B6: Path Exam 1 (1-9) (I'm so sorry this is so long)
1/468
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
469 Terms
steroid and thyroid hormones
what type of hormones are hydrophobic, with the ability to penetrate the membrane and target cytoplasmic receptors?
juxtacrine signaling
What type of hormone signaling:
-signaling molecule remains on secreting cell surface or ECM
-requires cell contact
anterior
parts of the _____ pituitary:
-pars tuberalis
-pars intermedia
-pars distalis
posterior
parts of the anterior pituitary:
-infundibular stalk
-pars nervosa
sella turcica on the sphenoid bone
where is the pituitary gland found?
neurohypophysis
origin of __________:
-bud grows down from the diencephalon as a stalk
adenohypophysis
origin of __________:
-hypophyseal (rathke) pouch from ectoderm growing cranially
neurohypophysis
posterior pituitary is aka:
adenohypophysis
anterior pituitary is aka:
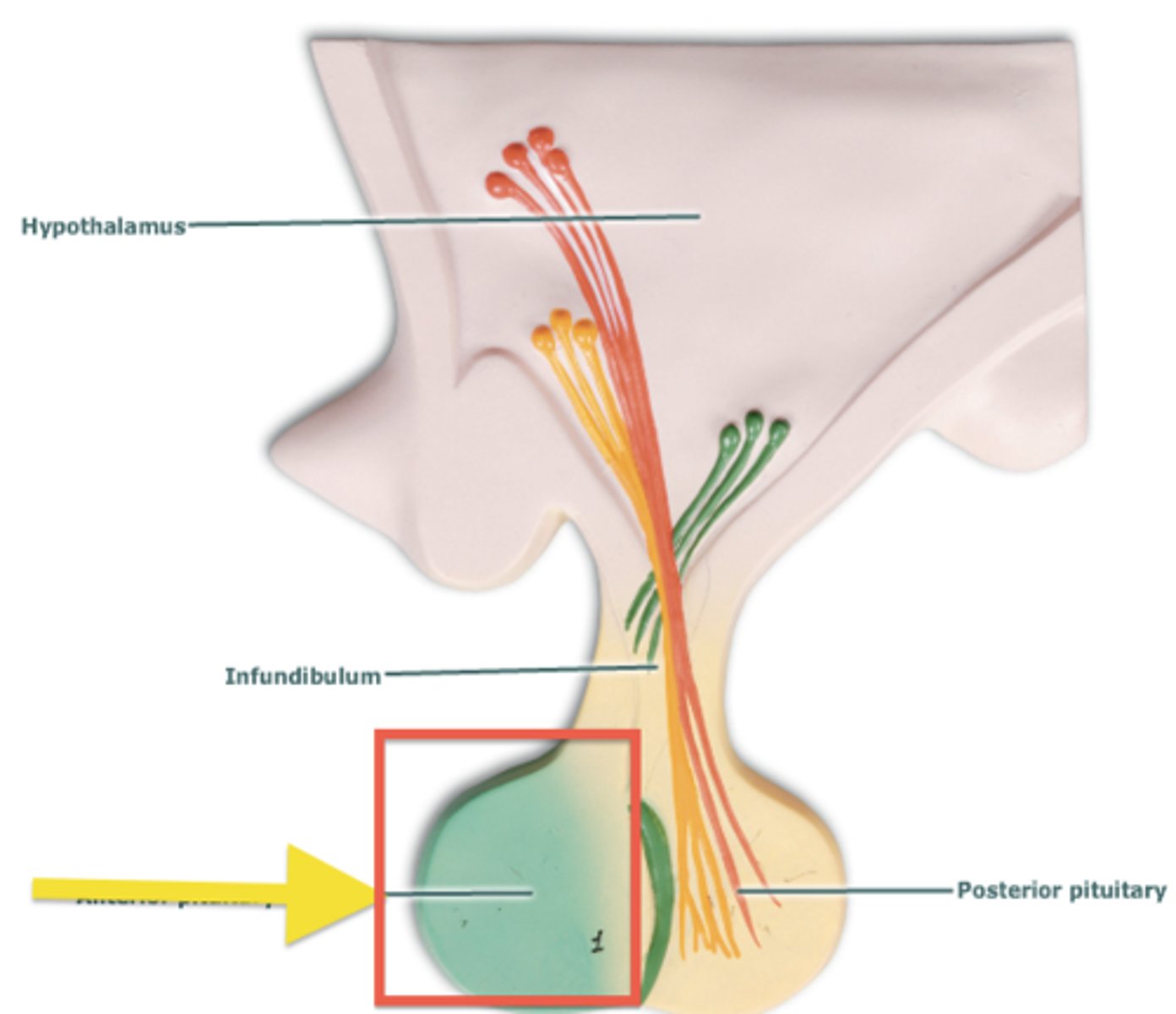
anterior pituitary
ID dark-stained tissue
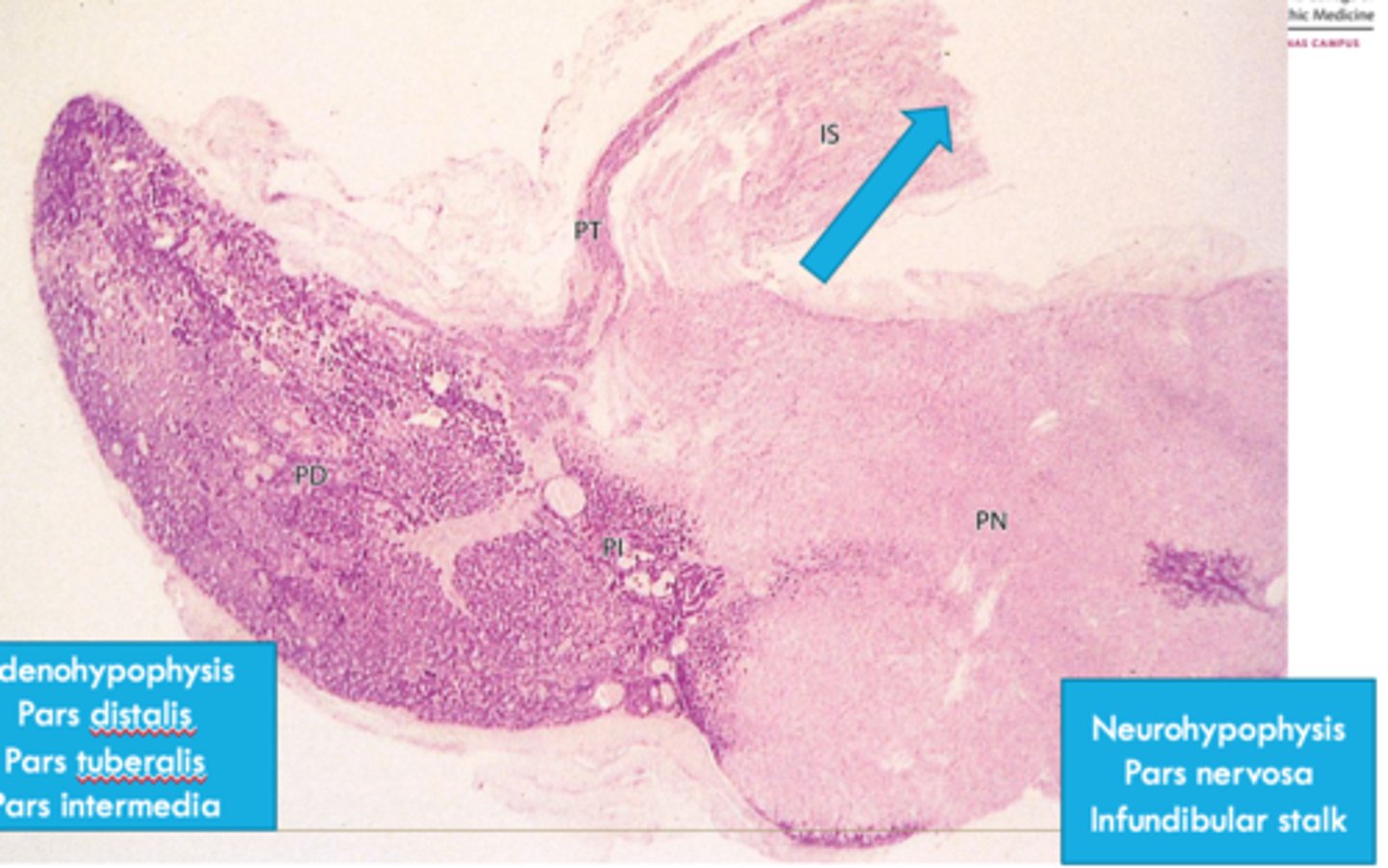
posterior pituitary
ID light-stained tissue
-derived from neural tissue (hypothalamus)
paraventricular (oxytocin) and supraoptic (ADH)
axons from the ______ and _______ nuclei of the hypothalamus extend through the infubdibulum into the posterior pituitary
-then released into capillaries from the posterior pituitary
superior hypophyseal artery
delivers blood to the capillary network in the median eminence and infundibular stalk
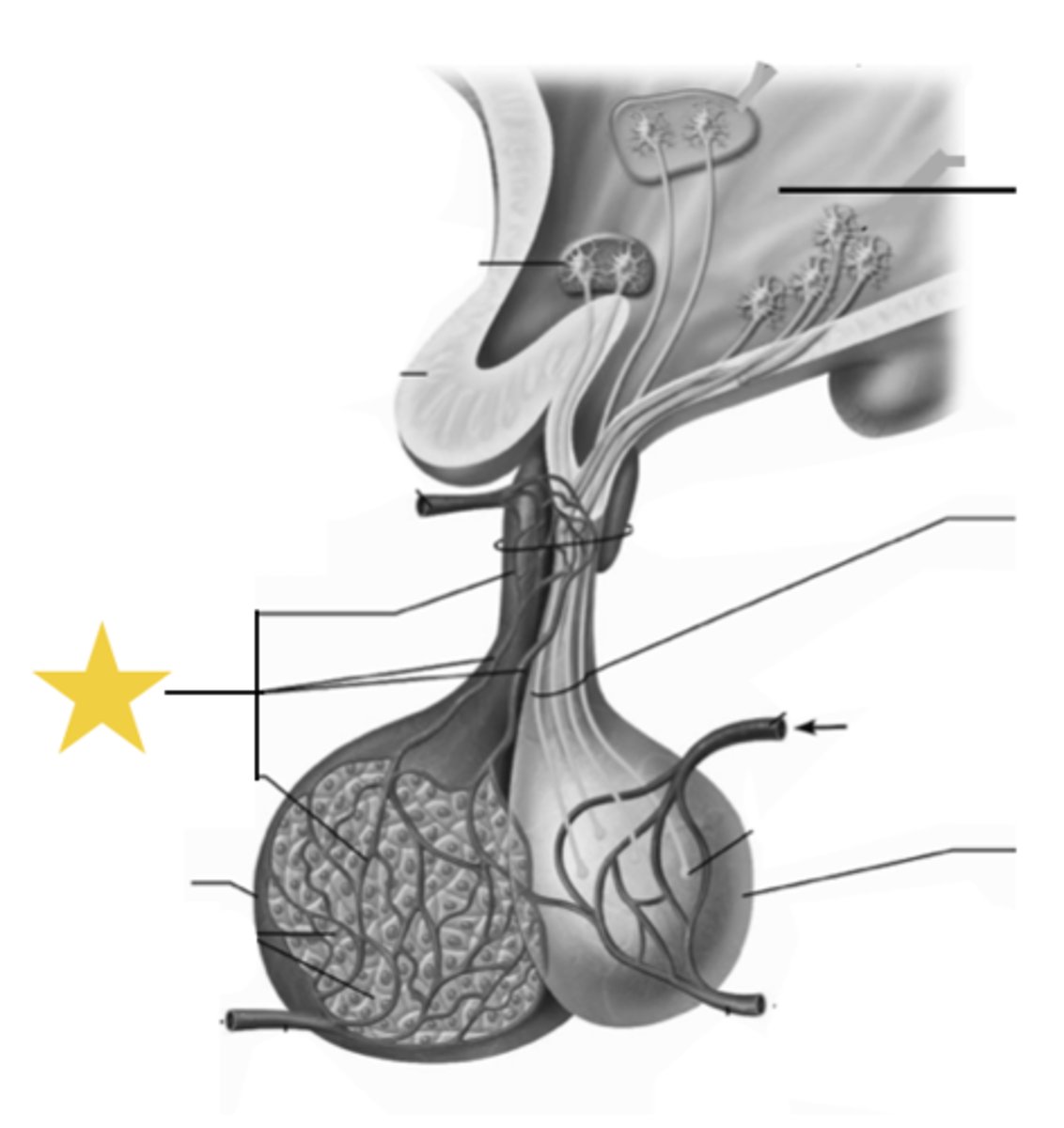
inferior hypophyseal artery
blood supply to the neurohypophysis
hypothalamic/hypophyseal portal system
function of ________________ ______ ________:
-Carries neuropeptides from median eminence to neurohypophysis where they can stimulate or inhibit hormone release
LH and FSH
gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) stimulates the release of ______ and ________
somatostatin
inhibits release of somatotropin (GH) and TSSH
dopamine
hormone that inhibits the release of prolactin
pars distalis
what part of anterior pituitary?
chromophils (acidophils/basophils) & chromophobes
what cells compose the pars distalis?
