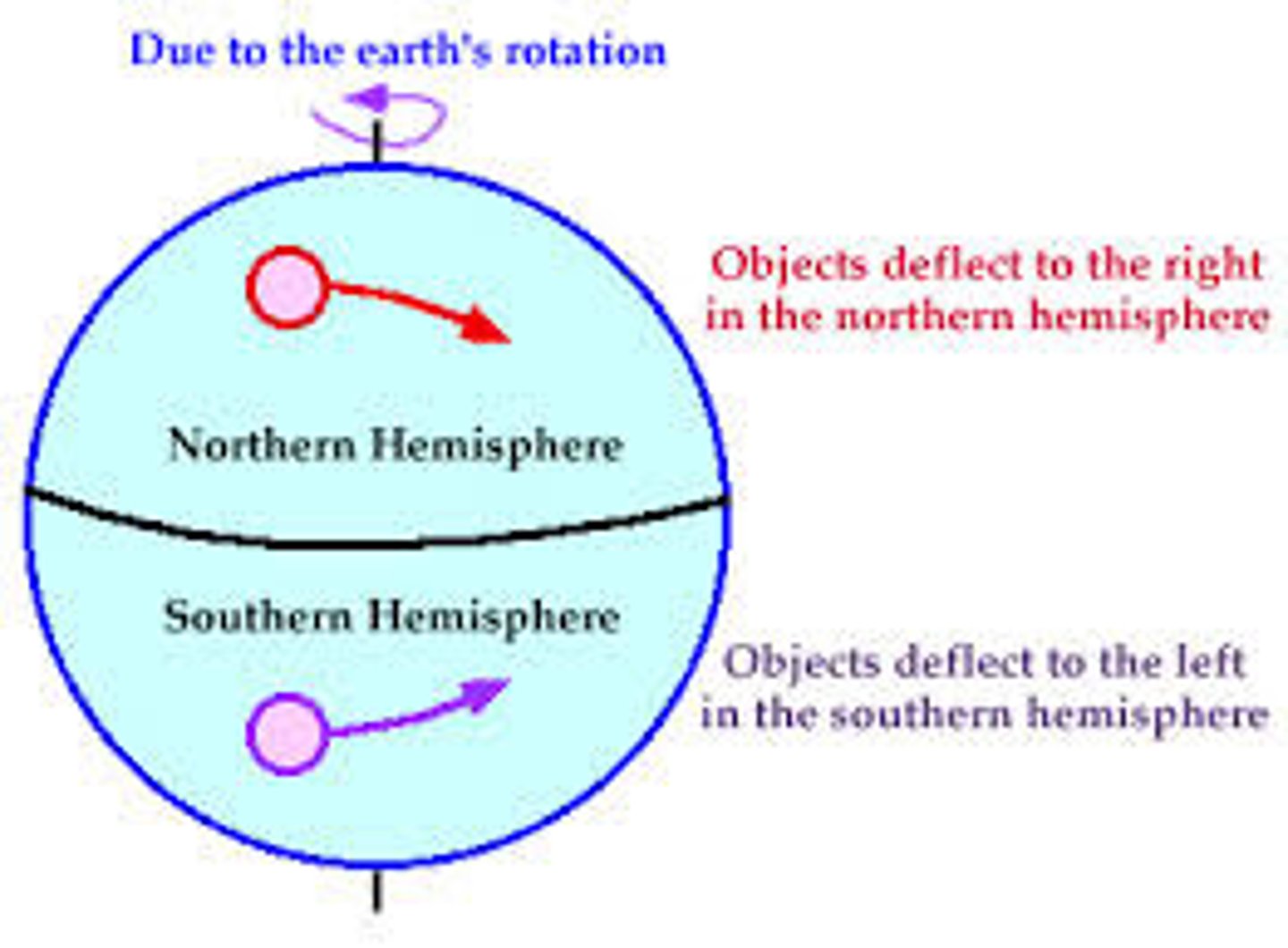
Coriolis Force
A strong force created by the Earth's rotation (within 5º of the equator), can cause hurricanes and tropical storms
Cumulonimbus Clouds
Tall clouds created by the condensation of water vapour

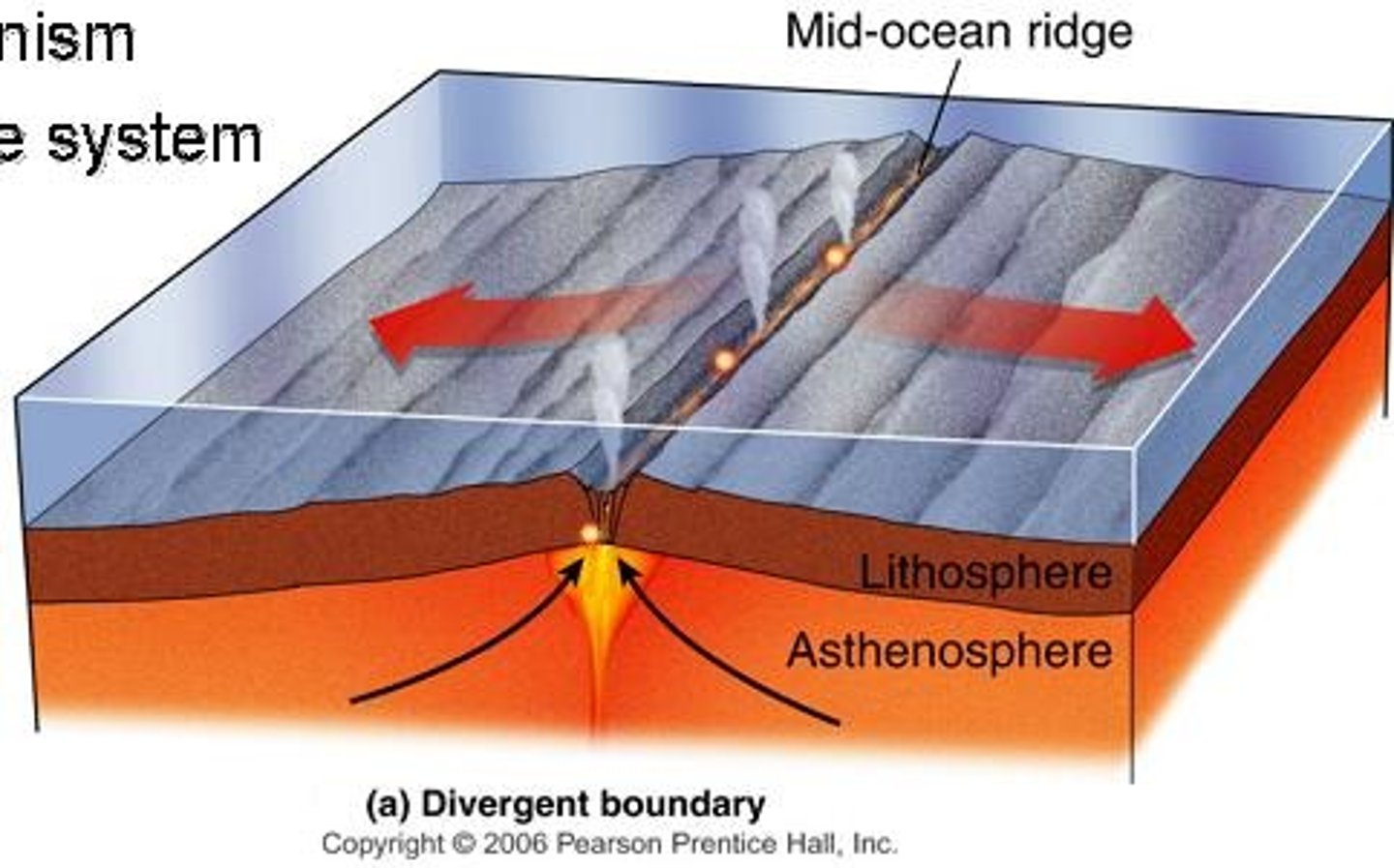
Divergent Plate Boundary
Where two tectonic plates move away from each other
Enhanced Greenhouse Effect
The increased effectiveness of the greenhouse effect, causing global warming
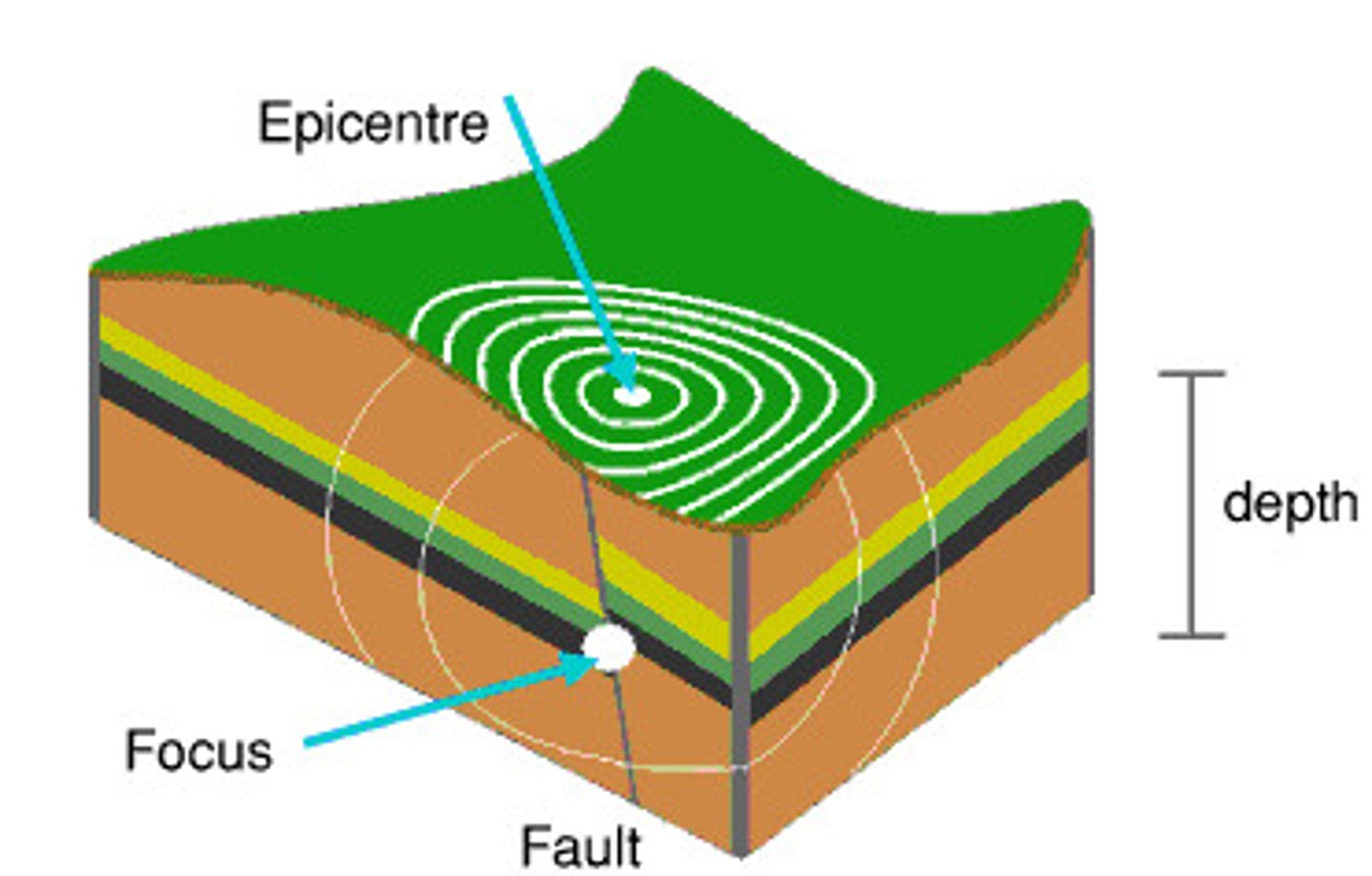
Epicentre
The point on the surface of the Earth directly above the focus
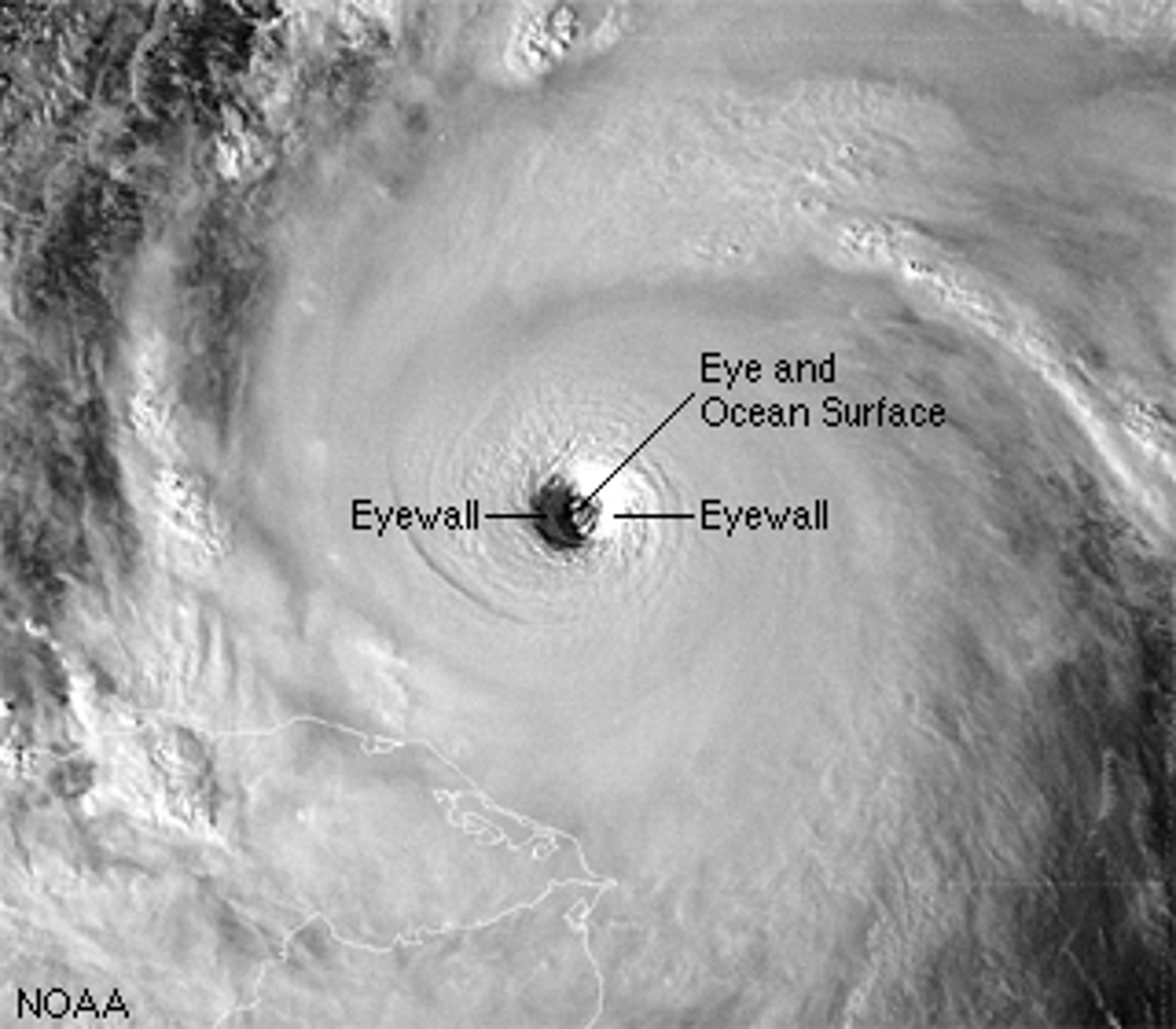
Eye of the Storm
The centre of a storm, consists of calm, descending dense air
