Restorative quiz 1
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Class I
affecting the pits and fissures of
the teeth
Surfaces involved in class I restorations
Occlusal pits and fissures of premolars and molars
◦Buccal pits and fissures of mandibular molars
◦Lingual pits and fissures of the maxillary molars
◦Lingual pits of maxillary incisors, most frequently in the pit near the cingulum
Class II
Proximal surface of molars and premolars
Surfaces involved in class II restorations
◦Two-surface restoration of posterior teeth
◦Three-surface restoration of posterior teeth
◦Multisurface, four-surface (or more) restoration of
posterior teeth
a class II can involve as many as ___ surfaces of a tooth
5
Class III
Affects the interproximal surface
of incisors and canines (anterior teeth)
Class IV
Involves a larger surface area, including the incisal edges and interproximal surface of incisors and
canines
Class V
Towards Gingiva
Class VI
Cusp Tips from grinding and wearing down occlusal surface
Indications for restorative dentistry
±Initial or recurring decay (cavity fillings)
± Replacing a failed restoration
± Replace missing teeth
± Abrasion or wearing away of tooth structure
± Erosion of tooth structure
Cavity preparation
process of removing diseased tooth structure while leaving healthy tooth structure, allowing for the tooth to support a restoration
What 2 steps is cavity preparation divided into?
Initial and Final
Forms of initial cavity prep (hint: there’s 4)
outline form
resistance form
retention form
convenience form
outline form
design and initial depth of sound tooth structure
resistance form
primary shape and placement of cavity walls
retention form
to resist displacement or removal
convenience form
accessibility in preparing and restoring the tooth
Final cavity preparation
•Removing any enamel, diseased dentin, or old restorative material (or a combination)
•Inserting additional resistance and retention notches, grooves, and coves
•Placing protective dental materials (lining agents, bases, desensitizing, or bonding agents)
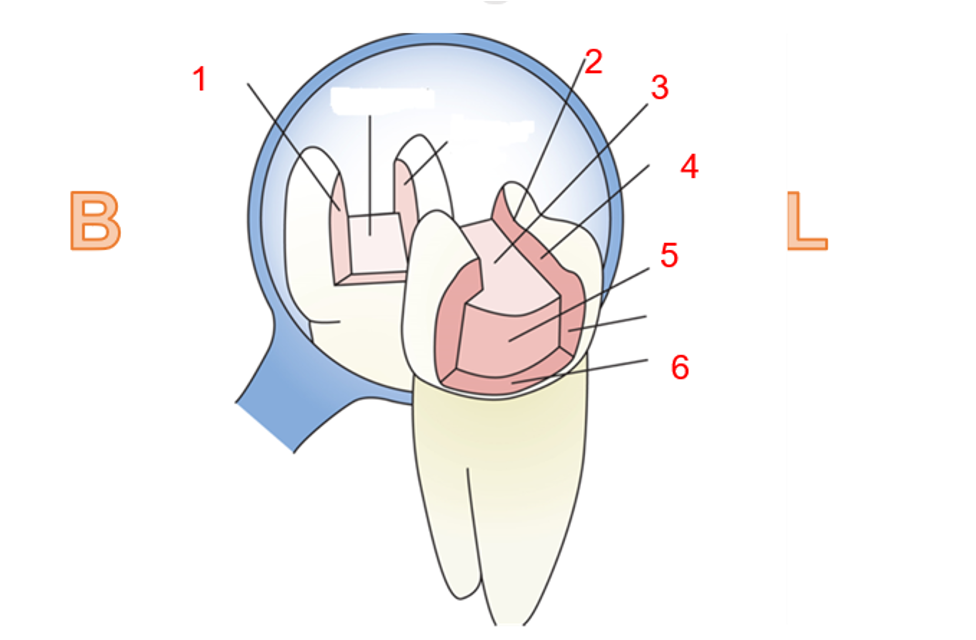
What is 1
Buccal wall
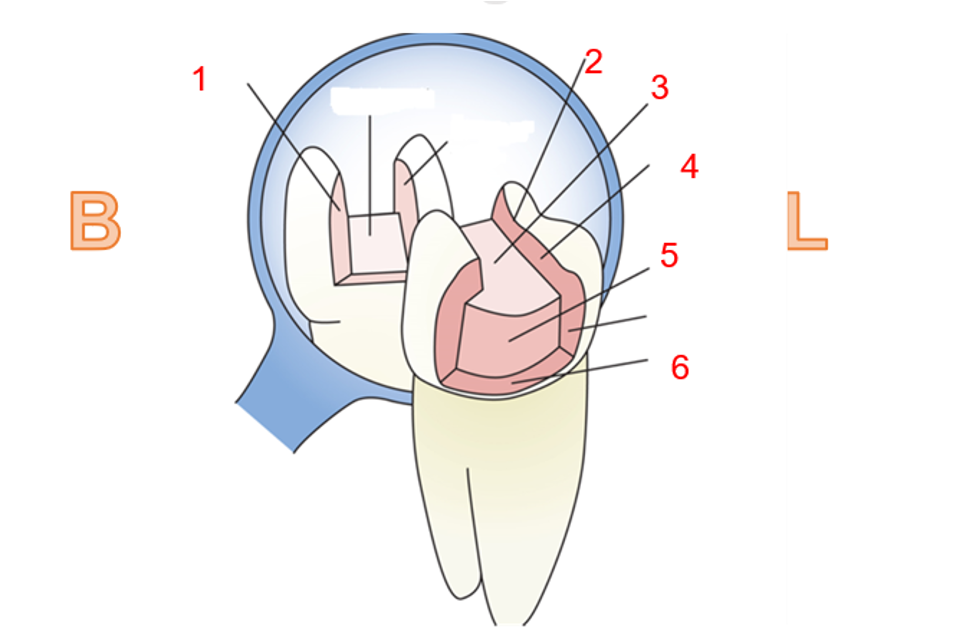
what is 2?
Cavosurface margin
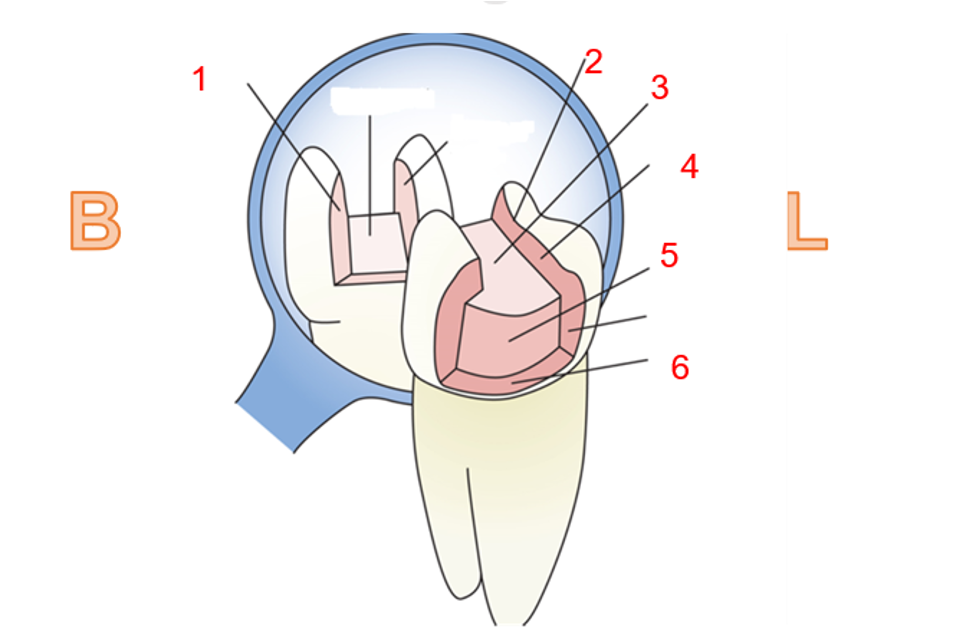
what is 3?
pulpal wall
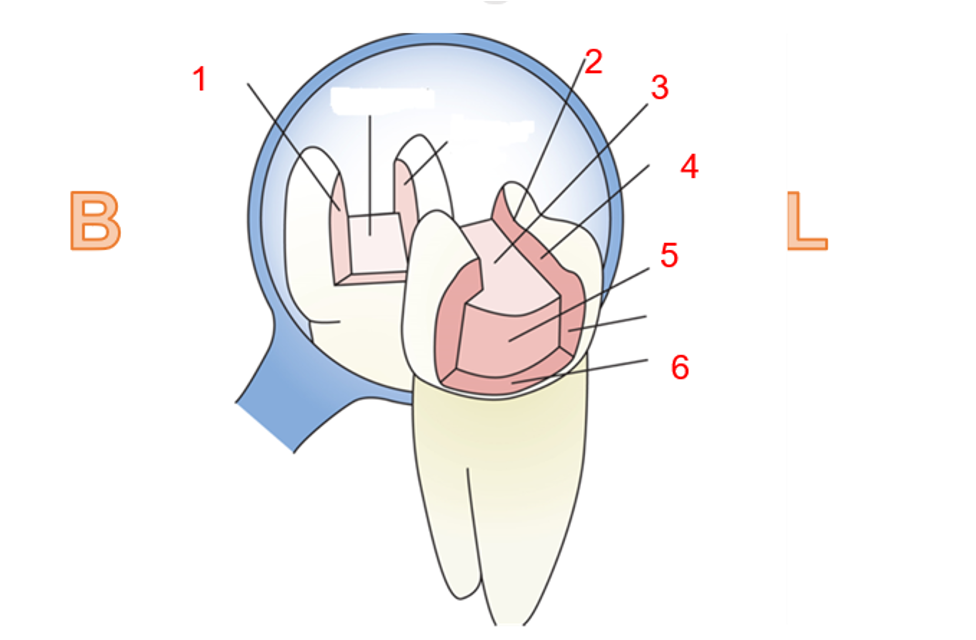
what is 4?