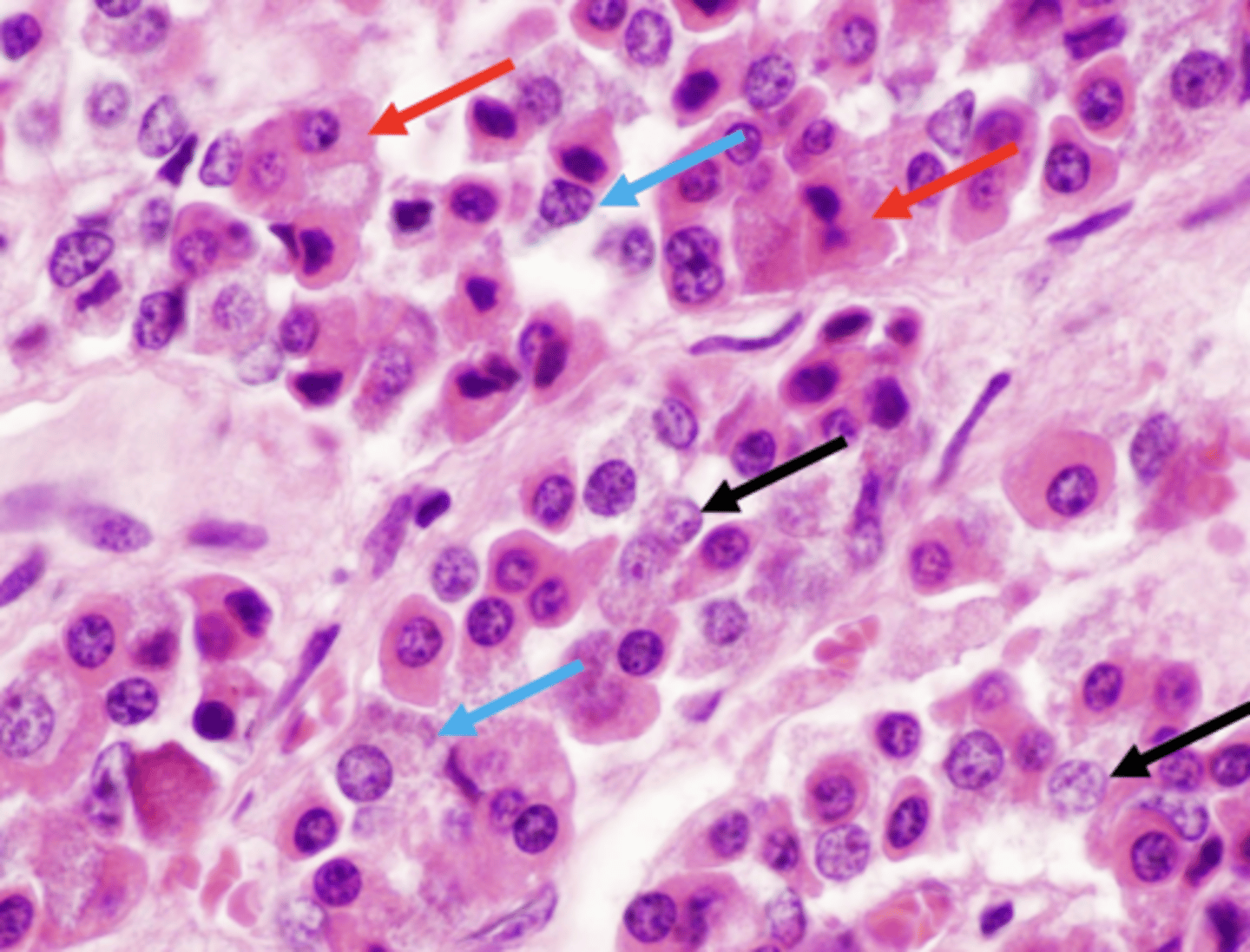
chromophils
secretory cells in which hormone is stored in cytoplasmic granules
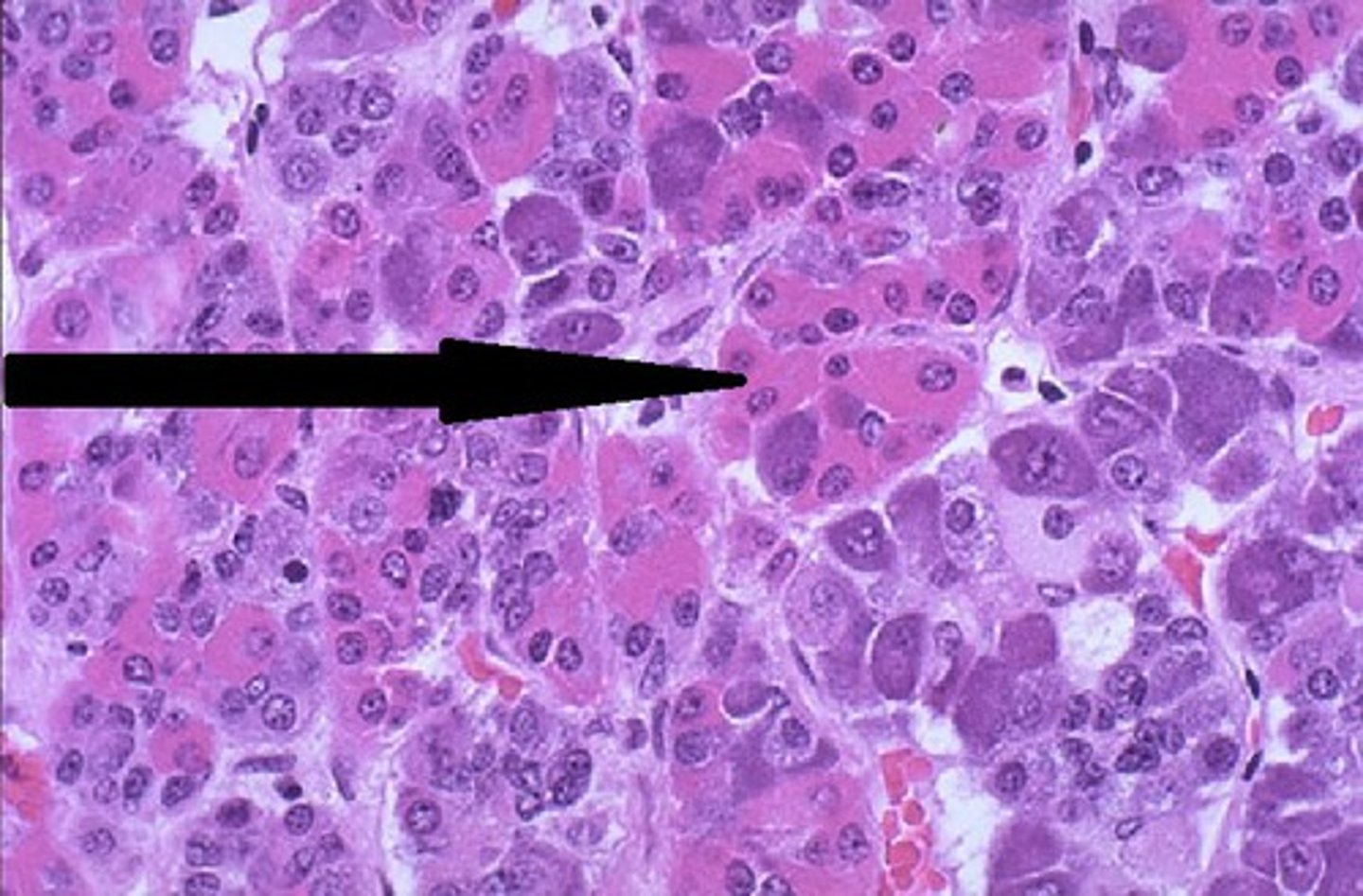
acidophils
darkly staining pink granule cells in pars distails
somatotrophs (growth hormone)
lactotrophs (PRL)
cells/hormones released from acidophils in pars distalis (2):
acidophils
ID A
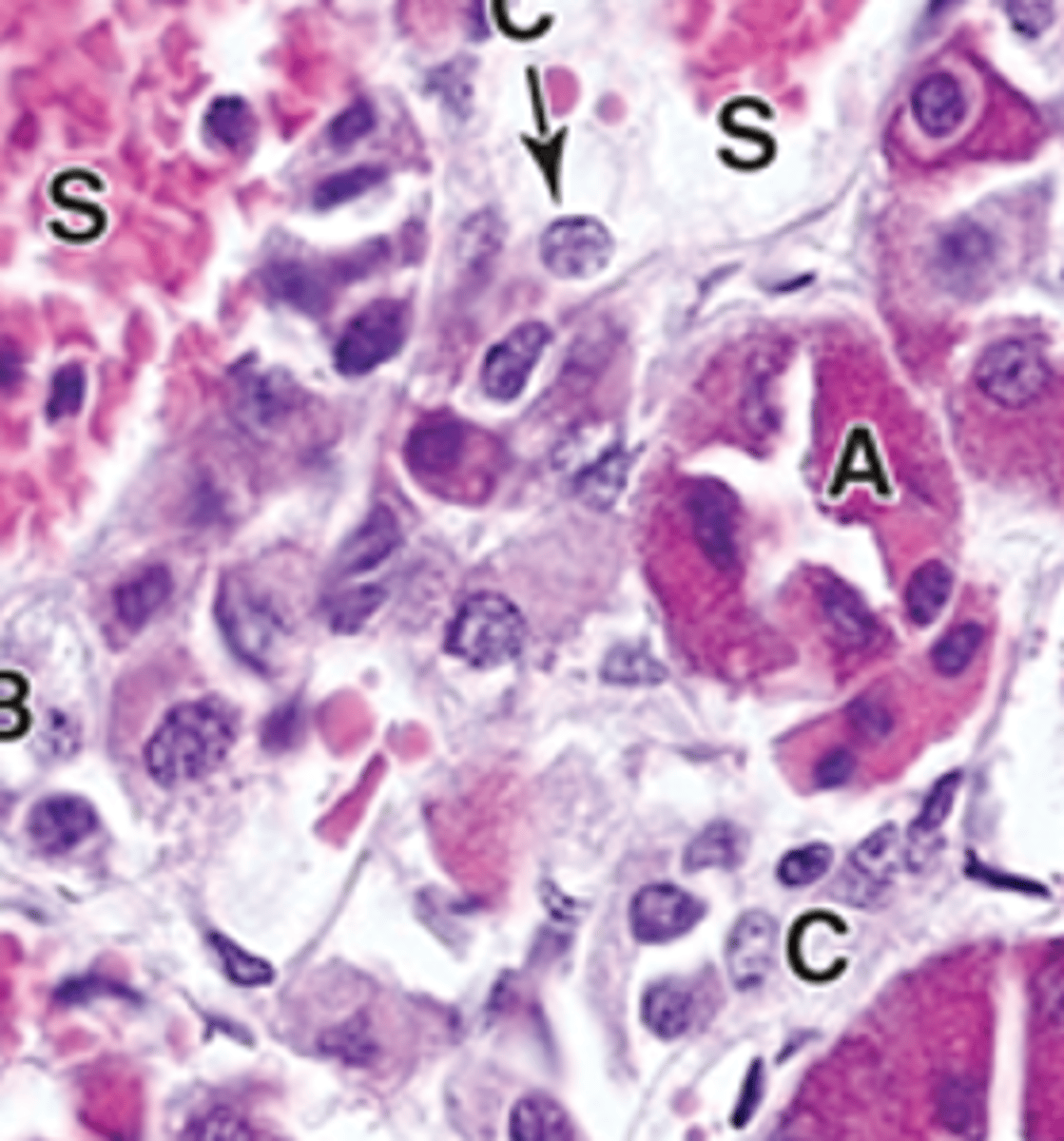
basophils
ID B
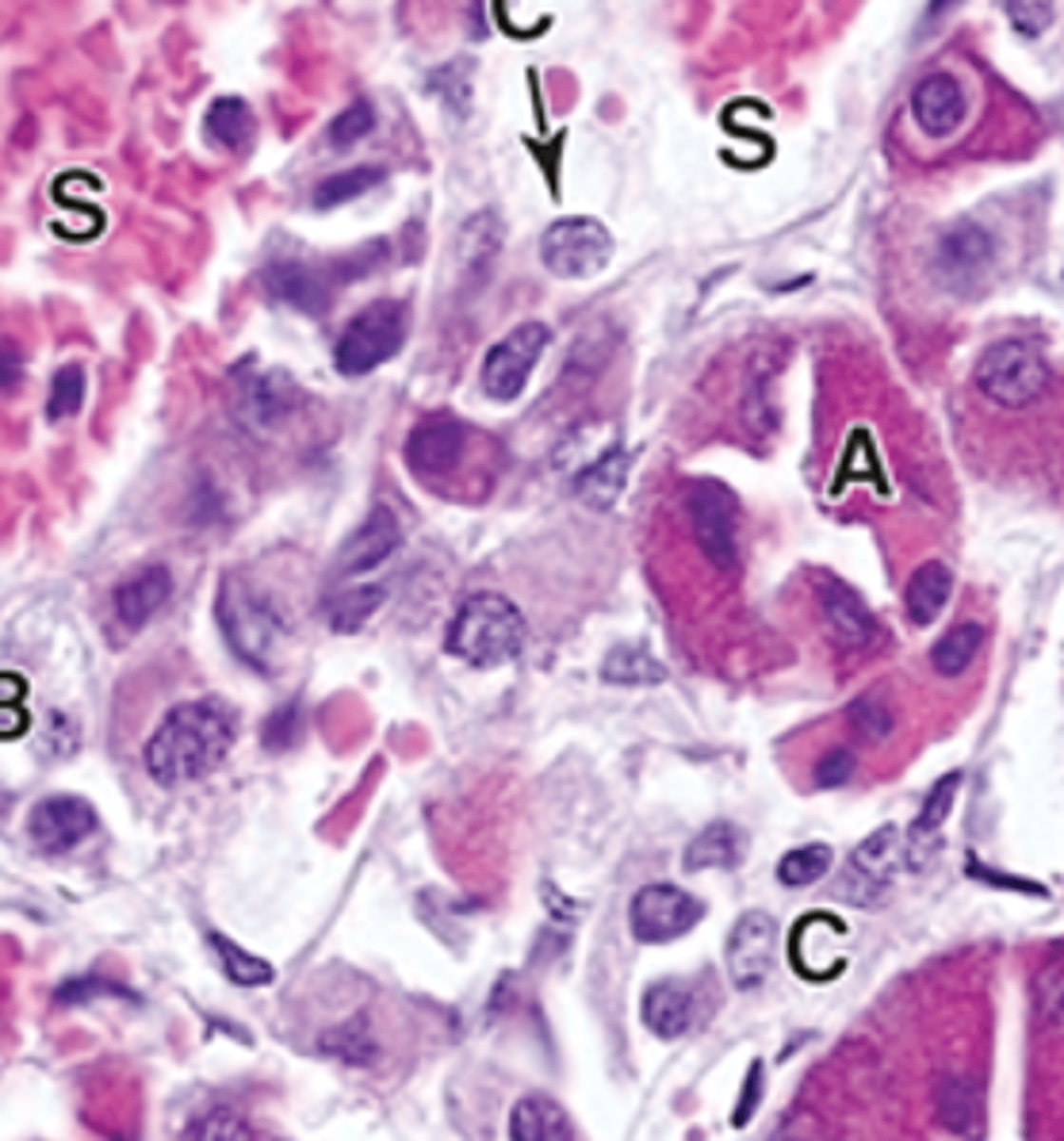
chromaphobes
ID C
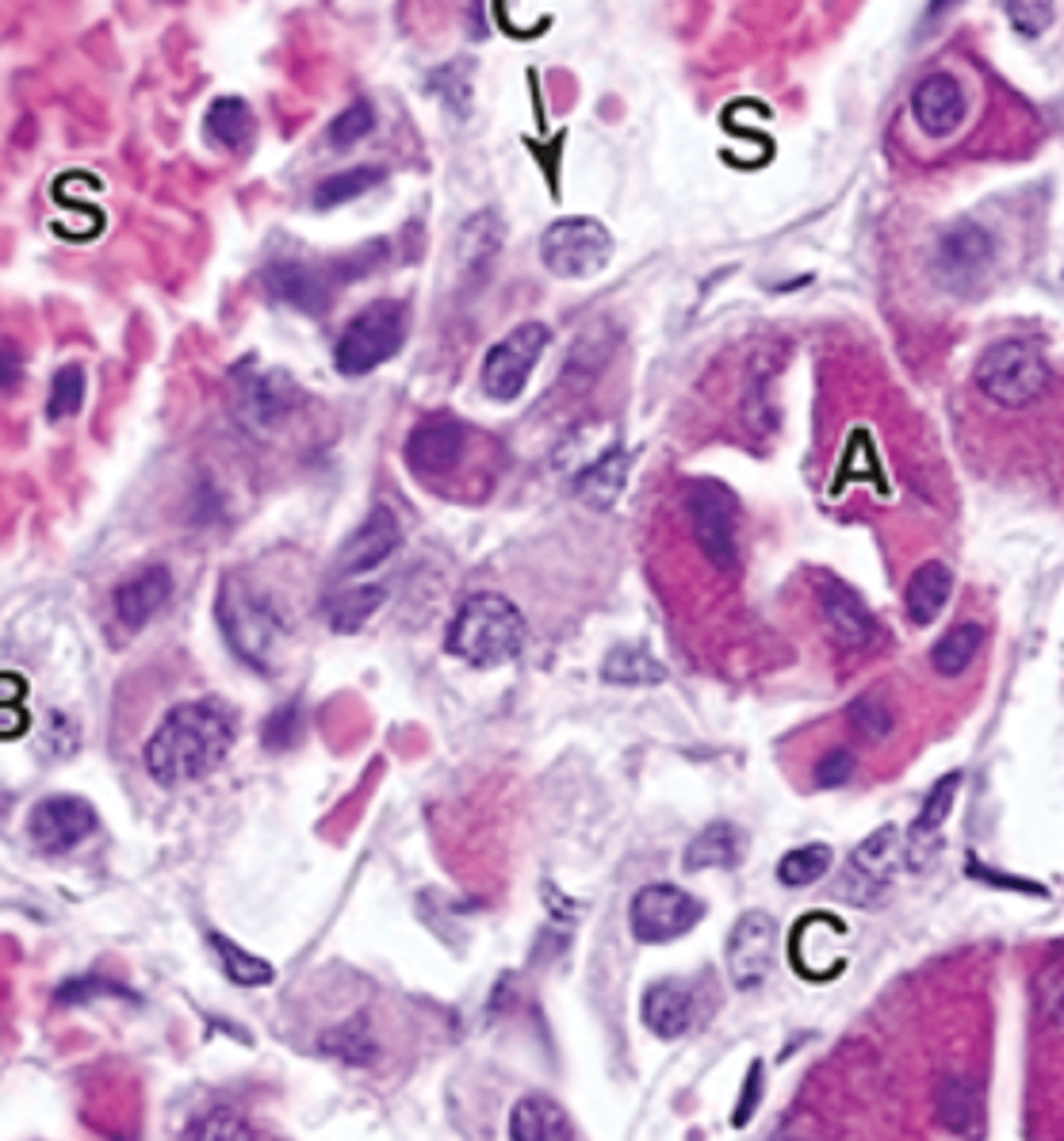
corticotrophs (ACTH)
gonadotrophs (FSH / LH)
thyrotrophs (TSH)
cells/hormones released from basophils in pars distalis
pro-piomelanocortin (gets cleaved to make ACTH)
what do corticotrophs secrete?
chromophobes
function of ________ in pars distalis:
include stem and undifferentiated progenitor cells or any degranulated cells
FSH and LH
these hormones act on gonads to stimulate development of gametes (sperm and oocyte)
ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone)
acts on the adrenal cortex to cause release of corticosteroids (cortisol)
