Intro to Nutrition Study Guide (Exam #1)
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Define nutrients and list the 6 classes of them
Compounds in foods that sustain body processes. There are six classes of nutrients: carbohydrates, fats (lipids), proteins, vitamins, minerals, and water
Organic (in nutrition/chemistry)
compounds that contain carbon or carbon-carbon bonds.
Essential nutrient
Nutrients that must be consumed from foods because they cannot be made in the body in sufficient quantities to meet its needs and support health.
Energy
Capacity to do work.
Energy-yielding nutrients
Three nutrients that provide energy to the body to fuel physiological functions: carbohydrates, lipids, and protein.
Kilocalories
Amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1 kilogram of water 1 degree centigrade; used to express the measurement of energy in foods; 1 kilocalorie is equal to 1,000 calories.
Phytochemicals
Non-nutritive plant compounds, found in fruits and vegetables, that may play a role in fighting chronic diseases.
Energy density:
Measurement of the kilocalories in a food compared with the weight (grams) of the food.
Nutrient density
Measurement of the nutrients in a food compared with the kilocalorie content; nutrient-dense foods are high in nutrients and low in kilocalories.
Micronutrients (define and list them)
Essential nutrients the body needs in smaller amounts: vitamins and minerals.
Macronutrient (define and list them)
Essential nutrients, including water and the energy-containing carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins that the body needs in large amounts.
Vitamins
Thirteen essential, organic micronutrients that are needed by the body for normal functions.
Minerals
Inorganic elements essential to the nutrition of humans
Science of nutrition
Science that studies how nutrients and other components of foods nourish the body and affect body functions and overall health.
Control Group
In experimental research, the group that does not receive the treatment but may be given a placebo instead; used as a standard for comparison.
placebo
Inactive substance, such as a sugar pill, administered to a control group during an experiment.
Correlation
A measure of the relationship between two variables
double-blind placebo-controlled study
Experimental study in which neither the researchers nor the subjects in the study are aware of who is receiving the treatment or the placebo
Experimental group
In experimental research, the group of participants given a specific treatment, such as a drug, as part of the study.
Experimental studies
studies in which the independent variables are directly manipulated and the effects on the dependent variable are examined
Epidemiological studies
Research that studies the variables that influence health in a population; it is often observational.
Dietary Reference Intake (DRIs)
Reference values for nutrients developed by the Food and Nutrition Board of the National Academy of Medicine, used to plan and evaluate the diets of healthy people in the United States and Canada. It includes the Estimated Average Requirement (EAR), the Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA), the Adequate Intake (AI), and the Tolerable Upper Intake Level (UL).
Estimated Average Requirement (EAR)
Average daily amount of a nutrient needed by 50 percent of the individuals in a similar age and gender group.
Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA)
Recommended daily amount of a nutrient that meets the needs of nearly all individuals (97-98 percent) in a similar age and gender group. The RDA is set higher than the EAR.
Adequate Intake (AI)
Approximate daily amount of a nutrient that is sufficient to meet the needs of similar individuals within a population group. The Food and Nutrition Board uses ______ ______ for nutrients that do not have enough scientific evidence to calculate an RDA.
Tolerable Upper Intake Level (UL)
Maximum daily amount of a nutrient considered safe in a group of similar individuals.
Estimated Energy Requirement (EER)
Average kilocalorie intake that is estimated to maintain energy balance based on a person's gender, age, height, body weight, and level of physical activity
Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Ranges: (AMDR)
Healthy range of intakes for the energy-containing nutrients—carbohydrates, proteins, and fats—expressed as a percentage of total daily energy.
Nutrition Assessment
a comprehensive analysis of a person's nutrition status that uses health, socioeconomic, drug, and diet histories; anthropometric measurements; physical examinations; and laboratory tests.
Anthropometric
Used to asses the size, shape, and composition of the human body, BMI or a growth chart.
Deficiency
contains a set of health objectives for the nation to achieve over the second decade of the twenty-first century. Mainly to reduce the number of obese adults and children in the US and increase the amount of fruits and vegetables eaten.
Registered Dietitian Nutritionist (RDN)
A health professional who has completed at least a bachelor's degree in nutrition from an accredited university or college in the United States, completed a supervised practice, and passed an exam administered by the Commission on Dietetic Registration, the credentialing agency for the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics (AND).
List the areas that influence our food choices, Which of these is MOST influential in the food choices we make?
-Taste and Enjoyment
-nutrition knowledge
-Habits and Emotions
-Time, Convenience, and Cost
-Advertising
-Social Life and Trends
-Culture and Environment
Tates is the most influential
Are carbohydrates organic or inorganic? Are they energy yielding? Are they a macronutrient or micronutrient?
They are organic, energy yielding, and a macronutrient
Are proteins organic or inorganic? Are they energy yielding? Are they a macronutrient or micronutrient?
They are organic, energy yielding, and a macronutrient
Are lipids organic or inorganic? Are they energy yielding? Are they a macronutrient or micronutrient?
They are organic, energy yielding, and a macronutrient
Are vitamins organic or inorganic? Are they energy yielding? Are they a macronutrient or micronutrient?