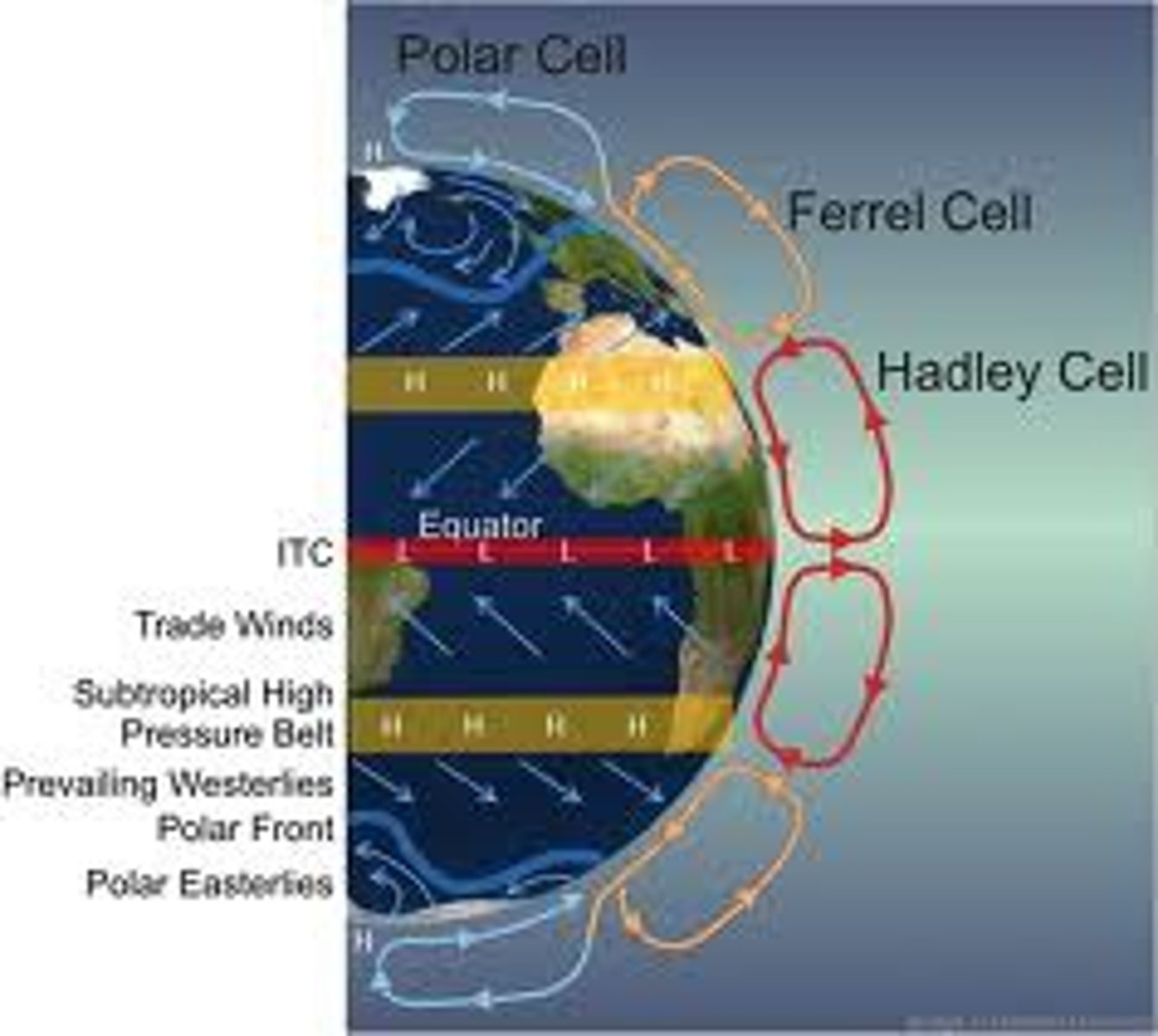
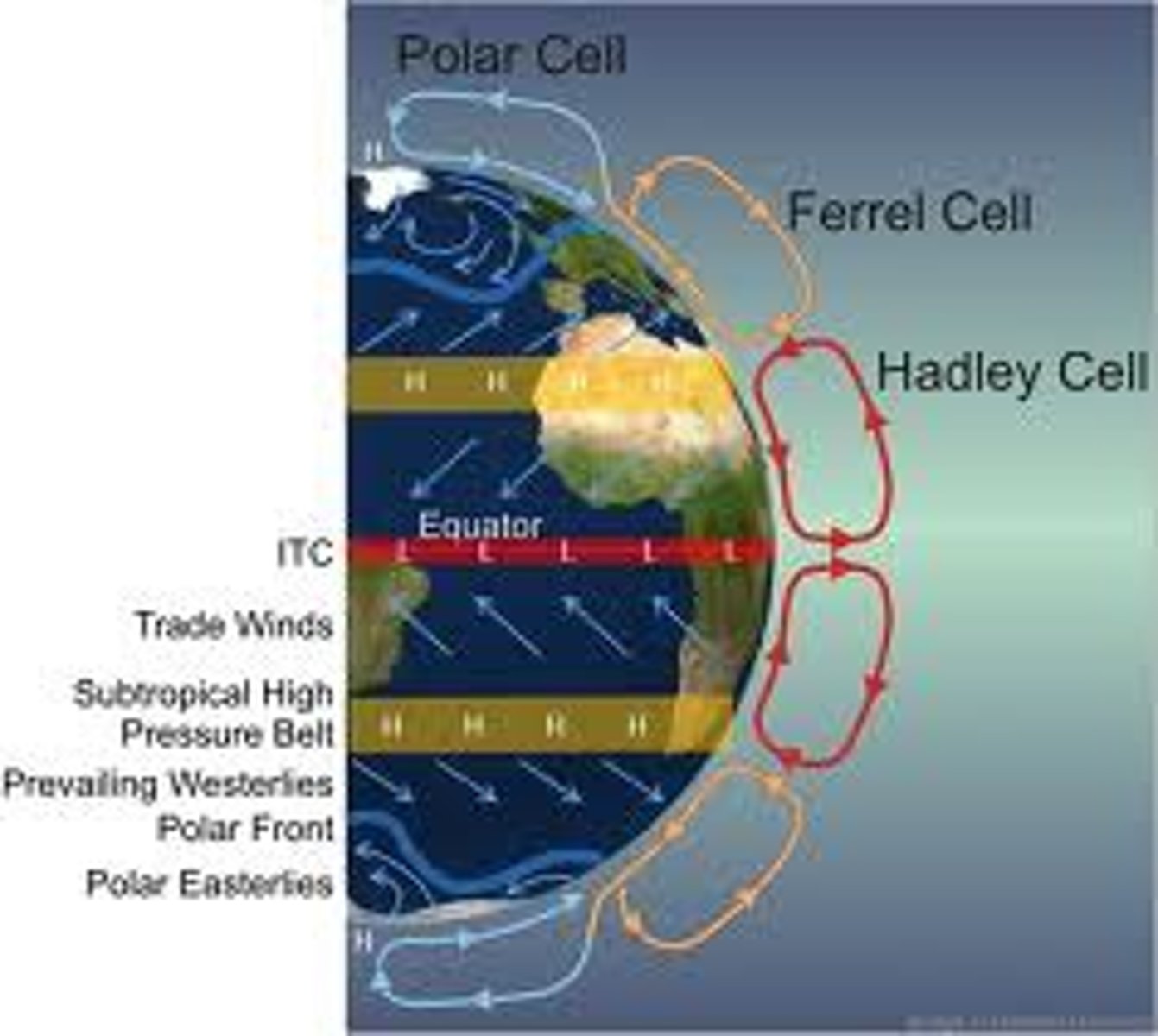
Ferrel Cell
Part of the globe circulation model, where Earth's atmosphere consists of cool, descending, dry air
Friction
The force which resists the movement of one surface over another
Geothermal
Heat produced inside Earth

Glacial
A cold period of time during which the Earth's glaciers expanded widely
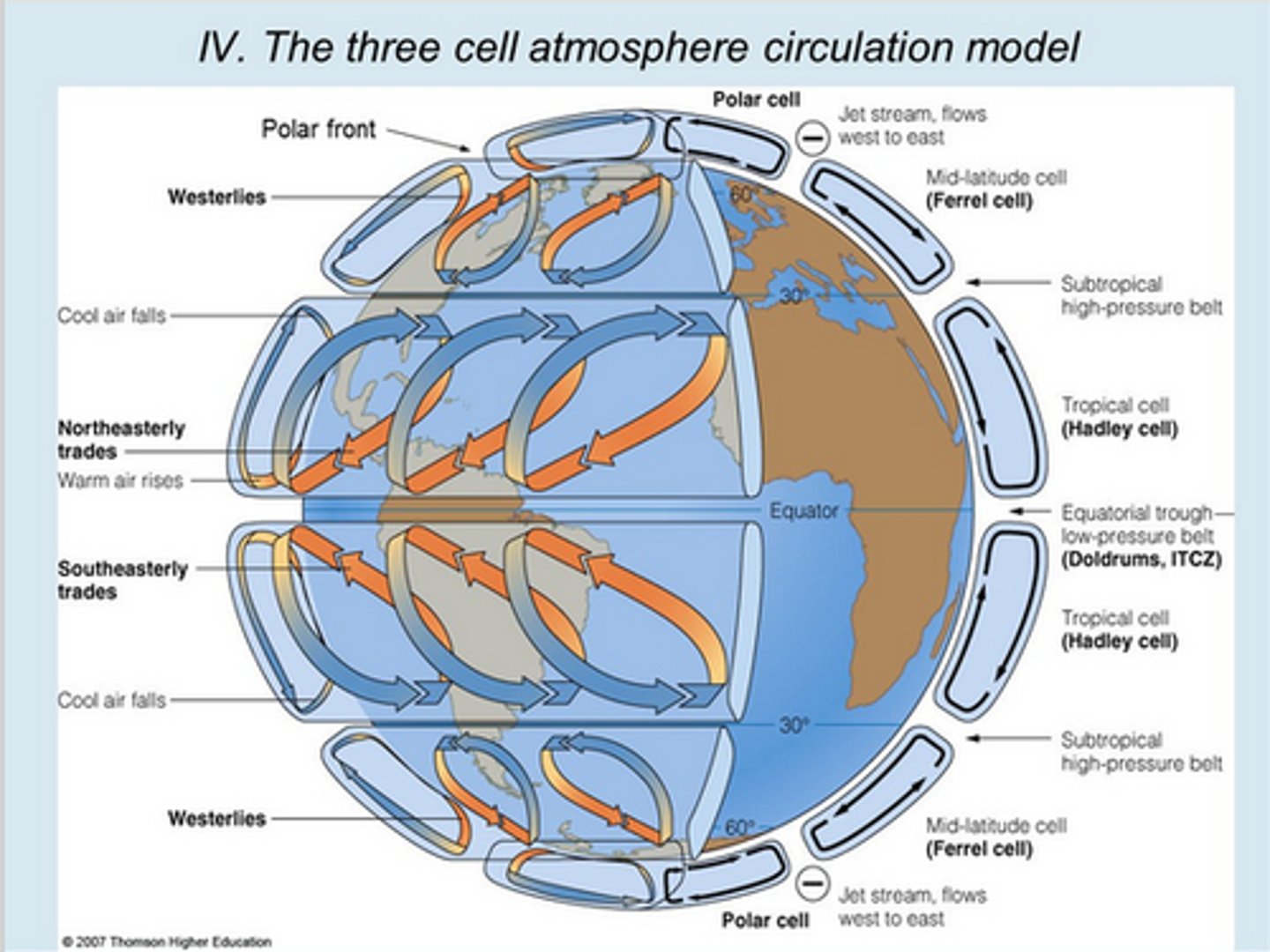
Global Circulation Model
Theory explaining how the atmosphere operates in three cells either side of the equator
Greenhouse Effect
The way that gases in the atmosphere trap heat from the sun
Greenhouse Gas
