secondary messengers
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
cAMP phosphodiesterase
converts cAMP to AMP to terminate signal
CREB
cAMP response element binding protein
transcription factor which regulates gene expression by binding to cyclic nucleotide response element
secondary messenger
molecules that relay signals from cell surface receptors to target molecules inside the cell or nucleus
nucleotides
monomers of DNA
adenylyl cyclase
converts ATP to cAMP
cleaves off 2 phosphates from ATP and cyclises remaining phosphate from 5 to 3' of sugar
mechanism of PKA activation
2x cAMP bind to each regulatory subunit
allows for release of catalytic dimer in activated form
transcription factor
regulatory protein that binds to DNA and affects transcription of specific genes
how is the soluble form of cGMP activated
by nitric oxide - lipid soluble gas
cyclic nucleotides
cAMP and cGMP
hydrolysis
breakdown of compound by addition of water
kinase
enzyme that catalyses transfer of phosphate group from ATP to specified molecule
targets of cAMP
binds to CN (ligand) gated ion channels
binds to and activates PKA - initiates kinase cascade
PKA structure
4 subunits - 2 catalytic and 2 regulatory
how does cGMP regulate phototransduction ?
in dark cGMP continually produced
ion channels stay open due to Na+ influx - releases neurotransmitters
in light cGMP levels drop, ion channels close and and reduction in neurotransmitters detected by brain
rhodopsin
the pigment in rod cells that causes light sensitivity
activates transducin
transducin
the G-protein that couples rhodopsin to phosphodiesterase in rod photoreceptors which breaks down cGMP
2 configurations of retinal cofactor in rhodopsin
11-cis and all trans
nitric oxide synthase
converts L-arginine and O2 to citrulline and nitric oxide
targets of nitric oxide
pathogens, G cyclase, smooth muscle (relaxes it)
retinol is derived from...
vitamin A
isomer
