Biochemistry lecture 22
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Citric acid cycle
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
why must metabolic pathways be controlled?
To link supply with demand (storage and release)
2) To allow cells/organisms to respond to environmental changes, eg. temperature, diet, microenvironment
3) To maintain a constant internal environment (homeostasis)
4) To enable different tissues to interact (eg. liver, adipose,muscle)
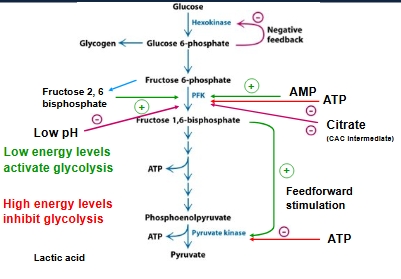
Control of glycolysis mechanisms
Controlling the amount of an enzyme is very slow so often changing the activity is more important for control - achieved by allosteric control (still takes a bit more time) or phosphrylation (instantaneous, by kinases and dep by phosphatases

Control of glycolysis in process
Important enzymes:
Hexokinase - activated and deactivated by negative feedback
Phosphofructokinase - AMP activates this enzyme, fructose 2,6 bisphosphate (only in liver but biggest positive modulator of F6P to F16BP.
Pyruvate kinase
F16BP accumulation activates action of pyruvate kinase
Inhibition:
High ATP levels inhibit PFK and pyruvate kinase
Also low pH
Citrate accumulation inhibits PFK
Fates of pyruvate
P enters into mitochondria
Once in, major pathway (oxidative decarboxylation) of pyruvate to acetyl coA losing a molecule of CO2 by enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase
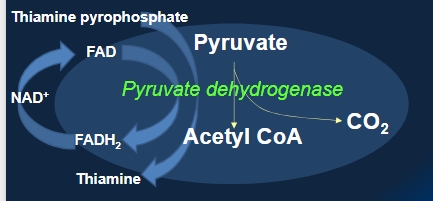
Pyruvate dehydrogenase
(132 subunit multienzyme complex)
(E1) Pyruvate dehydrogenase
(E2) Dihydrolipoyl transacetylase
(E3) Dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase
Vitamins required for pyruvate entry into citric acid cycle
B1 as thiamine pyrophosphate
Riboflavin as FADH2
Niacin as NAD
vitamin B1 deficiency
Thiamine is found in grain husks and meat
Polished rice = deficiency
Beri-beri “extreme weakness”:
loss of appetite
lassitude
numbness of limbs and extremities
atropy
Wernicke-Korsakoff encephalopathy - links to this issue in brain
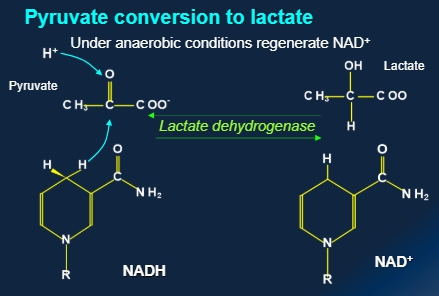
Pyruvate conversion
To fatty acids and amino acids and lactate
When ATP levels are high acetyl CoA diverted to a more efficient storage molecule
During anabolic growth pyruvate isaminated to non-essential amino acids
Under anaerobic conditions regenerate NAD+ - lactate
Pyruvate to lactate
Chemical drawings of pyruvate to lactate
Lactate dehydrogenase?
Pyruvate converted to ethanol
Under anaerobic conditions regenerate NAD+
Yeast and some bacteria
Two step process to regenerate NAD+
Citric acid cycle
Krebs cycle
TCA cycle
Purpose is to harvest high-energy electrons from carbon fuels
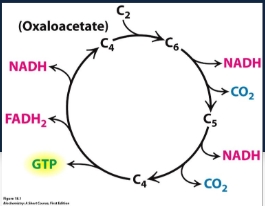
What molecules are generated in CAC?