Gases that trap heat around the Earth e.g carbon dioxide and methane
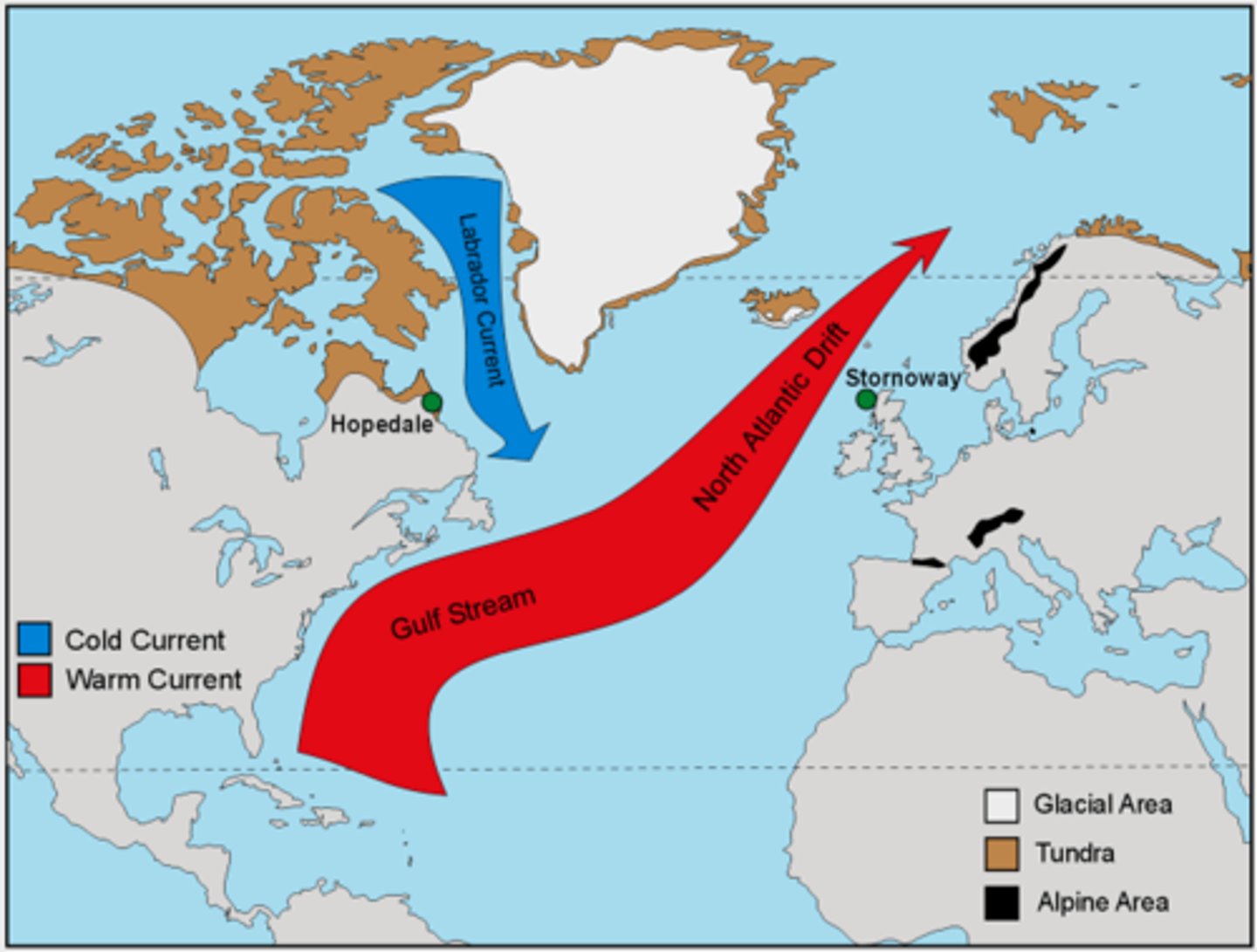
Gulf Stream
A warm ocean current which begins in the Gulf of Mexico and is blown NE across the North Atlantic
Hadley Cell
Largest section of the global circulation model, caused by heating and cooling of Earth's atmosphere
Hot Spots
Columns of heat in the Earth's mantle found in the middle of a tectonic plate
Hurricane
Tropical Cyclone
Ice Cores evidence of climate change
Columns of ice that are extracted from ice sheets and used to construct temperature patterns
Interglacial
A long period of warmer conditions between glacials
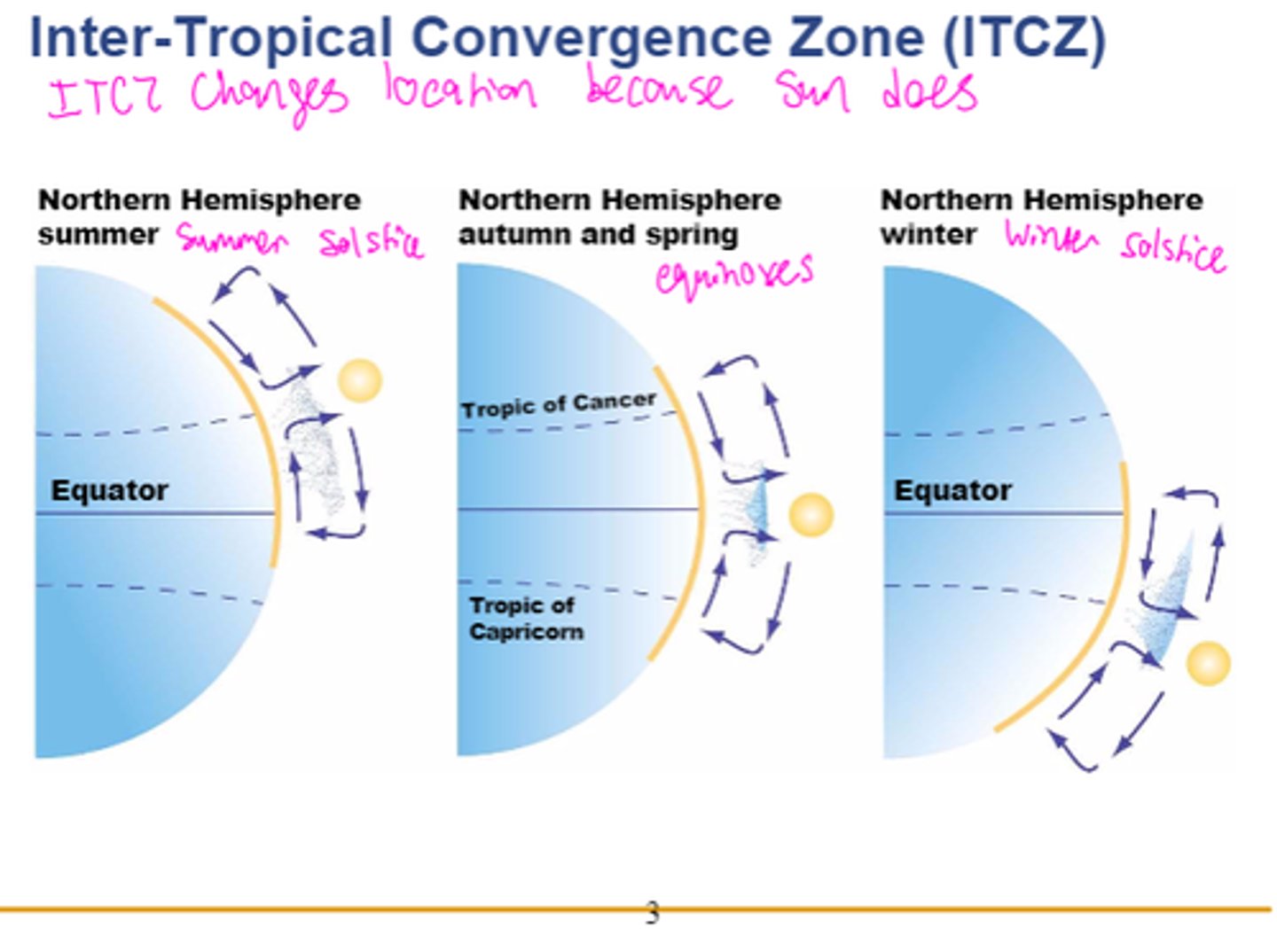
Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ)
Narrow zone of low pressure near the equator where northern and southern air masses converge
Lava Flows
The movement of lava, can be slow and thick or runny and fast
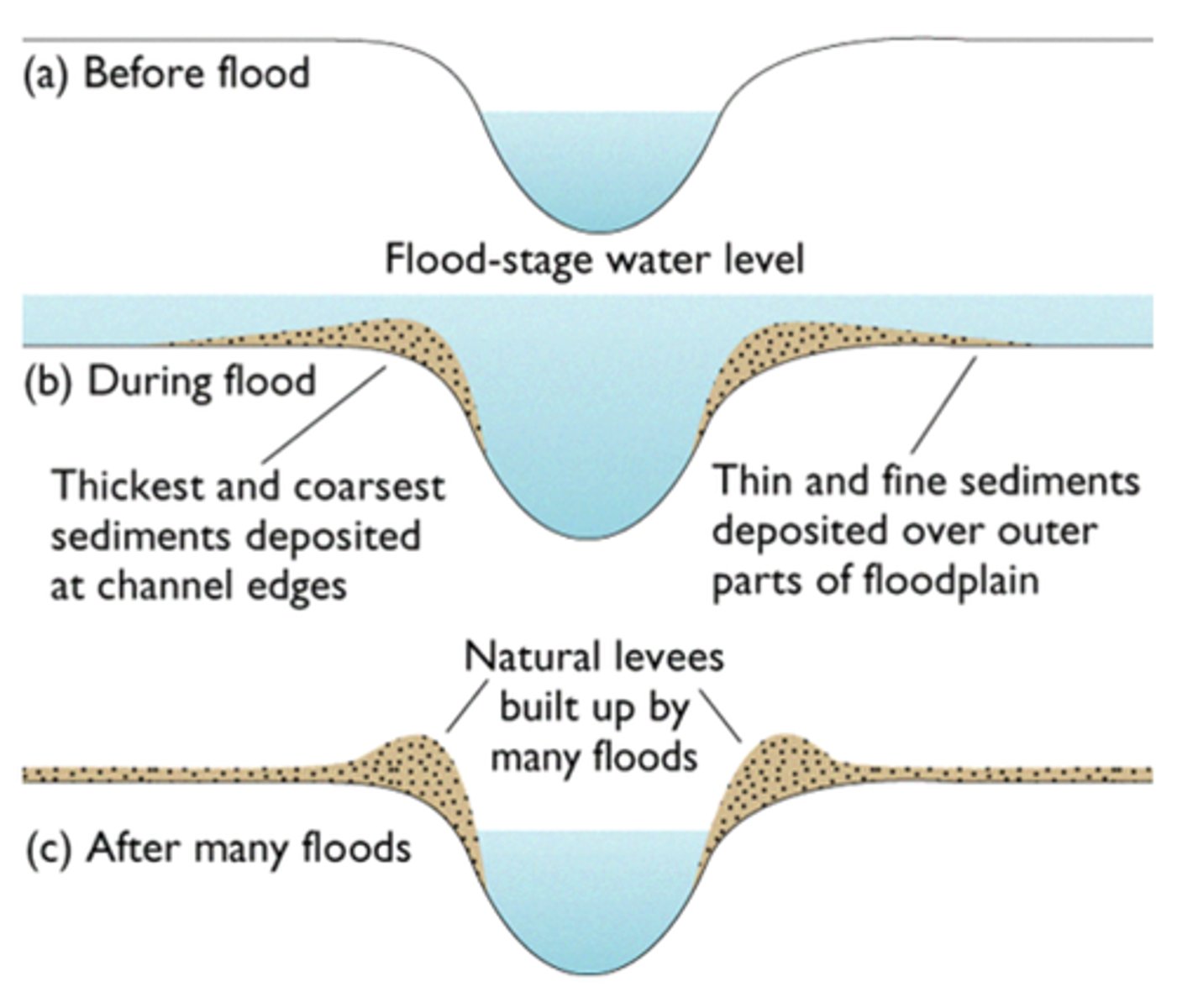
Levée
Embankments found either side of a river, formed naturally by regular flooding or built up by people to protect against flooding
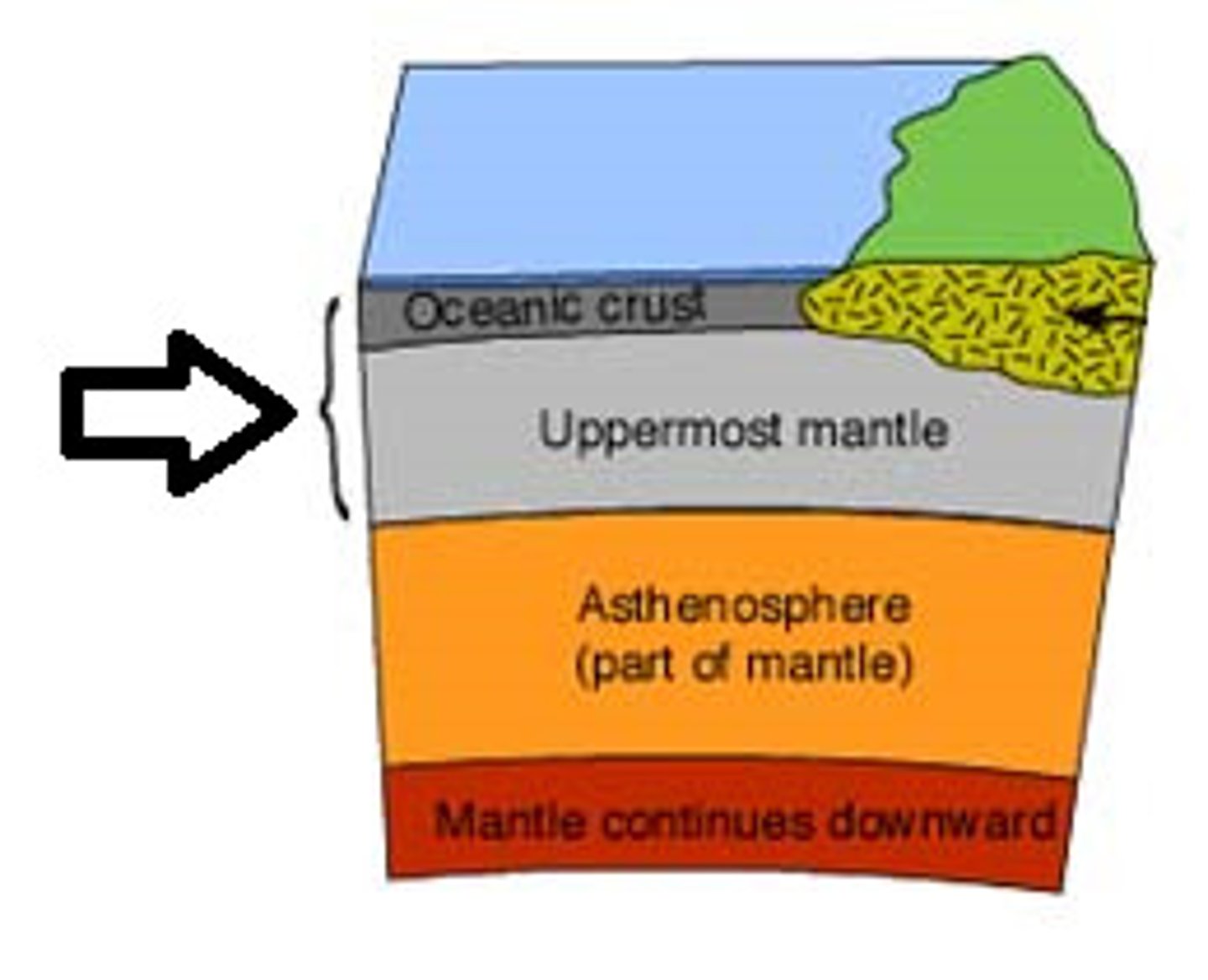
Lithosphere
The cool and brittle uppermost layer of the mantle
Magma
Melted rock beneath the Earth's surface
Magnitude
Expression of total energy released by an earthquake
Mantle
The middle layer of the Earth, 2900km thick, jam like consistency
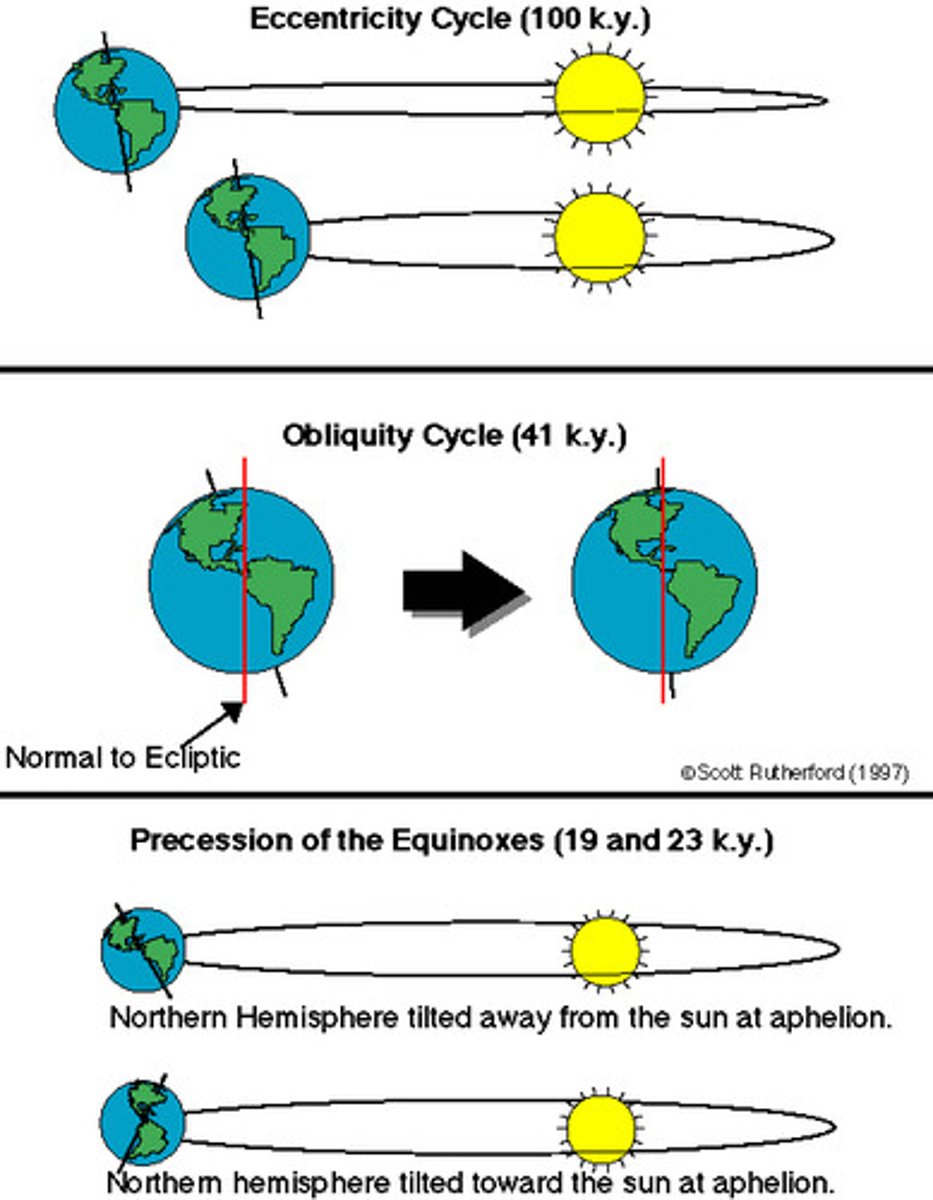
