Bio 192 Lab Quiz 3 Blood Typing and Hematocrit Review
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
what is the name of the process of incompatible blood types clumping when mixed?
agglutination
what is the normal blood clotting process called?
coagulation
what are the possible antigens for a person's blood type?
A, B, and D (aka Rh factor)
what determines a person's blood type?
The presence or absence of antigens on their RBCs
a person makes ________________ against the ______________ they DON'T have
antibodies; antigens
*this is a very important concept to understand*
what is the difference between genotype and phenotype?
Genotype: set of genes in the DNA that are responsible for a trait
Phenotype: the physical expression of a certain trait
which of these examples describes a genotype, and which a phenotype?
A+/A-
A+
A+/A- : genotype
A+ : phenotype
what phenotype will AA genotype have?
A
what phenotype will AO genotype have?
A
what phenotype will AB genotype have?
AB
what phenotype will BO genotype have?
B
what phenotype will BB genotype have?
B
what phenotype will OO genotype have?
O
would a genotype with +/+ genotype have the Rh factor?
yes, so they would have a positive blood type
would a genotype with +/- have the Rh factor?
yes, so they would have a positive blood type
would a genotype with -/- have the Rh factor?
no, so they would have a negative blood type
when determining blood type compatibility between a donor and a recipient, you should consider what _________________ the recipient makes and the ______________ of the donor
antibodies; antigens
*Note: to determine blood type compatibility, decide what antibodies the recipient makes (remember we make antibodies AGAINST the antigens we don't have) and see if that is compatible with the antigens from the donor's blood*
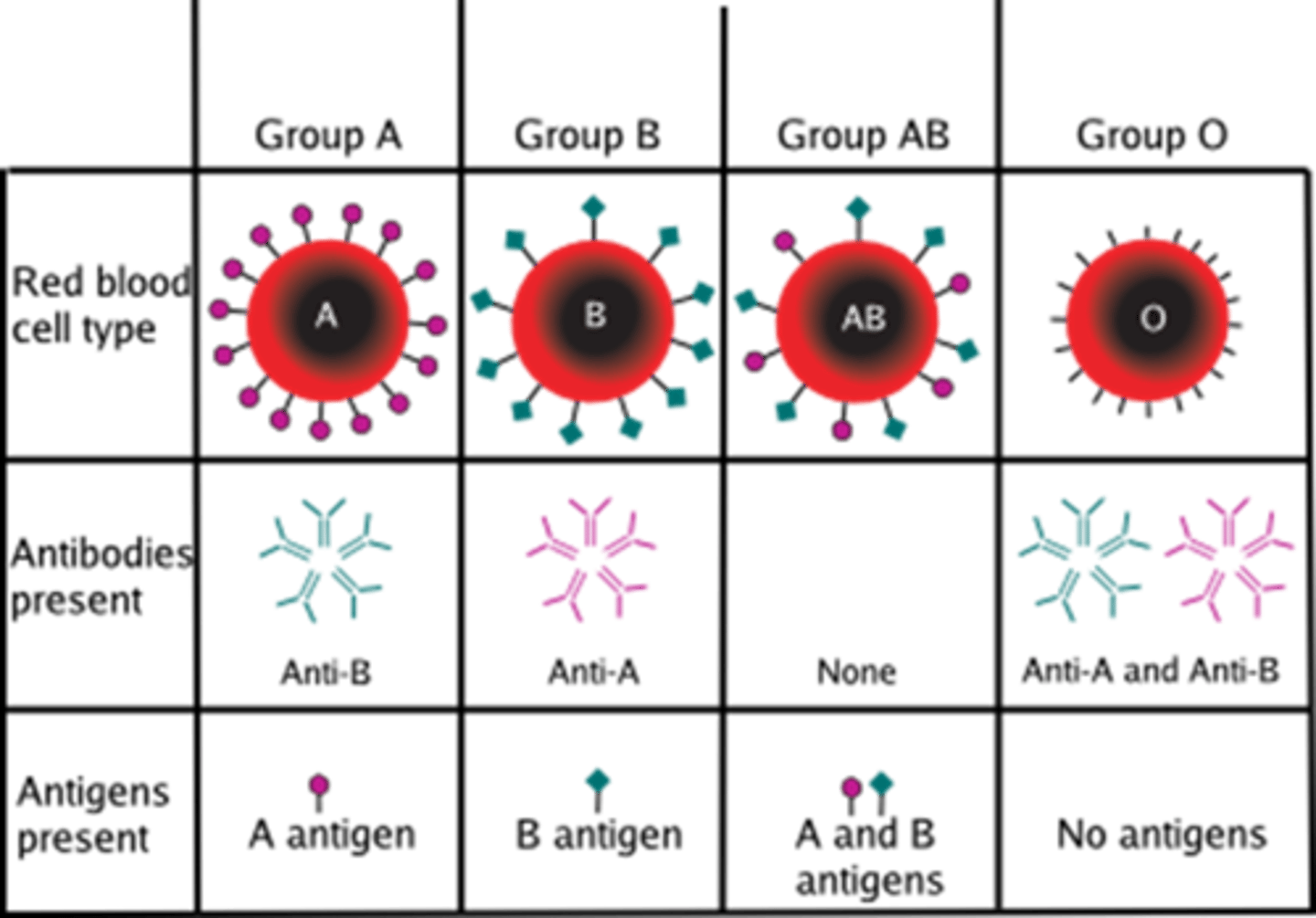
a recipient's ________________ will bind to a donor's ______________ in an incompatible blood cross
antibodies; antigens
*important to understand*
what antigens and antibodies are present in A+ blood?
antigens: A and D
antibodies: anti-B
explain the idea of second exposure?
a person who has a negative blood type will only begin to make anti-D antibodies after first exposure to a positive blood type; once a person will a negative blood type has been exposed to a positive blood type, the body begins producing anti-D antibodies and can never receive positive blood