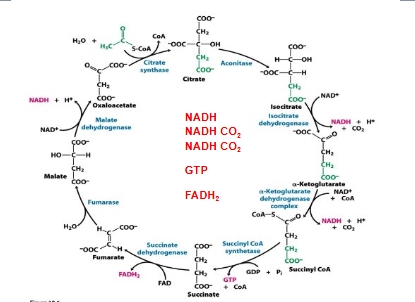
CAC stages
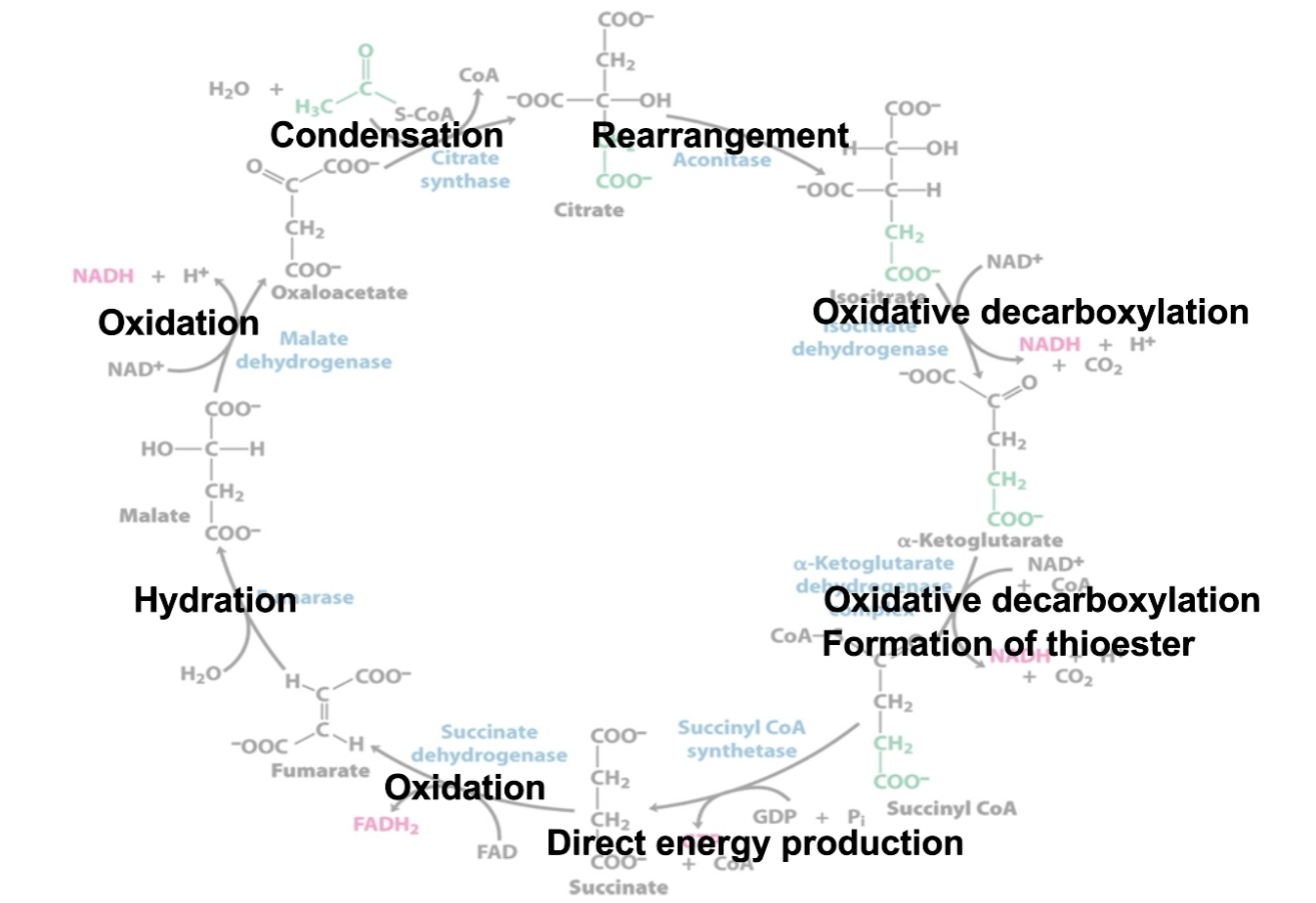
What is generated at each stage of CAC?
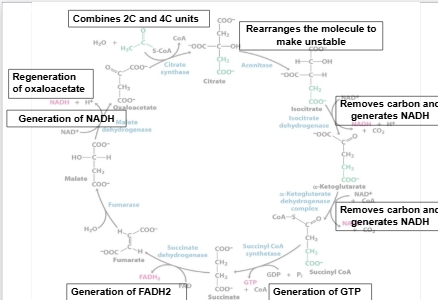
Mnemonic for CAC
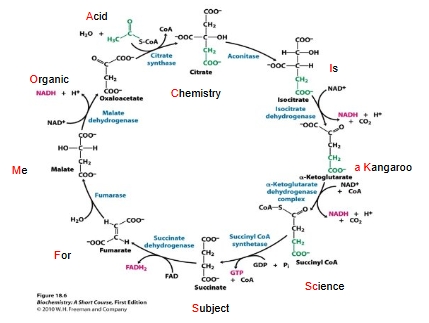
CAC
Is both catabolic and anabolic
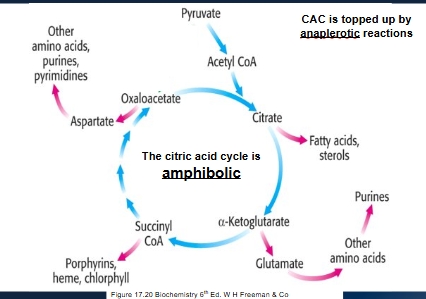
Control of the CAC
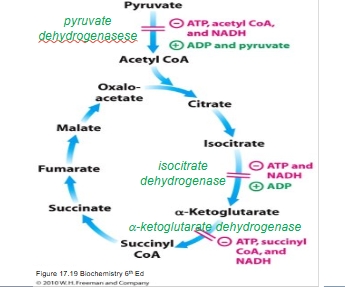
Catabolism so far
