Basic Concepts of Chemistry
1/76
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Comprehensive set for the entire first chapter of NCERT Chemistry class XI. When studying, enable only "Answer with Definition". For question types, enable only "Flashcards". Let me know if you want me to add/change anything!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
What is matter?
Anything which occupies space and has mass.
What are pure substances?
All constituent particles of the substance have the same chemical nature.
What is a mixture?
A substance that contains particles of two or more pure substances which may be present in any ratio.
What is a homogenous mixture?
Composition of the mixture is uniform throughout.
What is a heterogeneous mixture?
Composition of the mixture is not uniform throughout.
Elements?
Can neither be decomposed nor built from simpler substances by ordinary physical and chemical methods. It contains only one kind of atoms.
Most abundant element in the universe?
Hydrogen
Most abundant element in the Earth’s crust?
Oxygen
Most abundant metal in the earth’s crust?
Aluminium
What are compounds?
Forms of matter that can be formed by combining two or more elements in a definite ratio by mass.
What are organic compounds?
Hydrides of carbon (hydrocarbons) and their derivatives
What are inorganic compounds?
Compounds of all elements except for hydrides of carbon (hydrocarbons) and their derivatives.
What does the suffix ‘micro’ mean?
10-6
What does the suffix ‘milli’ mean?
10-3
What does the suffix ‘nano’ mean?
10-9
What does the suffix ‘pico’ mean?
10-12
What does the suffix ‘femto’ mean?
10-15
What does the suffix ‘atto’ mean?
10-18
What is precision?
It is the closeness of the set of values obtained from identical measurements of a quantity.
What is accuracy?
It is a measure of the difference between the experimental value or the mean value of a set of measurements and the true value.
How much is amstrong in metres?
10-10m
How much is 1 eV in Joules?
1.602189 * 10-19 J
How much is 1 calorie in Joules?
4.184 J
How much is 1 bar in pascal and N m-2?
105 Pa and 105 N m-2
How much is 1atm in pascal and N m-2?
101325 in both units
How much is 1 dyne in Newtons?
105 N
How much is 1 Litre in decimetre3?
1 dm3
How much is 1 Litre in m3?
10-3 m3
What is Law of Conservation of Mass?
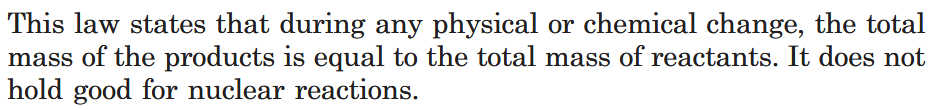
What is Law of Definite Proportions?
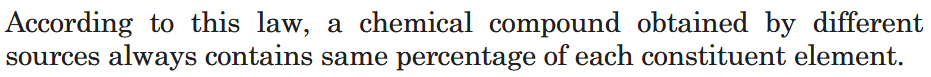
What is Law of Multiple Proportions?

What is Law of Reciprocal Proportions?

What is Gay Lussac’s Law of Gaseous Volumes?

What is Avogadro’s Hypothesis?
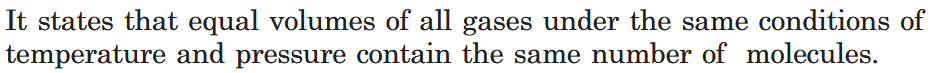
What are the basic postulates of Dalton’s Atomic Theory?
All substances are made up of tiny, indivisible particles, called atoms.
In each element, the atoms are all alike and have the same mass. The atoms of different elements differ in mass.
Atoms can neither be created nor destroyed during any physical or chemical change.
Compounds or molecules result from combination of atoms in some simple numerical ratio.
What are the limitations of Dalton’s Atomic Theory?