compounds with same chemical formula but different structures
phospholipase
cleaves fatty acids from phospholipids
phosphatidylinositol
abundant in membrane
hydroxyl-rich side group
extracellular
polar inositol head group
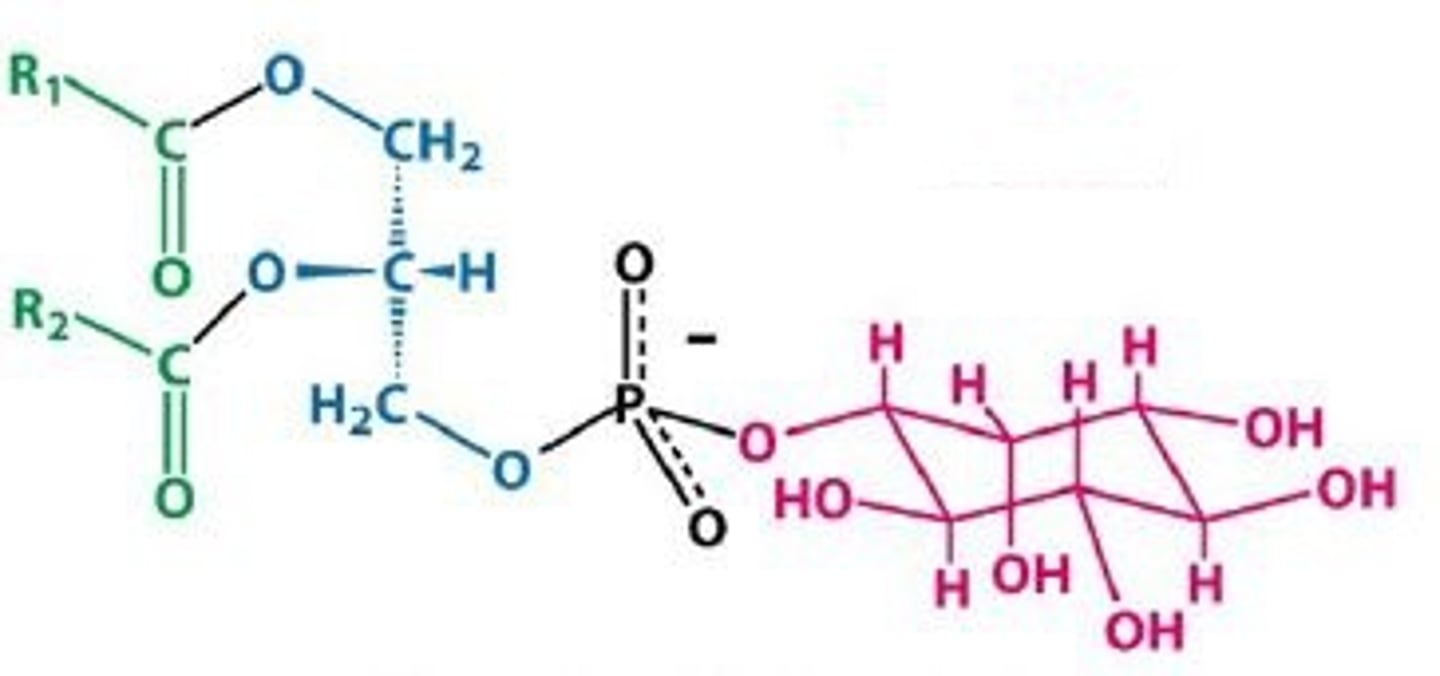
what 2 secondary messengers are produced from phosphotidylinositol ?
inositol triphosphate (PIP3) and DAG
what enzyme is responsible for the cleavage of phospholipids to form secondary messengers ?
phospholipase A or C
PIP3
inositol triphosphate
polar head group
water soluble so acts in cytosol
controls calcium release
DAG
diacylglycerol - hydrophobic
activates PKC by increasing its affinity for calcium ions
calciosome
specialised area of ER high in Ca2+
how many Ca2+ are needed to open calcium channel ?
4
calmodulin
calcium modulated signalling protein - facilitates contraction in smooth muscles
how many binding sites does calmodulin have ?
4 - but each Ca2+ bound to 6O2
apart from DAG what does PKC need to be activated ?
PPS - phosphatidylserine
where is PPS found ?
mem
signal transduction
transmission of molecular signals from extra to intracellular
phosphatase
enzyme - removes phosphate group
what is the role of calcium in inositol phospholipid signal transduction ?
mediates calmodulin activity
aids DAG in activating PKC
kDa
kilodalton
atomic mass unit used to describe molecular weight of large molecules eg. proteins
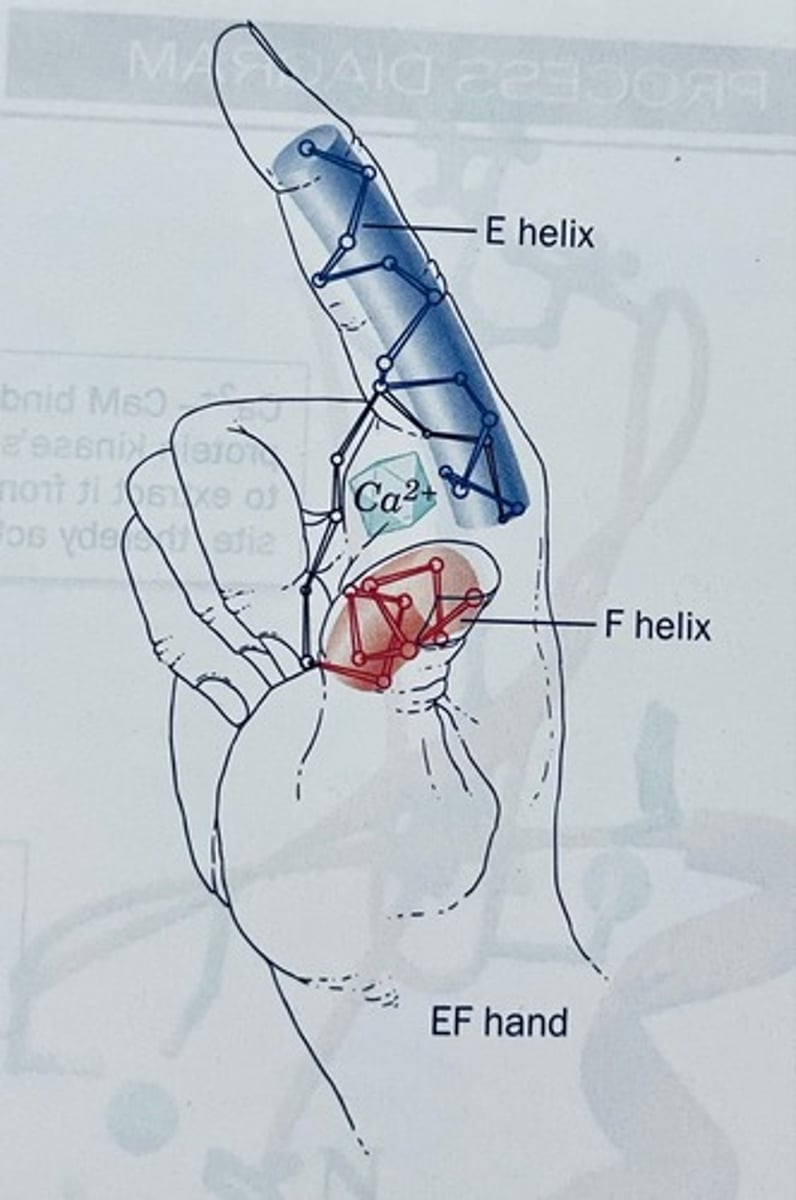
EF hands
Ca2+ binding motif that consists of E and F helix with binding site in centre
what are the 2 PKC domains ?
regulatory and catalytic
V1
pseudosubstrate site
folded to sit across active site and prevent binding of sub
V3
hinge region
what PKC domains respond to calcium and DAG ?
C1 and 2
role of RACK proteins in PKC activation
translocate PKC to relevant membrane areas
what allows for the prolonged activation of PKC after calcium levels drop ?
downstream target of initial PKC is lipase enzyme that produces more DAG