Milankovitch Cycles-natural cause of climate change
The three long-term cycles of the Earth around the Sun
North Atlantic Drift
A warm ocean current that branches off of the Gulf Stream
Ocean Currents
Permanent or semi-permanent large scale horizontal movements of the ocean's waters
Oceanic Crust
The part of Earth's crust which is underneath oceans (6-8km thick)
Plate Boundaries
Where tectonic plates meet
Plumes
Upwelling of molten rock through the asthenosphere to the lithosphere
Polar Cell
Sections of the Earth's atmosphere found above the North and South Pole, consisting of cold, descending, dry air
Polar Desert
Areas in Antarctica and The Arctic that have a cold, dry climate
Predict
Saying something that will happen in the future
Primary Effects
The primary impacts of an event, usually occurring instantly
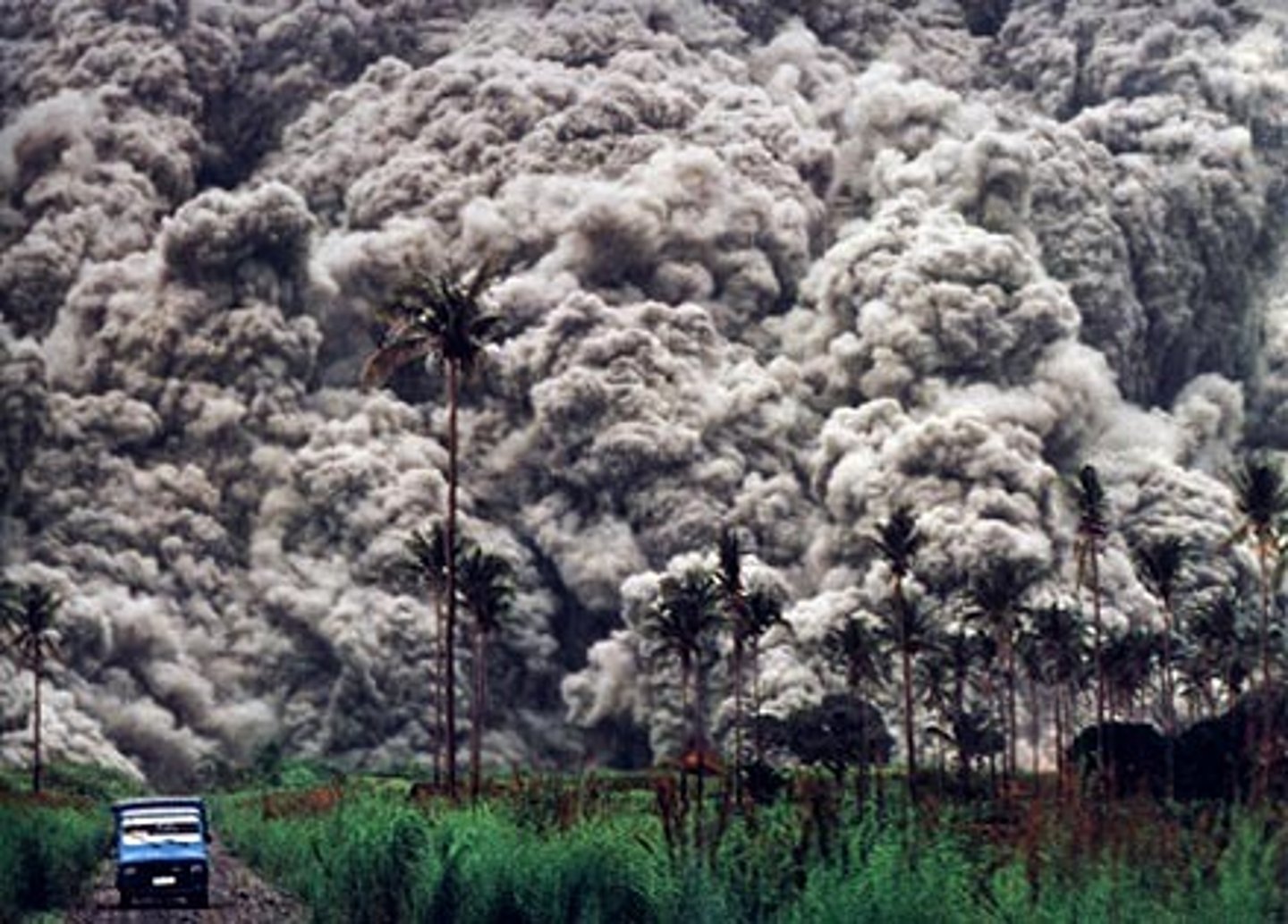
Pyroclasts
Fragments of volcanic material that is thrown out during explosive eruptions

Quaternary
The last 2.6 million years
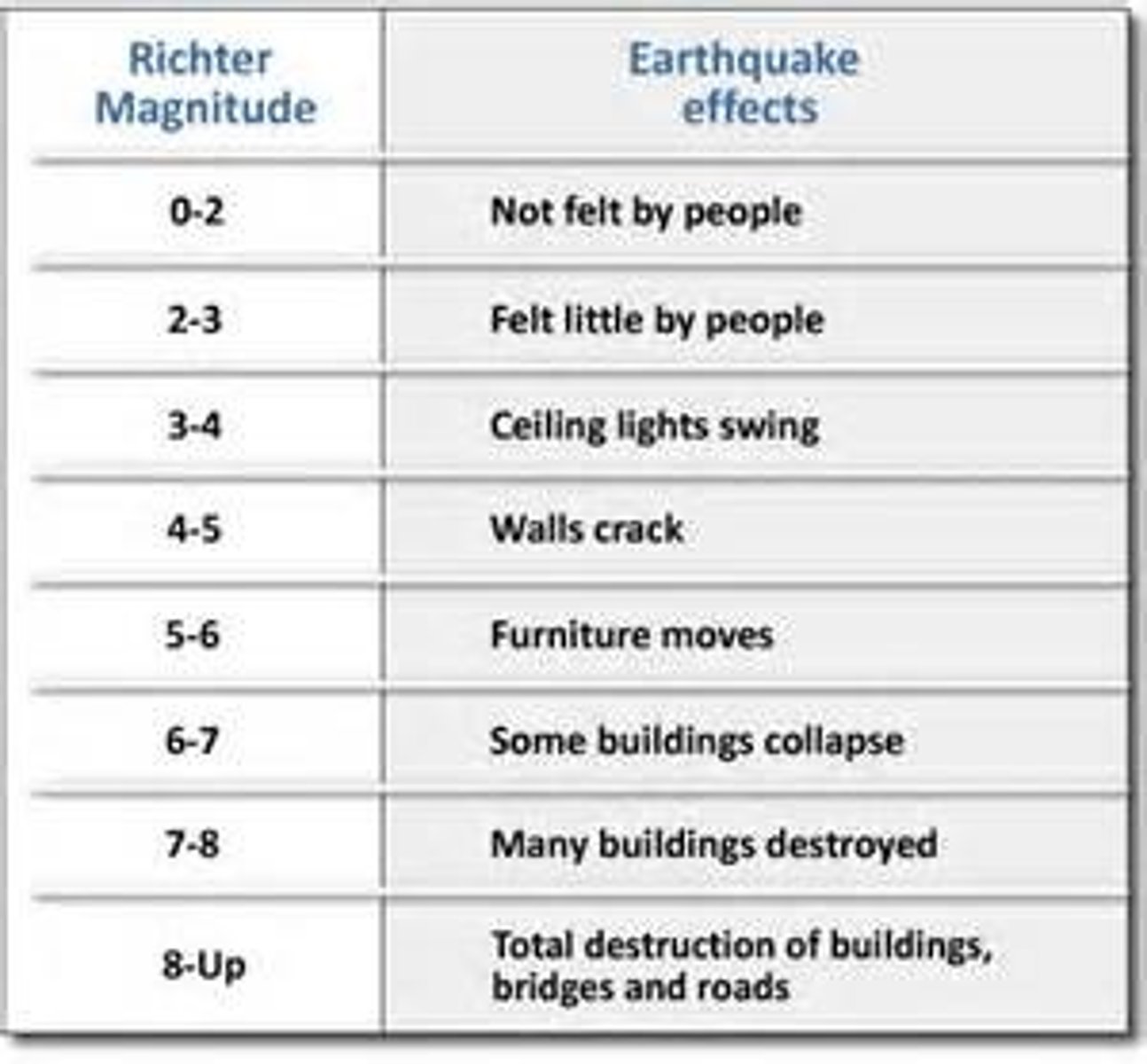
Richter Scale
A scale for measuring the magnitude of an earthquake
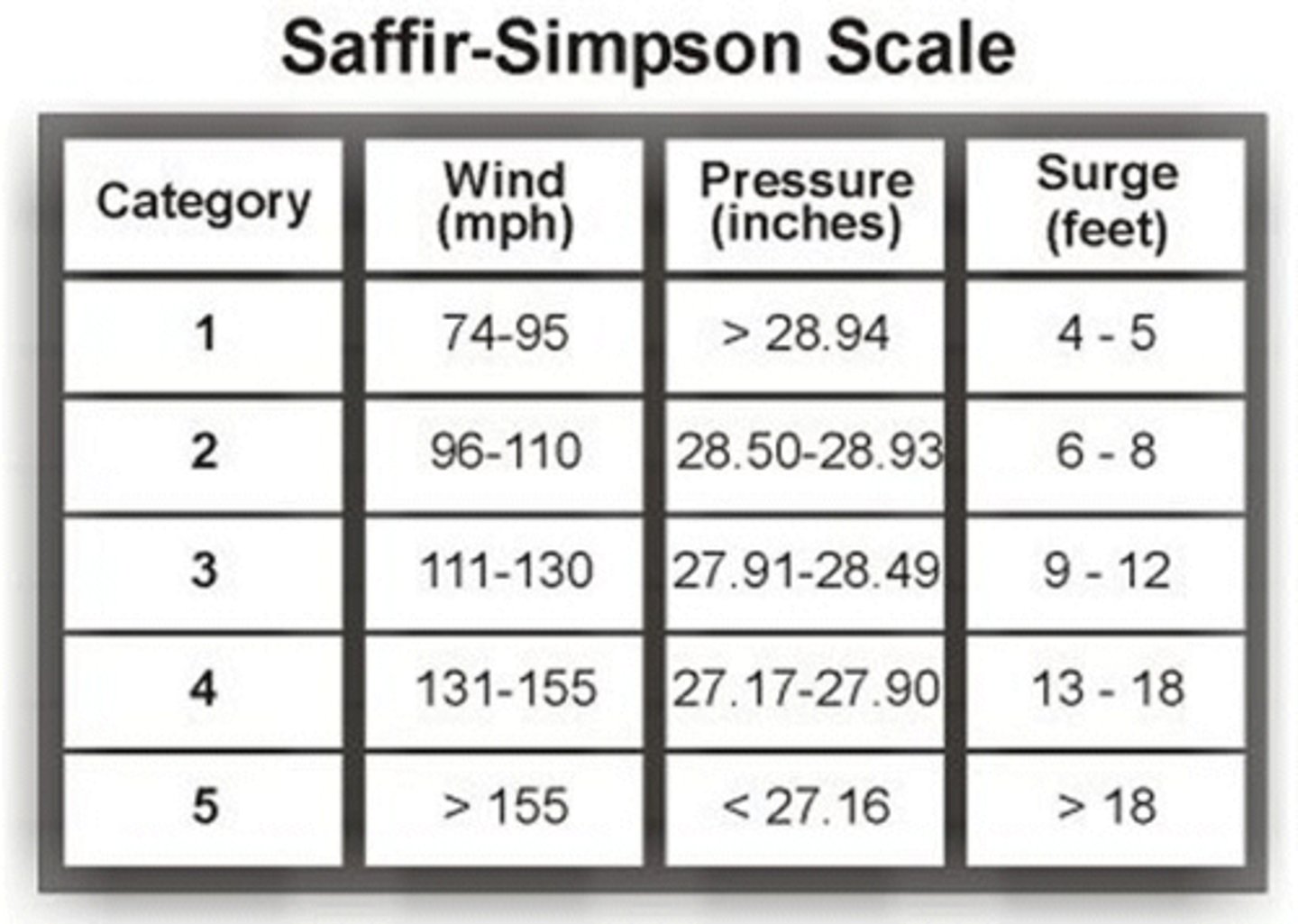
Saffir-Simpson Scale-hurricanes
A scale that classifies hurricanes into 5 different categories according to the wind strength
Secondary Effects
the indirect impacts of an event
fires,landslides,diseases,tsunami.