They are organic, not energy yielding, and a micronutrient
Are minerals organic or inorganic? Are they energy yielding? Are they a macronutrient or micronutrient?
They are inorganic, not energy yielding, and a micronutrient
is water organic or inorganic? Are they energy yielding? Are they a macronutrient or micronutrient?
it is inorganic, not energy yielding, and a macronutrient
How many calories per gram does fat provide?
9 calories per gram
How many calories per gram does protein provide?
4 calories per gram
How many calories per gram does carbohydrate provide?
4 calories per gram
Which of the energy-yielding or macronutrients is the MOST energy-dense?
Lipids (Fats)
What are the AMDRs for adults?
-45-65 percent carbohydrates
-10-35 percent protein
-20-35 percent fat.
Experimental vs. Epidemiological Studies
Experimental: Researcher intervenes (e.g., gives treatment).
Epidemiological: Observes natural patterns without intervention.
Experimental = can show causation; Epidemiological = shows correlation.
Types & Pros/Cons - Experimental Studies
Types: RCTs, clinical trials, lab animal studies.
Pros: Can prove cause & effect, controlled, less bias.
Cons: Expensive, time-consuming, ethical limits
Types & Pros/Cons - Epidemiological Studies
Types: Cohort, case-control, cross-sectional, ecological.
Pros: Study large groups, find risk factors, cost-effective.
Cons: No causation, more bias/confounding, relies on self-report.
What do we use to calculate the EER for someone?
Age
Sex
Weight (kg)
Height (cm)
Physical Activity Level (PAL)
Components of an Anthropometric nutrition assessment:
-What is it?
-What do we use it for?
-Examples:
-Measurements of the body.
-To assess growth, development, and body composition.
-Height and weight, Body Mass Index (BMI), Waist circumference, Skinfold thickness
Components of laboratory tests in a nutrition assessment:
-What is it?
-What do we use it for?
-Examples:
-Blood, urine, or stool tests that provide biochemical data.
-To detect nutrient deficiencies or excesses and assess organ function.
-Blood glucose (for diabetes), Hemoglobin (for anemia), Serum albumin (for protein status), Vitamin D levels
Components of historical information in a nutrition assessment:
-What is it?
-What do we use it for?
-Examples:
-A person's medical, dietary, and lifestyle history.
-To understand factors that may affect nutritional status.
-Medical conditions (e.g., celiac disease), Medication use, 24-hour dietary recall or food frequency questionnaire, Alcohol/smoking history
malnutrition
Characterized by an inappropriate level of essential nutrients to maintain health; overnourishment and undernourishment are forms of malnutrition.
Name the top 3 causes of death in the United States. Which of those 3 are strongly related to nutrition?
heart disease, cancer, stroke, and type 2 diabetes. Heart disease and type 2 diabetes are related to nutrition
Give at 3 tips for evaluating whether an article or website with nutrition information in it is areliable source of information
1. Check to see if the article is peer reviewed
2. Double blind placebo-controlled studies are the gold standard for scientific research
3. Make sure the studies were conducted on an adequate number of subjects
Dietary Guidelines for Americans (DGA)
a set of recommendations about smart eating and physical activity for all Americans
Eating patterns
the quantities, proportions, variety, or combination of different foods, drinks, and nutrients in diets, and the frequency with which they are habitually consumed.
MyPlate: What is it, what do we use it for?
a website providing nutritional information and educational tools based on the Dietary Guidelines for Americans and the Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs).
Healthy Eating Index
a measure of diet quality used to assess how well a set of foods aligns with key recommendations and dietary patterns published in the Dietary Guidelines for Americans (Dietary Guidelines)
fortified foods
foods in which nutrients are added that did not originally exist in the food, or which existed in insignificant amounts
enriched foods
foods in which nutrients that were lost during processing have been added back, so that the food meets a specified standard
Daily Value (DV)
recommended daily amount of a nutrient; used on food labels to help people see how a food fits into their diet
Percent Daily Value (%DV)
the percentage of a Daily Value recommendation found in a specified serving of food for key nutrients based on a 2000-kcalorie diet.
Nutrient Claims
statements that characterize the quantity of a nutrient in a food
Health claims on food labels
health claims are statements made about a food product or ingredient linking to a reduced risk of disease. FDA limits the use of health messages, a may or might qualifier must be used in statement. Before a health claim can be made: 1. a food must be a good source of fiber, protein, vit A, vit C, calcium or iron. 2. a single serving may not contain more than any of the following constituents: 13 g of fat, 4 g of saturated fat, 60 mg of cholesterol, 480 mg of sodium. If a food exceeds any one of these, no health claim can be made.
Structure-Function Claims
describe how a nutrient or dietary compound affects the structure or function of the human body
To claim a food is "high" or "rich" in a particular nutrient, how much of that ingredient does the product have to contain?
the product must contain 20% or more of the Daily Value (DV) of that nutrient per serving.
To claim a food is a "good source of" a particular nutrient, how much of that ingredient does the product have to contain?
10-19% of the DV
What are the parts of My Plate?
fruits, vegetables, grains, protein, & dairy

What are some of the key recommendations for intake associated withMy Plate or the USDA Food Patterns?
