Antifungals (1)
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Alkylamines
Naftifine, Butenafine, Terbinafine
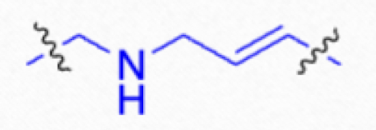
What Antifungal group is this?
Alkylamines
Which drug(s) is/are a strong inhibitor of CYP2D6, which can lead to increasing the drug conc of codeine and desipramine? (this drug can also lead to liver toxicity)
terbinafine
Thiocarbamates
Tolnaftate, tolciclate
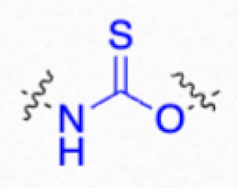
which antifungal is this structure?
Thiocarbamates
Which drugs class inhibits CYP51 in fungal cells?
Lanosterol Demethylase Inhibitors (-Azoles)
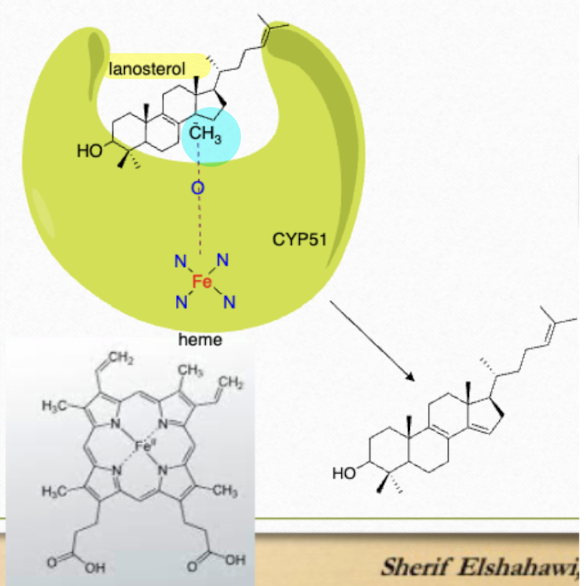
when functioning, what occurs in CYP51 between lanosterol and heme?
iron (in heme) binds to O2 and attack the methyl (14(alpha) in the lanosterol
Which Azoles have imidazoles (N at the 3 position)?
1 gen: Miconazole (Monistat), Clotrimazole (Mycelex)
2 gen: Ketoconazole (Nizoral)

Which Azoles have triazole (N at the 4 position)?
Fluconazole, Fosfluconazole, Itraconazole, Voriconazole, Posaconazole, Efinaconazole, Isavuconazole
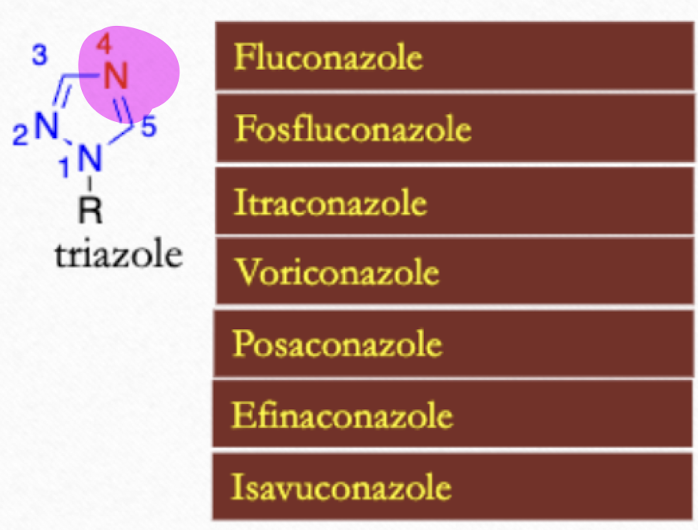
Which Azoles have tetrazole (N at the 4 position)?
Oteseconazole

What is the basic structural element of -Azoles?
imidazole
What is the MOA of Azole?