Seismometer
A machine used to record the magnitude of an earthquake
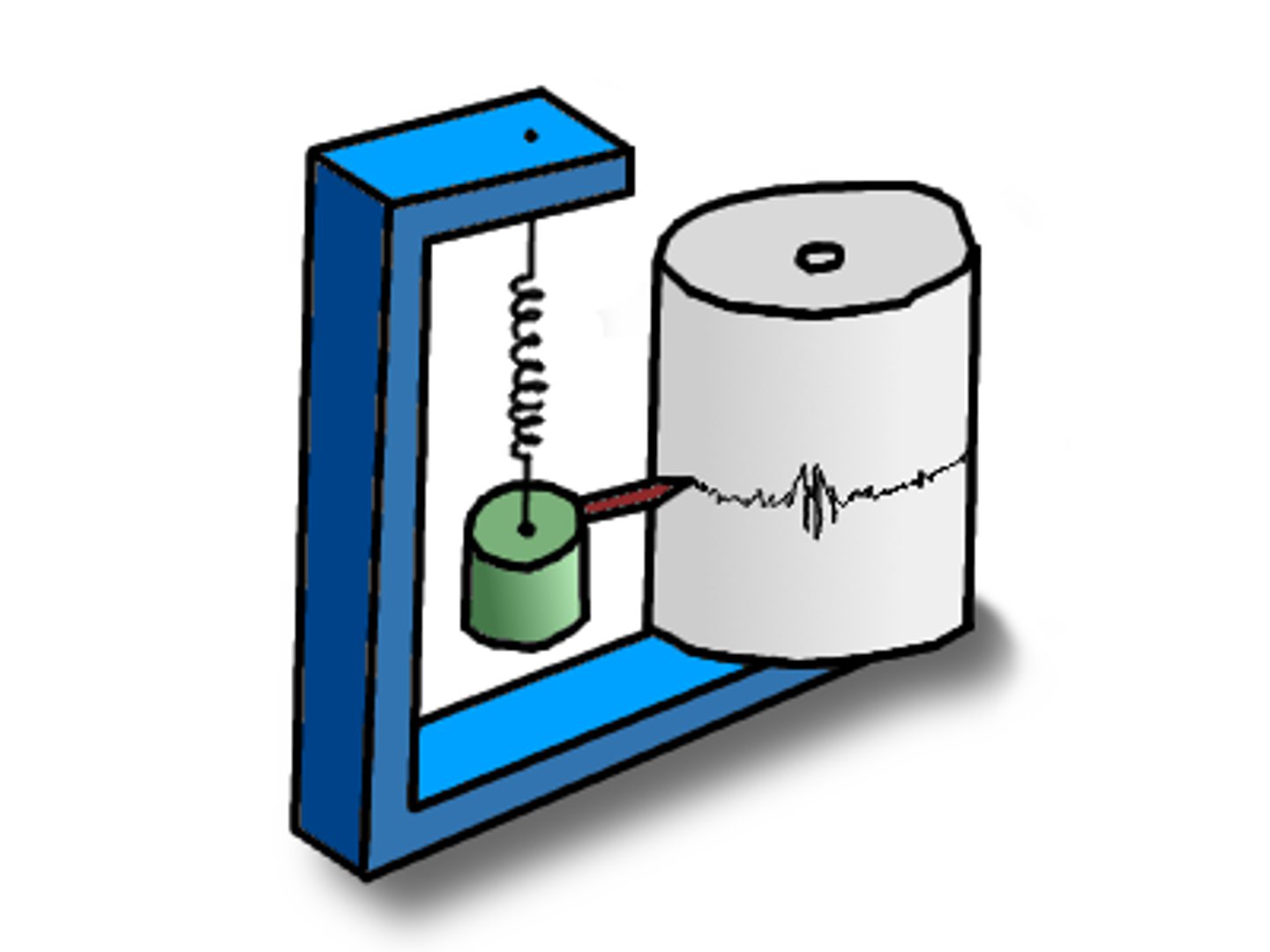
Storm Surge
A rapid rise in the level of the sea caused by low pressure, strong winds
Stratovolcano
Type of volcano characterised by steep sides (Composite Cone)
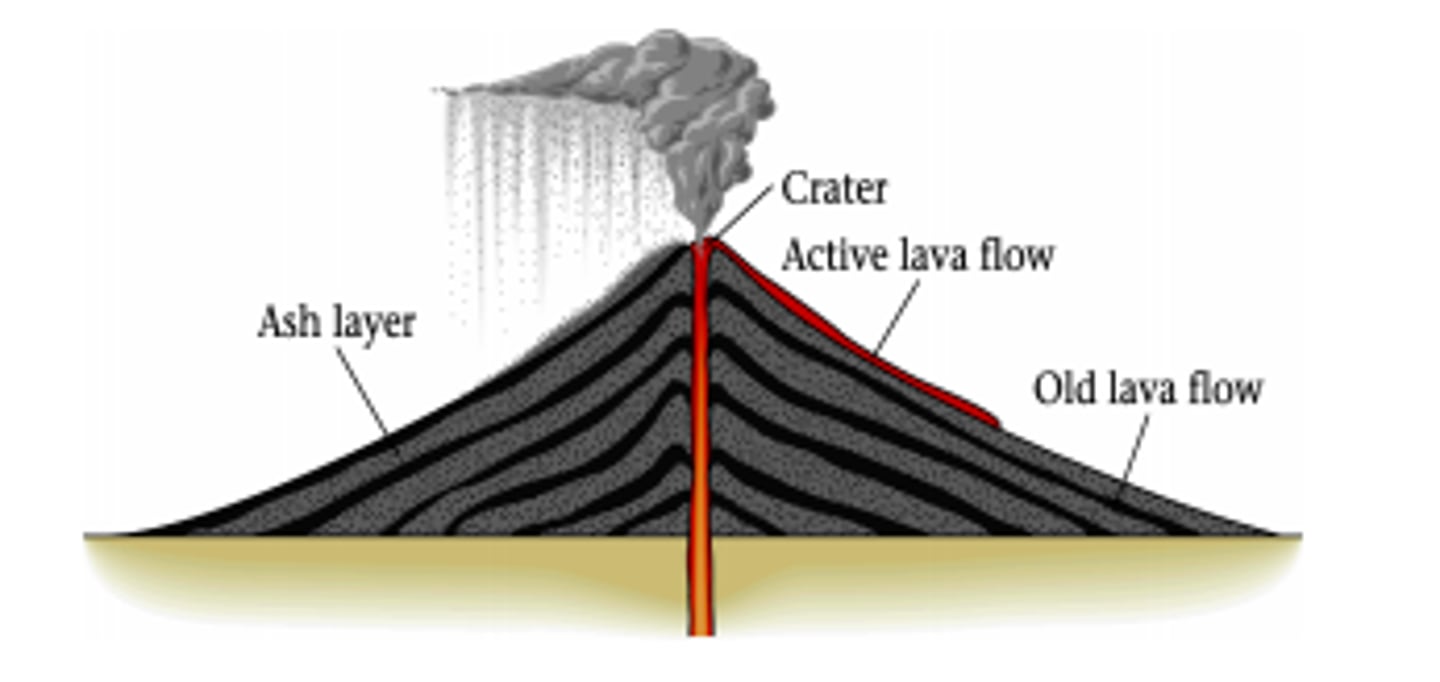
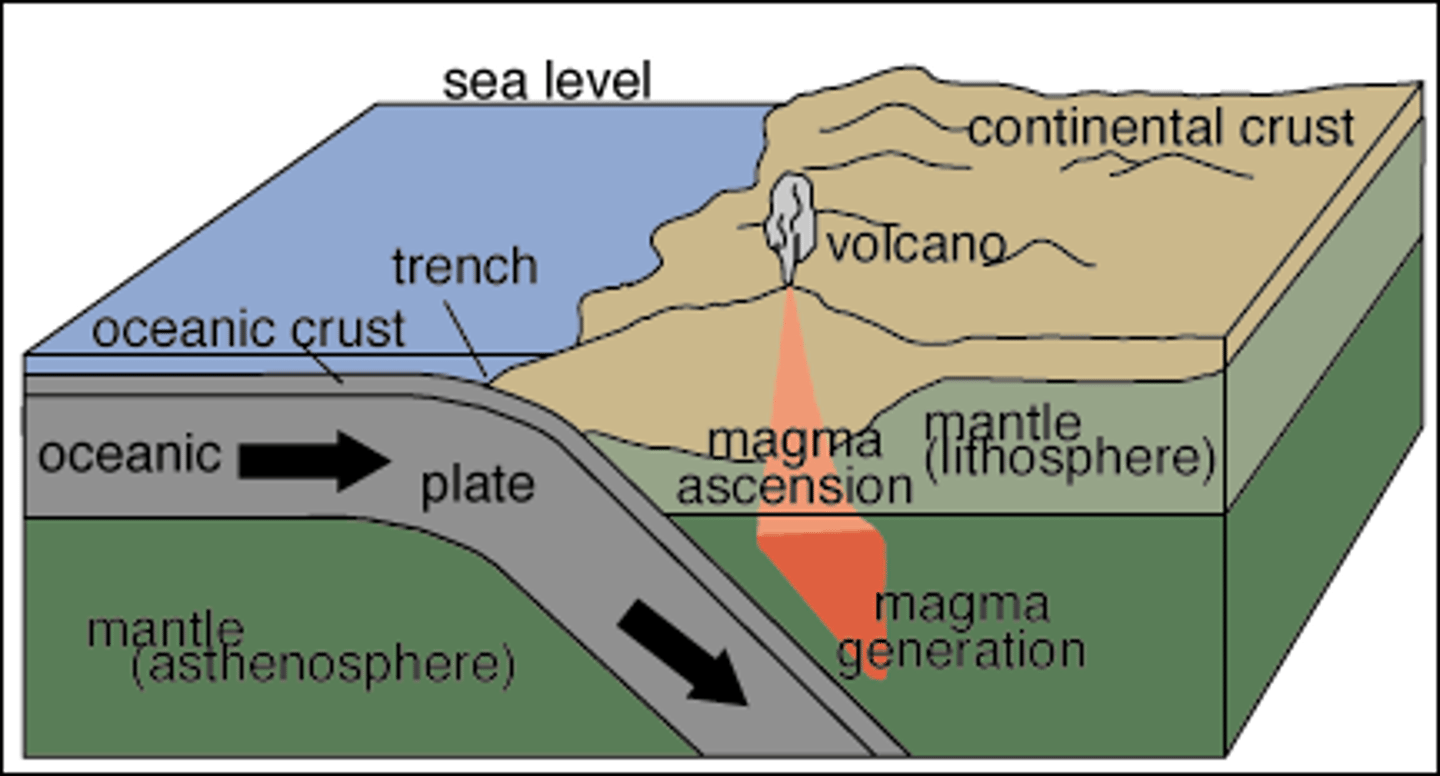
Subduction
Describes oceanic crust sinking into the mantle at a convergent plate boundary
Sunspots-natural cause of climate change
A dark patch that occasionally appears on the surface of the sun
Tectonic Hazards
Natural events caused by movement of Earth's plates
Tectonic Plate
'Pieces' of the Earth's surface
Thermal Expansion
As a result of heating, expansion occurs
Trade Winds
Easterly winds that blow from high to low pressure
Tree Rings
Each ring in the trunk of a tree represents a years growth
Tropical Cyclone
An area of low pressure with winds moving in a spiral around calm centre point
Tropics
Regions either side of the equator where the Sun moves directly overhead
Tsunami
Huge tidal waves caused by earthquakes beneath the sea bed, can travel up to 900km/h
Typhoon
Term given to a tropical cyclone in the western North Pacific
Volcanic Explosivity Index
Measures the explosiveness of a volcano on a scale of 1-8
Biogas
Gas produced by the breakdown of organic matter
Bottom-up Development
Often run by NGO's, non governmental development involving communities
Cash Crops
Crops sold for cash to be traded on global markets
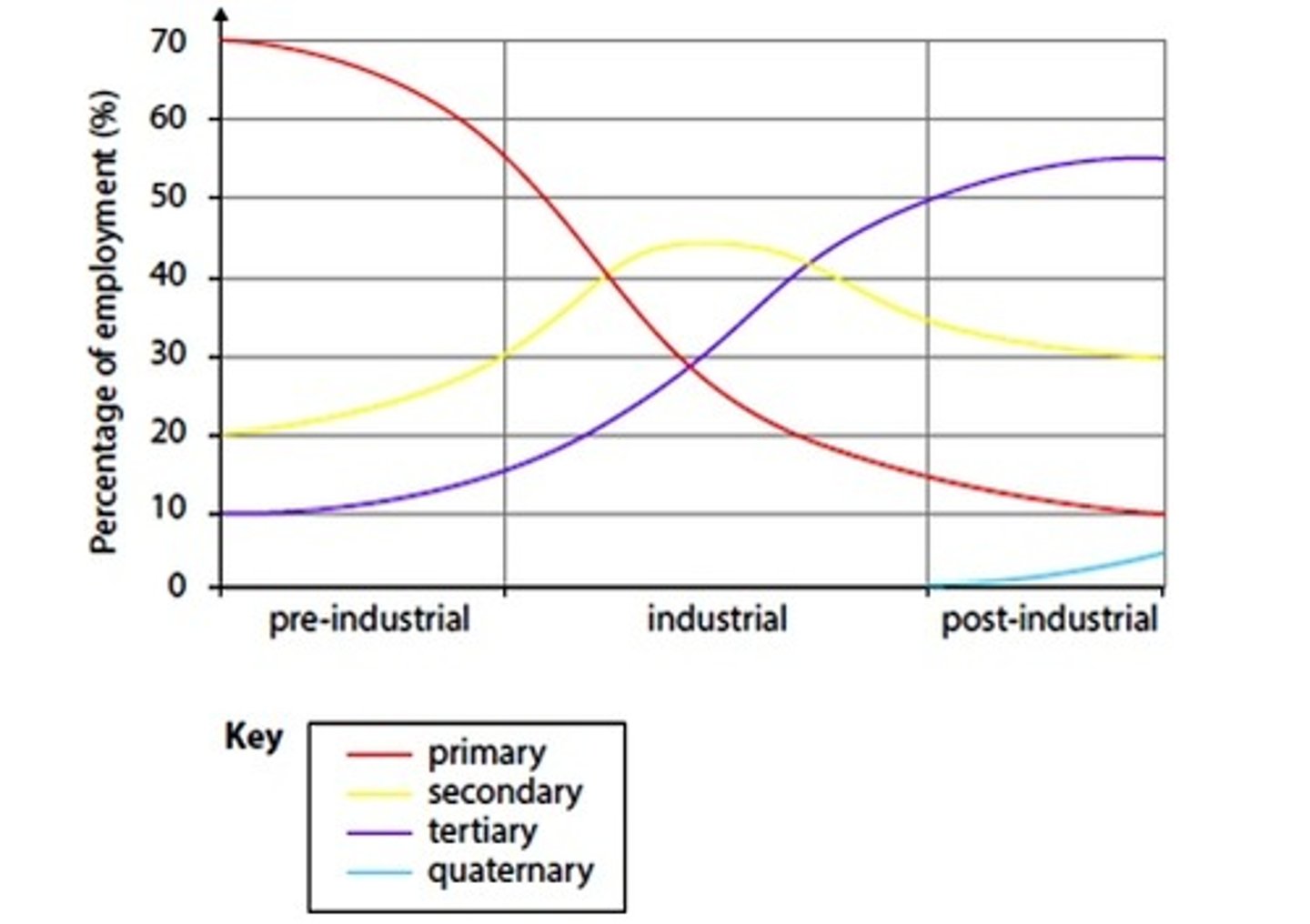
Clark-Fisher Model
Explains the change in employment structure as countries develop their economies
Colonisation
When another country takes over a foreign land and applies a system of power
Commodities
Items of value that can be traded for money
Communism
A system of government which believes in sharing wealth between all people
Containerisation
The transport of goods using container ships
Core Region
Areas within a country that are important economic hubs
Development Indicators
HDI
GDP
Measures of how a country is improving
Emerging Developing Country (EDC)
A country with medium-high human development and recent economic growth
Fertility Rate
Average number of births per woman
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