-It emphasizes proportionality of the food groups. Half the plate is for fruits and vegetables, a quarter for grains, and a quarter for proteins. Plus a small dish on the side for low fat dairy products.
-Choose nutrient dense foods
-Have variety in your diet
-Stay within your calorie budget
-Daily physical activity
What are the five types of vegetables in the vegetable group on Myplate?
-Broccoli
-Tomatoes
-Pinto Beans
-Yams
-Green peppers
Which group develops the Dietary Guidelines?
The U.S. Departments of Agriculture (USDA) and Health and Human Services (HHS)
What things must be listed on a food label?
the product's name, a statement of the net quantity of contents, a list of ingredients, the name and address of the manufacturer or distributor, and nutrition information
What determines the order for the ingredient list on a food label?
ingredients are listed in descending order of predominance by weight
What do the numbers on the Nutrition Facts panel represent?
The Daily Values are reference amounts (expressed in grams, milligrams, or micrograms) of nutrients to consume or not to exceed each day.
What has been added to the Updated Food Label?
highlighting "Calories" and "Serving size" with larger, bolder text, and adding "Added Sugars" in grams and as a percentage of the Daily Value (DV)
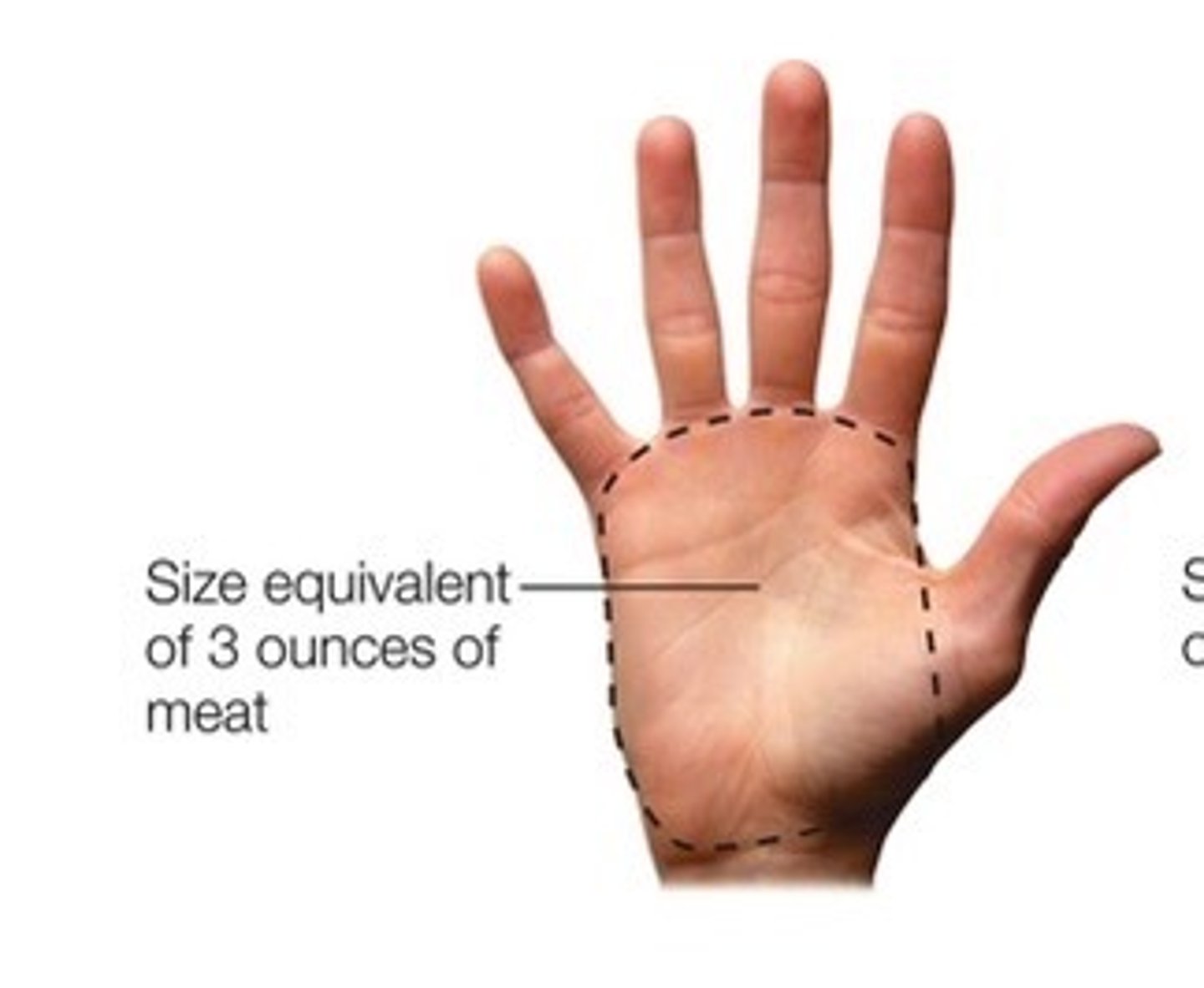
How would you roughly estimate a 3oz portion of meat?