What is atomic mass?
It is the average relative atomic mass of an atom.
It indicates that how many times an atom of that element is heavier as compared with 1/12th
part of the mass of one atom of carbon-12.
What is the formula for atomic mass?
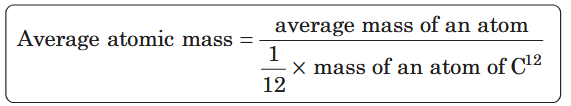
What is the significance of the word “average” in average atomic mass?
It takes into account the fact that most elements exist in the world as a mixture of their various isotopes in different proportions.
What is the formula for average atomic mass?
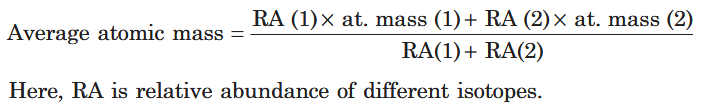
How do you calculate the average atomic mass of volatile chlorides?
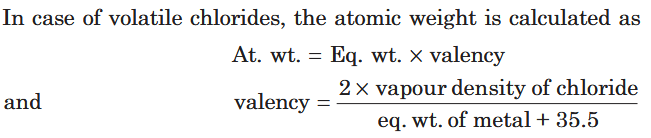
What is Dulong and Petit’s rule in the form of a formula?
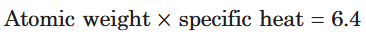
What is molecular mass?
The sum of atomic masses of the elements present in a molecule.
What is mole?
The amount of substance which contains same number of elementary particles (atoms, molecules or ions) as the number of atoms present in 12g of carbon (C-12).
What is avogadro’s constant?
6.02214076 × 1023 also denoted as NA
What is Gram Atomic Mass?
Atomic mass of an element expressed in gram is called its gram atomic mass or gram-atom or mole-atom.
How do you calculate molecular mass from vapour density?
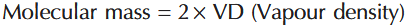
What is Formula mass?
Some substances such as sodium chloride do not contain discrete molecules as their constituent units. The formula such as NaCl is used to calculate the formula mass instead of molecular mass as in the solid state sodium chloride does not exist as a single entity. e.g. formula mass of sodium chloride is 58.5 u.
What is Equivalent mass?
It is the mass of an element or a compound which would combine with or displaces (by weight) 1 part of hydrogen or 8 parts of oxygen or 35.5 parts of chlorine.
How do you calculate Equivalent mass of a metal? How is it related to mass?

How do you calculate Equivalent Mass of a compound?
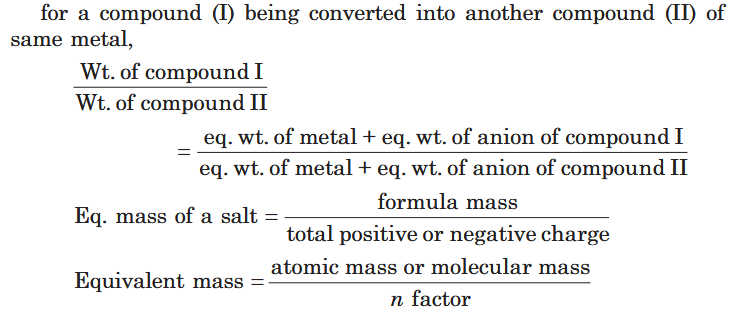
How do you calculate n-factor for:
acids
bases
ions
redox titrations
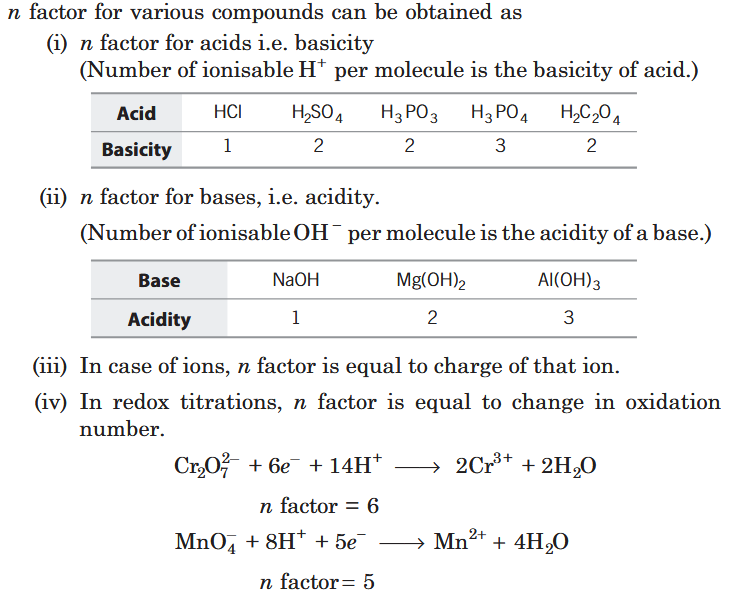
How do you calculate the equivalent mass of an organic acid?

