Tissue Mechanics (Exam 2)
1/82
Earn XP
Description and Tags
BME 312 - Fall 2025
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
4 types of tissue in human body
connective tissues (45%)
muscle tissue (80%)
neural tissue (2%)
epithelial tissue (3%)
3 types of muscle tissues
skeletal muscle
cardiac muscle
smooth muscle
skeletal/striated muscle fibers
cause the movement of bones/limbs
occur in muscles attached to the skeleton
striated in appearance and under voluntary control
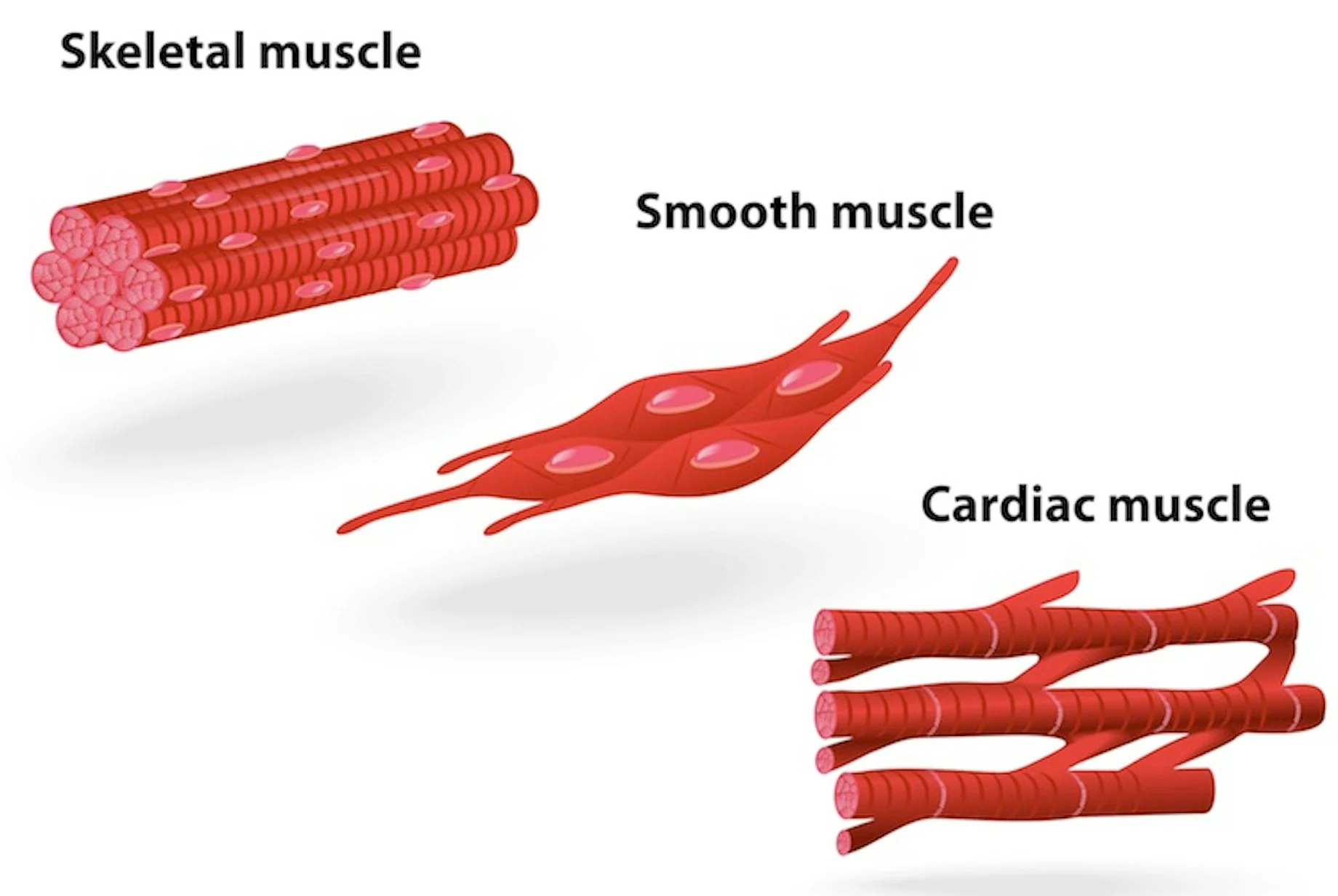
smooth muscle fibers
located in wall of hollow visceral organs, EXCEPT the heart (which is spindle-shaped)
under involuntary control
non-striated
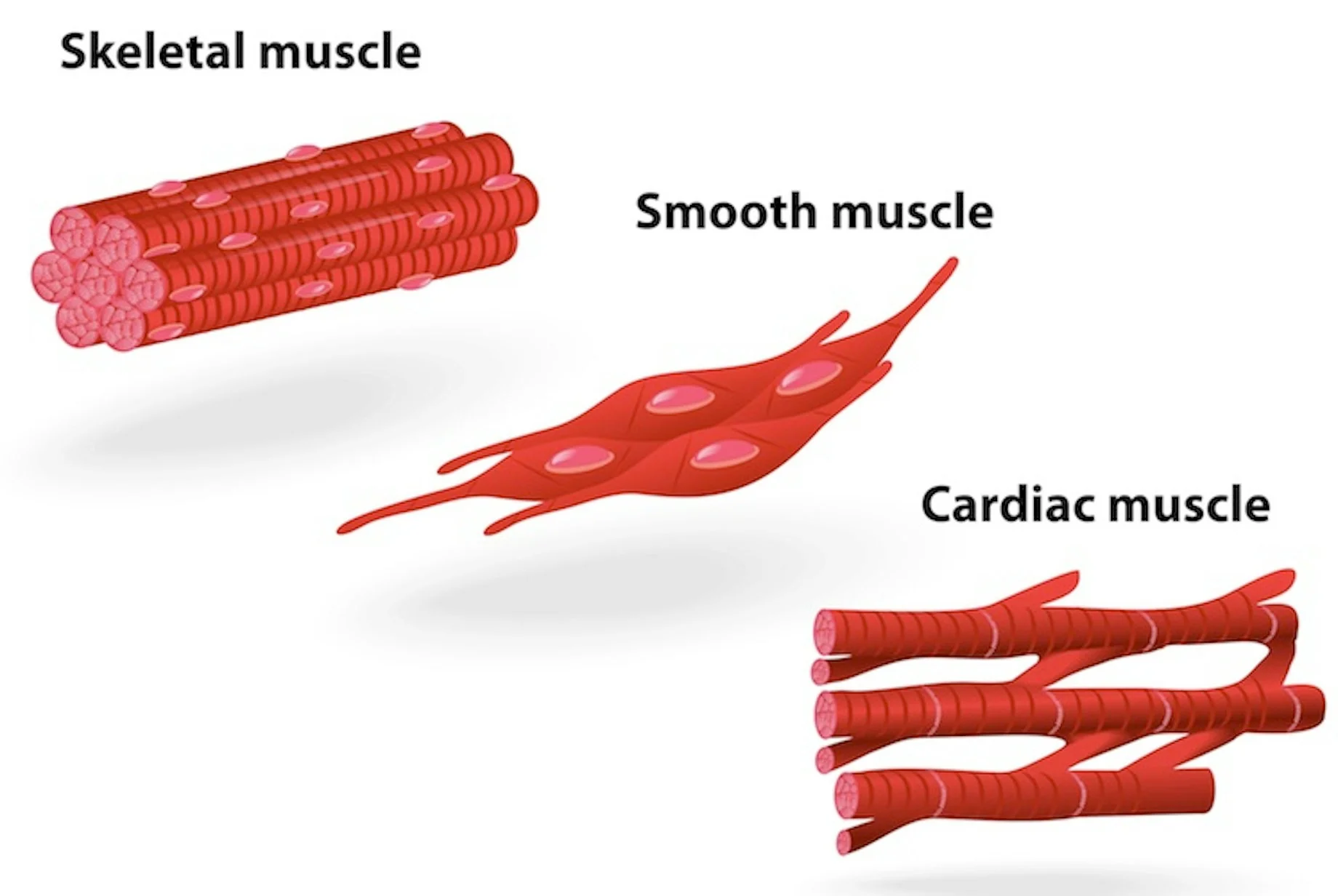
cardiac muscle cells
form the wall of the heart
under involuntary control
striated
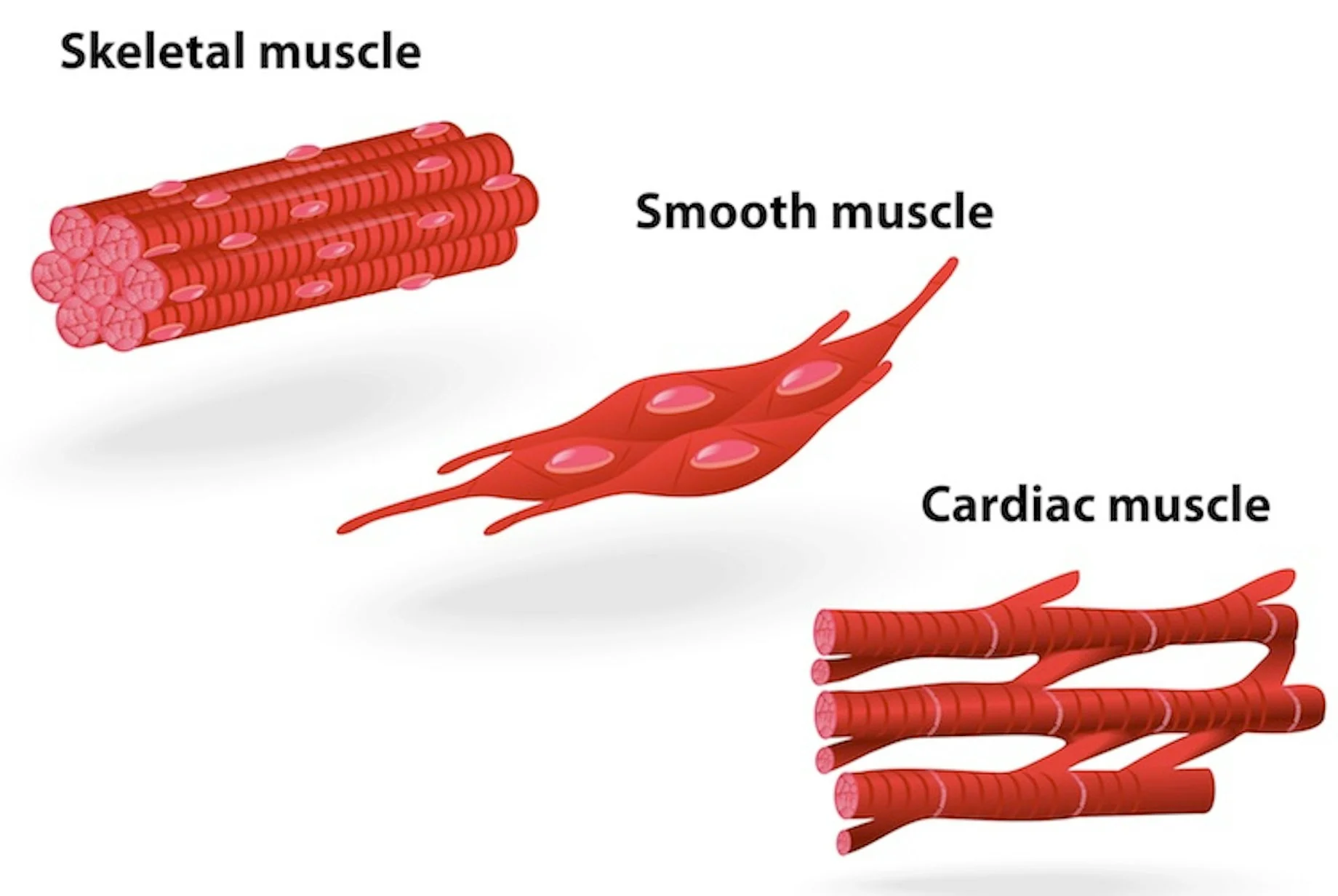
skeletal muscles
generate forces for movement
converts chemical energy into mechanical work
composed of muscles fibers and myofibrils
have viscoelastic behavior
viscoelastic behavior
you can see the curve and different thickness of muscles
it will go back to its original (unstretched) size and shape
after the muscle is stretched and released