The meat should be about the size of your palm
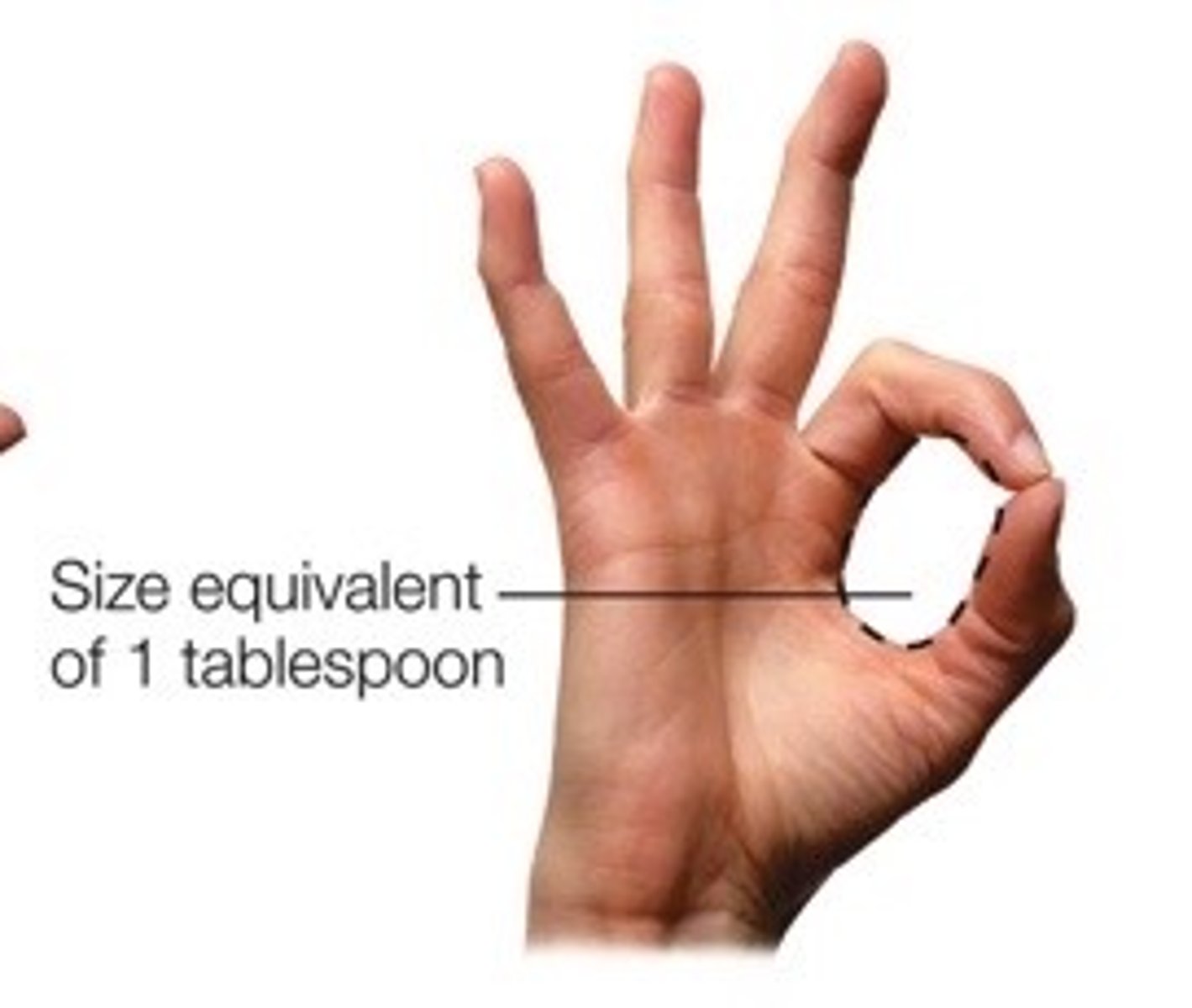
How would you roughly estimate a tablespoon of a liquid?
How would you roughly estimate a 1 cup serving size?