pars intermedia
What part of the pituitary:
-posterior portion of the anterior pituitary
-in contact with neural tissue
-most active during fetal development
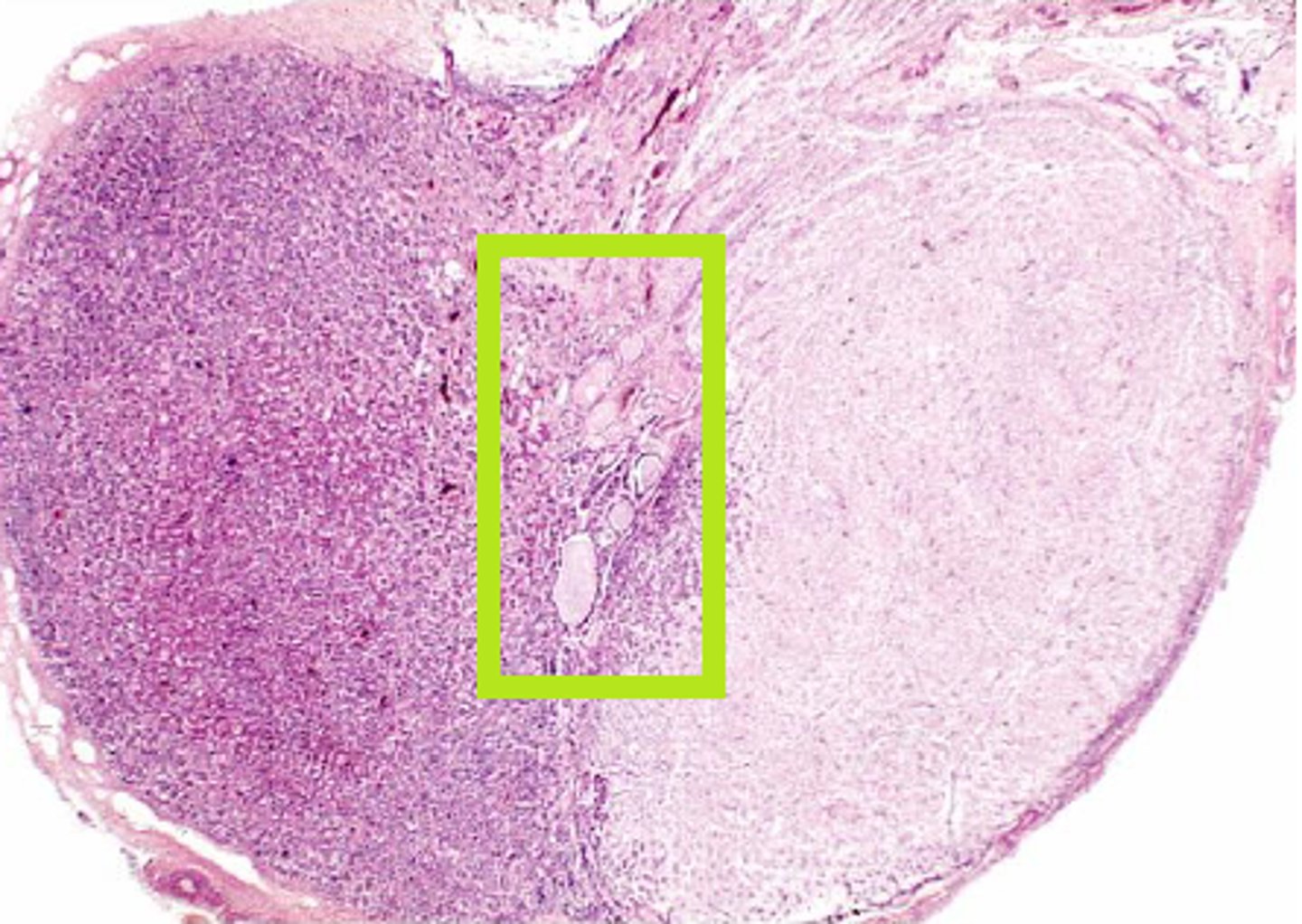
basophils, chromophobes, and colloid filled cysts (remnants of embryonic hypophyseal pouch)
components of pars intermedia
pars tuberalis
What part of the pituitary:
-part of anterior pituitary that wraps around the infundibulum
-composed of epithelial tissue within a thin wrapping of connective tissue
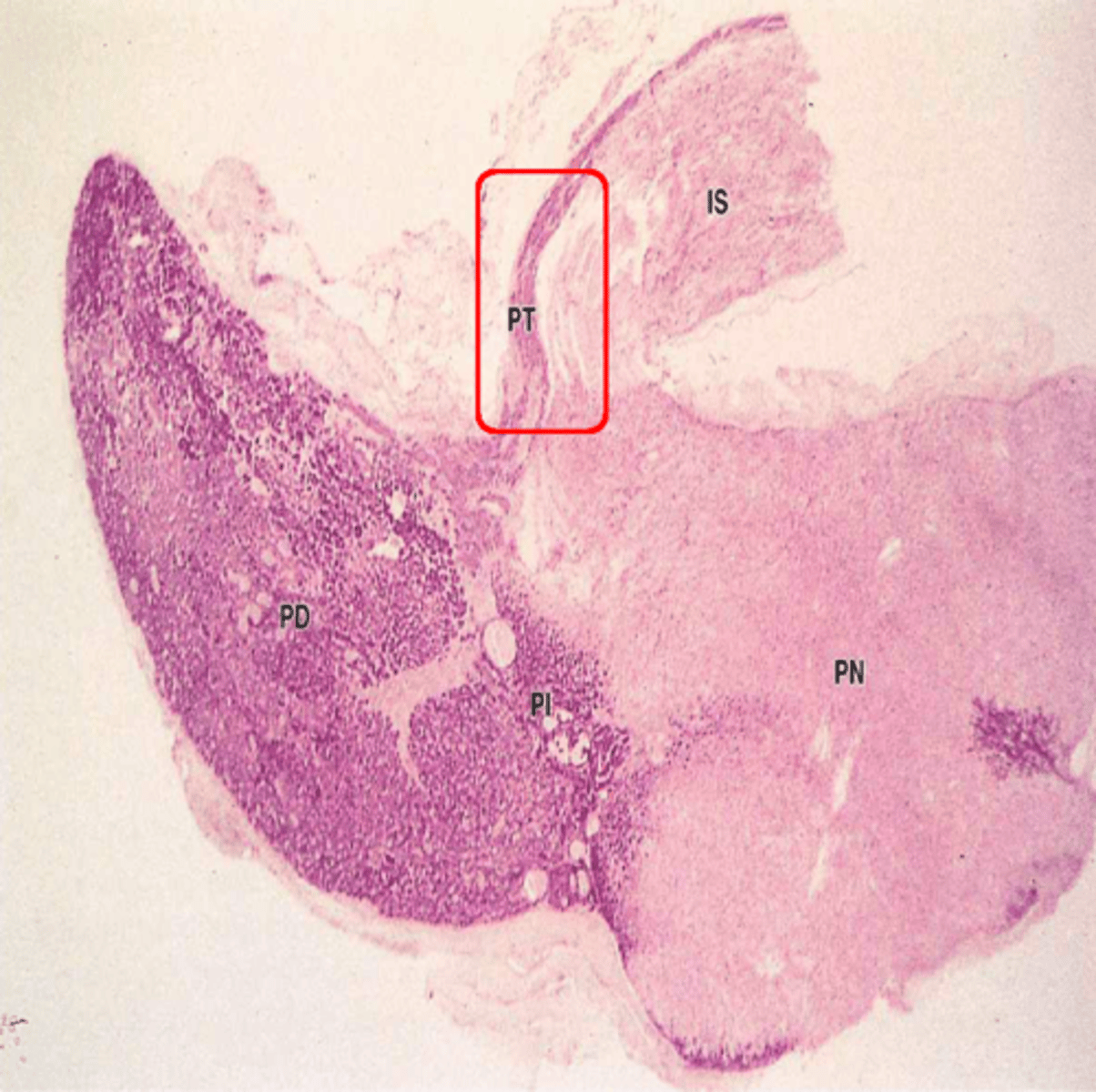
pituitary adenomas
tumors producing excessive numbers of functional acidophils or basophils
gigantism
adenomas involving somatotropic cells in children
acromegaly
adenomas involving somatotropic cells in adults
posterior pituitary
this part of pituitary does not contain the cells that synthesize its hormones
-ADH and oxytocin come from nuclei from hypothalamus
ADH and oxytocin
hormones released from posterior pituitary
pars nervosa
What part of the pituitary:
made up of modified glial cells and axons that have descended from the hypothalamus
herring bodies
eosinophilic neurosecretory bodies in the terminal ends of axons in the pars nervosa
-contain granules of ADH or oxytocin bound to neurophysin I or II proteins--> protein cleaved when stimulated
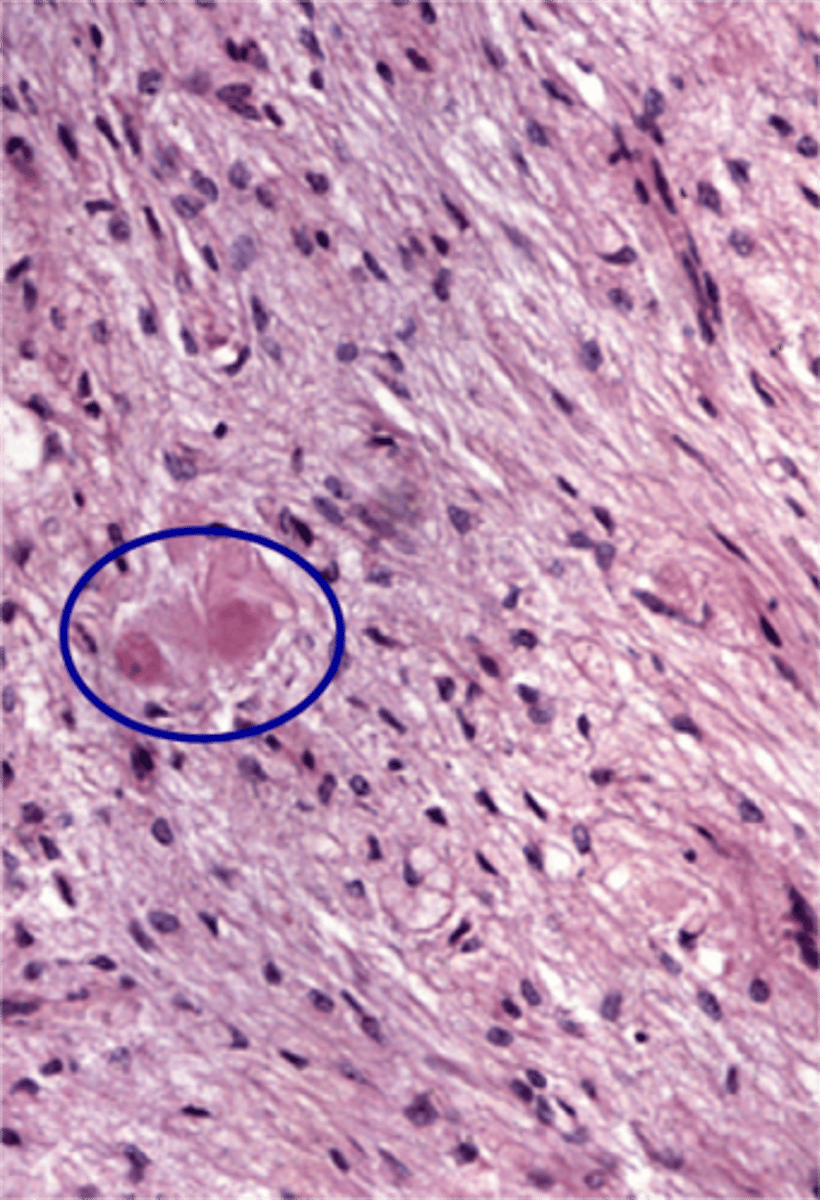
neurosecretory (herring) bodies and pituicytes
what makes up the pars nervosa?
foregut endoderm
origin of the thyroid gland
Thyroxine/tetraiodothyronine (T4) , tri-iodothyronine (T3), and calcitonin
hormones synthesized by the thyroid gland
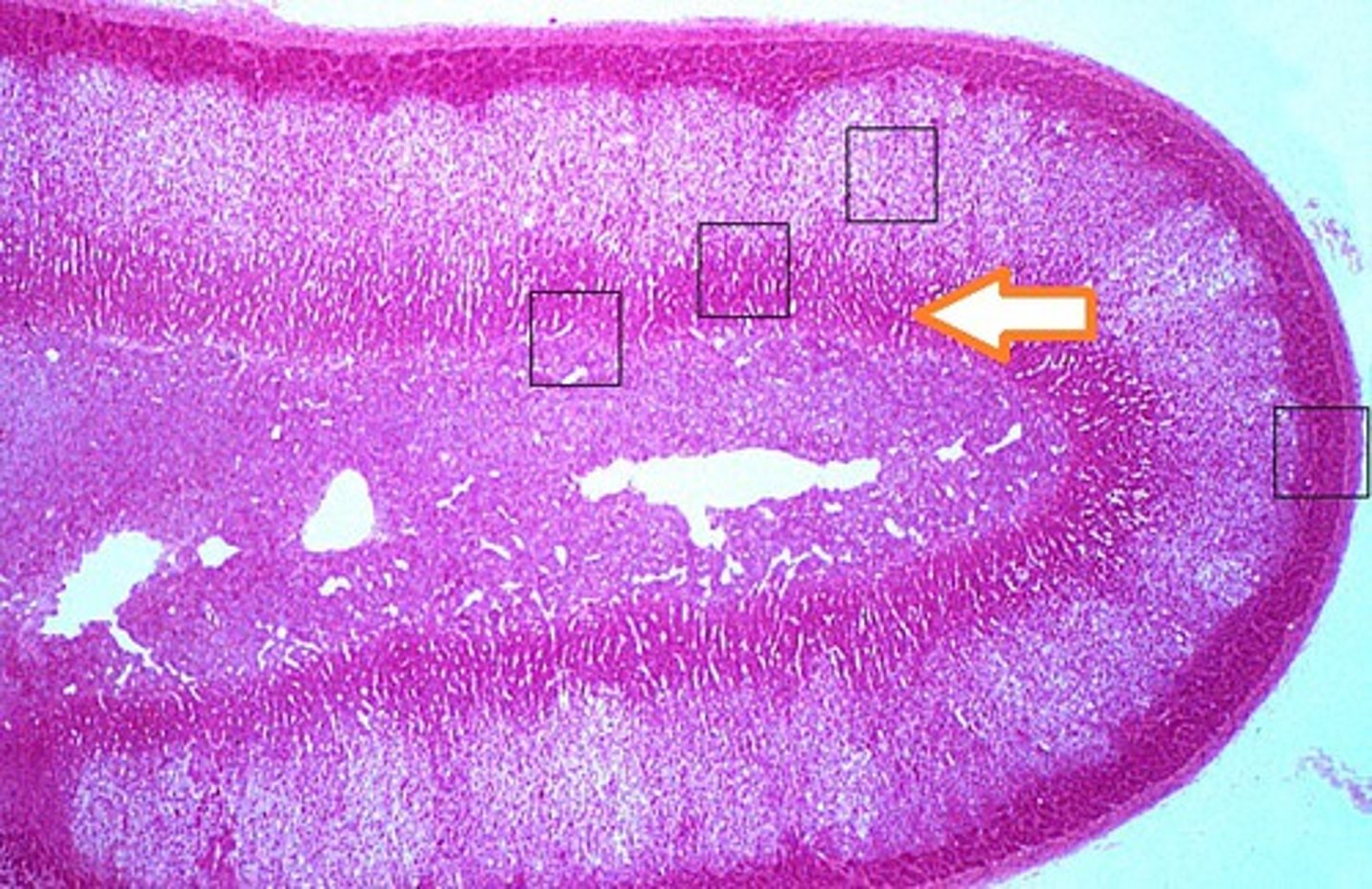
thyroid gland
What structure:
-parenchyma composed of rounded follicles line by simple cuboidal/columnar epithelium , containing gelatinous acidophilic colloid
Thyroglobulin
colloid in thyroid glands contain this, a precursor for active thyroid hormones
thyroid gland
Only endocrine gland in which a significant portion of secretory product is stored (outside of cells)
TSH from the anterior pituitary
what stimulates thyrocytes?