viscous = internal resistance to motion
types of muscle contractions
concentric
static
eccentric
concentric contractions
occurs simultaneously as the length of muscle decreases
biceps during the flexion of forearm
static contraction
occurs while muscle length remains constant
biceps are flexed and held without any movement
eccentric contractions
occurs as the length of the muscle increases
biceps are extended (forearm)
functions of the muscle
agonist
antagonist
agonist muscle
causes movement through concentric contractions
shortens the muscle length to cause joint movement
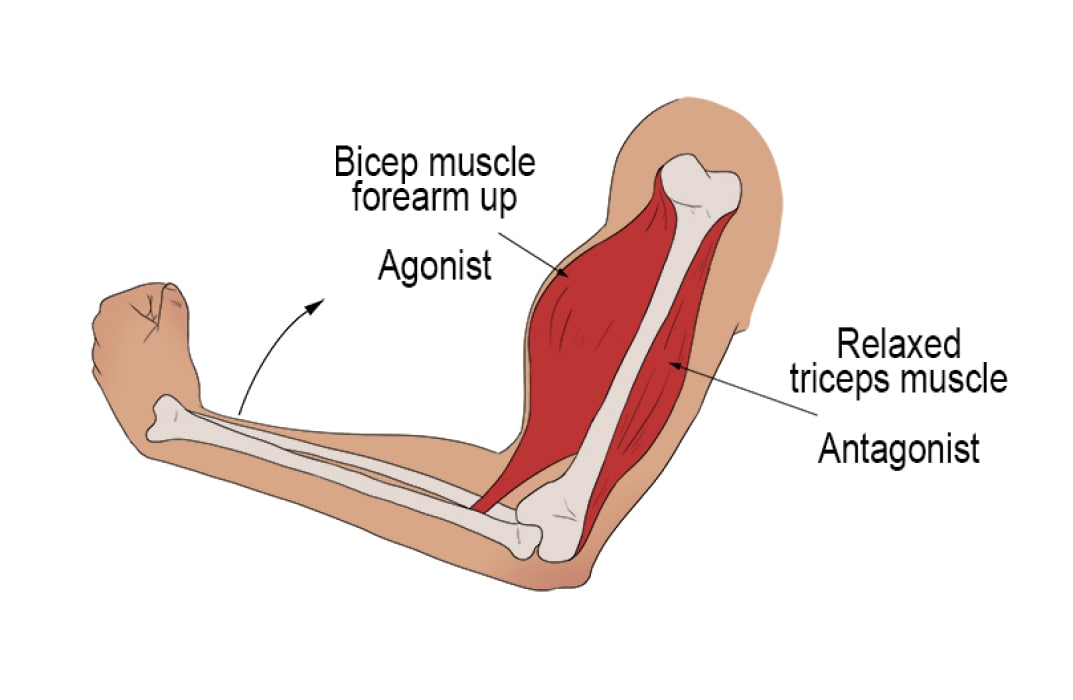
antagonist muscle
causes movement through eccentric contractions to control the movement
lengthens the muscle
decelerates the motion of the joint
assumptions and limitations
locations of muscle attachments are known
anatomical axes of rotation of joints are known
line of action of muscle tension is known
segmental weights and COGs are known
dynamic aspect of problems are ignored
friction factors of joints are negligible
2D problems will be considered
mechanics of skeletal muscles