N-3 (imidazole) or N-4 (triazole and tetrazole) bind to the heme iron of CYP51 to prevent the activation of O2 and inhibit oxidation or steroidal substrates (precursors of ergosterol)
Compare the different types of Azoles in terms of specificity and side effects: imidazole, triazoles, tetrazoles
imidazoles: lower specificity (more side effects)
triazoles: higher specificity (fewer side effects)
tetrazoles: highest specificity to fungal CYP51 (lowest specificity to human CYP51 and least DDIs)
Other than the basic imidazole, what are the other structural elements of the azoles (and the effects they provide)?
1-3 aromatic rings: increase lipophilicity
one or more halogens (F, Cl) (F present is more potent) at 2’ or 4’
substitutions at other positions → inactive compounds
-OH (or other hydrophilic groups) increase solubility
Which Azoles inhibit 3A4 primarily? (KIP)
ketoconazole
itraconazole
posaconazole
fluconzole, voriconazole, and oteseconazole have SOME
Which Azoles inhibit 2C9 primarily? (F)
fluconazole
voriconazole has SOME
Which Azoles inhibit 2C19 primarily? (V)
voriconazole
Which azoles are substrates for 3A4? (KI)
ketoconazole
Itraconazole
Which azoles are substrates for 2C19? (V)
voriconazole
What are the characteristics of FIRST gen imidazoles?
broad spectrum activity
lipophilicity
poor aqueous solubility
typically formulated as creams
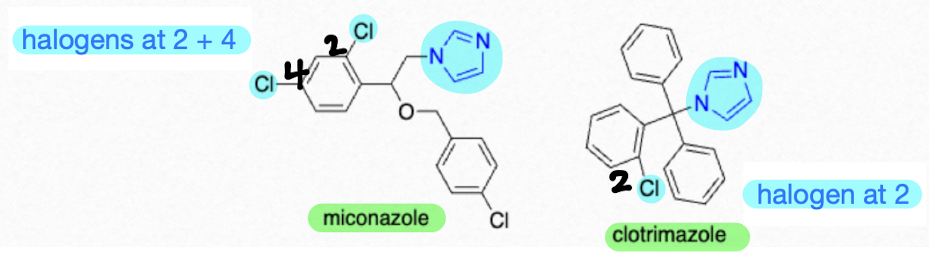
What are the differences in terms of structure between miconazole and clotrimazole?
miconazole: Cl at 2’ + 4’
clotrimazole: Cl at 2’ only
What are the structural characteristics of SECOND gen imidazoles?
low pH increase absorption (acid lowering will decrease bioavailability)
broad spectrum
powerful inhibitor of CYP3A4
severe liver damage with systemic admin
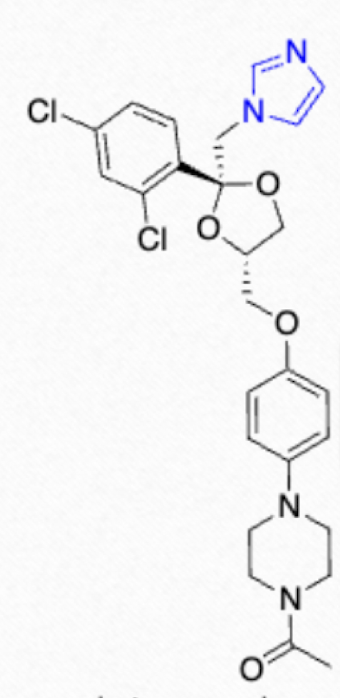
Which azole/class is this structure?
Second gen imidazole (ketoconazole)
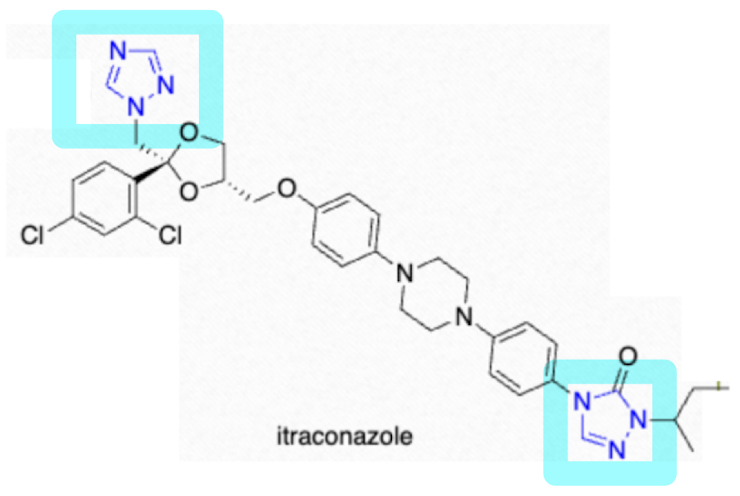
Which Triazole is a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor, absorbed by high acidity, has poor penetration of CSF, taken with food, and cannot be taken with grapefruit and multivalent ions?