Unrestricted flow of money from one country to another
Frank's Dependency Theory
Describes how the core, semi periphery and periphery rely on each other for resources and goods-cant develop since they are exploited.
DISADVANTAGE:
outdated
india and china prove it wrong
doesn't add any other factors

Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
The total value of goods and services produced by a country in one year
Globalisation
The increasing integration of economies and societies around the world particularly through international trade
High Income Countries (HIC's)
Countries where employment is dominated by tertiary and quaternary sectors
Human Development Index (HDI)
A standard means of measuring human development
Industrialisation
When an agricultural society begins to depend on industries instead
Infant Mortality
Number of children per 1000 who die before their 1st birthday
Infrastructure
The basic services needed for an industrial country to operate
Inter-Governmental Organisations (IGO's)
Governments and agencies working together
Irrigation
The artificial watering of land
Maternal Mortality
Number of mothers per 100,000 who die during childbirth
Life Expectancy
Average number of years a person can expect to live
Low Income Countries (LIC's)
Countries where employment is dominated by the primary sector
Middle Income Countries (MIC's)
Countries where employment is dominated by the secondary sector
Multiplier Effect
1.TNC'S set up factories or industry
2.factory workers spend money locally
3.local services receive more trade.
4.more tax
5.government can invest in economy.
Non-Governmental Companies (NGO's)
Organisations which aim to improve quality of life
Population Structure
The number of sex in each age group
Purchasing Power Parity (PPP)
Shows what can be bought in each country
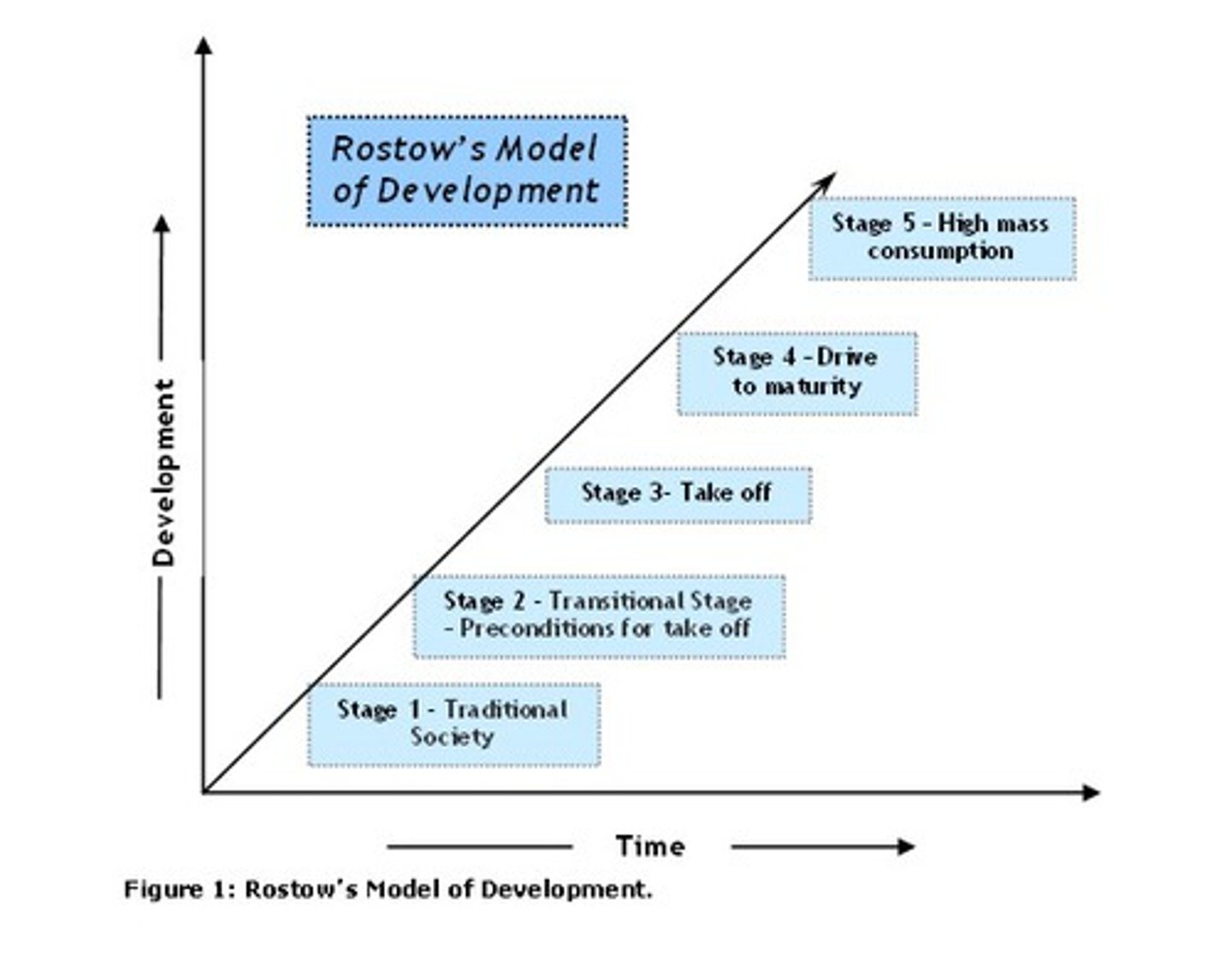
Roster's Theory
Shows the economic growth of a country
DISADVANTAGE:
1.assumens countries start at same place
2.outdated
3.does not include any other factors.
inequality in development -7
1.colonialism or not
2.topography
3.climate
4.international relations
5.government
6.health
7.education
Quaternary Sector
Employment based on specialised knowledge and skill(science,IT)