skeletal muscles attach to at least 2 bones controlling the relative motion of one segment with respect to the other
contraction can occur as a result of muscle shortening/lengthening
can occur without any change in the muscle length
How are skeletal muscles attached?
attached via aponeuroses and/or tendons to at least 2 bone
What is a unique ability of muscle tissue?
contraction
What is the result of a muscle contraction?
ALWAYS tension
A muscle can only exert what?
ONLY exert a pull but NOT a push
structure of skeletal muscle
consist of 100,000 muscle fibers
cells acts together to perform the functions of the specific muscle (they are part of)
voluntary muscle is under conscious control
causes movement of skeletal system (moving limbs and bones)
striated muscle
is also the skin (muscles of facial expressions in the head and neck)
Voluntary muscle is under what?
conscious control
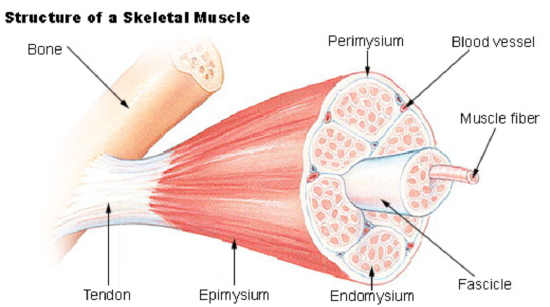
parts of skeletal muscle
tendon
tendon sheath
fascia
superficial fascia
deep fascia
epimysium
perimysium
endomysium
muscle fiber
fascicle
tendon (skeletal muscle)
attaches muscle to bone
tough pale color (whitish)
cord-like
formed many parallel bundles of collagen fibers