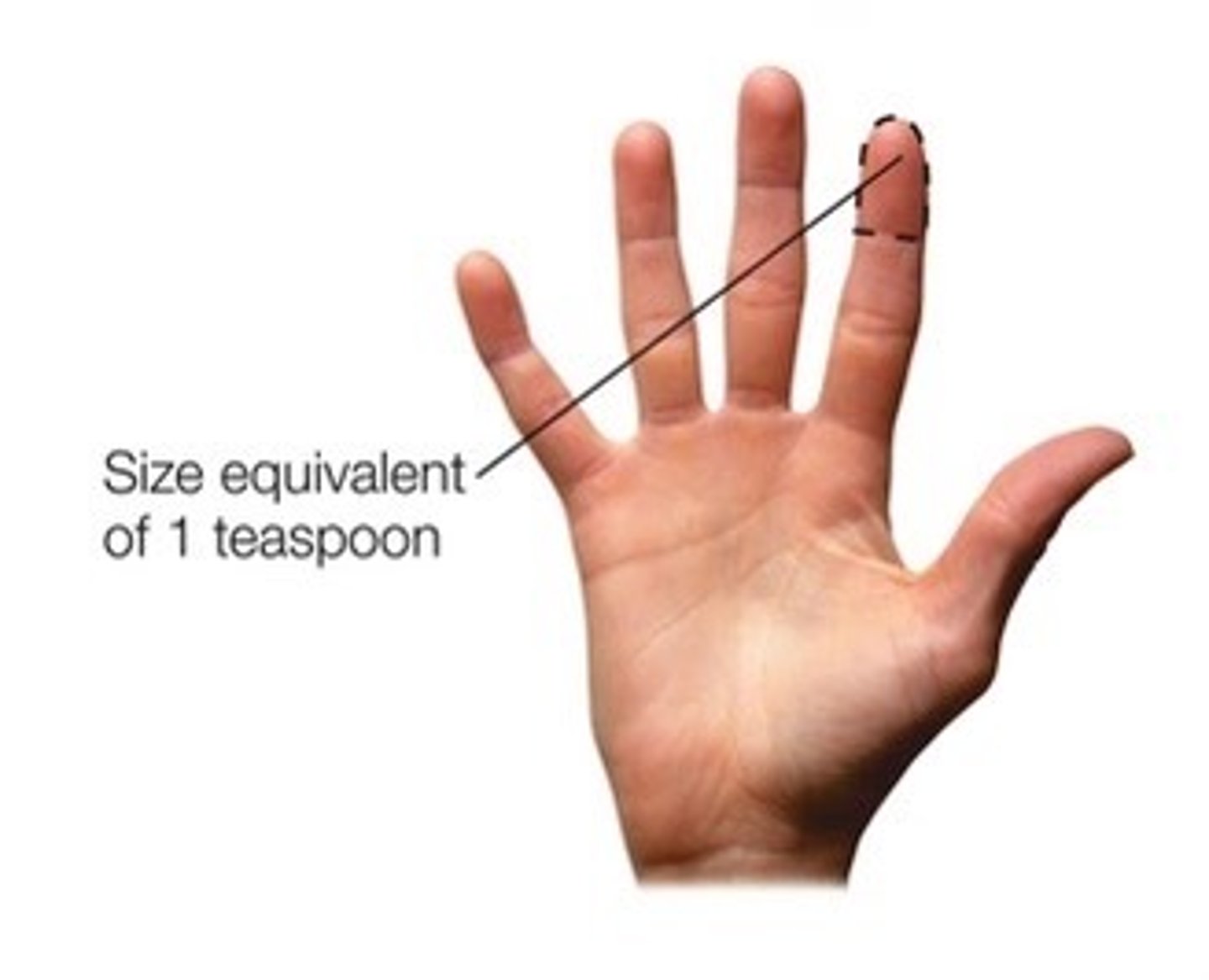
How would you roughly estimate a teaspoon serving size?
Digestion
Breakdown of food substances into simpler forms that can be absorbed and used
Absorption
The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of the digestive system into the blood
GI Tract
stomach, colon. intestines, anus rectum
*Oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum & anal canal
*mouth -> esophagus -> LES -> stomach -> pyloric sphincter -> SI -> ileocecal sphincter -> LI -> rectum -> anus -> anal sphincter
Lumen
space within a tubular part or organ, such as the space within a blood vessel (the hollow part)
Bolus