Itraconazole (Sporanox)
Which Triazole is metabolized by CYP3A4 and who’s bioavailability will be decreased by rifampin, phenytoin, and carbamazepine?
itraconazole
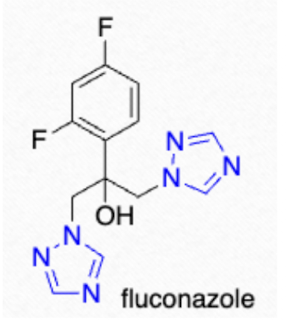
Which Triazole has GOOD CSF concentration, has two triazole rings (increased water solubility), is a strong inhibitor of CYP2C9, is 100-fold more potent than ketoconazole, and can be secreted in breastmilk?
fluconazole (Diflucan)
which triazole is highly-water soluble and a PRODRUG (90% rapidly converted to active)?
fosfluconazole (Prodif)
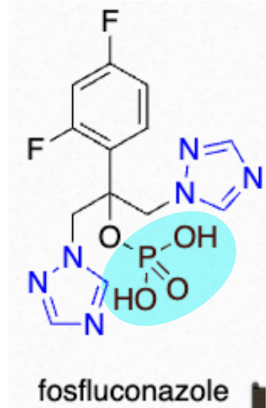
Which triazole has a phosphate ester that is rapidly removed by alkaline phosphatases? what is the active form of this prodrug?
fosfluconazole → fluconazole
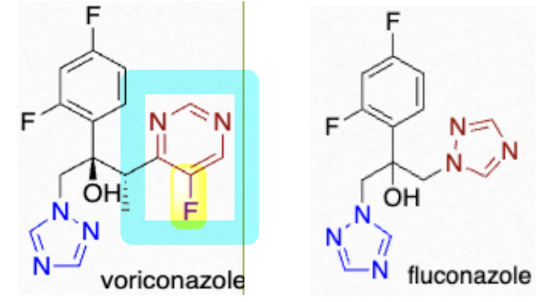
Which triazole is absorbed in GI, has a pyrimidine ring instead of a 2nd triazole, metabolized via hepatic route to active hydroxylated, and glycosylated analogs, inhibits CYP3A4, and AEs include photosensitive dermatitis and neurologic issues?
voriconazole (Vfend)
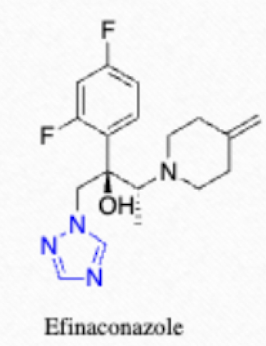
Which Triazole has a low affinity for nail keratin and its active form is R. R diasteromer?
efinaconazole
Which Triazole has a prodrug that is a sulfate salt and is active against black fungus?
isavuconazole (prodrug = isavuconazonium sulfate)
What is the tetrazole?
oteseconazole
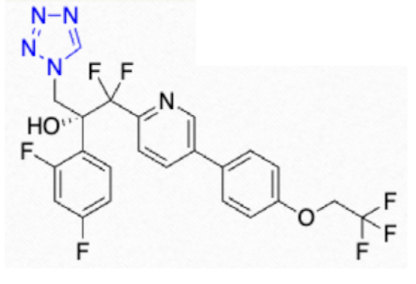
What are the benefits of tetrazoles over triazoles and imidazoles?
highly selective for cyp51 and little interaction with human cypp450s due to tetrazole moiety → less DDIs
What are the downsides with oteseconazole?
upregulation of efflux pumps CDR1 and MDR1 and fungal CYP51
CI: in pregnant and lactating women due to embryo-fetal toxicity risks