flexible
bend around other tissues, changing position as they move
tendon sheath (skeletal muscle)
surround the tendons by tubular double layer sacs
lined with synovial membrane
contains synovial fluid
function of tendon sheath (skeletal muscle)
minimize friction associated with movement at the joint
facilitate movement of the joint
fascia (skeletal muscle)
means bandage
form of sheets of broad bands of fibrous connective tissue
cover muscles or organs
form an outer-wrapping
superficial fascia (skeletal muscle)
consist of areola connective tissue and adipose tissue
referred to as subcutaneous layer of skin
deep fascia (skeletal muscle)
holds the muscles together
consists of dense fibrous connective tissue
epimysium (skeletal muscle)
fibrous elastic tissue that surrounds muscle
many fascicles that form a single muscle
____________ surrounds the total group of muscle
perimysium (skeletal muscle)
fibrous sheath that surrounds and protects bundles of muscle fibers
shown as thing grey line in the cross-section of skeletal muscle
endomysium (skeletal muscle)
connective tissue sheath that surrounds each single muscle fiber
muscle fiber (skeletal muscle)
aka muscle cells
special cells that are able to contract, causing movement
fascicle (skeletal muscle)
expresses as a fascicules
refers to a bundle of muscle fibers or nerves
structure of skeletal muscle
Z line
M band
I band

structure of skeletal muscles (con’t)
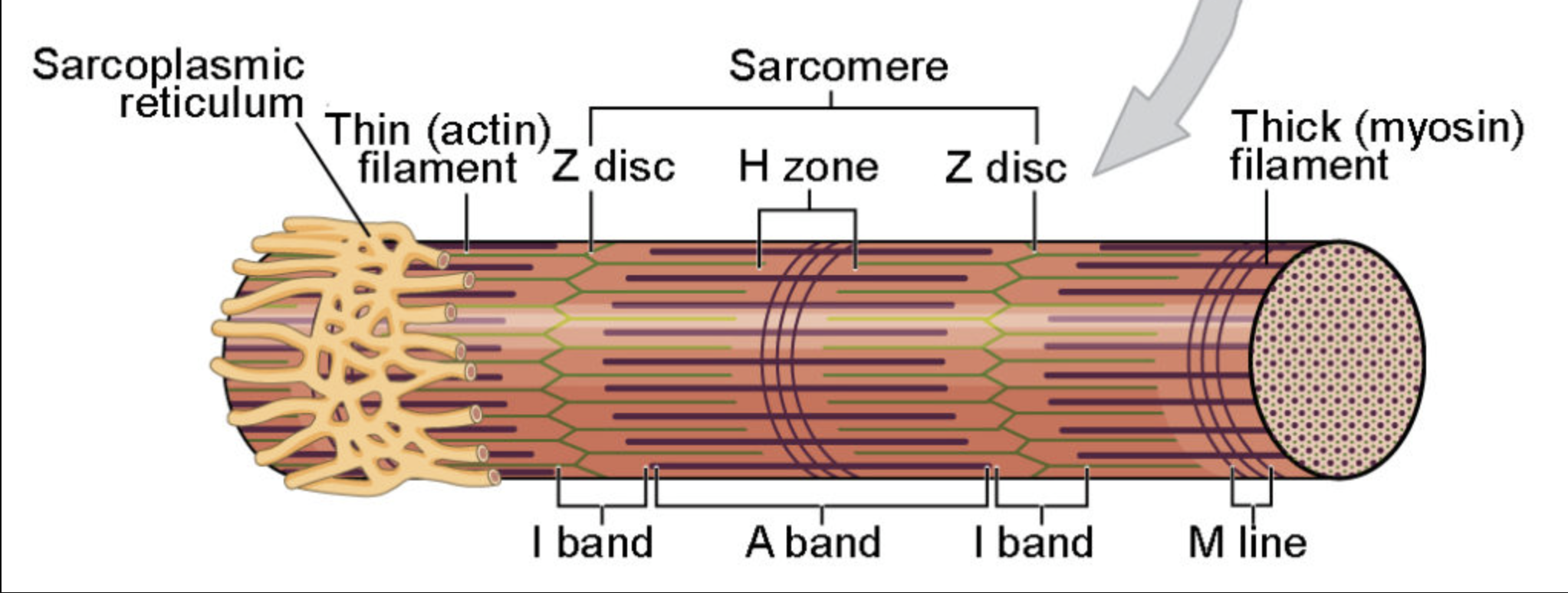
structure of a muscle cell
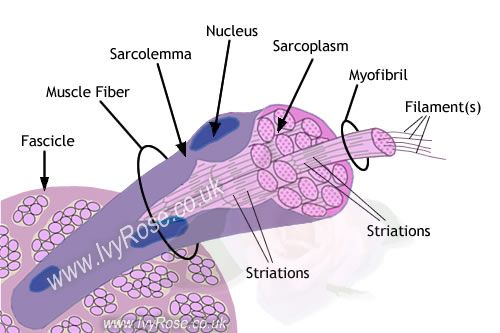
myofibrils (micro structure of skeletal muscle)
small contractile filaments located within the cytoplasm of striated muscle cells
filaments cause the distinctive appearance of skeletal
consist of bands of alternative high and low refractive index
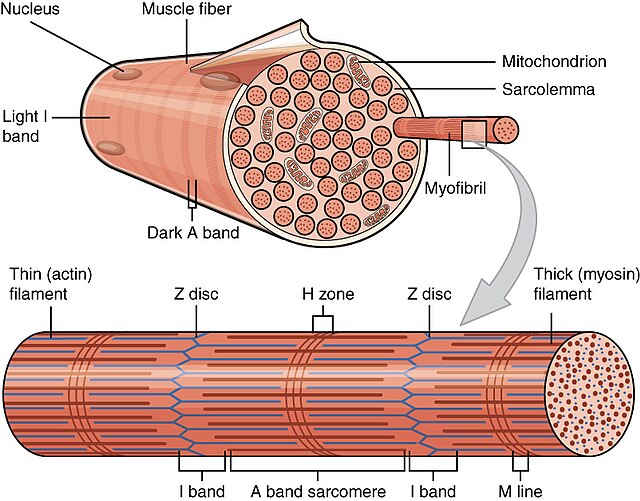
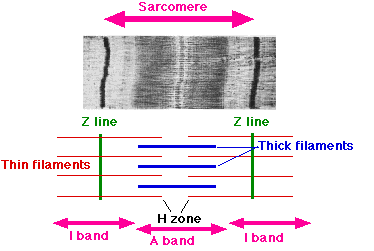
sacromere
thick filaments
thin filaments
H zone
thick filaments
produce the dark A band
thin filaments
extend in each direction from the Z line
DO NOT overlap the thick filaments
create the light I band
H zone
portion of the A band where the thick and thin filaments DO NOT overlap
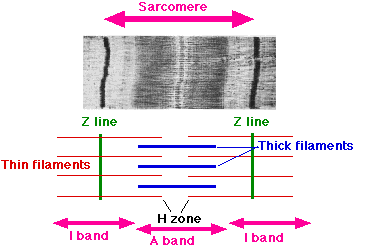
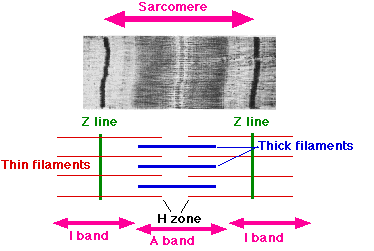
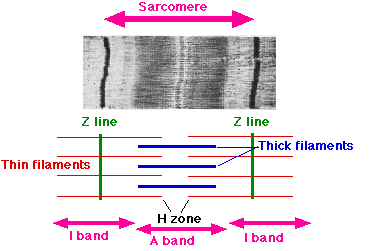
sacromere
entire array of thick and thin filaments between the Z lines