A term used to describe food after it has been chewed and mixed with saliva
Chyme
Partially digested, semiliquid food mixed with digestive enzymes and acids in the stomach.
Catalyst
substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction
Enzyme
A type of protein that speeds up a chemical reaction in a living thing
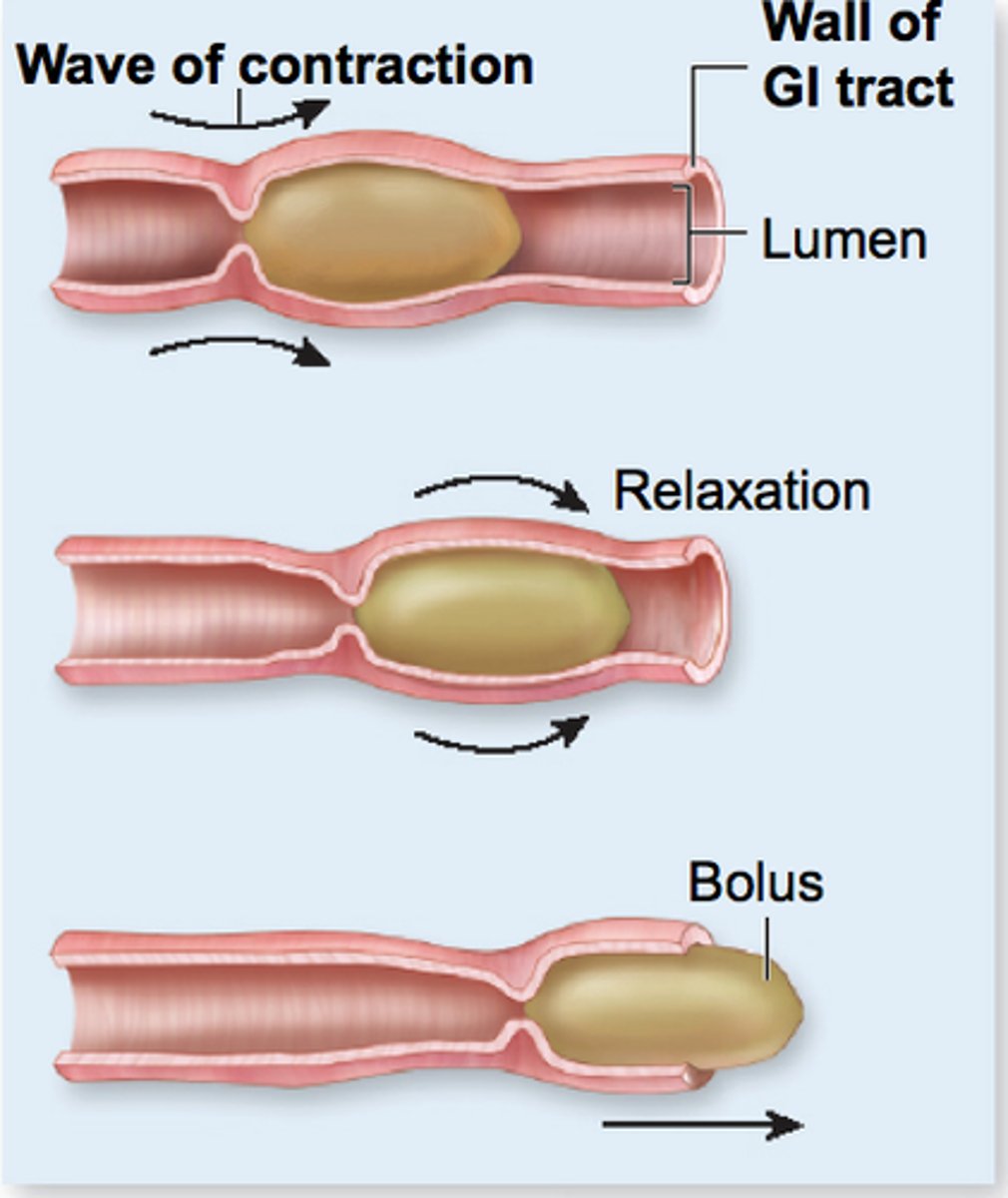
Peristalsis
Involuntary waves of muscle contraction that keep food moving along in one direction through the digestive system.
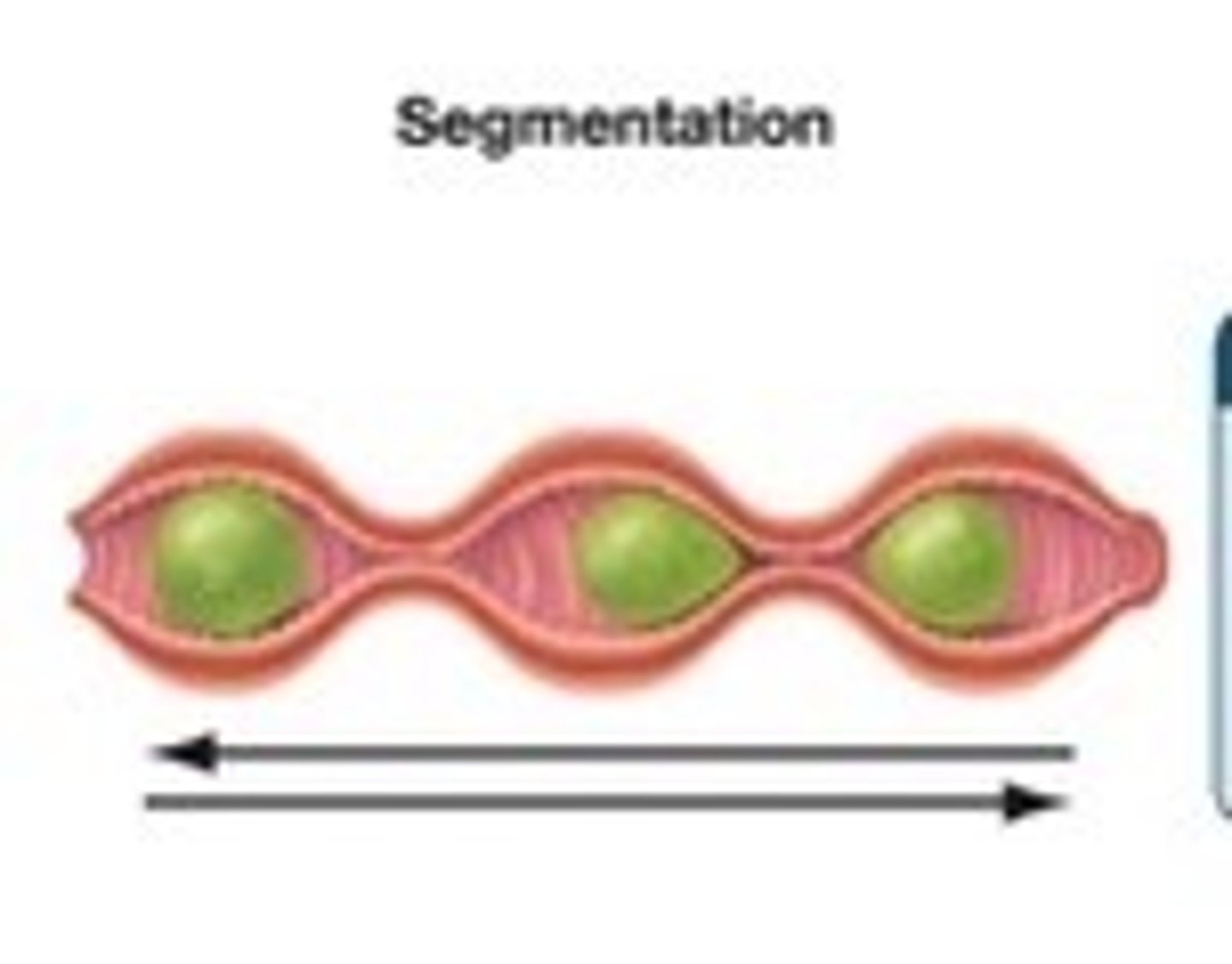
Segmentation
Muscular contractions of the small intestine that move food back and forth, breaking the mixture into smaller and smaller pieces and combining it with digestive juices.