parafollicular C cells
What structure:
-cells in the thyroid gland found within the basal lamina of follicular epithelium or as clusters; stains less strongly than follicular cells
-secrete calcitonin
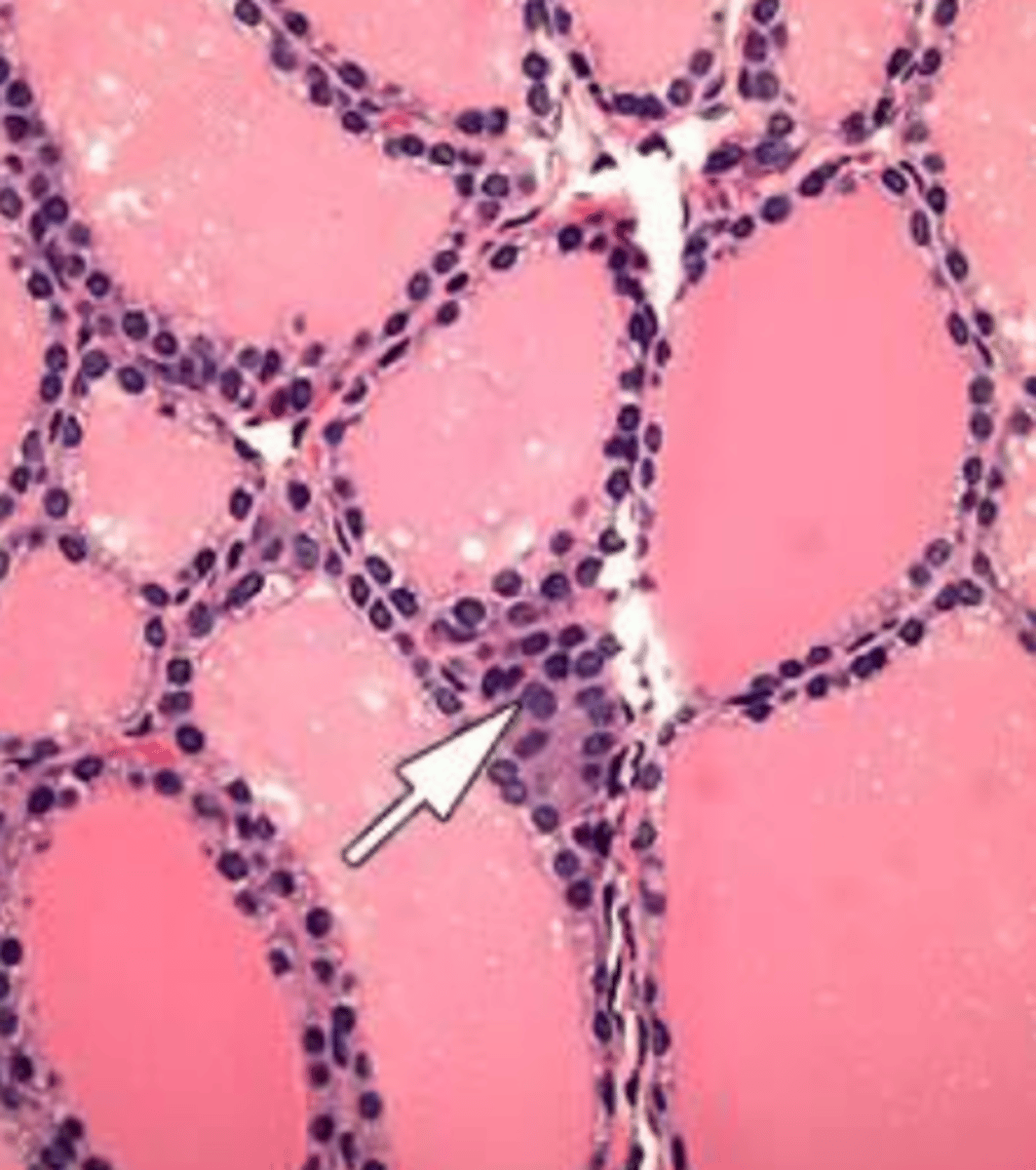
calcitonin
function of _______:
-inhibit osteoclast activity when triggered by high calcium
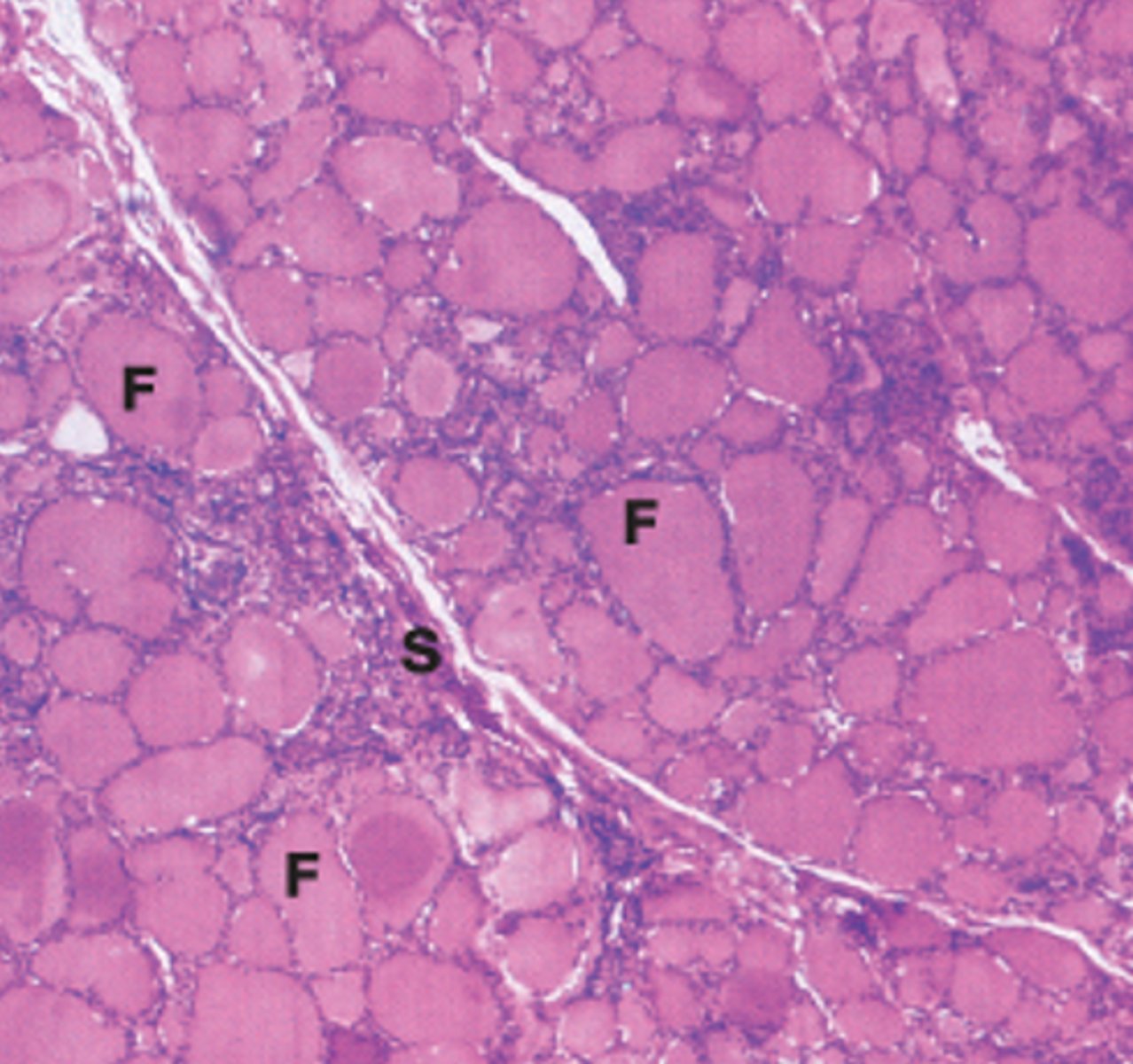
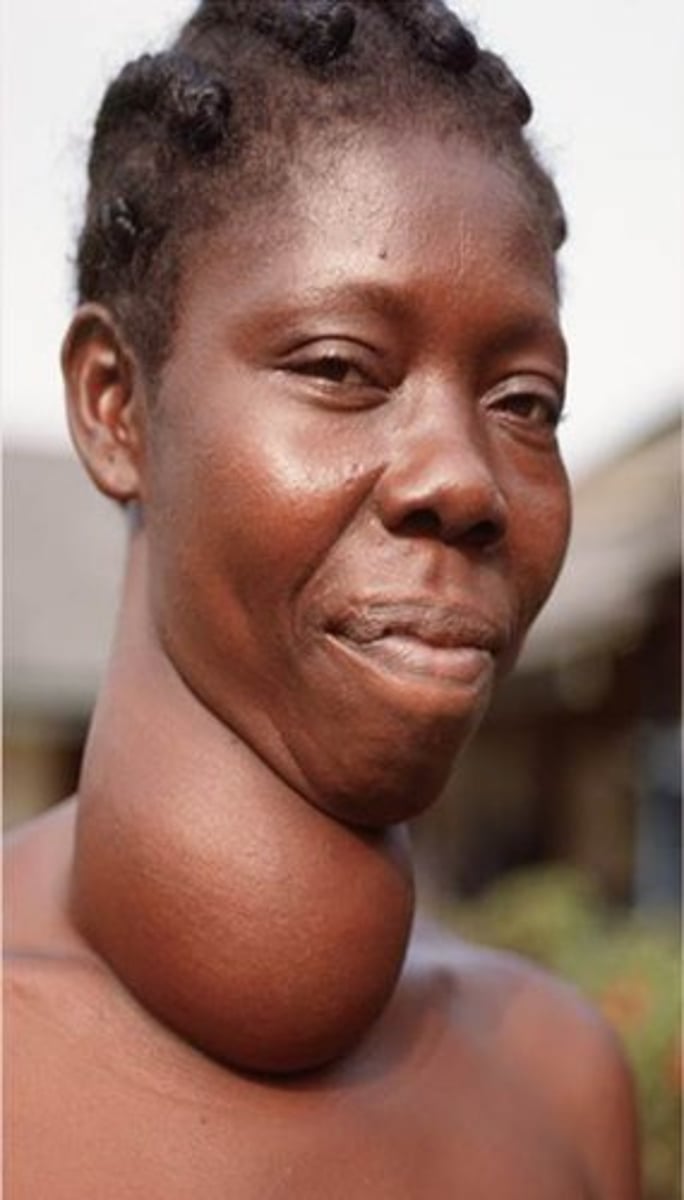
iodine
_____ deficiency inhibits thyroid hormone production, causing excess TSH----> excessive growth of thyroid follicles causing goiter
glycoprotein thyroglobulin, precursors for T3 and T4
colloid within thyroid gland contains
iodine
______ is essential for the production of thyroid hormone, as iodination of tyrosol residues allows formation of pre T3 and T4
Graves disease
autoimmune disorder in which antibodies produce chronic stimulation of the follicular cells and release of thyroid hormones (hyperthyroidism)
thyroiditis
inflammation of the thyroid gland resutling in hypothyroidism
Hyperthyroidism
Symptoms of _______:
-Nervousness, weight loss despite increased appetite, excessive sweating and heat intolerance, palpitations, frequent bowel movements, muscular weakness of the proximal type and tremor
hypothyroidism
Symptoms of _______:
Fatigue, lethargy. Modest weight gain with anorexia. Dry, coarse skin and cold intolerance. Swelling of face, hands, and legs. Constipation. Weakness, muscle cramps, arthralgias, paresthesias, impaired memory and hearing.
