Micro (ECON1001)
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key economic concepts related to production, costs, market demand, and opportunity costs.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Scarcity
The condition of having limited resources to meet unlimited wants.
Opportunity Cost
The value of the next best forgone alternative when making a choice.
Ceteris Paribus
A Latin phrase meaning 'all other things being equal'; used to isolate the impact of one factor.
Marginal Analysis
Examination of the additional benefits and costs of a decision.
PPF (Production Possibility Frontier)
A graph showing the maximum output combinations of two goods that can be produced with available resources.
Absolute Advantage
When a party can produce more of a good or service than another party using the same resources.
Comparative Advantage
When a party can produce a good or service at a lower opportunity cost than another party.
Marginal Benefit
The additional benefit received from consuming one more unit of a good or service.
Diminishing Marginal Benefit
The decrease in additional satisfaction gained from consuming additional units of a good.
Market Demand Curve
A curve derived from summing the individual demand curves at each price level.
Fixed Costs
Costs that do not vary with the level of output.
Variable Costs
Costs that vary with the quantity of output produced.
Marginal Cost
The increase in total cost that arises from producing one additional unit.
Long Run Average Cost (LRAC)
The average cost per unit of output when all inputs are variable.
Economies of Scale
Cost advantages that a firm experiences as it increases output.
Diminishing Marginal Product
A reduction in the additional output gained from increasing an input.
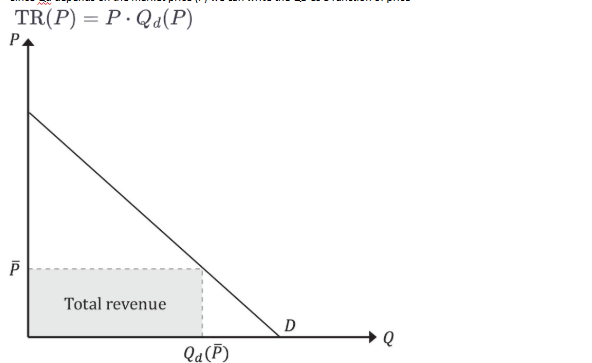
Total Revenue (TR)
The total income generated from selling goods or services, calculated as price times quantity.
Economic Profit
Profit calculated as total revenue minus total costs.
What is the difference between correlation and causation?
Correlation indicates a relationship between two variables, while causation implies that one variable directly affects or causes a change in another.
(W4) Consumer surplus
The difference between what consumers are willing to pay for a good or service versus what they actually pay.