lingual wall
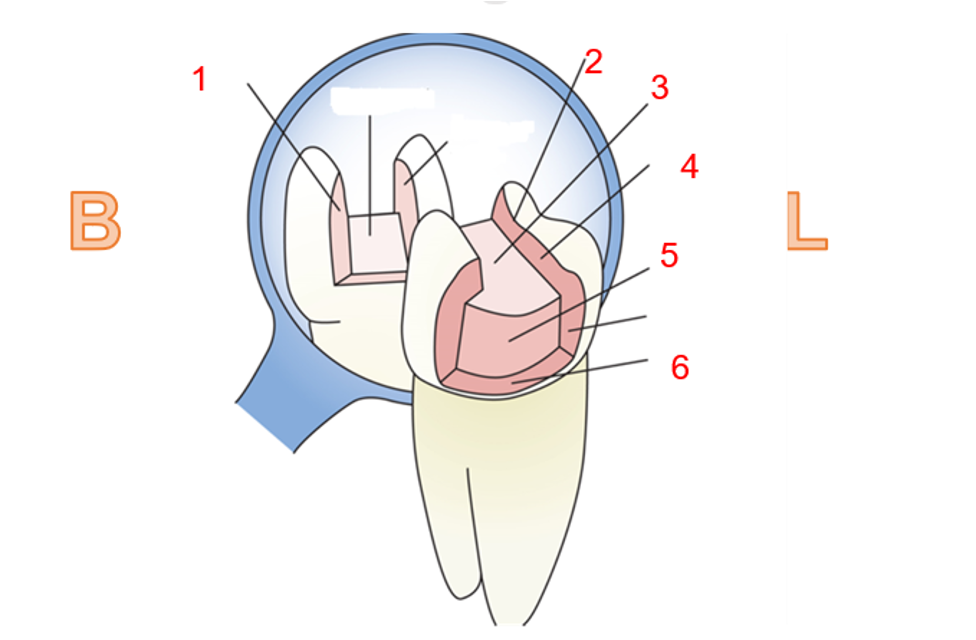
what is 5?
axial wall

what is 6?
gingival wall
Proximal box
area of a class II cavity prep consisting of 3 vertical walls (buccal, lingual, axial) and 1 horizontal wall (gingival)
line angle
angle formed by the junction of 2 walls/surfaces
point angle
angle formed by the junction of 3 walls/surfaces
list 11 steps of restorative procedure… okay go
prepare set up
communicate with patient
position patient
dentist evaluates the tooth to be restored
apply topical and local anesthetic
place moisture control (dental dam)
complete tooth prep and maintain operative field
transfer and place dental materials
burnish, carve and finish restoration
remove isolation
evaluate occlusion and complete final polishing of restoration
dental assistants role in restorative procedure
prepare the setup
provide moisture control and better visualization (HVE and tri-syringe)
transfer instruments and accessories
What happens if during tooth prep, the loss of tooth structure becomes greater than what is remaining of the natural tooth structure?
The dentist must decide whether to:
•Restore the tooth with a direct restoration
•Change the treatment plan and advise the patient that an indirect restoration would be more suitable
retention pins
stronger system used for retaining and supporting restorations. Has deep threads that grip dentin when screwed into tooth structure. one pin is placed for each missing cusp.
What is the internal surface of a cavity preparation that runs parallel to the long axis of the tooth called?
axial wall
How many tooth surfaces does a Class I restoration typically involve?
1
During a Class III restoration, the dentist will enter the tooth from the lingual in order to reduce the size of the restoration from the ______ aspect.
facial