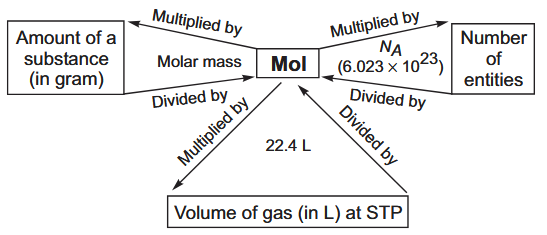
What is the conversion between mol, atoms and gram atomic mass?
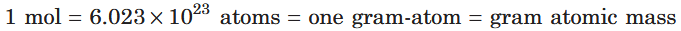
What is the conversion between mol, molecules and gram molecular mass?
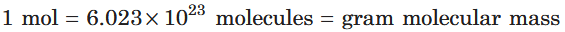
In gaseous state at STP, what is the conversion between mole and litre?
1 mol = 22.4 L
How do you calculate the number of moles in a given substance?

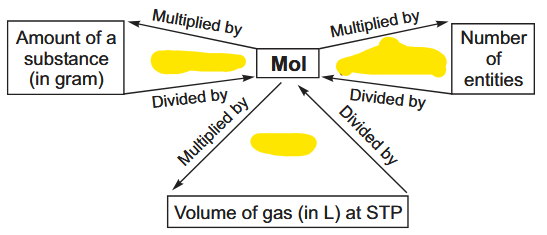
Fill in the blanks.
How do you calculate the number of molecules, given the number of moles?
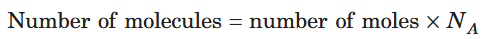
How do you calculate the number of molecules in 1g of the substance, given the gram-molar mass of the substance?
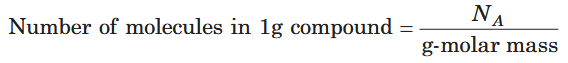
What is the Loschmidt number? What is its value?
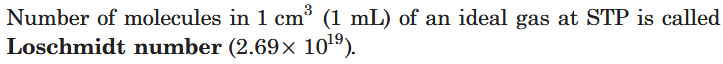
How much is 1 amu or u (unified mass)?
What is the relation between amu, Avogadro’s number, Avogram, Aston, Dalton?
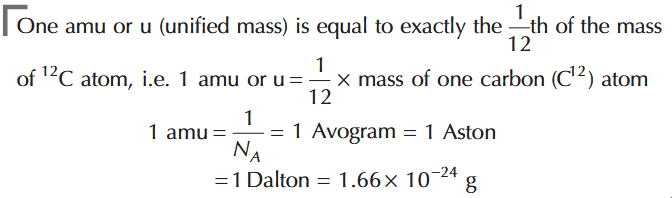
How much does one mole of electrons weigh?
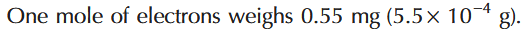
What is Empirical formula?
Empirical formula is the simplest formula of a compound giving simplest whole number ratio of atoms present in one molecule.
What is the empirical formula of Benzene? (C6H6)
CH
How do you derive molecular formula from empirical formula?

What is molar mass?
mass of one mole of a substance in grams. It is numerically equal to molecular mass.
What is Stoichiometry?
The relative proportions in which the reactants react and the products are formed.
What is Limiting reagent?
It is the reactant which is completely consumed during the reaction.
What is Excess reagent?
It is the reactant which is not completely consumed and remains unreacted during the reaction.
In a irreversible chemical reaction, the extent of product can be computed on the basis of limiting reagent in the chemical reaction.
Did you know this?
Yes.
What is percent yield? How do you calculate it?

What is the formula for converting between Fahrenheit and Celsius?
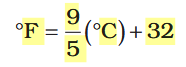
What is the formula for converting between Kelvin and Celsius?
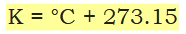
What is Avogadro’s Law?
Equal volumes of all gases at the same temperature and pressure should contain equal number of molecules.
How do you calculate the percentage composition of a compound?
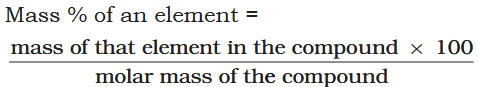
How do you derive a compound’s empirical and molecular formulas given the percentage composition and molar mass of the compound?
Write all the percentages as ‘grams’ and assume you have 100g of each constituent element.
Divide the masses obtained above by their respective molar masses. This gives the number of moles of each constituent element.
Find the simplest ratio of the number of moles of each constituent element by dividing them all with the smallest value among them.
Write down the empirical formula by mentioning the numbers after writing the symbols of respective elements
Divide the molar mass given in the question by the empirical formula mass to obtain n. Then multiply each element in the empirical formula by n to obtain molecular formula.