pH
a scale that measures how acidic or basic (alkaline) a substance is
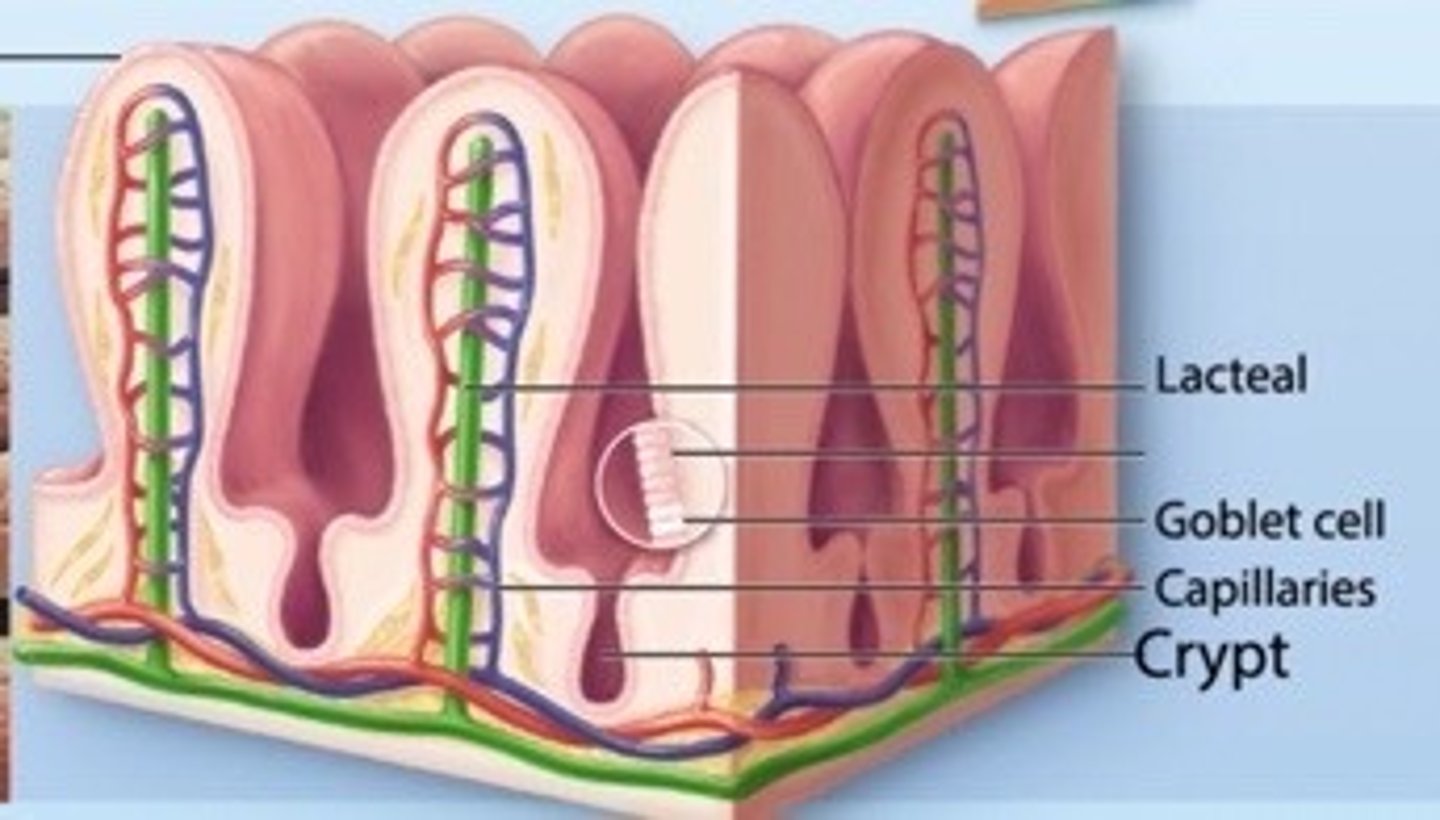
villi and microvilli
Small hair-like projections on the walls of the small intestine that increase surface area for absorption
Crypt
Glands at the base of the villi; they contain stem cells that manufacture young cells to replace the cells of the villi when they die.
