Biology Unit 1 and 2 Exam Prep (based of learning goals)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 11:31 PM on 8/20/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
1
New cards
cell membrane(plasma membrane)
phospholipid bilayer with embedded protein molecules that serves to control what substances enter and exit a cell
2
New cards
protein channels
proteins in the membrane whose role it is to pass molecules that cannot go through the membrane
3
New cards
Phospholipids
A molecule that is a constituent of the inner bilayer of biological membranes, having a polar, hydrophilic head and a nonpolar, hydrophobic tail.
4
New cards
Cholesterol
A type of fat made by the body from saturated fat; a minor part of fat in foods.
5
New cards
Glycoproteins
Membrane carbohydrates that are covalently bonded to proteins.
6
New cards
Passive Transport (Diffusion)
the movement of substances across a cell membrane without the use of energy by the cell, with the concentration gradient
7
New cards
active transport
Energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration difference
8
New cards
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
9
New cards
Endcytosis
a form of active transport that usually moves large polar molecules that cannot pass through the hydrophobic cell membrane into the cell
10
New cards
Phagocytosis
A type of endocytosis in which a cell engulfs large particles or whole cells
11
New cards
surface area to volume ratio
a variable that decreases as cells grow, so that it sets a limit to the size of cells.
12
New cards
prokaryotic cell
A type of cell lacking a membrane-enclosed nucleus and membrane-enclosed organelles; found only in the domains Bacteria and Archaea.
13
New cards
Eukaryotic cells
Larger, complex, with nucleus, membrane bound organelles, DNA tightly wrapped around histone proteins in chromosomes, cellulose in plant cell walls.
14
New cards
DORA C (how to differentiate between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells)
DNA, (membrane bound) Organelles, Reproduction, Average size, Cellularism
15
New cards
Monosaccharides
Single sugar molecules
16
New cards
Disaccharide
A double sugar, consisting of two monosaccharides joined by dehydration synthesis.
17
New cards
Polysaccharides
Carbohydrates that are made up of more than two monosaccharides
18
New cards
Urea (CO(NH2)2)
a form of ammonia that is produced in the liver. Excreted by all mammals, some fish and most amphibians. It is 100, 000 times less toxic than ammonia
19
New cards
Amomonia
a small highly toxic molecule that is excreted with no energy cost by aquatic invertebrates and most fish.
20
New cards
Uric Acid (C5H4N4O3)
Converted from ammonia and made from NH3 at high energy cost. Excreted as a white paste by birds, insects, land snails, and some reptiles. It has a very low solubility and virtually non-toxic.
21
New cards
metabolic heat
energy released within an organism during the process of cellular respiration
22
New cards
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
System of internal membranes within the cytoplasm. Membranes are rough due to the presence of ribosomes. functions in transport of substances such as proteins within the cytoplasm
23
New cards
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
An endomembrane system where lipids are synthesized, calcium levels are regulated, and toxic substances are broken down.
24
New cards
Chloroplast
An organelle found in plant and algae cells where photosynthesis occurs
25
New cards
Mitochondria
site of cellular respiration
26
New cards
Plastids
pigments, tannins, and polyphenols
27
New cards
Lysosomes
the removal of cellular products and waste
28
New cards
folding membrane in the mitochondria
increases surface area for enzyme controlled reactions
29
New cards
what factors can affect reaction rate of enzymes
temperature, pH, the presence of inhibitors, and the concentrations of reactants and products.
30
New cards
ATP energy
adenosine triphosphate
31
New cards
Photosynthesis
enzyme-controlled series of chemical reactions that occurs in the chloroplast in plant cells and uses light energy to synthesise organic compounds (glucose), and the overall process can be summarised in a balanced chemical equation
32
New cards
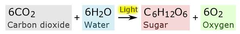
Phtosynthesis equation
6CO2 + 6H2O ------> C6H12O6 + 6O2
33
New cards
light-dependent reactions
reactions of photosynthesis that use energy from light to produce ATP and NADPH
34
New cards
Light Independent Reactions (Calvin Cycle)
set of reactions in photosynthesis that do not require light; energy from ATP and NADPH is used to build high-energy compounds such as sugar; also called the Calvin cycle
35
New cards
relationship between light-dependent reactions and light independent reactions
The light-dependent reactions pass electrons through an electron transport chain to the light-independent reactions. The light-dependent reactions produce carbon dioxide, which is then used by the light-independent reactions.