3 examples of lipid derived secondary messengers
IP3, DAG, ecoisanoids
eicosanoids are derived from...
arachidonic acid
linoleic acid
essential fatty acid
pre-cursor for AA
essential fatty acids
cannot be synthesised by the body
lysophospholipid
phospholipid from which one fatty acid has been removed
3 ecosanoid types
prostaglandins
thromboxane
leukotrienes
role of prostaglandins
inflammation response
stops platelet aggregation
role of thromboxane
promotes blood coagulation (clotting)
role of leukotrienes
inflammatory mediator
leukotriene effects
muscle contraction
pulmonary artery constriction
increase capillary permeability
mucus secretion
in what cells is leukotriene generation triggered
mast (immune)
PGH synthase
converts AA to PGH2
PGH2
precursor for PGs, thromboxane and leukotrienes
what is meant by "PGH synthase is a bifunctional enzyme" ?
catalyses 2 reactions - COX and peroxidase
what is aspirin an example of
secondary metabolism product
how does aspirin act to decrease the symptoms of inflammation?
acts on PGH synthase - acetylates serine amino acid adjacent to active site thus blocking it
prevents PGH from activating PGH2
analgesic
drug that relieves pain
antipyretic
reduces fever
side effects of aspirin
gastric bleeding
hepatic and cerebral damage in children
why does aspirin have negative side effects ?
inhibits both isoforms of PGH
PGH1 is housekeeping enzyme
agonist
molecule that, by binding to a receptor site, stimulates a response
antagonist
block active site
marine fats are high in...
n-3PUFAs
n-3PUFA example
EPA
EPA benefits
in high levels preferentially used by PGH synthase to form 3 series TxA and PGI which decrease likelihood of clot formation and thus cardiovascular disease
2 common asthma treatments
ventolin and bectotide
Salbutamol (Ventolin)
short acting beta-2 andrenergic receptor agonist
causes smooth muscle to relax allowing for bronchial dilation