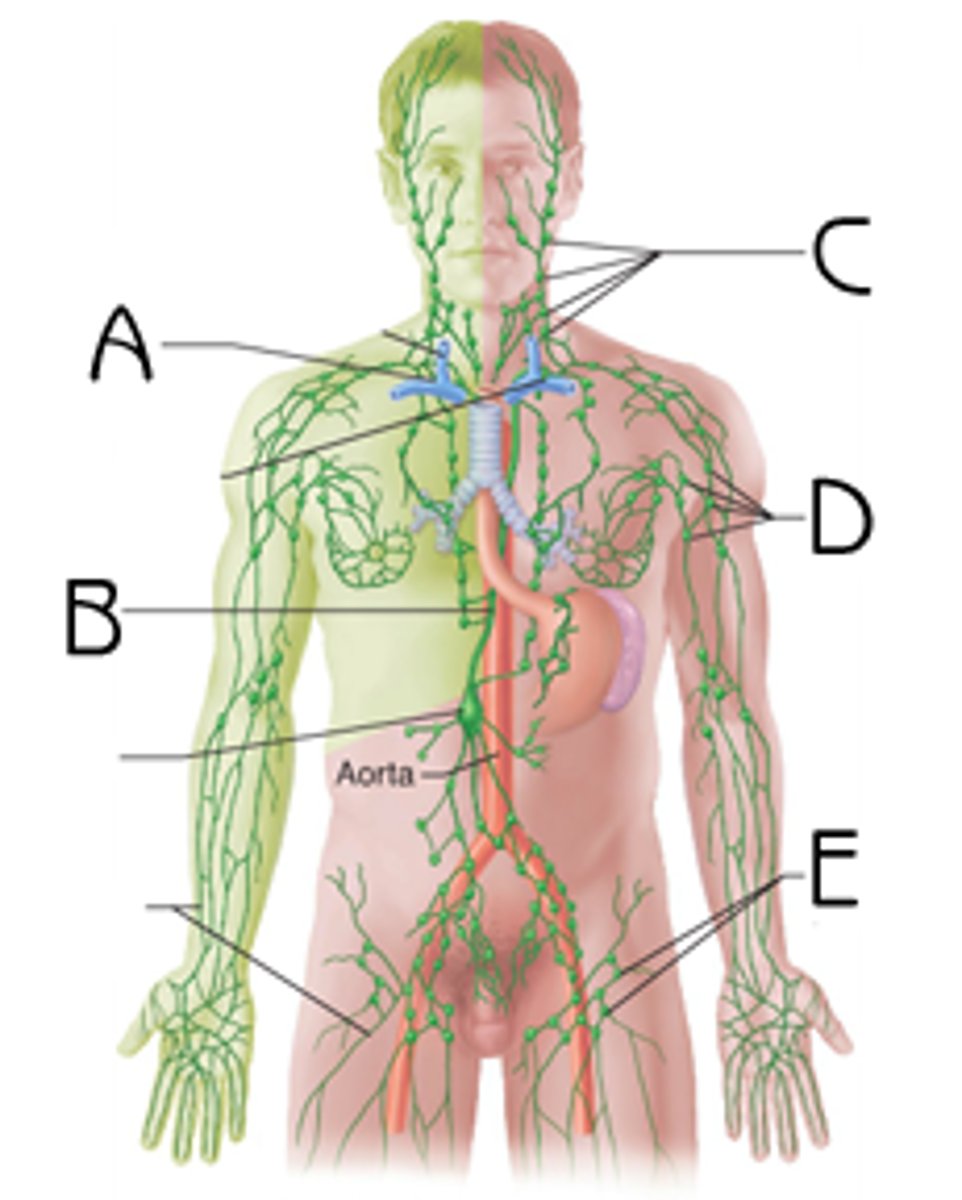
Lymphatic System
System of interconnected vessels that contains lymph fluid in which fat-soluble nutrients are carried; also includes bone marrow, lymph nodes, and other tissues and organs that produce and store defensive cells.
GI microbiota
a complex community of microorganisms, primarily bacteria, residing within the digestive tract
Prebiotic
substance that stimulates bacterial growth in the large intestines
Probiotic
live bacteria that when consumed live temporarily in the colon and confer health benefits on the host
Homeostasis
relatively constant internal physical and chemical conditions that organisms maintain
Hormones
chemical messengers that are manufactured by the endocrine glands, travel through the bloodstream, and affect other tissues
Gastrin
Hormone released from the stomach that stimulates the release of acid.
Secretin
A hormone secreted from the duodenum that stimulates the stomach to release pepsin, the liver to make bile, and the pancreas to release digestive juice