Producer surplus
The difference between the amount producers are willing to accept for a good or service versus the actual price they receive.
Value of Time Savings
The monetary estimate of the benefits derived from reduced travel time, calculated per person per hour.
At a given market price a firm should sell up until…
P = MC
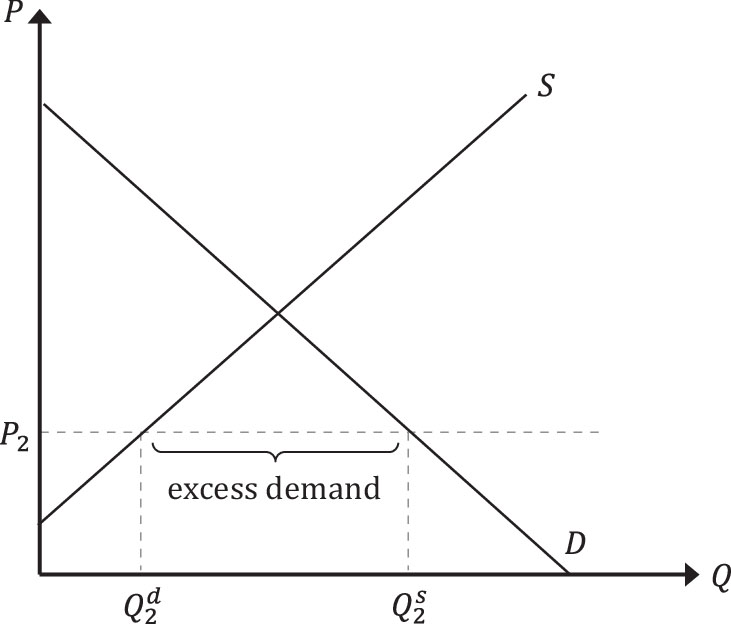
(W5) Explain this figure
At P2 there is not enough QS to fulfil QD
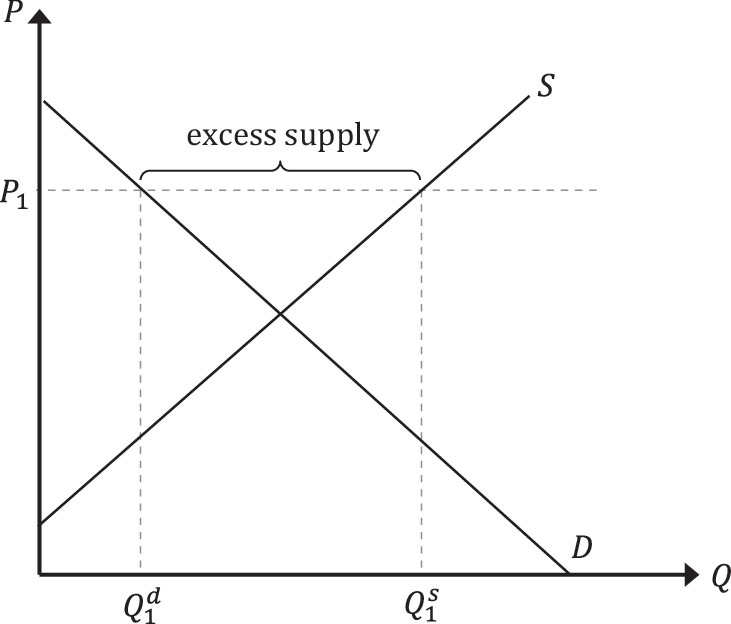
Explain this figure
At price P1 the QD does not meet QS, resulting in excess supply
What is comparative static analysis?
How the market equilibrium is affected by the change or event
What is a welfare analysis?
how consumers and firms benefit within markets
What is pareto efficiency?
When it is not possible to make someone better off without making someone else worse off
What is the basic elasticity formula (not point or arc method)
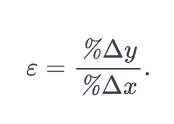
How do you find the proportional change (%) of a variable
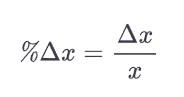
How do you find elasticity at a single point
With the point method
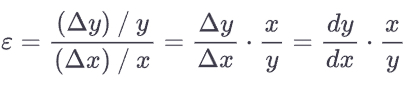
How to find elasticity moving from one point to another
Midpoint (arc) method
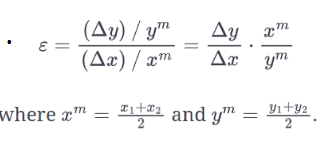
How to find elasticity of demand in both the midpoint and point method?
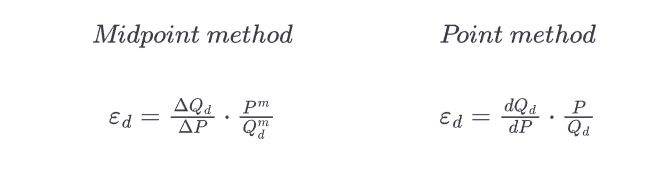
At what point is demand inelastic, elastic, unit elastic and perfectly elastic

How would we find how a total revenue in the market will change as price changes?
How do you find the cross price elasticity (how sensitive the QD of good A is to changes in price of good B) in both point and midpoint method?

How do you find income elasticity (how sensitive the QD of a good is (Q) to changes in income (Y)) in both the point and midpoint method?
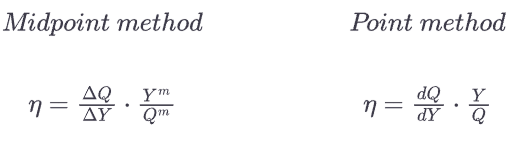
Characterise all types of goods
If n < 0, demand for a good decreases when income rises, this is an inferior good
If n = 0, demand for the good does not change when income rises, this is an neutral good
If 0 < n < 1, when income rises by 1% demand for the good increases by less than 1%, this is a normal good
If n > 1, when income rises by 1%, demand for the good increase by more than 1%, this isi a luxury good