shortening of the _________ in a myofibril produces the shortening of the myofibril
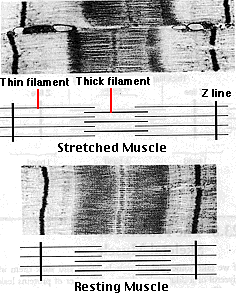
electron microscopy model of muscle contractions
Z lines come closer together
width of the I bands decreases
width of the H zones decreases
there is NO change in the width of the A band
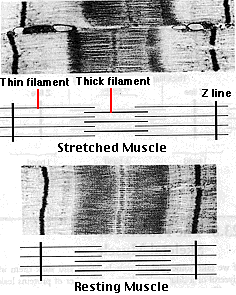
electron microscopy model of muscle stretching
width of the I bands and H zones increase
there is NO change in the width of the A band
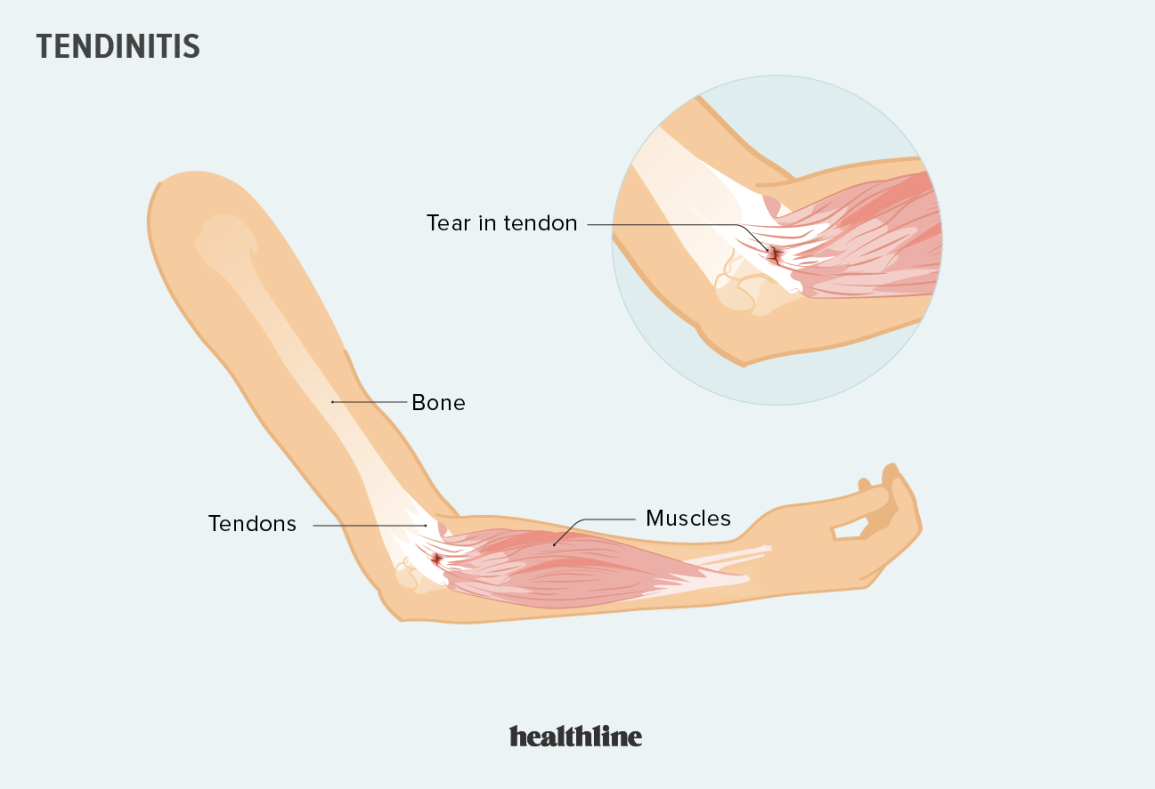
tendonitis
overuse of the tendon
weak point is where the muscle and tendon connect (common area for tendonitis)
striated muscle
striated appearance of the muscle fiber is created by a pattern of alternating dark A bands and light I bands
A bands are bisected by H zone
I bands are bisected by Z line
each myofibril is made up of arrays of parallel filaments
diameters of thick and thin filaments (striated muscle)
thick filaments = 15 nm
composed of the protein myosin
thin filaments = 5 nm
composed mainly of actin with smaller amounts of troponin and tropomyosin
What are actin, troponin, and tropomyosin?