36
New cards
Glycolysis
the breakdown of glucose by enzymes, releasing energy and pyruvic acid. requires oxygen
37
New cards
Krebs cycle
second stage of cellular respiration, in which pyruvic acid is broken down into carbon dioxide in a series of energy-extracting reactions. requires oxygen
38
New cards
electron transport chain
A sequence of electron carrier molecules (membrane proteins) that shuttle electrons during the redox reactions that release energy used to make ATP. requires oxygen
39
New cards
aerobic respiration
Respiration that requires oxygen
40
New cards
aerobic respiration equation
glucose + oxygen -> carbon dioxide + water
41
New cards
an undersupply of oxygen,
ATP is produced from glucose by the reaction sequence known as anaerobic respiration
42
New cards
energy transfer
Movement of energy from one place or object to another
43
New cards
stem cells
unspecialized cells that are able to renew themselves for long periods of time by cell division
44
New cards
Stem Cell Hierarchy
totipotent < pluripotent < multipotent < unipotent
45
New cards
hierarchal structure of organization
cells, tissues, organs, systems
46
New cards
gas exchange
the process of obtaining oxygen from the environment and releasing carbon dioxide
47
New cards
Caperillaries
facilitates the exchange of materials (water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, ions and nutrients) between the internal environment and cells
48
New cards
Villi
Fingerlike extensions of the intestinal mucosa that increase the surface area for absorption
49
New cards
Amalayse
Enzyme in saliva that breaks the chemical bonds in starches
50
New cards
Protease
enzyme that breaks down proteins
51
New cards
Lipase
pancreatic enzyme necessary to digest fats
52
New cards
Nitrogenous waste products
ammonia, urea, uric acid
53
New cards
Loop of Henle
section of the nephron tubule that conserves water and minimizes the volume of urine
54
New cards
nephron
functional unit of the kidney
55
New cards
collecting tubule
the structure in the nephron that collects urine from the distal convoluted tubule
56
New cards
glomerular filtration
The first step in urine formation in which substances in blood pass through the filtration membrane and the filtrate enters the proximal convoluted tubule of the nephron.
57
New cards
Selective reabsorption
The absorption of certain selected molecules back into the blood from the fluid in the nephron tubule.
58
New cards
Secretion
a process by which substances are produced and discharged from a cell, gland, or organ for a particular function in the organism or for excretion.
59
New cards
Stomata
Small openings on the underside of a leaf through which oxygen and carbon dioxide can move
60
New cards
gaurd cells
pairs of cells that surround stomata and control opening and closing
61
New cards
Gas exchange in plants
-Stomata allows gases to go in and out of the leaf
-Air spaces between the mesophyll cells allow gases to pass through
-Air spaces between the mesophyll cells allow gases to pass through
62
New cards
photosynthesis relationship with main tissue
The cells in a middle layer of leaf tissue called the mesophyll are the primary site of photosynthesis
63
New cards
Xylem
vascular tissue that carries water upward from the roots to every part of a plant
64
New cards
Phloem
Living vascular tissue that carries sugar and organic substances throughout a plant
65
New cards
Xylem vs. Phloem
The xylem distributes water and dissolved minerals upward through the plant, from the roots to the leaves. The phloem carries food downward from the leaves to the roots.
66
New cards
Rate of transpiration affecters
light, temperature, wind, humidity
67
New cards
transport of products of photosynthesis
translocation and it occurs in the phloem
68
New cards
infectious diease
invasion by a pathogen and can be transmitted from one host to another
69
New cards
non-infectious disease
genetic and lifestyle diseases
70
New cards
Prions
misfolded proteins
71
New cards
Viruses
tiny particles, smaller than bacteria and other pathogens, which must invade living cells in order to reproduce; when they invade, the cells are damaged or destroyed in the process releasing new particles to infect other cells
72
New cards
Bacteria
Single celled, prokaryotic organisms that sometimes trigger the immune system.
73
New cards
Fungi
any of a group of spore-producing organisms feeding on organic matter, including moulds, yeast, mushrooms, and toadstools.
74
New cards
Protists
A eukaryotic organism that cannot be classified as an animal, plant, or fungus.
75
New cards
paracites
Organisms that grow feed and shelter on another organism
76
New cards
invasion factors
allow for host membrane breakdown and for the bacteria to pass into host cells
77
New cards
adherence factors
molecules that bind to host cell receptors
78
New cards
Capsules
prevent phagocytosis
79
New cards
Toxins
Various poisonous substances produced by some microorganisms (bacteria and viruses).
80
New cards
lifestyle changes
changes in a person's daily habits or behavior
81
New cards
disease specific vectors
fleas on rats
82
New cards
adaptive immune system
Respond to specific antigens; Responds by remembering signature molecules, called antigens, from pathogens to which the body has previously been exposed
83
New cards
Passive immune system
1st line of defense
84
New cards
leaf structure
cuticle, vascular tissue, epidermis, mesophyll cells, guard cells, stomata
85
New cards
Prostaglandins
Modified fatty acids that are produced by a wide range of cells.
86
New cards
innate immunity
Immunity that is present before exposure and effective from birth. Responds to a broad range of pathogens.
87
New cards
artificial immunity
acquired through a medical procedure such as a vaccine
88
New cards
Phagocytes
A type of white blood cell that ingests invading microbes
89
New cards
vasodilation
A widening of the diameter of a blood vessel.
90
New cards
adaptive immune responses in vertebrates
humoral (production of antibodies by B lymphocytes) and cell-mediated (T lymphocytes), memory cells are produced in both situations
91
New cards
Homeostasis
a stimulus-response model in which change in the condition of the external or internal environment is detected and appropriate responses occur via negative feedback
92
New cards
sensory receptors
chemo, thermos, mechano, photo, noci
93
New cards
effectors are either ... or ...
muscles or glands
94
New cards
catabolic reactions
breakdown of molecules
95
New cards
anabolic reactions
build up large chemicals and require energy