inferior thyroid arteries
vasculature of parathyroid glands arise from
4th pouch
origin of superior parathyroid glands
3rd pouch
origin of inferior parathyroid glands
chief cells release PTH which increases serum calcium levels
function of parathyroid glands
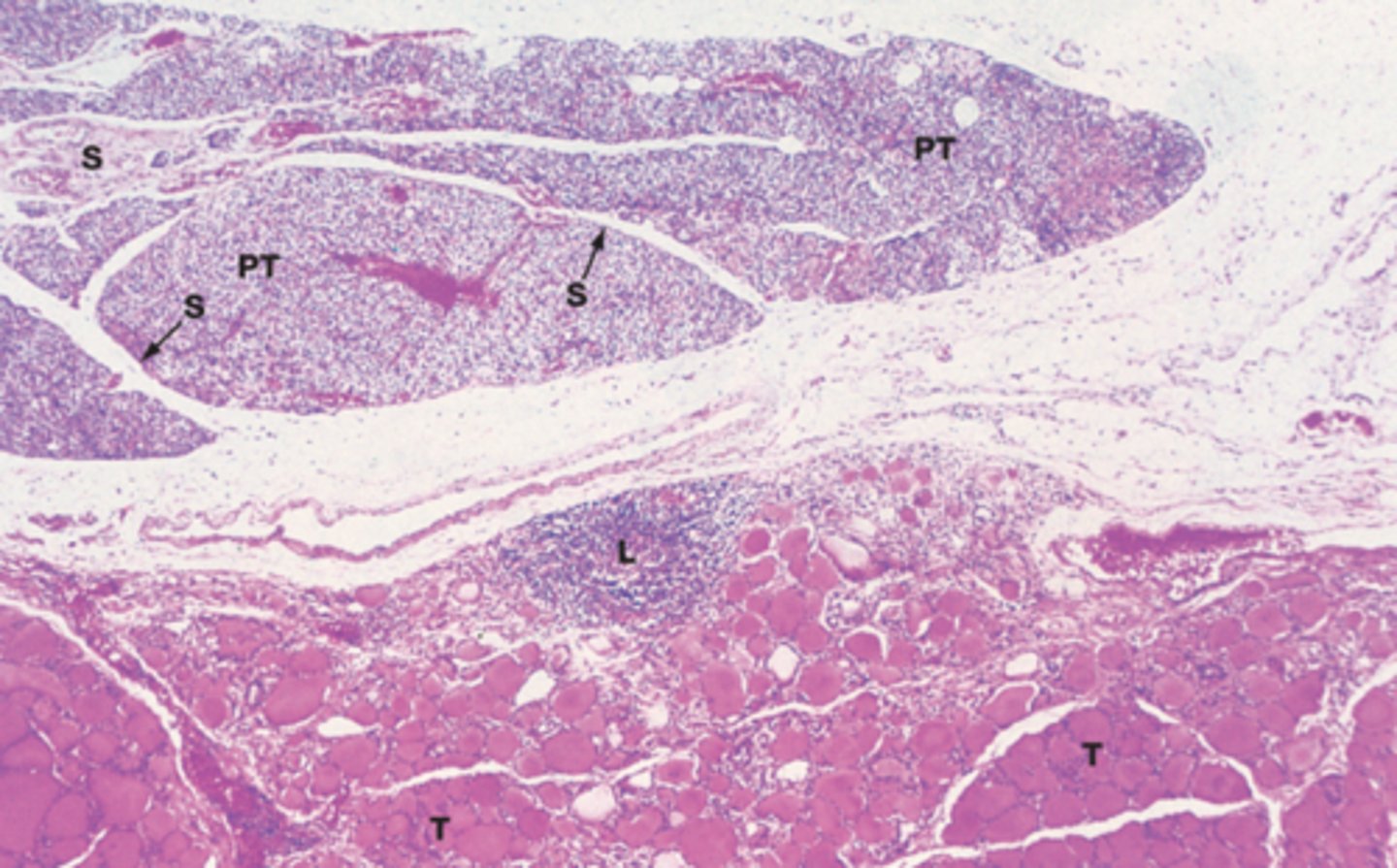
parathyroid glands
What structure:
histology: thin capsule with trabeculae that divide parenchyma into lobules
-lots of capillaries
principal (chief) cells
oxyphil cells
cell types of parathyroid glands
principal chief cells
What cell of the parathyroid gland:
-most abundant
-small, light staining pale cytoplasm and central nuclei
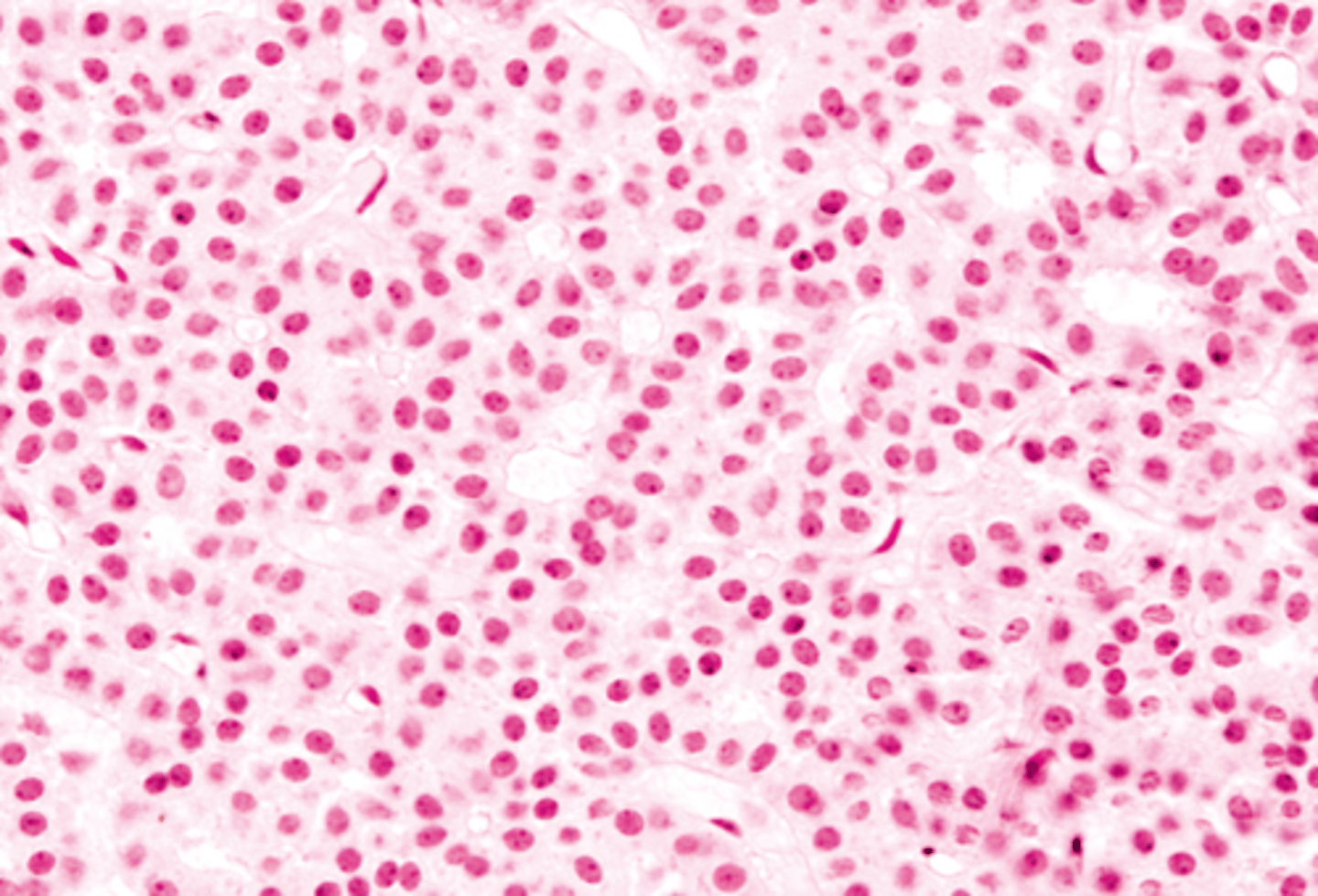
oxyphil cellls
What cell of the parathyroid gland:
-larger
-have abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm, contain many mitochondria
-unknown function, more abundant in old people
Osteoblasts produce osteoclast-stimulating factor to increase osteoclasts and Ca+
Distal convoluted tubules: Stimulates CA reabsorption and inhibits phosphate reabsorption
Increases Ca absorption in small intestine by stimulating vitamin D activation
targets of PTH
hypoparathyroidism
In cases of ___________:
-bone become more mineralized and denser and striated muscle exhibits abnormal contractions due to inadequate calcium
-tetany, weakness, HA, prolonged QT
hyperparathyroidism
In cases of ___________:
-stimulates osteoclast number and activity, leading to increased levels of blood calcium
-renala stones, diseases of bones/bone pain, psychic moans, peptic ulcers
neural crest
embryonic origins of adrenal medulla
mesoderm
embryonic origins of adrenal cortex
Mineralocorticoids, Glucocorticoids, Weak androgens
adrenal cortex secretes:
NE and epinephrine
adrenal medulla secretes:
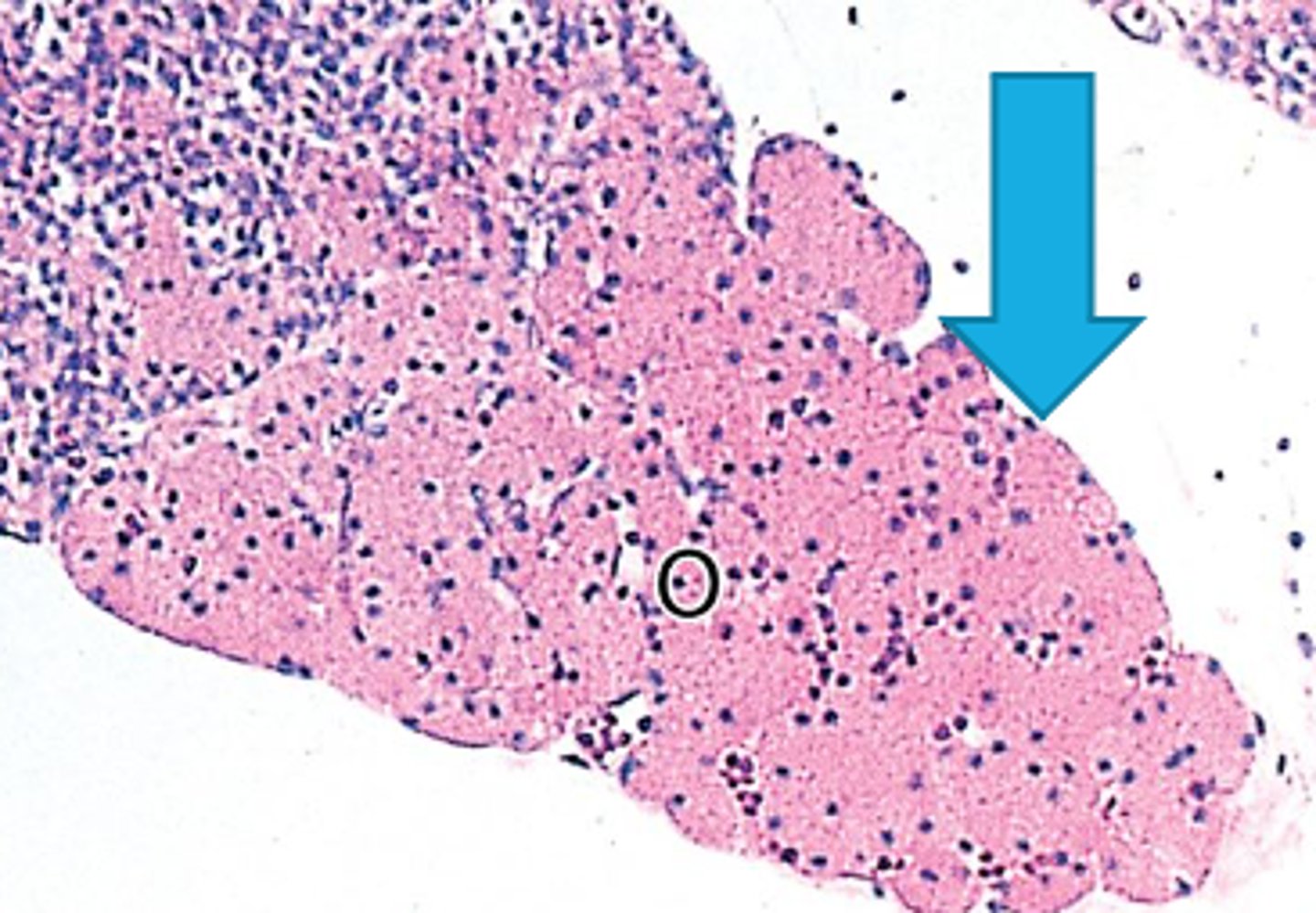
zona glomerulosa
What zone of the adrenal cortex:
-located immediately inside the capsule
-composed of columnar cells in spherical/ovoid groups
zona glomerulosa
What zone of the adrenal cortex:
-makes mineralcorticoids (aldosterone)
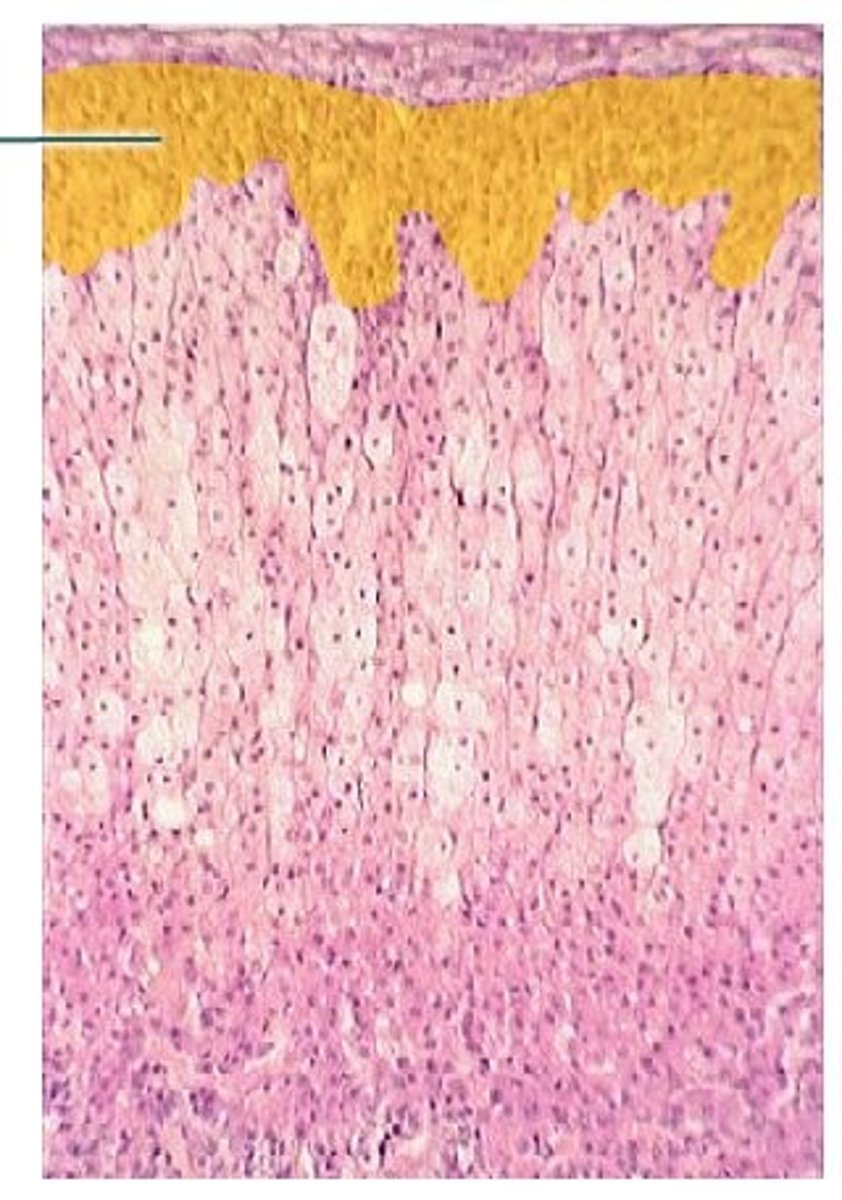
zona fasciculata
What zone of the adrenal cortex:
-middle layer
-composed of basophilic cells in parallel columns sepaarated by capillaries
zona fasciculata
What zone of the adrenal cortex:
-makes glucocorticoiods (cortisol)
-affects carbohydrate metabolism by stimulating gluconeogenesis and glycogen synthesis; suppresses immune function, controlled by ACTH
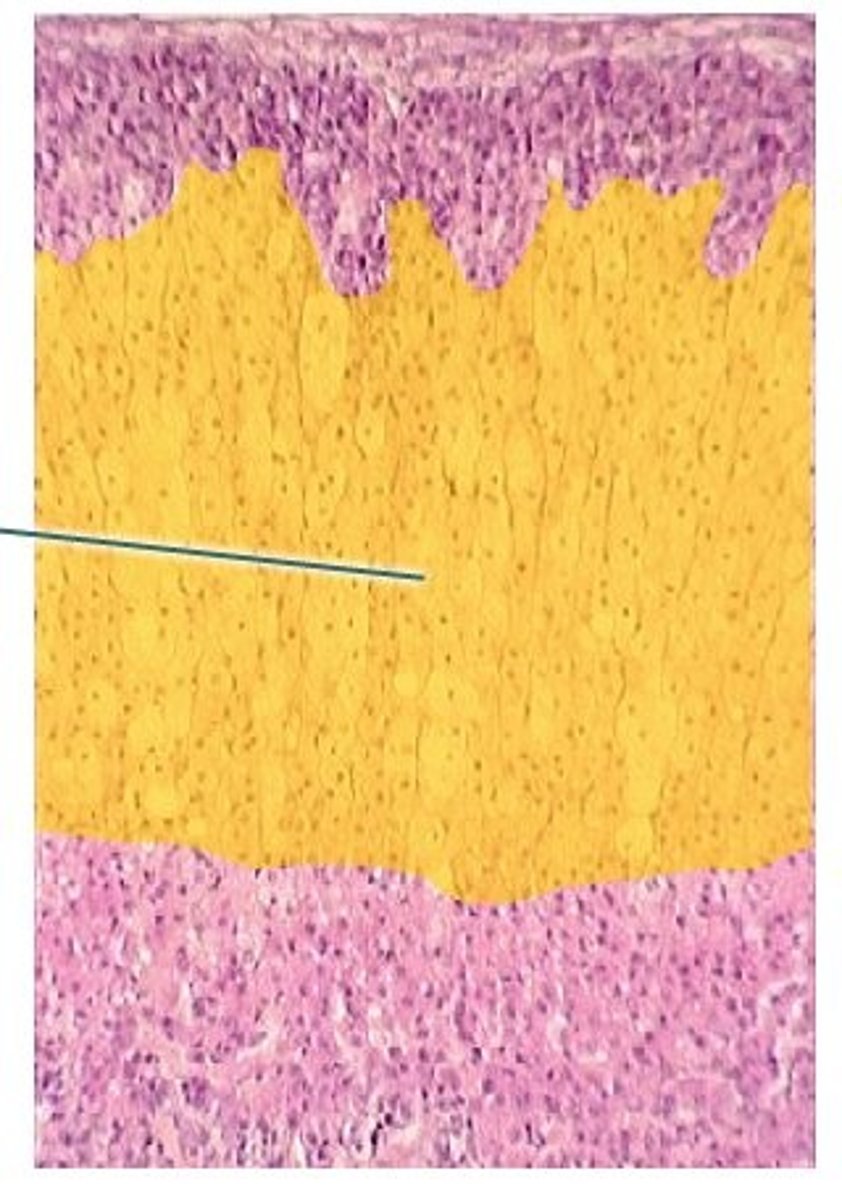
zona reticularis
What zone of the adrenal cortex:
-innermost layer of adrenal cortex
-composed of branching/anastomosing cords of darker staining small cells
zona reticularis
What zone of the adrenal cortex:
-makes weak androgens
-stimulated by ACTH
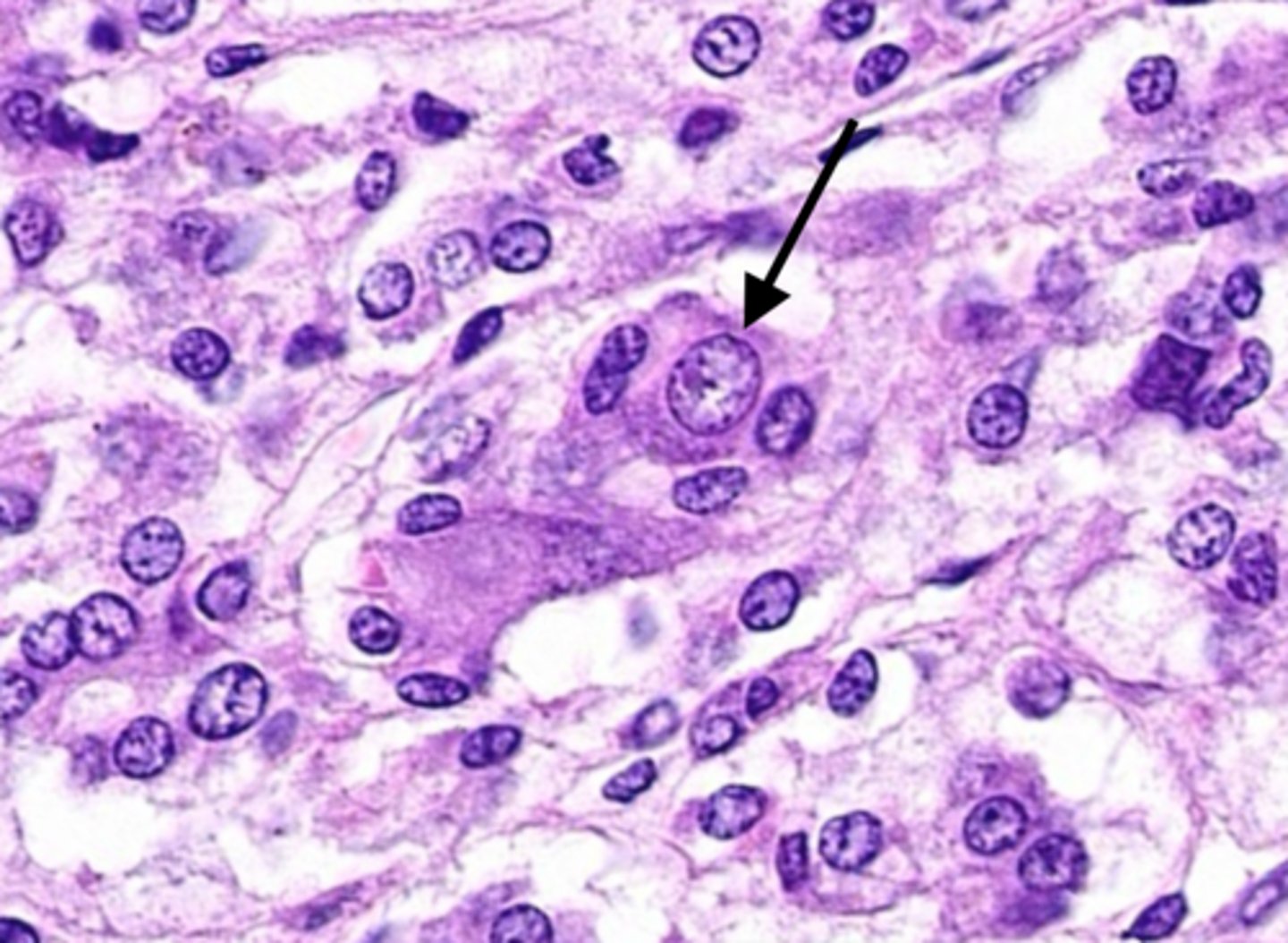
chromaffin cells
cells of the adrenal medulla
-secrete mostlyl epi, NE
norepinephrine
which catechholamine:
-Constricts vessels in GI system and skin, increases blood flow to heart, muscles and brain
-Elevates blood glucose
neuroectoderm (in the posterior wall of the 3rd ventricle)
origin of the pineal gland
pinealocytes
cells producing melatonin, low moleculaara weight tryptophan derivative
pituitary adenomas
-benign neoplasms of the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland
-extra-axial tumors (external to brain parenchyma)
pituitary adenomas
most frequent primary intracranial neoplasm
30-50 years
avg age of presentation of pituitary adenomas
Prolactinoma