proteins
motor units
minimum unit of contraction
small in muscles over which we have precise control
a single motor neuron triggers fewer than 10 fibers in the muscles controlling eye movements
motor units (con’t)
all motor neurons leading to skeletal muscles have branching axons
each terminates in a neuromuscular junction with a single muscle fiber
nerve impulses passing down a single motor neuron will trigger contraction in all the muscle fibers
which the branches of that neuron terminated
motor units (con’t)
although the response of a motor unit is all-or-none, the strength of the response of the entire muscle is determined by the number of motor units activated
What is the size of the motor units in the muscles controlling the larynx?
small as 2-3 fibers per motor neuron
A single motor unit for a muscle like the gastrocnemius muscle include…
1000 - 2000 fibers (scattered uniformly through the muscle)
tonus
partial contraction of skeletal muscles
even at rest, there is still ________
maintained by the activation of a few motor units at all times even at rest
fueling muscle contraction
ATP = immediate source of energy for muscle contraction
although a muscle fiber consists of ATP enough for a few twitches, the “ATP pool” is replenished as needed
What are the three sources for high-energy phosphate to keep the ATP pool filled?
creatine phosphate
glycogen
cellular respiration (in mitochondria of the fibers)
creatine phosphate
phosphate group is attached by a “high-energy” bond like one in ATP
derives its high-energy phosphate from ATP
can donate it back to ADP to form ATP
pool of creatine phosphate in the fiber is 10 times larger than that of ATP
serves as a modest reservoir of ATP
glycogen
skeletal muscle fibers contains about 1% glycogen
muscle fiber can degrade glycogen by glycogenolysis
produces glucose-1-phosphate
enters the glycolytic pathway to yield 2 molecules of ATP for each pair of lactic acid molecules produced
sufficient to keep muscle functioning if it fails to receive sufficient oxygen to meet its ATP needs by respiration
limited resource
muscle will start to depend on cellular respiration
cellular respiration
not only required to meet ATP needs of muscle engaged in prolonged activity
causes more rapid and deep breathing
afterwards, required to enable the body to resynthesize glycogen from the lactic acid produced earlier
deep breathing continues for a time after exercise is stopped
body must repay its oxygen debt
cellular respiration (con’t)
oxygen debt
demand for oxygen is greater than the supply
means that the body is working hard, and breathing in a lot of oxygen (lung cannot absorb enough to cope with the level of activity)
if this process happens, the body is mainly utilizing the anaerobic energy system
lactic acid builds up (undesirable waste product)
types of muscle fibers
convergent
circular
multipennate
parallel
fusiform
unipennate
bipennate
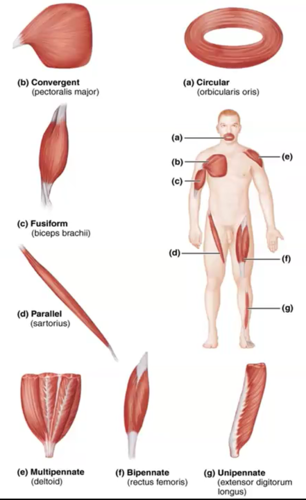
parallel/fusiform muscle fibers
run parallel to each other
contract over a great distance
have good endurance
NOT very strong
examples include sartorius, rectus abdominus muscles
convergent muscle fibers
converge on the insertion to maximize the force of muscle contraction
examples include deltoid, pectoralis major muscle
pennate muscle fibers
three types of pennate muscles (depends on location of muscle)
unipennate
bipennate
multipennate
strong but tie easily
circular muscle fibers
muscle fibers surrounded opening to act as a sphincter
examples include orbicularis, orbicularis oculi muscles
types of muscle contractions
isotonic
isokinetic
isotonic muscle contraction
force remains constant
isokinetic muscle contraction
rate of change of muscle is not constant
angular velocity remains constant
muscle translations cause joint rotations
center of joint rotation is not in a fixed position in human joints
What are isokinetic dynamometers?