This is why we always assume second exposure, because although a person with negative blood type could theoretically receive positive blood once in their life, afterward they can never receive positive blood again as an agglutination reaction would occur. Better to assume they make the anti-D antibodies already than cause a transfusion reaction
what is the name for the D antigen, and what does it determine?
Rh factor; presence or absence of this antigen determine positive or negative blood type
what antigens and antibodies are present in A- blood?
antigens: A
antibodies: anti-B and anti-D
what antigens and antibodies are present in B+ blood?
antigens: B and D
antibodies: anti-A
what antigens and antibodies are present in B- blood?
antigens: B
antibodies: anti-A and anti-D
what antigens and antibodies are present in AB+ blood?
antigens: A, B, and D
antibodies: none
what antigens and antibodies are present in AB- blood?
antigens: A and B
antibodies: anti-D
what antigens and antibodies are present in O+ blood?
antigens: D
antibodies: anti-A and anti-B
what antigens and antibodies are present in O- blood?
antigens: none
antibodies: anti-A, anti-B, and anti-D
What blood type is the universal recipient, and why?
AB+
this blood type contains all the antigens, so therefore they don't make any antibodies. No antibodies means they can receive any blood type because no antibodies will bind to a donor's recipient
What blood type is the universal donor, and why?
O-
this blood type contains no antigens, so it can donate to any blood type as no recipient's antibodies can bind to antigens
What are the components of blood?
plasma (55%) and formed elements (45%)
what makes up the formed elements?
red layer: erythrocytes (aka packed cell volume)
white layer: (aka buffy coat) platelets and leukocytes (< 1%)
How is hematocrit calculated?
(PCV/total volume of blood) x 100%
*PCV = red blood cell count*
what is the normal hematocrit values for males vs. females? Why the difference?
Males: 45-52%
Females: 37-48%
Men have a higher testosterone count, which stimulates release of erythropoietin which is the hormone responsible for RBC production