most frequent type of pituitary adenoma
nonfunctioning adenoma
2nd most frequent type of pituitary adenoma
adenomas that secrete FSH, LH, and TSH
most rare pituitary adenomas
mass effect
effect of local _____ ______ of pituitary adenomas
-bitemporal heminaopsia
-cavernous sinus syndrome (LOF of eye muscles)
-elevated intracranial pressure
stalk section effect
effect of pituitary adenoma that distorts the pituitary stalk---> reduction in most pituitary hormones due to lack of communication with hypothalamus
reduce most of the pituitary hormones but will give rise to hyperprolactinemia secondary to lack of inhibition (decreased dopamine)
effect of stalk section effect
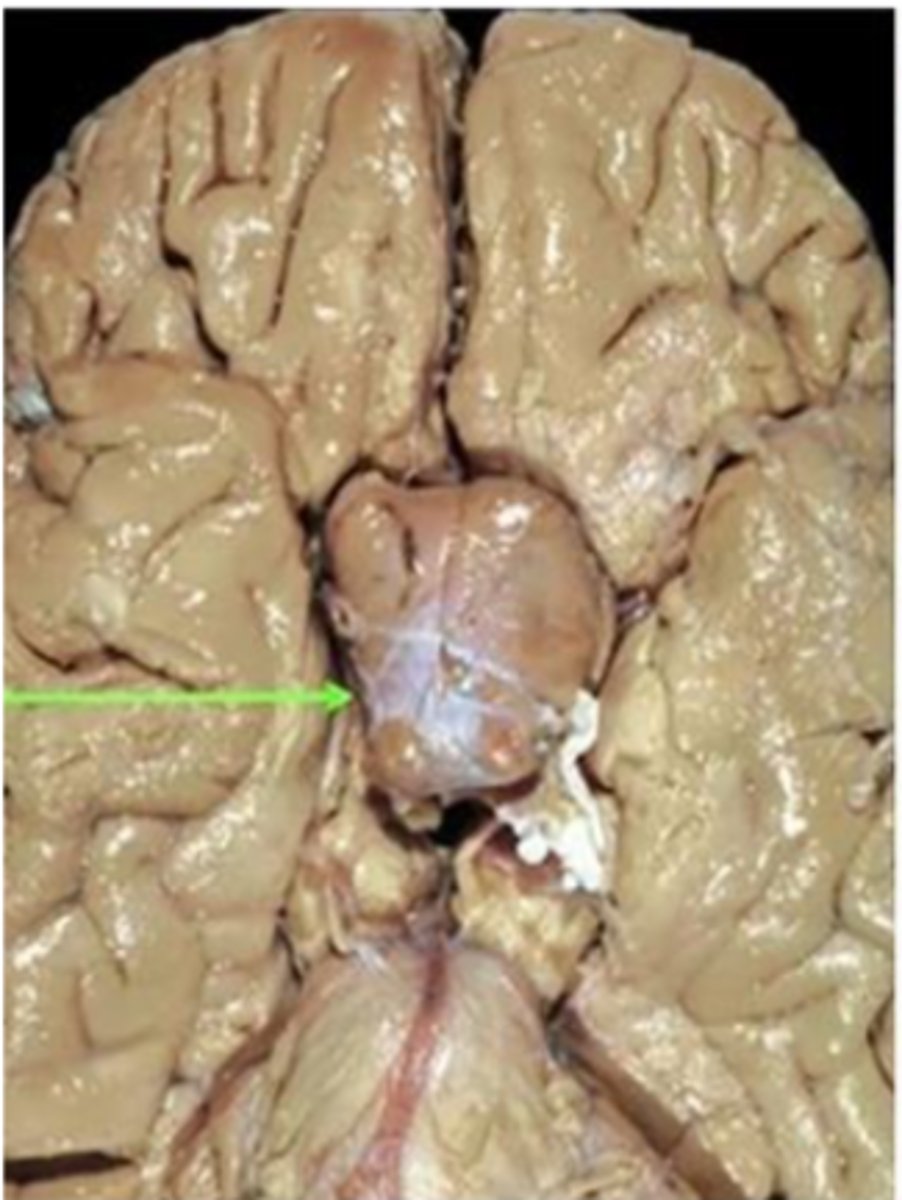
pituitary adenoma
gross pathology of _______ _________
-tan-to purple in color and creamy in texture
-macro or micro
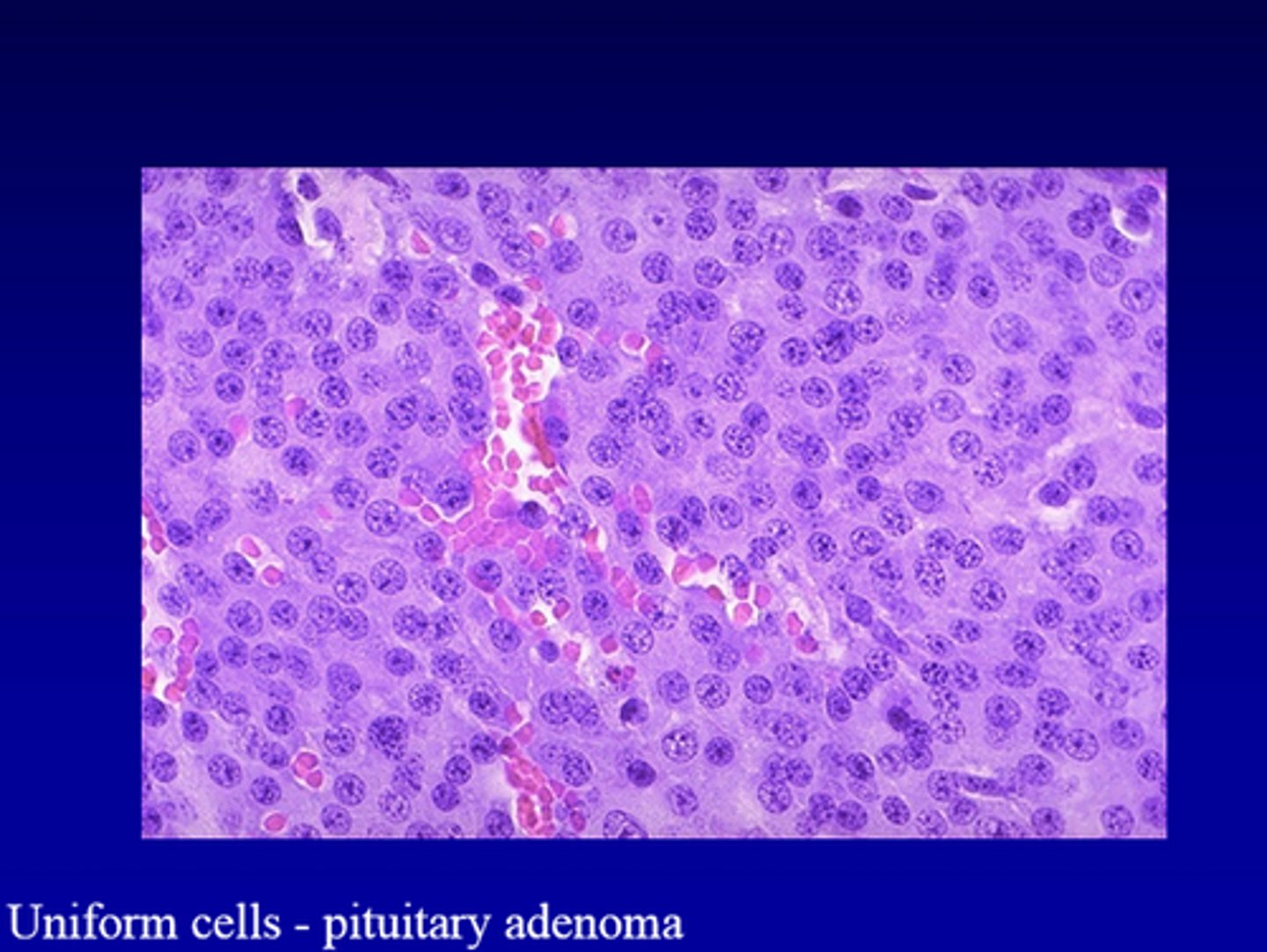
pituitary adenoma
histology of _______ _________
-uniform, polygonal cells arranged in thin cords and ribbons; monotonous appearance of small round cells
-see acidophils, basophils, and chromophobes
GNAS1
gene associated with somatotroph adenoma
-codes for alpha subunit--->cAMP activated PKA----> excessive GH secretion
USP8
gene associated with corticotroph adenomas
Psammoma bodies
distinct histological finding of prolactinomas
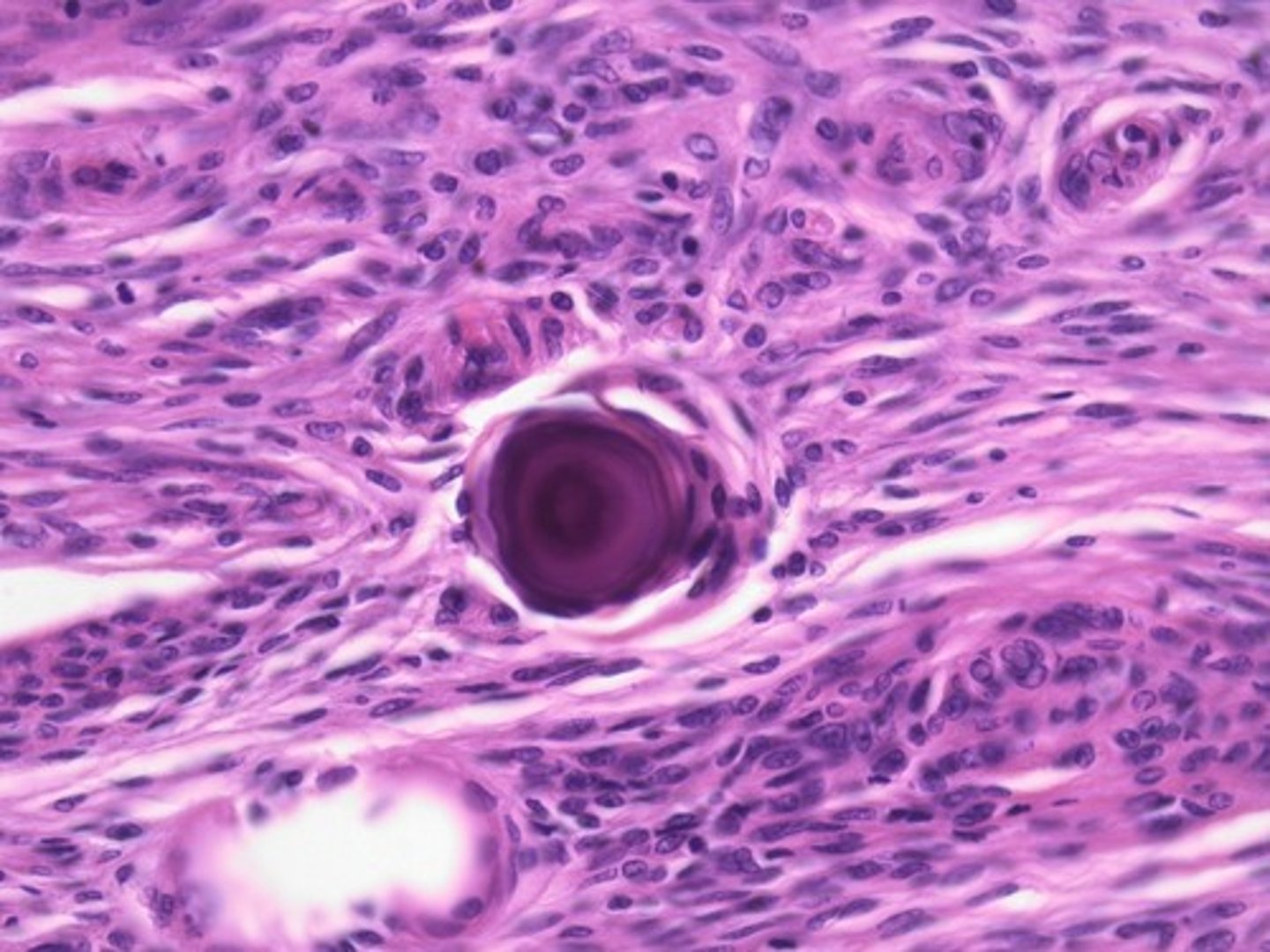
prolactinomas
electron microscopy findings of _______:
-abundant rough ER, prominent golgi complel, but sparse secretory granules
amenorrhea, galactorrhea, and infertility
effects of prolactinoma in women:
loss of libido, erectile dysfunction
effects of prolactinoma in men
-densely granulated (acidophilic)
-sparsely granulated (chromophobe)
types of somatotroph adenoma