devices that have been developed for muscle training
process for fueling muscle contraction
isometric contraction
stimulated muscle is held so that it cannot shorten (“same length”)
simply exerts tension
isotonic contractions
if the muscle is allowed to shorten (“same tension”)
cardiac muscles
very strong
myofibrils of each cell are branched
myofibrils of cardiac muscle is made of single cells and each with a single nucleus
branches interlock with those of adjacent fibers by adherent junctions
strong junctions enable the heart to contract forcefully without ripping the fibers apart
involuntary, striated muscle that is forced in the walls of the heart
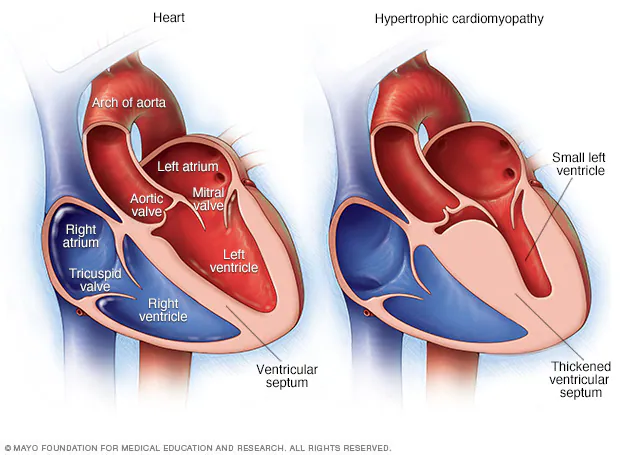
cardiomyopathy
abnormal structure and function of the heart related to heart muscle
think of a closed system (P1V1 = P2V2)
myocardial infarction (MI) or acute myocardial infarction (AMI)
heart attack
occurs when a branch of blood vessels stops supplying blood to a part of the heart causing damage to the heart muscle
symptoms of MI or AMI (heart attack)
chest pain
discomfort travels into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw
What happens in a stroke?
one-sided
speech slurring, can’t lift hands, drooping face
diseases of smooth muscle
multisystemic smooth muscle dysfunction syndromes
achalasia
multisystemic smooth muscle dysfunction syndromes
disease relating to activity of smooth muscle throughout the body
it is impaired
blood vessel abnormalities
a decreased response of the pupils to light
a weak bladder
weakened of the muscle used for digestion of food
hyperperistalsis
achalasia
over contracted condition of the smooth muscle portion of the esophagus
lower esophagus and lower esophageal sphincter
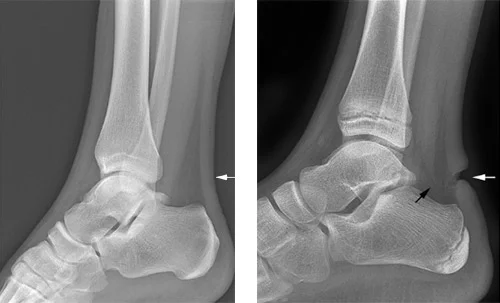
torn quadriceps tendon
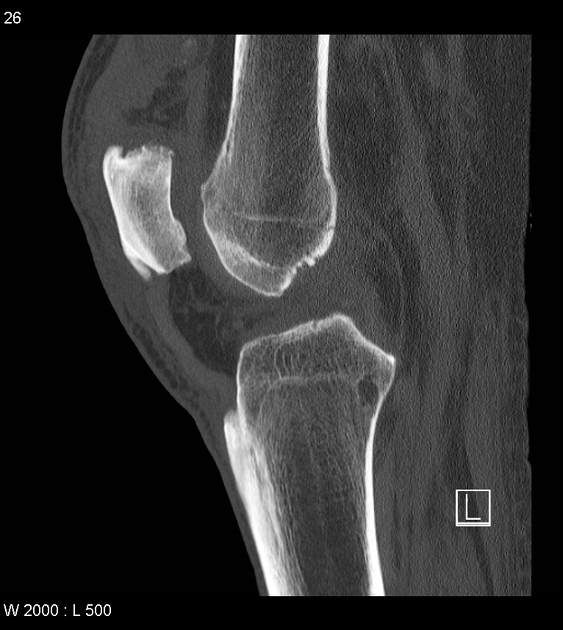
torn Achilles tendon